Structure 1.1 Intro to the particulate nature of matter
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Structure 1.1.1 Structure 1.1.2 Structure 1.1.3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Define Elements
primary constituents of matter, that can’t be chemically broken down into simpler substances.
Define Compounds
Consist of atoms of different elements chemically bonded together in a fixed ratio.
Define Mixtures
Contain more than one element or compound in no fixed ratio, which are not chemically bonded and can be separated by physical methods.
What are the characteristics of matter
Occupies volume in space
Has a mass
Made up of particles
Particles are in constant motion
What is the atomic theory
The atomic theory states that all matter is composed of Atoms which can’t be created or destroyed, they are only rearranged during chemical reaction. Physical and chemical properties depend on the bonding and arrangement of these atoms.
What are pure substances
made up of only one type of particle or molecule.
They have a fixed composition and distinct chemical properties.
exist in either element or compound form.
Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means, such as oxygen or gold.
Compounds are pure substances composed of two or more elements chemically combined in fixed ratios, such as water (H2O) or sodium chloride (NaCl).
Pure substances have specific physical and chemical properties, including melting point, boiling point, and reactivity, that distinguish them from mixtures.
Atom
smallest unit of matter that contain specific properties.
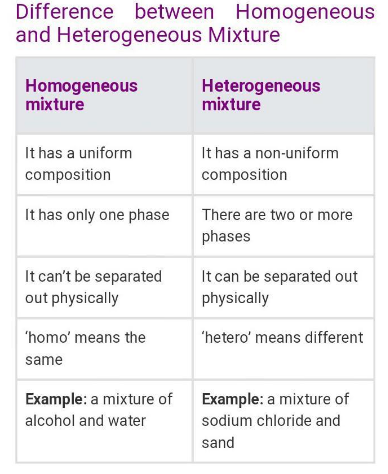
Homogenous mixtures
Homogeneous mixtures are uniform in composition and properties throughout. They have a consistent distribution of substances and cannot be visually distinguished. Examples include saltwater, air, and sugar dissolved in water.
Heterogenous mixture
Heterogeneous mixtures are mixtures that have non-uniform composition and properties. In these mixtures, the components are not evenly distributed and can be distinguished by the naked eye or under a microscope. Examples of heterogeneous mixtures include a mixture of oil and water, a salad with different ingredients, and a mixture of sand and water.
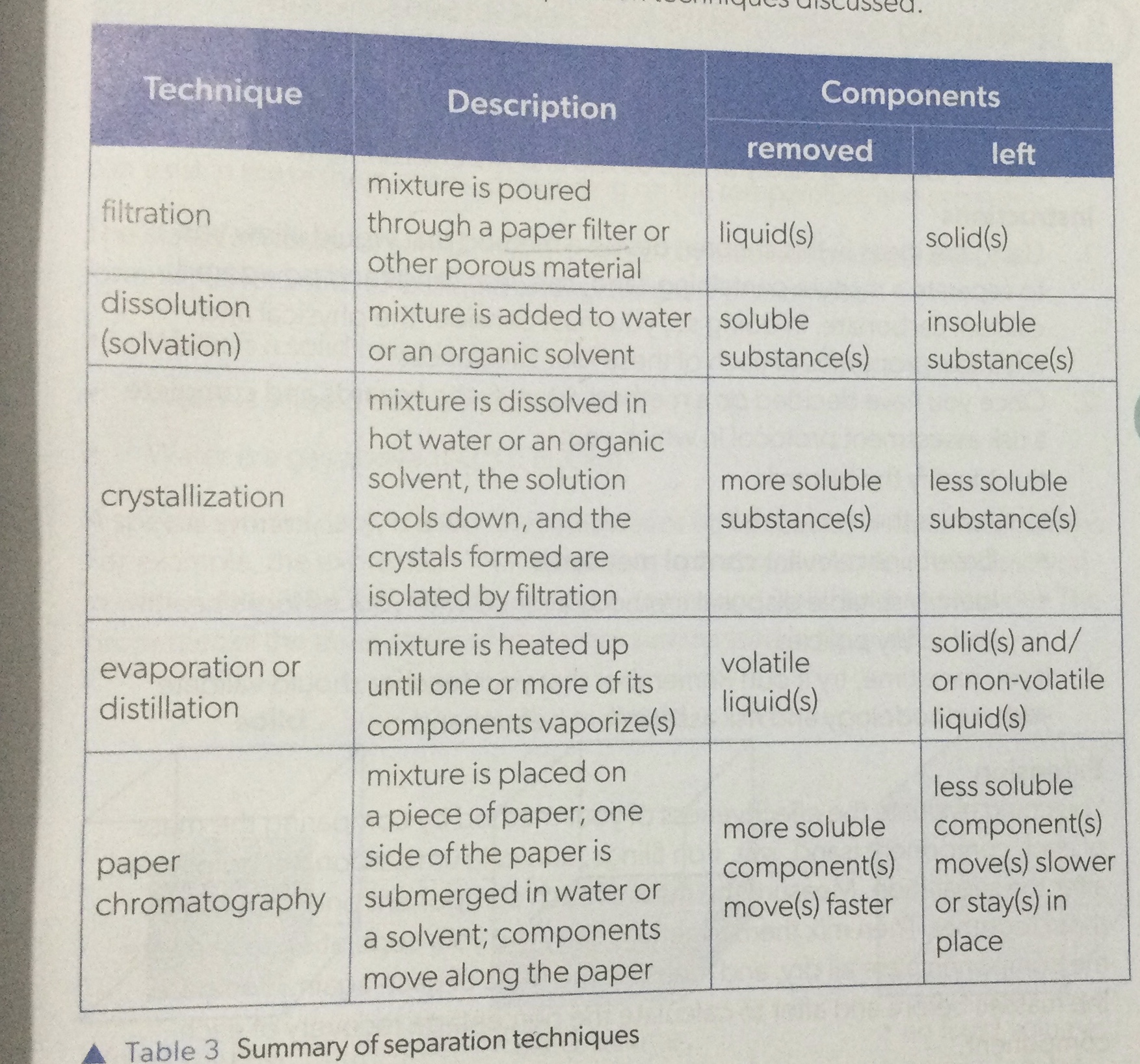
Outline the process of Filtration
Process of Filtration:
Pour mixture into a filter funnel.
Filter paper traps solid particles, allowing liquid to pass through.
Solid particles remain on the filter paper.
Collected liquid is called the filtrate.
Filtrate can be further processed or analyzed.
Filtration is used to separate solids from liquids based on particle size.
outline the process of Crytallisation
The process of crystallization involves the following steps:
Dissolve the solute in a suitable solvent.
Apply heat to the solution to increase the solubility of the solute.
Allow the solution to cool slowly, promoting the formation of crystals.
As the solution cools, the solute molecules arrange themselves in an orderly pattern, leading to the formation of crystals.
Separate the crystals from the remaining solution using techniques such as filtration or decantation.
Wash the crystals with a suitable solvent to remove impurities.
Dry the crystals to remove any remaining solvent and ensure purity.
Measure and record the yield of crystals obtained.
Analyze the crystals for desired properties, such as size, shape, and purity.
Techniques of seperation
Distinguish between homogenous and heterogenous mixtures
Describe the properties of solids
fixed volume
fixed shape
can’t be compressed
attractive forces between particles are strong
Particles vibrate in fixed positions but don’t move around
Describe the properties of liquids
Fixed volume
no fixed shape
can’t be compressed
attractive forces between particles are weaker than solids
particles vibrate, rotate and move around
Describe the properties of gases
no fixed volume
no fixed shape
can be compressed
attractive forces between particles are negligible
particles vibrate, rotate and move around faster than in a liquid
Solid → Gas
Sublimation
Gas → Solid
Deposition
Solid → liquid
melting
Liquid → solid
freezing
Liquid → Gas
Evaporation
Gas → Liquid
Condensation
Define Endothermic
Energy is absorbed by the particles from the surroundings
Define Exothermic
Particles releasing energy to the surroundings
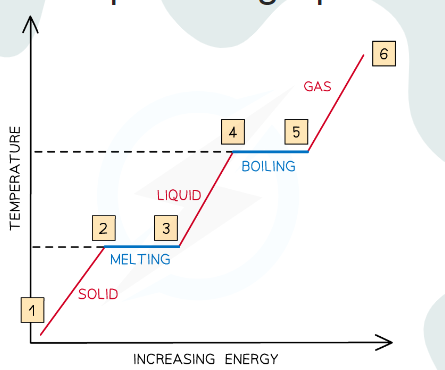
Analyze this graph
Between 1 & 2, the particles are vibrating and gaining kinetic energy and the temperature rises
Between 2 & 3, all the energy goes into breaking bonds – there is no increase in kinetic energy or temperature
Between 3 & 4, the particles are moving around and gaining in kinetic energy
Between 4 & 5, the substance is boiling, so bonds are breaking and there is no increase in kinetic energy or temperature
From 5 & 6, the particles are moving around rapidly and increasing in kinetic energy
Define Temperature
Measure of average kinetic energy of particles
What is the relationship between kelvin temperature and average kinetic energy of particles?
Kelvin temperature is proportional to the average kinetic energy of particles
What is Absolute zero (0K)?
Temperature at which particles cannot transfer any kinetic energy on collisions
Converting Celcius to Kelvin
Temperature in Celcius + 273.15
explain why the kelvin temperature is directly proportional to average kinetic energy but the celcius temperature is not, even though a 1 degree temperature increment is the same in each scale?
In the Kelvin scale, temperature is directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of the particles. As the temperature increases, the average kinetic energy of the particles increases as well.
The Celsius scale is a relative scale, meaning it is based on the properties of a specific substance (water) rather than being an absolute scale like the Kelvin scale.
The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale where zero Kelvin (0 K) corresponds to absolute zero, the lowest possible temperature where molecular motion ceases entirely.