AP biology final
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Which of the following describes the most likely way in which two water molecules will interact?
A metallic bond will form between the hydrogens in each water molecule.
A covalent bond will form between the hydrogen of one water molecule and the oxygen of the other water molecule.
An ionic bond will form between the oxygens in each water molecule.
A hydrogen bond will form between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the oxygen atom of the other water molecule.
A hydrogen bond will form between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the oxygen atom of the other water molecule.
A new dish soap claims that it is able to remove grease from pots and pans while still fully dissolving in the dishwasher water.
Which of the following best explains the ideal structure of the dish soap molecule?
A. The dish soap molecule must be polar at one end to dissolve grease, and nonpolar at the other end so it can dissolve in water.
B. The dish soap molecule must be nonpolar at one end to dissolve grease, and polar at the other end so it can dissolve in water.
C. The dish soap molecule must be polar so that it can dissolve both grease and water.
D. The dish soap molecule must be nonpolar so that it can dissolve in both grease and water.
B. The dish soap molecule must be nonpolar at one end to dissolve grease, and polar at the other end so it can dissolve in water.
Which statement best describes why water is an effective solvent?
A. Water’s polarity allows it to dissolve ionic and polar compounds.
B. Water is an ionic compound that attracts other like molecules.
C. Water’s relatively small size allows it to fit between individual atoms, driving them apart.
D. Water’s hydrophobic nature separates polar and non-polar substances.
A. Water’s polarity allows it to dissolve ionic and polar compounds.
Which of the following gives water its cohesive properties?
A. Hydrogen bonds between the hydrogens in one water molecule are attracted to the oxygens of other water molecules.
B. The overall negative charge of water molecules prevents attraction to other substances.
C. Ionic bonds hold neighboring water molecules together.
D. Water's polarity makes it attracted to other charged molecules.
A. Hydrogen bonds between the hydrogens in one water molecule are attracted to the oxygens of other water molecules.
Given the structure of water, H2O which of the following must be true?
A. Each water molecule will form covalent bonds with its neighbors.
B. Water has an overall negative charge.
C. Water is able to easily dissolve nonpolar substances.
D. Each water molecule can form four hydrogen bonds.
D. Each water molecule can form four hydrogen bonds.
Which of the following observations could be best explained by water’s high surface tension?
A. A tree takes up water from its roots.
B. A human sweats in order to cool down.
C. A leaf floats on the surface of a puddle.
D. A local pond is slow to freeze, despite low air temperature.
C. A leaf floats on the surface of a puddle.
Which of the following best describes water's ability to dissolve certain substances such as glucose, but remain separate from other substances such as oils?
A. Water molecules can only form ionic bonds with polar molecules, such as glucose.
B. Water has an overall negative charge, which allows it to easily dissolve nonpolar substances like glucose.
C. Due to hydrogen bonding, water is more dense as a liquid than a solid.
D. Water molecules are polar, consisting of two partially positive hydrogen atoms, and one partially negative oxygen atom.
D. Water molecules are polar, consisting of two partially positive hydrogen atoms, and one partially negative oxygen atom.
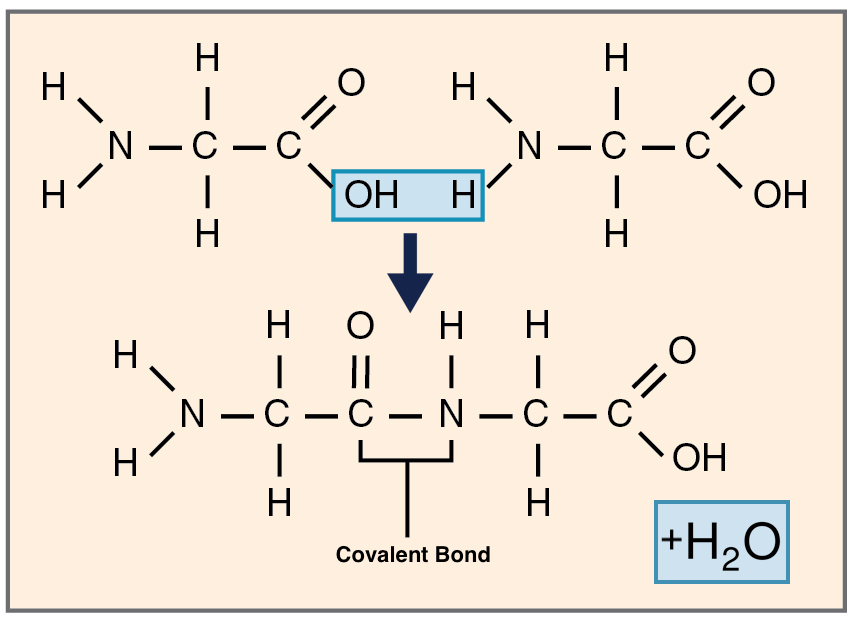
In the reaction depicted above, two amino acids have combined to form a dipeptide.
Which of the following best describes the role of water in the reaction?
A. Waters forms as result of a combination between the amino group (-NH2) of one amino acid and the carboxyl group (-COOH) of the other amino acid.
B. Water is a reactant that is added in order to drive the dehydration synthesis reaction between the amino acid monomers.
C. Water is a product that forms as a result of the hydrolysis of the dipeptide.
D. Water is a product that forms as a result of a dehydration synthesis reaction between the two amino acid monomers
D. Water is a product that forms as a result of a dehydration synthesis reaction between the two amino acid monomers
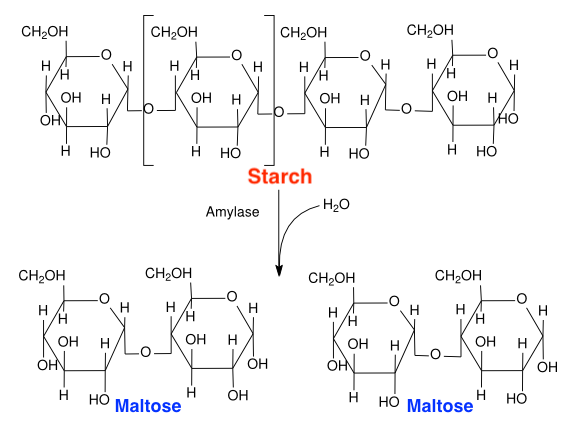
The human body is capable of digesting the complex polymer starch into simpler subunits. This digestive process requires the presence of water and the enzyme amylase in order to break down starch into maltose. This is depicted below.
Which of the following statements best describes the digestion of starch into maltose?
A. This is a hydrolysis reaction that requires water to break down a complex polymer into simpler subunits.
B. This is a dehydration synthesis reaction that produces water when forming a complex polymer from simpler subunits.
C. This is a dehydration synthesis reaction that requires water to form a complex polymer from simpler subunits.
D. This is a hydrolysis reaction that forms water by breaking down a complex polymer into simpler subunits.
A. This is a hydrolysis reaction that requires water to break down a complex polymer into simpler subunits.
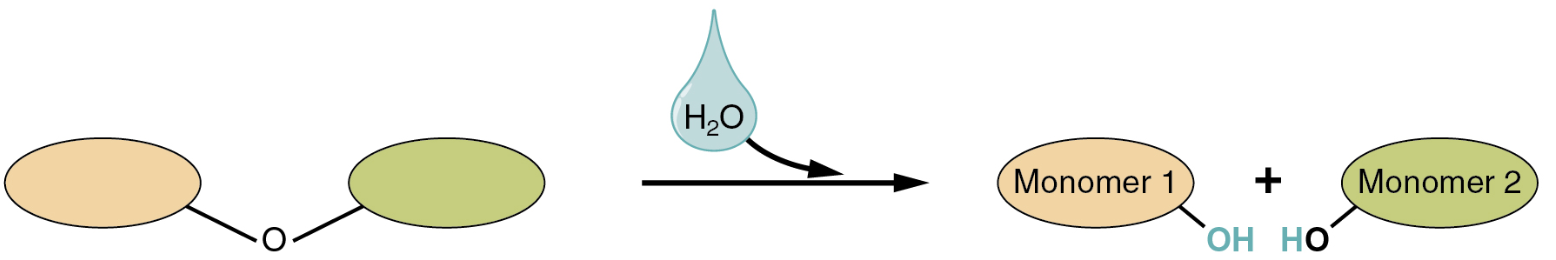
Which of the following best describes the role that water plays in the reaction depicted above?
A. As a reactant, water cleaves the covalent bond that holds the dimer (two monomers) together.
B. In the reverse of this reaction, water is used to promote hydrolysis.
C. When water is added, the two monomers form a covalent bond that holds the dimer together.
D. Water is a product of this dehydration synthesis reaction.
A. As a reactant, water cleaves the covalent bond that holds the dimer (two monomers) together.
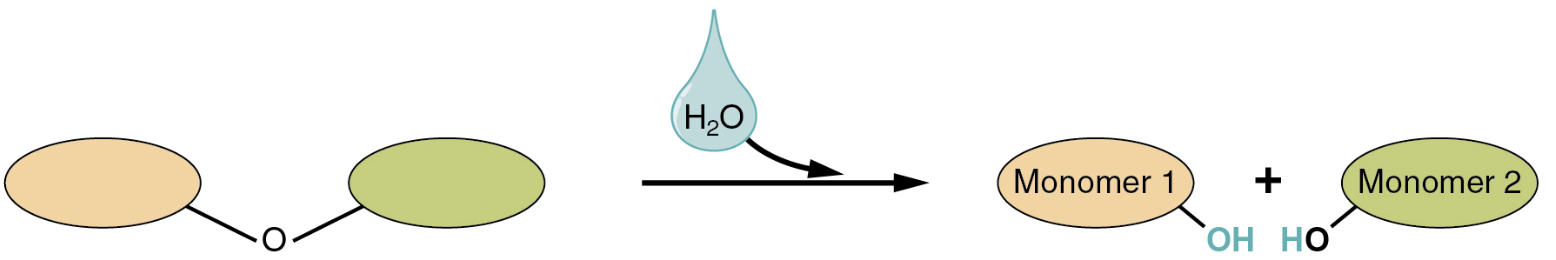
Based on the reaction depicted above, which of the following statements is true?
A. If water is not added to the reaction, dehydration synthesis will not occur.
B. The reverse of this reaction requires the addition of water in order to build the dimer.
C. If water is not added to the reaction, hydrolysis will not occur.
D. The reverse of this reaction requires the removal of water from the reaction in order to break down the dimer.
C. If water is not added to the reaction, hydrolysis will not occur.
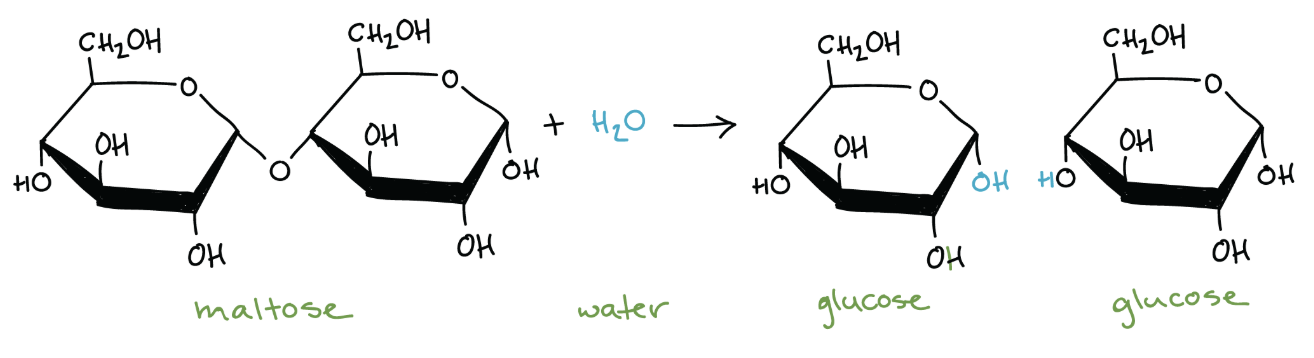
In the reaction depicted above, maltose is broken down into two molecules of glucose.
Which of the following best explains the process of this reaction?
A. The reverse of this reaction would require the addition of water to build the maltose dimer from the glucose monomers.
B. The ionic bond of maltose is broken down through the addition of water in this hydrolysis reaction.
C. This breakdown process requires the release of water as a product of the reaction.
D. The addition of a water molecule cleaves the covalent bond holding maltose together.
D. The addition of a water molecule cleaves the covalent bond holding maltose together.
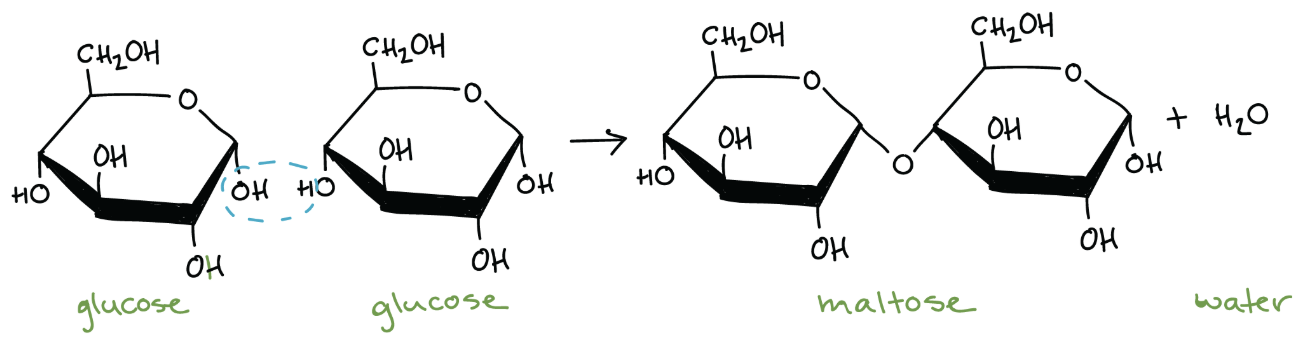
In the reaction above, two glucose monomers combine to form the dimer maltose.
Which of the following best explains the process of this reaction?
A. A covalent bond forms through dehydration synthesis, which results in the formation of maltose and water.
B. Water is added to the reaction to promote the formation of a covalent bond between the glucose monomers.
C. An ionic bond forms through dehydration synthesis, which combines the two glucose monomers and forms the maltose dimer.
D. To form a covalent bond, the monomers underwent a hydrolysis reaction.
A. A covalent bond forms through dehydration synthesis, which results in the formation of maltose and water.
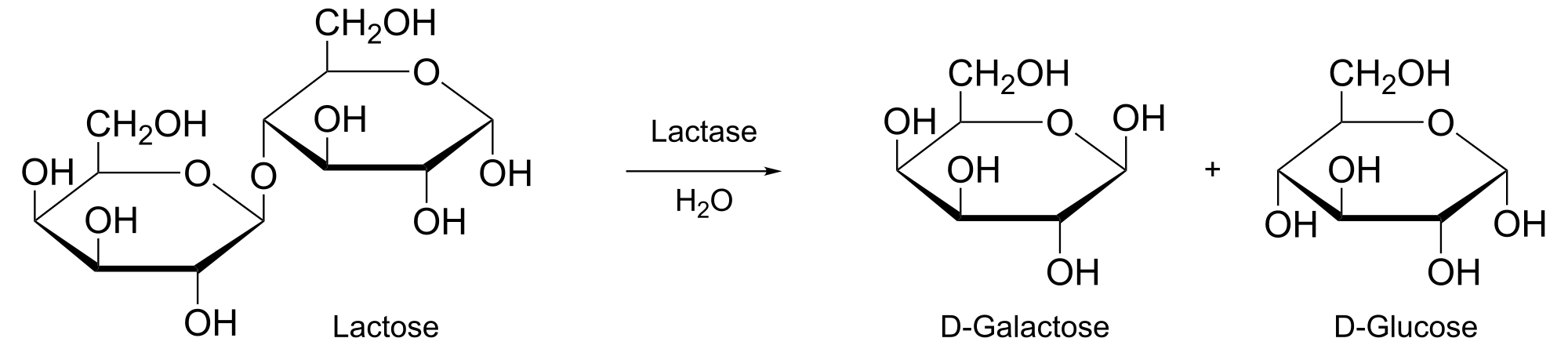
Lactose is a dimer sugar composed of two monomeric subunits (galactose and glucose). In an investigation, researchers placed intestinal cells in a nutrient medium containing lactose. The researchers determined that the lactose had broken down to galactose and glucose in the manner depicted in the reaction below.
The cells were then modified and re-exposed to the lactose medium. The researchers were no longer able to detect the presence of galactose and glucose.
Which of the following conclusions best explains an outcome of this modification?
A. The cells were able to perform dehydration synthesis reactions in order to break down lactose into its monomeric subunits.
B. The cells were unable to hydrolyze the lactose dimer into its monomeric subunits.
C. The cells were able to undergo a reverse reaction and build lactose.
D. The cells were unable to hydrolyze lactose, resulting in the formation of a covalent bond between galactose and glucose.
B. The cells were unable to hydrolyze the lactose dimer into its monomeric subunits
Which of the following questions would a researcher most likely ask if they wanted to know whether a hydrolysis reaction or a dehydration synthesis reaction is occurring?
A. Are the monomers identical to one another?
B. Is water a reactant or product of the reaction?
C. Is an enzyme involved in the reaction?
D. Which polymer is involved in the reaction?
B. Is water a reactant or product of the reaction?
Glycogen is a highly branched macromolecule usually stored in liver and muscle cells. If blood glucose levels decrease, glycogen breaks down to release glucose in a process called glycogenolysis. In this process, the glycogen polysaccharide goes through hydrolysis and breaks down into glucose monosaccharides.
If a toxin were to inhibit glycogenolysis, which of the following statements best predicts a consequence of this inhibition?
A. The covalent bonds within an individual glucose monomer will not be cleaved.
B. In response to the detection of low glucose levels, glycogen will continuously be broken down to release glucose.
C. In response to the detection of low glucose levels, more glucose will be released from stored glycogen.
D. The covalent bonds between individual glucose monomers will not be cleaved.
D. The covalent bonds between individual glucose monomers will not be cleaved.
Glycogen is a highly branched macromolecule usually stored in liver and muscle cells. If blood glucose levels decrease, glycogen breaks down to release glucose in a process called glycogenolysis. In this process, the glycogen polysaccharide goes through hydrolysis and breaks down into glucose monosaccharides.
If a toxin were to inhibit glycogenolysis, which of the following statements best predicts a consequence of this inhibition?
A. The covalent bonds within an individual glucose monomer will not be cleaved.
B. In response to the detection of low glucose levels, glycogen will continuously be broken down to release glucose.
C. In response to the detection of low glucose levels, more glucose will be released from stored glycogen.
D. The covalent bonds within an individual glucose monomer will not be cleaved.
D. The covalent bonds within an individual glucose monomer will not be cleaved.
Most species of shark are strict carnivores. However, bonnethead sharks (Sphyrna tiburo) have been observed consuming seagrass within their natural habitat. Like other plants, seagrasses contain cellulose within their cell walls.
Based on the information above, which of the following best supports the claim that bonnethead sharks are capable of hydrolyzing cellulose during digestion?
A. Cellulose is consumed as glucose monosaccharides and is converted into a linear polysaccharide and during digestion.
B. Cellulose is consumed as a linear polysaccharide and is converted into branched glucose monosaccharides during digestion.
C. Cellulose is consumed as a linear polysaccharide and is broken down into glucose monosaccharides during digestion.
D. Cellulose is consumed as a linear polysaccharide and remains as a linear polysaccharide during digestion
C. Cellulose is consumed as a linear polysaccharide and is broken down into glucose monosaccharides during digestion.
In order to develop antibiotics, scientists need to understand how bacteria grow and reproduce. One factor that is essential for bacterial growth and reproduction is protein synthesis. By understanding how bacteria synthesize proteins, scientists can then attempt to develop antibiotics that block bacterial protein synthesis during an infection.
Which of the following questions will best direct an investigation on how to develop an antibiotic that inhibits protein synthesis in bacteria?
A. How can the phosphate end of the growing polypeptide chain be blocked?
B. How can the formation of covalent bonds between amino acids be blocked?
C. How can the formation of hydrogen bonds between amino acids be blocked?
D. How can the hydroxyl end of the growing polypeptide chain be blocked?
B. How can the formation of covalent bonds between amino acids be blocked?
In order to develop antibiotics, scientists need to understand how bacteria grow and reproduce. One factor that is essential for bacterial growth and reproduction is protein synthesis. By understanding how bacteria synthesize proteins, scientists can then attempt to develop antibiotics that block bacterial protein synthesis during an infection.
Which of the following questions will best direct an investigation on how to develop an antibiotic that inhibits protein synthesis in bacteria?
A. How can the 5' end of the growing polypeptide chain be blocked?
B. How can the carboxyl (-COOH) terminus of a growing polypeptide chain be blocked?
C. How can the amino (-NH2) terminus of a growing polypeptide chain be blocked?
D. How can the 3' end of the growing polypeptide chain be blocked?
B. How can the carboxyl (-COOH) terminus of a growing polypeptide chain be blocked?
Match the monomers with the correct polymers. Which of the following is an incorrect pair?
A. monosaccharides-carbohydrates
B. fatty acids-lipids
C. nucleotide-nucleic acids
D. amino acids-proteins
B. fatty acids-lipids
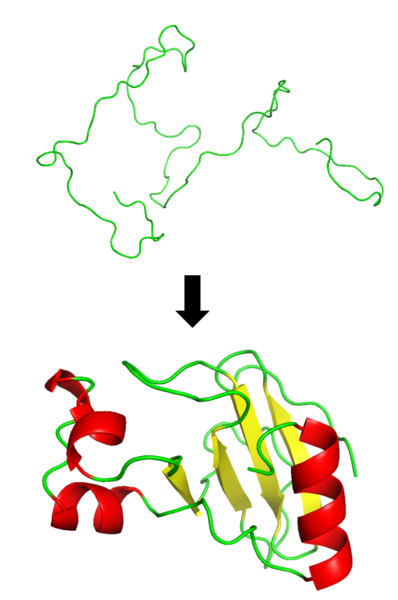
The image below depicts how the bacterial protein barnase undergoes modifications that involve changing its conformation, or shape. In order to function in the cell, barnase has to be folded from a nonfunctional conformation into a functional conformation.
Based on the information above, which of the following best describes the functional conformation of barnase?
A. The functional conformation of barnase has a secondary structure because it consists of a single alpha-helix.
B. The functional conformation of barnase has a quaternary structure because it consists of interactions between multiple polypeptide units.
C. The functional conformation of barnase has a tertiary structure because it consists of a polypeptide chain folded into a three-dimensional shape.
D. The functional conformation of barnase has a primary structure because it consists of a linear chain of amino acids.
C. The functional conformation of barnase has a tertiary structure because it consists of a polypeptide chain folded into a three-dimensional shape.
In a polypeptide chain consisted of 25 amino acids, scientists found a mutation at position #11 that glycine is substituted by serine. Glycine is a nonpolar amino acid, and serine is a polar amino acid. How does this mutation change the conformation of the protein?
A. The mutation has no effect on the overall shape of the protein since amino acids in a polypeptide chain does not determine the function of the protein.
B. The mutation has little effect on the function of the protein since it is determined by the genetic code in the DNA.
C. As the polypeptide chain continues to fold into tertiary structure, serine will moves towards the surface of the protein, results in misfolding of the protein.
D. As the polypeptide chain continues to fold into tertiary structure, serine will moves towards the interior of the protein, therefore the function of the protein remains the same.
C. As the polypeptide chain continues to fold into tertiary structure, serine will moves towards the surface of the protein, results in misfolding of the protein.
A cell is treated with a toxin that prevents the synthesis of new lysosomes. However, the cell continues to produce the hydrolytic enzymes normally found in lysosomes.
In which of the following structures are the hydrolytic enzymes most likely to accumulate?
A. Mitochondria
B. Nucleus
C. Smooth ER
D. Golgi Apparatus
D. Golgi Apparatus
Tay-Sachs disease is a genetic disorder that causes certain lipids known as gangliosides to accumulate in the neurons of the brain and spinal cord. As the gangliosides build up, neurons rapidly degenerate.
Which of the following cell structures is most likely associated with the accumulation of gangliosides?
A. Nucleus
B. Mitochondria
C.ER
D. Lysosomes
D. Lysosomes
Chlorophyll a is a pigment that absorbs light energy from the sun and gives plants their green color.
Which of the following plant cell structures is most likely to contain chlorophyll a?
A. Mitochondria
B. Ribosomes
C. Chloroplast
D. Vacuole
C. Chloroplast
Which of the following statements is true for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
A. The rough endoplasmic reticulum synthesizes lipids and modifies proteins.
B. The Golgi complex packages and sorts proteins for transport throughout the cell.
C. Ribosomes synthesize proteins using mRNA sequences.
D. Mitochondria produce ATP through cellular respiration.
C. Ribosomes synthesize proteins using mRNA sequences.

A lack of water can cause plant cells to become flaccid. This gives the plant a wilted appearance as shown in the figure below.
Which of the following cell structures is most likely responsible for the plant’s wilted appearance?
A. Central Vacuole
B. Nucleus
C. Mitochondria
D. Lysosomes
A. Central Vacuole
A student uses a microscope to compare a human skeletal muscle cell and a human epithelial cell. The student observes that the muscle cell has more mitochondria than the epithelial cell.
Which of the following conclusions is best supported by this observation?
A. The muscle cell requires more ATP than the epithelial cell.
B. The epithelial cell does not require ATP to function.
C. The epithelial cell requires more ATP than the muscle cell.
D. The muscle cells do not require ATP to function.
A. The muscle cell requires more ATP than the epithelial cell.
Cell X has a surface are of 60μm2 and a volume of 15μm3. Cell Y has a surface area of 36μm2 and a volume of 12μm3. Using the information, determine the surface area to volume ratio of each cell. What is the SA:V ration of the cell that will exchange materials with its environment at the fastest rate of diffusion?
A. 4μm
B. 3μm
C. 0.25μm
D. 0.33μm
A. 4μm

The physical characteristics of a cell influence how it functions. For example, the surface area and volume of a cell affect how efficiently waste is removed from the cell via diffusion. The table below shows data for four different cuboidal cells. Using the information from the table, which cell can remove waste via diffusion most efficiently?
A
B
C
D
A
Humans are made up of many types of cells, and these cells have a broad range of sizes. For example, a type of fat cell called an adipocyte has a radius of approximately 50, while a type of heart muscle cell called a cardiomyocyte has a radius of about 15μm
Surface area of a sphere: A = 4πr^2A=4πr2
A, equals, 4, π, r, squared
Assuming both cell types are perfectly spherical, approximately how many times larger is the surface area of an adipocyte compared to the surface area of a cardiomyocyte?
Round your answer to the nearest integer.
A. 0.09 times
B. 11 times
C. 100 times
D. 1000 times
B. 11 times
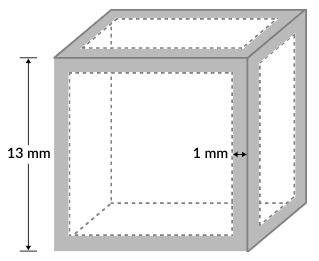
The figure above depicts an agar cube with a side length 13mm. In an experiment, students submerged the cube in orange dye for 12 hours. The orange dye permeated 1mm on each side, as indicated by the shading in the figure
V, equals, l, w, h
Calculate the volume of the agar cube that remained unpenetrated by the orange dye.
A. 1331 mm3
B. 1728 mm3
C. 1500 mm
D. 397mm3
A. 1331 mm3
Which of the following is true about the transportation of substances across the lipid region of the cell membrane?
A. Small nonpolar molecules can freely dissolve across the lipid region of the cell membrane.
B. Gases such as N2, O2, and CO2 require embedded transport proteins to dissolve across the lipid region of the cell membrane.
C. Polysaccharides can freely dissolve across the lipid region of the cell membrane.
D. Ions can freely dissolve across the lipid region of the cell membrane.
A. Small nonpolar molecules can freely dissolve across the lipid region of the cell membrane.
Which of the following best describes how substances move across the cell membrane?
A. Ions move across the cell membrane through embedded channel proteins.
B. Polar amino acids freely move across the cell membrane.
C. Hydrophilic amino acids freely move across the cell membrane.
D. Nucleic acids freely move across the cell membrane.
A. Ions move across the cell membrane through embedded channel proteins.
Which of the following best describes the permeability of the cell wall?
A. Only water passes across the cell wall because it is a semipermeable structural boundary.
B. Some substances pass across the cell wall because it is a semipermeable structural boundary.
C. All substances pass across the cell wall because it is a permeable structural boundary.
D. Substances cannot pass across the cell wall because it is an impermeable structural boundary.
B. Some substances pass across the cell wall because it is a semipermeable structural boundary.
Which of the following statements best describes the selective permeability of the cell membrane?
A. The cell membrane regulates the transport of intracellular substances out of, but not into the cell.
B. The cell membrane regulates the transport of extracellular substances into, but not out of the cell.
C. The cell membrane regulates the transport of specific substances into and out of the cell.
D. The cell membrane regulates the transport of all substances into and out of the cell.
C. The cell membrane regulates the transport of specific substances into and out of the cell.
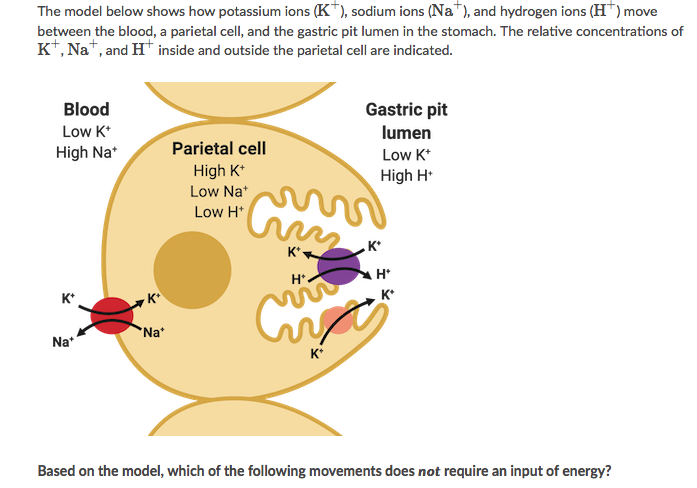
A. Na+moving out of a parietal cell into the blood
B. K+moving out of the blood into a parietal cell
C. K+ moving out of a parietal cell into the gastric pit lumen
D. H+ moving out of a parietal cell into the gastric pit lumen
C. K+ moving out of a parietal cell into the gastric pit lumen
A neuron stimulates muscle contraction by sending signals across the neuromuscular junction, or the point of contact between a neuron and a muscle cell. The signaling process begins when membrane-bound structures inside the neuron fuse with the cell membrane, releasing signaling molecules into the neuromuscular junction. These molecules then diffuse through the junction and binds to receptors on the surface of the muscle cell, leading to muscle contraction.
Botulism is a rare illness caused by a toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. This toxin, called botulinum toxin, inhibits the process by which signaling molecules are released from neurons at the neuromuscular junction. This disrupts the neuron-muscle cell signaling pathway, resulting in temporary paralysis.
Based on the information above, which of the following cell processes does botulinum toxin most likely inhibit?
A. Facilitated diffusion through membrane channels
B. Membrane transport mediated by transmembrane ATPases
C. Vesicle fusion during exocytosis
D. Receptor-mediated endocytosis
C. Vesicle fusion during exocytosis
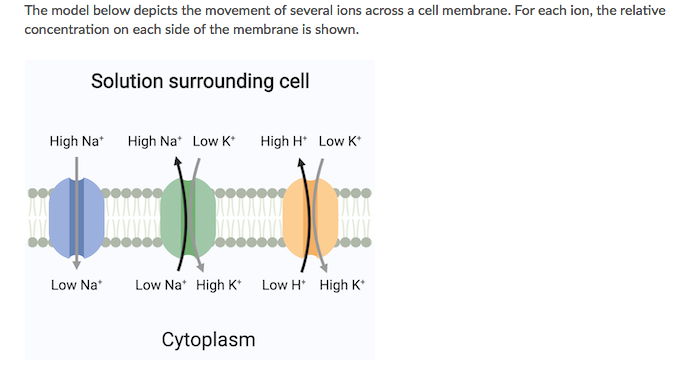
Which of the following statements accurately describes one of the movements shown in the model?
A. K movement into the cell does not require an input of energy.
B. Na moves out of the cell by passive transport.
C. Na movement into the cell does not require an input of energy.
D. H moves out of the cell by passive transport.
C. Na movement into the cell does not require an input of energy.
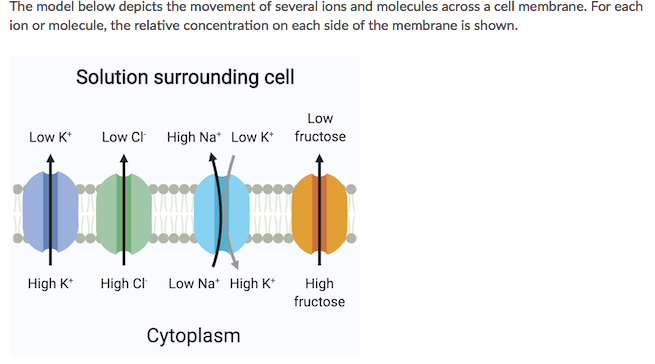
Which of the following statements accurately describes one of the movements shown in the model?
A. Cl is transported out of the cell by active transport.
B. K movement into the cell requires ATP
C. K is transported out of the cell by active transport.
D. Fructose movement out of the cell requires ATP
B. K movement into the cell requires ATP

What is the solute potential of the potato cubes?
A. 13 bar
B. -1.9 bar
C. 1.9 bar
D. -13 bar
D. -13 bar
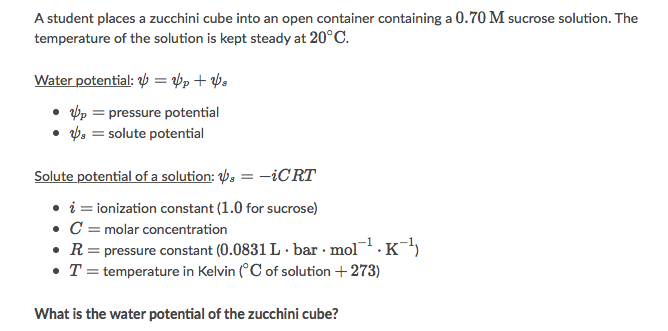
A. 17 bar
B. -1.2 bar
C. -17 bar
D. 1.2 bar
C. -17 bar

A. −8bar water will move into the cell
B. −22bar water will move into the cell
C. −8bar there will be no net movement of water
D. −22bar water will move out of the cell
C. −8bar there will be no net movement of water
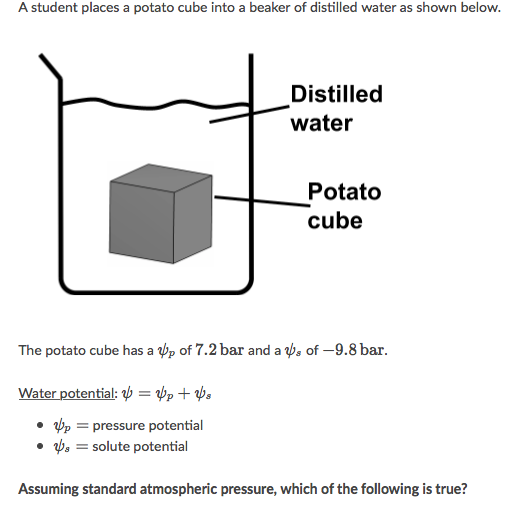
A. The potato cube has a water potential of 0 bar and the distilled water has a water potential of -17 bar
B. The potato cube has a water potential of −17.0 bar and the distilled water has a water potential of 0 bar
C. The potato cube has a water potential of 0 bar and the distilled water has a water potential of -2.6 bar
D. The potato cube has a water potential of −2.6 bar and the distilled water has a water potential of 0 bar.
D. The potato cube has a water potential of −2.6 bar and the distilled water has a water potential of 0 bar.

A. −9 bar water will move out of the cell
B. −15bar water will move into the cell
C. −9bar water will move into the cell
D. −15bar water will move out of the cell
A. −9 bar water will move out of the cell
Which of the following best explains how the light reactions of photosynthesis generate ATP?
A. As photosystem II (PSII) absorbs energy from light, electrons are excited to a higher energy level and accepted by ADP to form ATP.
B. A proton gradient drives the formation of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate via ATP synthase.
C. Energy from light excites ATP synthase, causing it to bind ADP with inorganic phosphate to form ATP.
D. ADP accepts excited electrons at the end of the electron transport chain (ETC) to form ATP.
B. A proton gradient drives the formation of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate via ATP synthase.
Which of the following best indicates that the light reactions of photosynthesis have completed and that the Calvin cycle has begun?
A. An electrochemical gradient forms across the thylakoid membrane.
B. ATP and NADPH accumulate in the stroma.
C. Electrons are transferred across the electron transport chain (ETC) on the thylakoid membrane.
D. A high concentration of carbohydrates is found in the thylakoid lumen.
B. ATP and NADPH accumulate in the stroma.
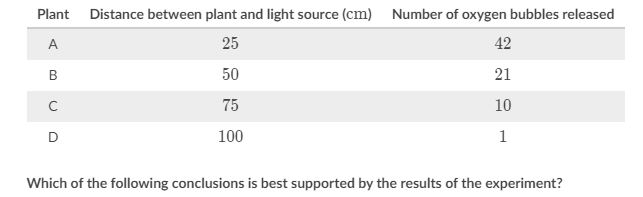
A group of students are conducting an experiment on Elodea canadensis, a species of aquatic plant. In order to test the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis, they place each Elodea canadensis plant into an aquarium tank and place each tank at a different distance from a light source.
After a few minutes, oxygen bubbles begin to form in each of the tanks. The students count the number of oxygen bubbles released during a 555 minute period for each tank. The results of their experiment are shown below.
A. A decrease in light intensity increases the rate of photosynthesis.
B. An increase in light intensity decreases the rate of photosynthesis.
C. Light intensity does not affect the rate of photosynthesis.
D. An increase in light intensity increases the rate of photosynthesis.
D. An increase in light intensity increases the rate of photosynthesis.
The cytochrome complex is an integral thylakoid membrane protein that forms an electrochemical gradient by pumping protons. In an experiment, researchers apply a toxin to a plant cell that inhibits the cytochrome complex.
Which of the following explains the most likely effect of this toxin on the light reactions of photosynthesis?
A. Hydrogen ions will move across the thylakoid membrane using simple diffusion.
B. NADP will not be reduced to NADPH.
C. ATP synthesis will not occur.
D. Carbohydrates will not be produced in the stroma.
C. ATP synthesis will not occur.
Which of the following best describes how the Calvin cycle and the light reactions of photosynthesis function together?
A. The Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH generated by the light reactions to synthesize carbohydrates.
B. The Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH generated by the light reactions to break down carbohydrates.
C. The Calvin cycle generates ATP and NADPH to excite electrons during the light reactions.
D. The Calvin cycle produces ATP and NADPH to drive the formation of an electrochemical gradient during the light reactions.
A. The Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH generated by the light reactions to synthesize carbohydrates.
A researcher claims that increased atmospheric carbon dioxide levels cause increased growth rates in plants. Which of the following statements best supports the researcher’s claim?
A. Atmospheric carbon dioxide is produced by the burning of fossil fuels, which are formed from the remains of living organisms such as plants.
B. Atmospheric carbon dioxide is a byproduct of cellular respiration, which is a metabolic process that occurs in plants and other living organisms.
C. Atmospheric carbon dioxide typically enters plant leaves through stomata, which plants rely on for regulating gas exchange with the atmosphere.
D. Atmospheric carbon dioxide is the raw material for photosynthesis, which plants rely on for producing sugars and other organic compounds.
D. Atmospheric carbon dioxide is the raw material for photosynthesis, which plants rely on for producing sugars and other organic compounds.
RuBisCO catalyzes the joining of carbon dioxide with RuBP during carbon fixation. In an experiment, researchers apply a toxin to a plant cell that inhibits RuBisCO.
Which of the following explains the most likely effect this toxin will have on the Calvin cycle?
A. Excited electrons will not be transferred across the electron transport chain.
B. Carbon and oxygen will not be released after the breakdown of carbon dioxide.
C. Carbon dioxide will not be converted into sugar.
D. ATP synthase will not catalyze the formation of ATP on the thylakoid membrane.
C. Carbon dioxide will not be converted into sugar.
When light is absorbed by pigments in photosystem II (PSII), energy is passed inward from pigment to pigment until it reaches the reaction center. Electrons are then boosted to a high energy level and captured by the primary electron acceptor.
Which of the following occurs immediately after the electrons from PSII are captured by the primary electron acceptor?
A. Water is broken down.
B. The electrons return to PSII.
C. ADP is converted to ATP.
D. NADP+ accepts the electrons.
A. Water is broken down.
Which of the following best describes what will result when a glucose-fed yeast cell is placed in an anaerobic environment?
A. The yeast cell will produce ATP through fermentation, generating CO2 and ethanol as byproducts.
B. The yeast cell will produce ATP through fermentation, generating lactic acid as byproducts.
C. Due to a lack of oxygen, the yeast cell will no longer produce ATP, and its ATP stores will be depleted.
D. Due to the presence of oxygen, the yeast cell will produce ATP through oxidative phosphorylation.
A. The yeast cell will produce ATP through fermentation, generating CO2 and ethanol as byproducts.
The human oral microbiota contains over 700700700 species of bacteria. One species often found in the oral cavity is Streptococcus mutans, an anaerobic bacterium strongly associated with the formation of dental cavities. S. mutans metabolizes glucose and other dietary sugars remaining in the mouth after a meal, producing lactic acid as a byproduct. Over time, high levels of lactic acid can erode tooth enamel, eventually leading to the formation of dental cavities.
Which of the following drugs would be most likely to prevent cavities caused by S. mutans?
A. A drug that inhibits the formation of a proton gradient across the cell membrane
B. A drug that prevents the movement of oxygen across the cell membrane
C. A drug that inhibits the production of NADH and FADH during the Krebs cycle
D. A drug that prevents the conversion of glucose into pyruvate
D. A drug that prevents the conversion of glucose into pyruvate
Cyanide poisoning is a type of poisoning caused by exposure to certain cyanide-containing compounds, such as hydrogen cyanide or cyanide salts. Inhalation or consumption of these compounds can cause histotoxic hypoxia, a condition in which cells are no longer able to take up or utilize oxygen during cellular respiration. As a result, ATP production during respiration is significantly reduced.
Based on the information above, which of the following is the most likely explanation for how cyanide causes histotoxic hypoxia?
A. Cyanide inhibits the enzymatic breakdown of glucose during glycolysis.
B. Cyanide inhibits the transfer of electrons to the final acceptor in the electron transport chain.
C. Cyanide inhibits the reduction of NAD and FAD during the Krebs cycle.
D. Cyanide inhibits the transport of pyruvate across the mitochondrial membrane.
B. Cyanide inhibits the transfer of electrons to the final acceptor in the electron transport chain.
Unlike most other cells in the human body, mature red blood cells (RBCs) do not contain a nucleus or mitochondria. This allows RBCs to carry more hemoglobin, and therefore oxygen, through the bloodstream.
Based on the information above, which of the following is most likely true about RBCs?
A. Due to a lack of mitochondria, RBCs do not produce ATP.
B. CO2 and ethanol are byproducts of ATP production in RBCs.
C. Oxygen is used as the terminal electron acceptor in RBCs.
D. RBCs generate lactate as a waste product.
A. Due to a lack of mitochondria, RBCs do not produce ATP.
Bacteroides is the predominant genus of bacteria found in the human gut microbiota. As anaerobic bacteria, Bacteroides undergo fermentation in the gut, converting otherwise nondigestible carbohydrates into fermentation products that are used by the host for energy.
Which of the following toxins would be most likely to disrupt carbohydrate metabolism in Bacteroides species?
A. A toxin that inhibits the function of ATP synthase
B. A toxin that prevents the formation of Krebs cycle products
C. A toxin that inhibits the function of an enzyme during glycolysis
D. A toxin that breaks down the membrane proteins of the electron transport chain
C. A toxin that inhibits the function of an enzyme during glycolysis
n mitochondria, the rate of ATP synthesis during oxidative phosphorylation is tightly coupled to the movement of electrons through the electron transport chain (ETC). When ADP levels rise and the demand for ATP synthesis increases, electron flow through the ETC also increases.
Based on the information above, which of the following best describes an effect of rising ADP levels in mitochondria?
A. Fewer protons will be pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
B. The flow of protons through ATP synthase will decrease.
C. NADH and FADH2 will be oxidized to NAD+ and FAD less rapidly.
D. Oxygen consumption will increase.
D. Oxygen consumption will increase.
Pancreatic amylase is a digestive enzyme found in the small intestine. It helps break down large starch molecules later in the digestive process. Pancreatic amylase is unable to break down lipids.
Which of the following best explains why pancreatic amylase is able to break down starches, but not lipids?
A. Lipids are too small to bind to enzymes.
B. Lipids are too hydrophobic to be broken down by enzymes.
C. Enzymes denature in the presence of lipids.
D. Enzymes bind only to their specific substrates.
D. Enzymes bind only to their specific substrates.
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an important signaling molecule in the nervous system. After it transmits a signal, ACh is broken down by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in a reaction known as ACh hydrolysis.
Which of the following best describes the effect AChE has on the hydrolysis of ACh?
A. AChE increases the activation energy of ACh hydrolysis, increasing the rate of this reaction.
B. AChE increases the activation energy of ACh hydrolysis, increasing its rate.
C. AChE decreases the activation energy of ACh hydrolysis, increasing the rate of this reaction.
D. AChE decreases the activation energy of ACh hydrolysis, decreasing the rate of this reaction.
C. AChE decreases the activation energy of ACh hydrolysis, increasing the rate of this reaction.
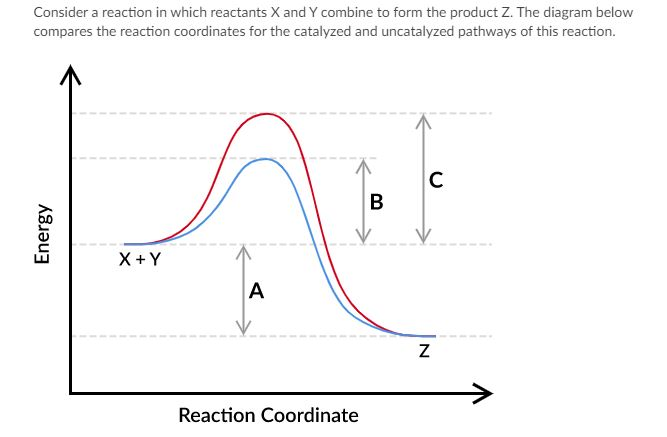
Which of the following statements about letter B is true?
A. Letter B represents the energy difference between the reactants and products for the uncatalyzed pathway.
B. Letter B represents the energy difference between the reactants and products for the catalyzed pathway.
C. Letter B represents the activation energy of the catalyzed reaction pathway.
D. Letter B represents the activation energy of the uncatalyzed reaction pathway.
C. Letter B represents the activation energy of the catalyzed reaction pathway.
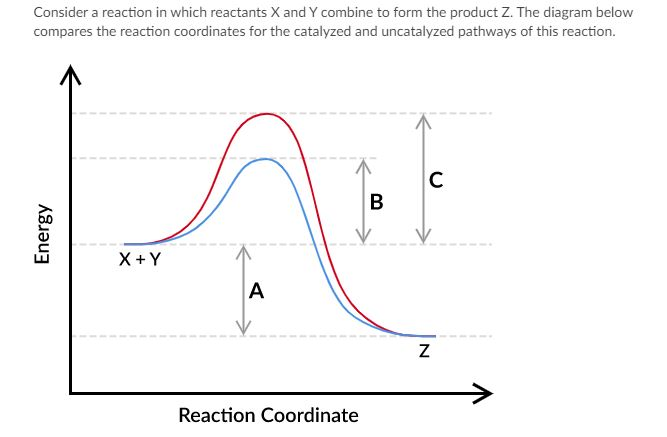
Which of the following statements about letter C is true?
A. Letter C represents the activation energy of the catalyzed reaction pathway.
B. Letter C represents the activation energy of the uncatalyzed reaction pathway.
C. Letter C represents the energy difference between the reactants and products for the uncatalyzed pathway.
D. Letter C represents the energy difference between the reactants and products for the catalyzed pathway.
B. Letter C represents the activation energy of the uncatalyzed reaction pathway.
Which of the following best describes the process of induced fit?
A. A substrate binds to the active site of an enzyme without either structure changing conformation.
B. A substrate binds to the active site of an enzyme, causing the conformation of the active site to change slightly.
C. A substrate binds to an allosteric site on an enzyme, causing the conformation of the allosteric site to change slightly.
D. A substrate changes conformation and then binds to the active site of an enzyme.
B. A substrate binds to the active site of an enzyme, causing the conformation of the active site to change slightly.
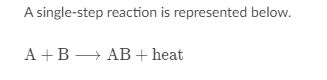
Which of the following best explains how the addition of an enzyme would affect the above reaction?
A. The enzyme would increase the activation energy of the reaction, increasing its rate.
B. The enzyme would decrease the activation energy of the reaction, increasing its rate.
C. The enzyme would increase the activation energy of the reaction, decreasing its rate.
D. The enzyme would decrease the activation energy of the reaction, decreasing its rate.
B. The enzyme would decrease the activation energy of the reaction, increasing its rate.
Maltase is an enzyme found in the small intestine. It helps break down maltose during the process of digestion.
Which of the following best describes what happens when maltose binds with maltase?
A. Maltose binds to the active site of maltase, causing the conformation of the active site to change slightly.
B. The conformation of maltose is already complementary to the active site of maltase, so maltose binds to the active site without either structure changing conformation.
C. The conformation of maltose changes, and then maltose binds to the active site of maltase.
A. Maltose binds to the active site of maltase, causing the conformation of the active site to change slightly.
Which of the following statements accurately describes an energy-releasing process that is coupled to an energy-requiring process in the cell?
A. The movement of motor proteins is powered by the formation of ADP and inorganic phosphate from ATP.
B. An exothermic chemical reaction is powered by ATP hydrolysis in the chloroplast
C. The transport of ions across a membrane is powered by the formation of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
D. An endothermic chemical reaction provides the energy for ATP hydrolysis in the mitochondria.
A. The movement of motor proteins is powered by the formation of ADP and inorganic phosphate from ATP.
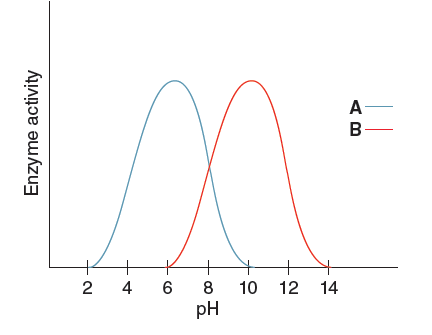
A solution of enzyme A has pH of 8. Based on the graph, which pH change would result a higher enzyme activity?
A. Decreasing the pH of the solution to 4
B. Increasing the pH of the solution to 10
C. Increasing the pH of the solution to 12
D. Decreasing the pH of the solution to 6
D. Decreasing the pH of the solution to 6
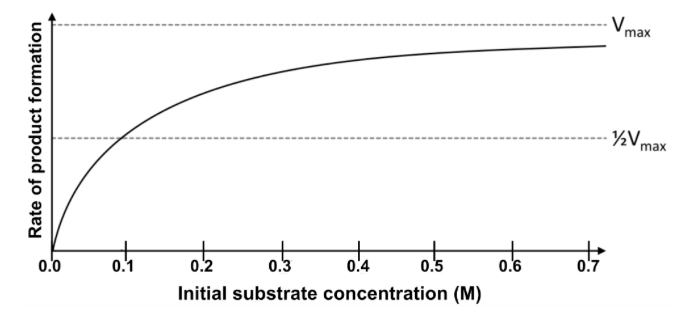
Several scientists are studying the effect of initial substrate concentration on the activity of an enzyme. They perform a series of enzyme-controlled reactions, keeping the concentration of enzyme constant but increasing the initial concentration of substrate in each trial. The graph below shows their results.
Based on the data above, which of the following best describes what happens to the rate of product formation at higher initial substrate concentrations?
A. The rate of product formation levels off because no substrate is available to bind with the enzyme.
B. The rate of product formation levels off because nearly all of the enzyme is bound to substrate.
C. The rate of product formation decreases because nearly all of the enzyme is bound to substrate.
D. The rate of product formation decreases because no substrate is available to bind with the enzyme.
B. The rate of product formation levels off because nearly all of the enzyme is bound to substrate.
Methotrexate is a drug that is commonly used to treat cancers and autoimmune diseases in humans. It functions by binding to the active site of the enzyme DHFR, preventing both DNA synthesis and excess cell proliferation.
Which of the following terms best describes methotrexate?
A. Noncompetitive inhibitor
B. Cofactor
C. Competitive inhibitor
D. Allosteric activator
C. Competitive inhibitor
Pepsin, a proteolytic enzyme found in the stomach, is essential for digestion. Pepsin functions optimally at approximately 37 o.
Which of the following would most likely result if pepsin’s environmental temperature was lowered from 37oC to 25oC?
A. Pepsin would catalyze reactions at a faster rate.
B. Pepsin would be less efficient at catalyzing reactions.
C. Pepsin would lose its three-dimensional shape.
D. Pepsin would more easily lower the activation energy of reactions.
B. Pepsin would be less efficient at catalyzing reactions.
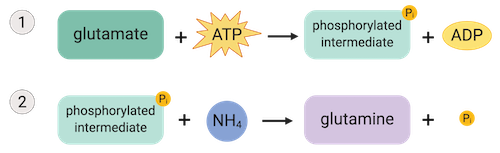
The enzyme glutamine synthetase facilitates the use of energy to combine glutamate and ammonia (NH4), forming glutamine. This process occurs in two steps, as represented in the following diagram.
Which of the following statements best describes the process carried out by glutamine synthetase?
A. Glutamine synthetase uses energy to hydrolyze ATP, which then drives the formation of glutamine from glutamate and ammonia.
B. Glutamine synthetase forms glutamine by coupling two endothermic reactions, both of which occur in the enzyme’s active site.
C. Glutamine synthetase uses an exothermic reaction to drive an endothermic one by catalyzing the formation of a phosphorylated intermediate.
D. Glutamine synthetase forms a phosphorylated intermediate by attaching a molecule of ATP to glutamate
C. Glutamine synthetase uses an exothermic reaction to drive an endothermic one by catalyzing the formation of a phosphorylated intermediate.
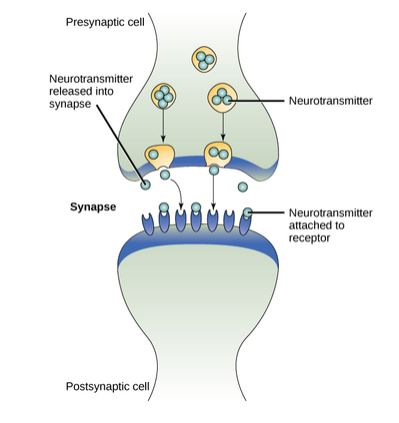
Which of the following best describes the cell communication occurring in the figure above?
A. A signal-emitting cell communicates with a nearby cell by releasing local regulators.
B. A signal-emitting cell communicates with a far-away cell by releasing long-distance signaling molecules.
C. A signal-emitting cell communicates with a nearby cell through direct cell-to-cell contact.
D. A signal-emitting cell communicates with a far-away cell by releasing local regulators.
A. A signal-emitting cell communicates with a nearby cell by releasing local regulators.
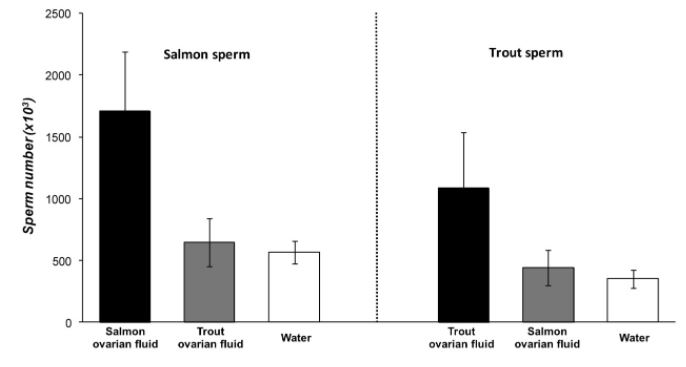
To complete external fertilization in fish, sperm cells must swim through open water in order to fertilize egg cells. During this process, females release a substance called ovarian fluid, which helps guide the sperm cells toward the egg cells. Researchers hypothesized that sperm cells are mainly attracted by ovarian fluid released from the same species.
To test this hypothesis, researchers performed an experiment in which they studied the effects of salmon ovarian fluid and trout ovarian fluid on salmon sperm. In each trial within the experiment, the researchers placed salmon sperm on one side of a porous membrane and either salmon ovarian fluid, trout ovarian fluid, or water on the other side. After two minutes, the researchers counted how many salmon sperm had passed through the membrane and into the fluid. The results are presented in the graph below.
Which of the following conclusions is best supported by the data above?
A. Salmon sperm respond more strongly to long-distance signaling molecules in trout ovarian fluid than to those in salmon ovarian fluid.
B. Salmon sperm respond more strongly to long-distance signaling molecules in salmon ovarian fluid than to those in trout ovarian fluid.
C. Salmon sperm respond more strongly to local regulators in salmon ovarian fluid than to those in trout ovarian fluid.
D. Salmon sperm respond more strongly to local regulators in trout ovarian fluid than to those in salmon ovarian fluid.
B. Salmon sperm respond more strongly to long-distance signaling molecules in salmon ovarian fluid than to those in trout ovarian fluid.
The tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) is a plant virus that infects a wide range of plants, including tobacco. In order to enter and travel through the cells of a plant, TMV produces a movement protein. This protein helps the virus travel directly between the cytoplasms of interconnected plant cells.
Which of the following best predicts how the movement protein modifies plant cells in order to help TMV travel from cell-to-cell?
A. The movement protein modifies the plasmodesmata between plant cells.
B. The movement protein modifies the vacuoles within plant cells.
C. The movement protein increases the formation of cell walls between plant cells.
D. The movement protein increases the formation of transport vesicles within plant cells.
A. The movement protein modifies the plasmodesmata between plant cells.
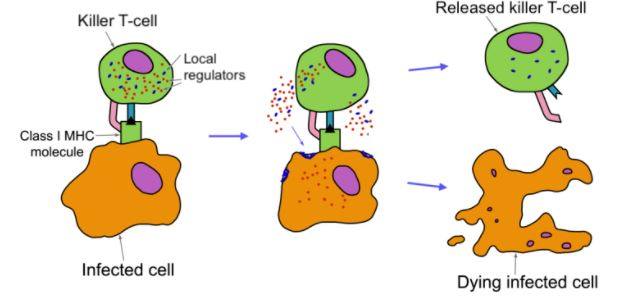
During an experiment, researchers introduced a substance that caused the Class I MHC molecule to break down.
Which of the following best describes how the cell-mediated immune response will be affected?
A. The killer T-cell will still bind to the infected cell, but the infected cell will instead be killed by a helper T-cell.
B. The killer T-cell will no longer bind to the infected cell, and as a result, the infected cell will not be killed.
C. The killer T-cell will still bind to the infected cell, but the infected cell will not be killed.
D. The killer T-cell will no longer bind to the infected cell, and the infected cell will instead be killed by killer T-cells releasing long-distance signals.
B. The killer T-cell will no longer bind to the infected cell, and as a result, the infected cell will not be killed.
During cell communication in the nervous system, chemical messengers called neurotransmitters travel between neurons. As they travel, neurotransmitters send messages from one neuron to another.
Which of the following best describes the role of neurotransmitters in neuron-to-neuron communication?
A. Neurotransmitters are local regulators that allow neurons to communicate over long distances.
B. Neurotransmitters are local regulators that allow neurons to communicate over short distances.
C. Neurotransmitters are long-distance signaling molecules that allow neurons to communicate over short distances.
D. Neurotransmitters are long-distance signaling molecules that allow neurons to communicate over long distances.
B. Neurotransmitters are local regulators that allow neurons to communicate over short distances.
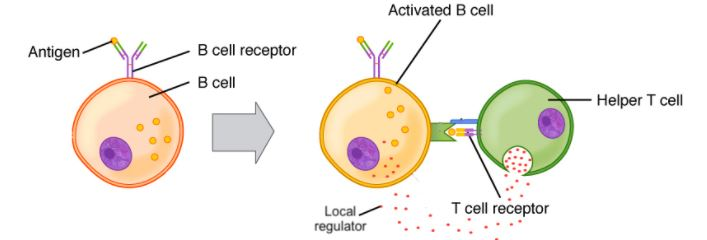
During the humoral immune response, helper T-cells activate B-cells through cell communication. This process is shown in the image below.
During an experiment, researchers introduced a substance that caused the T-cell receptor to break down.
Which of the following best describes how the humoral immune response will be affected?
A. The helper-T cell will no longer bind to the B-cell, as a result, B-cell will not be activated.
B. The helper-T cell will no longer bind the B-cell, but instead the helper-B cell will be activated by helper-T cell by releasing long-distance signals.
C. The helper-T cell still binds to the B-cell, but B-cell will instead be activated by the killer-T cell.
D. The helper-T cell will bind to the B-cell, but B-cell will not be activated.
A. The helper-T cell will no longer bind to the B-cell, as a result, B-cell will not be activated.
Mutations within genes coding for G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) can lead to one of two major outcomes—a loss-of-function or a gain-of-function. Loss-of-function mutations prevent signaling in GPCR pathways, even in the presence of signaling molecules. Gain-of-function mutations activate signaling in GPCR pathways, even in the absence of signaling molecules.
Which of the following is most likely to result from a loss-of-function GPCR mutation?
A. Signal transduction pathways that are inactive only if ligand-to-receptor binding does not occur
B. Signal transduction pathways that are activated without ligand-to-receptor binding
C. Signal transduction pathways that are activated by multiple types of ligands
D. Signal transduction pathways that are inactive even if ligand-to-receptor binding occurs
D. Signal transduction pathways that are inactive even if ligand-to-receptor binding occurs
The following is an excerpt from a scientific paper by Jean-Pierre Raufman.
Cholera, an infectious disease that can kill humans within a matter of hours, is a manifestation of a highly efficient and specific toxin delivery mechanism. This mechanism, which is shared by several bacteria, delivers a potent toxin to activate selectively the adenylyl cyclase system of human intestinal secretory cells. This increases production of the ‘‘second messenger’’ cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) that activates an intestinal crypt cell chloride ion channel, thereby resulting in massive fluid and electrolyte secretion into the lumen of the gut.
Raufman, J. P. (1998). Cholera. Am. J. Med. 104, 386–394.
Based on the information above, which of the following is most likely to be observed in the intestinal environment of a person infected with cholera?
A. Elevated levels of intracellular ATP
B. Reduced levels of intracellular cAMP
C. Reduced levels of extracellular chloride ions
D. Elevated levels of extracellular chloride ions
D. Elevated levels of extracellular chloride ions
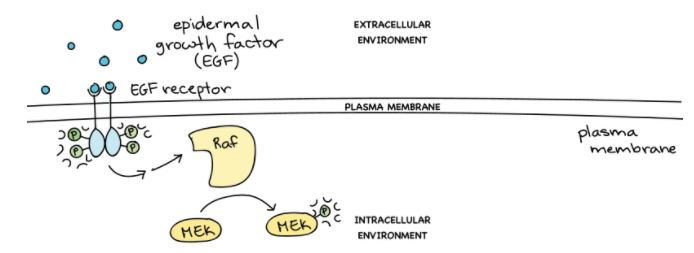
The information below shows and describes the initial steps of the MAPK/ERK signaling cascade.
When epidermal growth factor (EGF) ligands bind to their receptors, the receptors pair up and act as kinases, attaching phosphate groups to one another’s intracellular tails. The activated receptors then trigger a series of events that activate the kinase Raf.
Which of the following toxins will most likely inhibit the activation of MEK?
A. A toxin that prevents the transfer of a phosphate group to Raf
B. A toxin that prevents the kinase activity of Raf
C. A toxin that prevents the dephosphorylation activity of Raf
D. A toxin that prevents MEK from phosphorylating Raf
B. A toxin that prevents the kinase activity of Raf
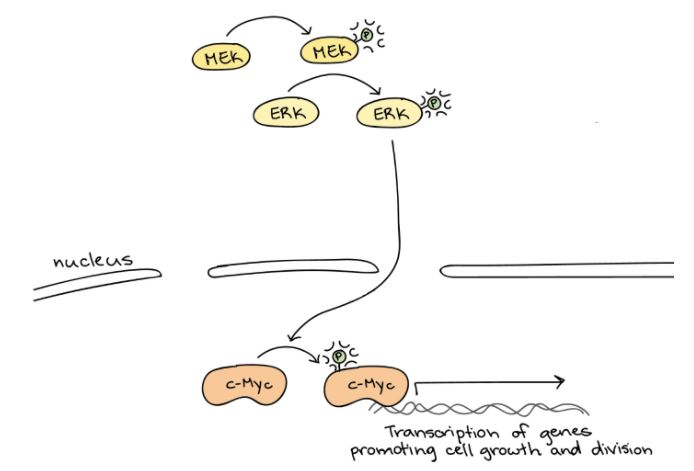
The information below shows and describes the intermediate steps of the MAPK/ERK signaling cascade.
After MEK is activated, it phosphorylates and activates ERK. ERK goes on to phosphorylate and activate a variety of target molecules, including transcription factors like c-Myc that promote cell growth and division.
Which of the following toxins will most likely inhibit the phosphorylation of c-Myc?
A. A toxin that prevents c-Myc from activating ERK
B. A toxin that prevents the phosphorylation of ERK
C. A toxin that prevents the dephosphorylation activity of MEK
D. A toxin that prevents the removal of a phosphate group from ERK
B. A toxin that prevents the phosphorylation of ERK
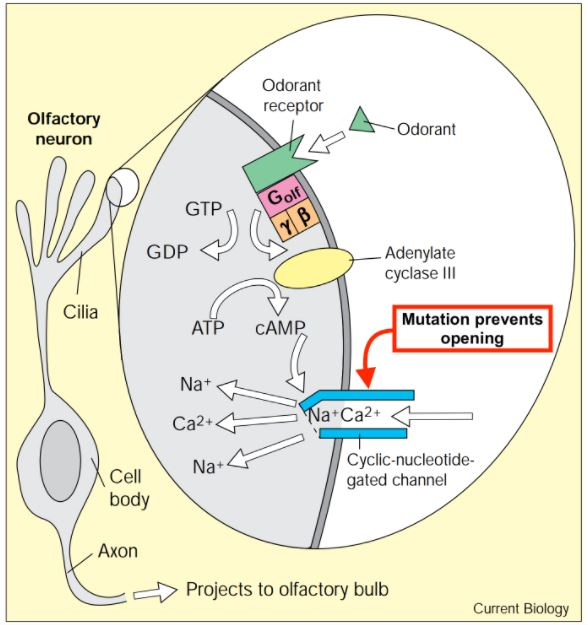
The following excerpt and image come from a scientific paper written by Ebrahimi & Chess. They discuss the role of G proteins in olfaction, or the sense of smell.
Each mammalian olfactory neuron appears to use the same machinery for transducing signals from its odorant receptor molecules. Upon odorant binding, the receptor is thought to activate Golf, a G protein.
mediated activation of adenylate cyclase III then raises intracellular cAMP levels, causing a cyclic-nucleotide-gated channel to open. The influx of cations through this channel ultimately leads to the formation of an action potential, which allows the primary neuron to signal to the brain.
A mutation in a component of this signal transduction pathway prevents the cyclic-nucleotide-gated channel from opening.
Which of the following scientific questions would best help researchers understand how the mutation prevents the cyclic-nucleotide-gated channel from opening?
A. Does mutation cause intracellular cAMP level to rise?
B. Does mutation cause the influx of cations into the cell?
C. Does the mutation block the activation of adenylate cyclase III?
D. Does mutation stimulate the conversion of ATP to cAMP?
C. Does the mutation block the activation of adenylate cyclase III?
Which of the following correctly describes how positive and negative feedback are different?
A. Negative feedback reverses changes in a system, while positive feedback amplifies changes in a system.
B. Positive feedback moves a system closer to its set point, while negative feedback moves a system further from its set point.
C. Positive feedback occurs only in response to stimuli, while negative feedback can occur in the absence of stimuli.
D. Negative feedback requires the detection of stimuli, while positive feedback functions independently of stimuli.
A. Negative feedback reverses changes in a system, while positive feedback amplifies changes in a system.
Which of the following statements about feedback mechanisms is most accurate?
A. Positive feedback mechanisms bring a system closer to its set point.
B. Positive feedback mechanisms maintain a system at its set point.
C. Negative feedback mechanisms move a system further from its set point.
D. Negative feedback mechanisms return a system to its set point.
D. Negative feedback mechanisms return a system to its set point.
he endocrine system maintains homeostasis in the body through the release of various hormones. For example, the pancreas releases the hormone insulin to help regulate blood glucose homeostasis.
Which of the following best describes the role of insulin in regulating blood glucose homeostasis?
A. Insulin is released in response to high blood glucose levels. This release triggers a negative feedback loop that returns blood glucose levels back to normal.
B. Insulin is released in response to high blood glucose levels. This release triggers a positive feedback loop that further increases blood glucose levels.
C. Insulin is released in response to low blood glucose levels. This release triggers a positive feedback loop that further decreases blood glucose levels.
D. Insulin is released in response to low blood glucose levels. This release triggers a negative feedback loop that returns blood glucose levels back to normal.
A. Insulin is released in response to high blood glucose levels. This release triggers a negative feedback loop that returns blood glucose levels back to normal.
A biologist is studying the genetics of a particular species of plant. He knows that one plant may contain hundreds of individual seeds, each of which is the result of a separate fertilization event. He determines that seed shape is controlled by a single gene with two alleles. The dominant allele results in round seeds, and the recessive allele results in wrinkled seeds.
In a follow-up experiment, the biologist crosses two heterozygous plants.
Which of the following is the best prediction for the frequency of wrinkled seeds that would result from this cross?
A. 0%
B. 25%
C. 50%
D. 100%
B. 25%
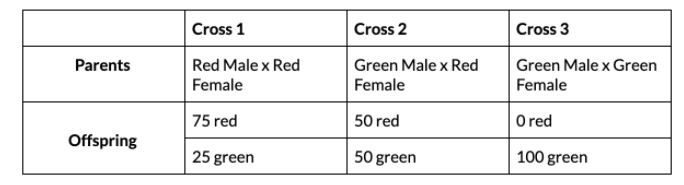
The data above represent the results of three different crosses in which a single gene determines whether a certain organism is red or green.
Which of the following best describes the mechanism of inheritance of the gene?
A. Color is a codominantly inherited trait because a 1:1 phenotypic ratio of red-to-green is observed in cross 2
B. The allele for green is an autosomal dominant allele because no red offspring are produced in cross 3
C. The allele for red is an autosomal recessive allele because no red offspring are produced in cross 3
D. The allele for green is an autosomal recessive allele because a 3:1 phenotypic ratio of red-to-green is observed in cross 1
D. The allele for green is an autosomal recessive allele because a 3:1 phenotype ratio of red to green is observed in cross 1
A group of students are studying flower color inheritance in the garden pea plant (Pisum sativum). They obtain a purple-flowered pea plant of unknown ancestry, allow it to self-pollinate, and collect 60 of its seeds. After planting the seeds, they observe the growth of 42 purple-flowered plants and 18 white-flowered plants.
Which of the following best explains the flower colors seen in the offspring?
A. A somatic mutation in the flower color gene produced the white flower color.
B. White flower color is a trait recessive to purple flower color.
C. Purple flowers and white flowers are codominant.
D. The flower color changes as the plants mature.
B. White flower color is a trait recessive to purple flower color.
In peas, yellow seed color (Y) is dominant over green seed color (y). Which of the following would be expected in the F1 generation of a monohybrid cross given that the P1 generation is a dominant homozygote crossed with a recessive homozygote?
A. Only plants that produce yellow seeds.
B. Only plants with the Yy genotype.
C. Plants with one yellow seed for every green seed.
D. Three plants with yellow seeds for every plant with green seeds.
B. Only plants with the Yy genotype.
In the F1 generation of 915 pea plants, there were 716 tall plants and 199 short plants. Tall is dominant over short. What was the parental cross?
A. tt x tt
B. Tt x Tt
C. TT x tt
D. Tt x tt
B. Tt x Tt
A couple has a son and a daughter, what is the probability of their next baby to be a girl or a boy?
A. 100%
B. 50%
C. 25%
D. 75%
A. 100%
A couple has 3 sons, what is the chance of having a girl next?
A. 100%
B. 50%
C. 25%
D. 75%
B. 50%
In pea plants, tall stem is a dominant trait over the dwarf stem. A student is asked to determine an unknown genotype for a pea plant with tall stem. In 1000 pea plants, he observed 567 plants with tall stem. What should the student do to find out the unknown genotype of a pea plant with tall stem?
A. He should perform a test cross by crossing a dwarf stem plant with another dwarf plant and observe the phenotypic ratio of the offspring.
B. He should perform a test cross by crossing a tall stem plant with another tall stem plant and observe the phenotypic ratio of the offspring.
C. He should perform a test cross by crossing a tall stem plant with a dwarf plant and observe the phenotypic ratio of the offspring.
D. All the answer choices are correct.
C. He should perform a test cross by crossing a tall stem plant with a dwarf plant and observe the phenotypic ratio of the offspring.