Meosis
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Genes
The code for the formation of proteins, which carry out most of the work for cells.
Homologous Chromosomes
Chromosomes that carry the same genes and control the same traits and that make up a pair, which is one from each parent.
Gametes
Sex cells (sperm and egg) Each have 23 chromosomes.
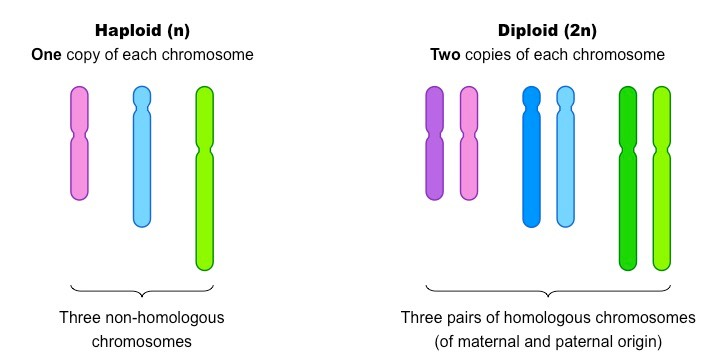
Haploid cells
These have one set of chromosomes
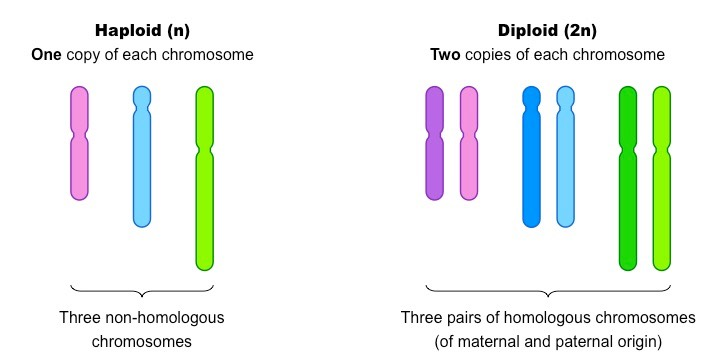
Diploid cells
These have two sets of chromosomes
Sex chromosomes
1 pair of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in a human cell determines an individual’s gender. An individual with two X chromosomes is considered female. An individual with one X chromosome and one Y chromosome is considered male.
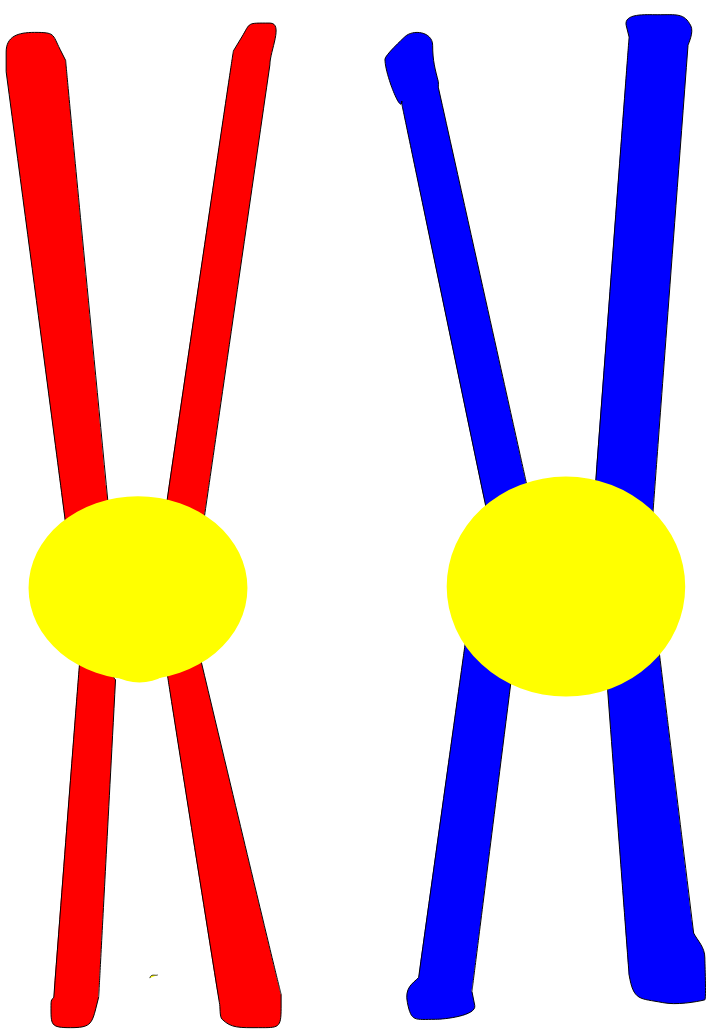
Autosomes
Other 22 pairs of chromosomes that are not sex chromosomes.
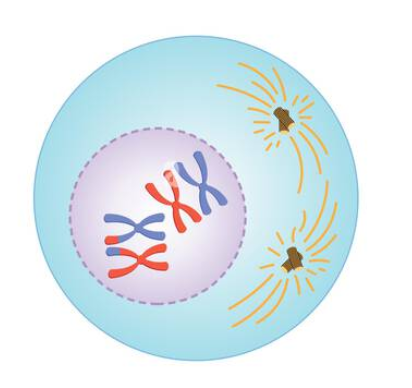
Prophase 1
Pairing of homologous chromosomes occurs, each chromosome consists of two chromatids.
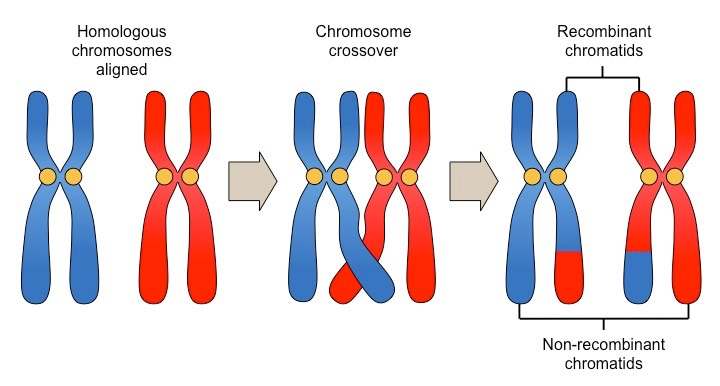
Crossing over produces exchange of genetic information
Nuclear envelope breaks down
Spindle fibers form.
Crossing over
The process by which chromosomal segments are exchanged between a pair of homologous chromosomes.
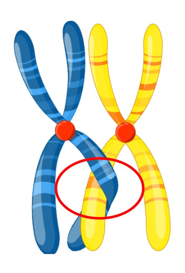
Synapsis
The homologous chromosomes are held tightly together along their lengths.
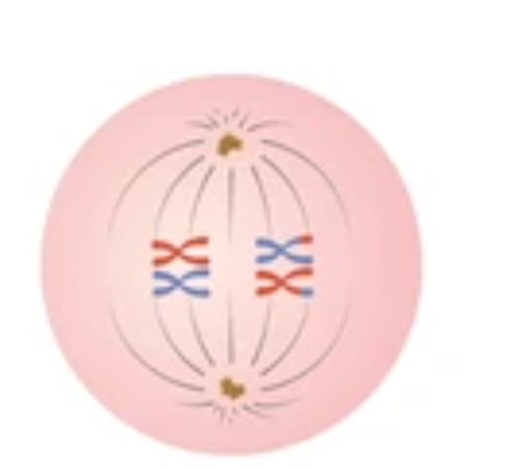
Metaphase 1
Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers
Homologous chromosomes line up at the equator
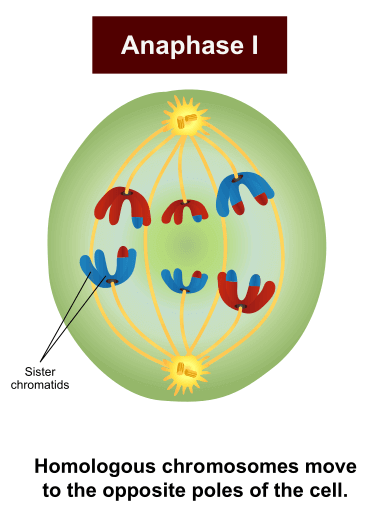
Anaphase 1
Homologous chromosome separate and move to opposite poles of the cells.
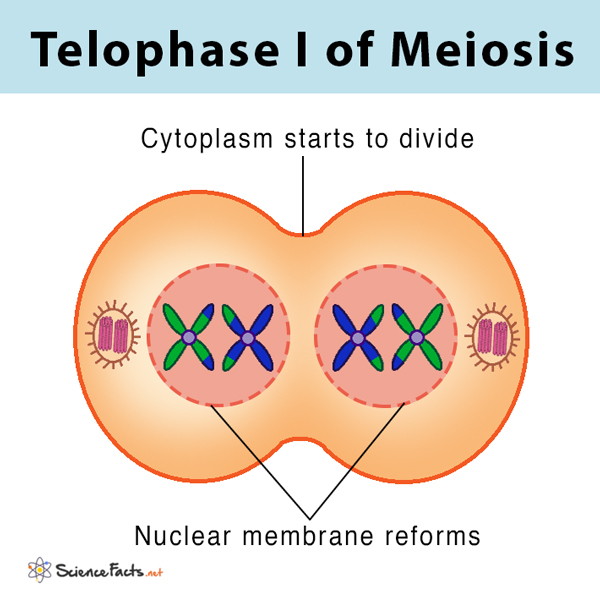
Telophase 1
The spindles break down
Chromosomes uncoil and form two nuclei
Cell divides

Prophase II
Chromosomes condenses
Spindle forms in each new cell
Spindle fibers attach to chromosomes
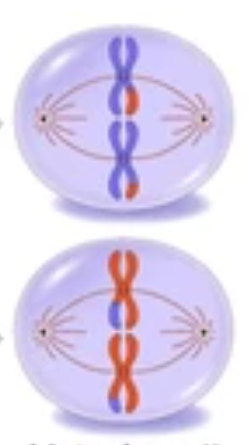
Metaphase II
Centromeres of chromosomes line up randomly at the equator of each cell.

Anaphase II
Centromeres split
Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles.
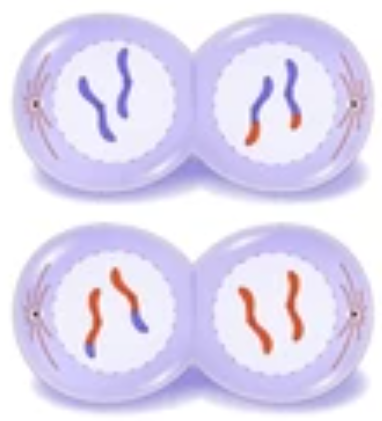
Telophase II
Four Nuclei forms around chromosomes
Spindles break down
Cell divides
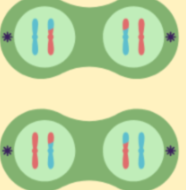
Products
Four daughter cells are made
Each nuclei has a haploid number of chromosomes.
Mitosis vs Meiosis
He I’m too lazy go read the book !
Telomeres
Protective caps that chromosomes end in
Karyotype
Pairs of homologous chromosomes that are arranged in decreasing size to produce a micrograph.
Nondisjunction
Cell division in which sister chromatids fail to separate properly.
Cellular differentiation
The process by which an unspecialized cell develops into a specialized cell with a defined structure and function.
Stem cell
Type of cell that can be directed to become a specialized cell.