IMMUNOLOGY MODULE 1-2
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What is innate immunity?
Initial defense against infections
what is adaptive immunity?
develops later and are mediated by lymphocytes and their products
learned response after you encounter so it will be faster to respond next time it invades
what cells are part of adaptive system?
lymphocytes
B lymphocytes
T lymphocytes
NK cells
antigen presenting cells
dendritic cells
what are antigens?
foreign pathogens
what are the type of adaptive immunity?
humoral immunity
B lymphocytes secrete antibodies that eliminate extracellular microbes
cell mediated immunity
different types of T lymphocytes recruit and activate phagocytes to destroy ingested microbes and kill infected cells
what is the difference between primary and secondary immune responses?
primary
1st exposure
mediated by lymphocytes called naive lymphocytes that are seeing antigens for the 1st time
secondary
rapid, larger, and better at eliminating antigen than the primary
result in activation of memory lymphocytes
Difference between IgG and IgM
IgG is not a specific antigen
IgM is a specific antigen
what are different types of lymphocytes
B lymphocytes
recognize soluble or cell surface antigens and differentiate into antibody-secreting cells
helper T- lymphocyte
recognize antigens on the surfaces of APC and secrete cytokinesis
cytotoxic T lymphocyte
recognize antigens in infected cells and kill those cells
Regulatory T cells
limit activation of other lymphocytes- prevent autoimmunity
NK cells
recognize changes on the surface of infected cells and kill these cells
What are CD3, CD4, CD8?
surface markers (used to identify specific cells) on each lymphocytes
How does the immune system respond to an antigen?
antibody binds an antigen directly, whereas a T receptor binds a complex of: an antigen fragment and a self molecule
cells inside holding virus protein- then it won’t know so they pish them outside in order to alert
Differences between MHC I and MHC II
MHC I
collect peptides derived from and synthesized in the cytosol and are this able to display fragments of viral and on the cell surface
present antigens derived from proteins in the cytosol
MHC II
peptides derived from bacteria and transported to the cell surface
bind and transport peptides derived from antigen has been bound and internalized by B cells antigen receptors
what are cytokines?
proteins released by cells that affect the behavior of other cells that bear receptors from them
affect behavior of other cells
cells release message —> trigger response
what are chemokines?
proteins that attract cells with specific chemokines receptors such as neutrophils and monocytes from the blood stream
chemical molecule to recruit help
why do macrophages express a variety of receptors?
allows to recognize different pathogens
What are the significance of TLR2 and TlR4?
TLR-pattern recognition receptor present on macrophages and other immune cells, and they are able to bind different microbial component
TLR 2-
cell wall components of gram positive
TLR 4-
cell wall components of gram negative
what type of immune system does macrophages have?
innate immunity—→ have many different type of antigen receptors
What are antigen presenting cells?
capture antigens, transport them to peripheral lymphoid tissues, and display them to lymphocytes
What do antibodies do?
antibodies
come from plasma cells
protect against pathogens or their products by binding to them blocking their accel to cells
What are neutralization, opsonization, and complement activation?
neutralization
cite is bind and block access to cells
opsonization
an immune process which use opsonin to tag foreign pathogens for elimination by phagocytes
coats the bacterium and foreign particles in order to mark
complement activation
pathogen is lysed and then in activates through a triggered-enzyme cascade
What leukocytes are derived from the common myeloid progenitor cell and the common lymphoid progenitor cells?
myeloid progenitor us the precursor of the
granulocytes, macrophages, dendric cells, and mast cells of the innate immune system
the common lymphoid progenitor cells
lymphocytes (T &B) and to NK (innate immunity)
Describe the activated function of each leukocyte
Neutrophils
direct actions against bacteria
release lysozyme which destroy bacteria
release defensin proteins that act like antibiotics poking holes in bacterial cell walls destroying them
release strong oxidants (bleach-like, strong chemicals ) that destroy bacteria
eosinophils
combat the effects of histamine in allergic reactions, phagocytize antigen-antibody complexes, and combat parasitic worms.
basophils and mast cells
liberate heparin, histamine, and serotonin in allergic reactions that intensify the inflammatory response.
B-lymphocytes
response to the presence of foreign substances called antigens, differentiate into tissue plasma cells that produce antibodies
memory cells
T-lymphocytes
destroy foreign invaders directly
cd 8
dendritic cells
mature antigen presenting cells
How do dendritic cells form a link between innate immune system and the adaptive immune system?
adaptive immune response
pathogen ingested by an immature dendritic cell in the infected tissue
Once absorbed travel through the lymph to the regional lymp nodes where they mature and interact with recirculating naive lymphocyte
dendritic
behave as an innate system
What are PAMPS? What effect do Pamps have on the immune system?
derived from microorganisms and recognized by pattern recognition receptor (PRR)-bearing cells of the innate immune system
difference between PAMPS and antigen
PAMPs
evoke an innate response
antigens
evoke an adaptive response if the innate response is not sufficient to eliminate the threat
describe the chain of events that occur during inflammation
Infection Stimulates Macrophages to Release Cytokines and Chemokines that Initiate an Inflammatory Response
Cytokines cause the dilation of local small blood vessels and changes in the endothelial cells of their walls.
These changes lead to the movement of leukocytes, such as neutrophils and monocytes, out of the blood vessel (extravasation) and into the infected tissue, guided by chemokines produced by the activated macrophages.
The blood vessels also become more permeable, allowing plasma proteins and fluid to leak into the tissues.
Together, these changes cause the characteristic inflammatory signs of heat, pain, redness, and swelling at the site of infection
why increase blood flow where is pain coming from
bring more leukocyte
when the buildup of fluid leads to swelling, and the swollen tissues push against sensitive nerve endings
Reason behind fluid in inflammation site
Interstitial fluid- lymphatic vessels (fluid drained)
Drainage of fluid to macrophages to “police/ t cells/ b cells”
Make plans for intruder
Designing “weapon” (DNA rearrangement)
Mass production
Attack (pathogens)
To make the pathogens move to the leukocytes
Function of lymphatic system
It keeps body fluid levels in balance and defends the body against infections
Lymph- vessels, tissues, organs, and glands work together to drain a watery fluid called lymph from throughout the body
What are interferons and what do they do?
INF:
Antiviral proteins produced by cells in response to viral infections
3 major functions:
Induce resistance to viral replication in uninfected cells
Induce MHC class 1 expression - more susceptible to be killed by CD8
Activate NK cells
Describe the complement system
Complement proteins- Synthesized by the liver
3 pathways
Classical
initiated by the binding of C1q to the pathogen surface.
Lectin
initiated by the binding of carbohydrates binding proteins to arrays of carbohydrates on the surface of pathogens.
Alternative
initiated by the binding of spontaneously activated C3 in plasma to the surface of pathogens
Describe how terminal complement proteins form the membrane-attack complex?
C5b triggers the assembly of a complex of one molecule each of C6, C7, and C8, in that order.
C7 and C8 undergo conformational changes, exposing hydrophobic domains that insert into the membrane. \
causes moderate membrane damage
serves to induce the polymerization of C9, again with the exposure of a hydrophobic site.
Draw an antibody molecule structure
What are the 5 classes of immunoglobulin
IgM
Produced after initial exposure to antigen
Promotes neutralization and agglutination of antigen
5-6 days
IgG
Crosses placenta- conferring passive immunity to fetus
Promotes opsonization, realization, agglutination of antigen
IgA
Present in tears, saliva, mucus, and breast milk
Provides localization defense of mucous membrane by agglutination and neutralization of antigens
Presence in breast confers passive immunity
IgE
Triggers release from mast cells and basophils of histamine and other chemicals that cause allergic reaction
IgD
Present primary of surface of naive B-cells that have not been exposed to antigen
Which ones are monomers?
IgG
IgE
IgD
Passive vs active immunity
Active
Immune system responding to antigen
Passive
Immune provided from someone else (
Antibodies not provided from the person
Vaccines
Mother’s
Explain what are hypervariable regions are on the body
Explain what complementary -determining region and variable framework regions are
Hypervariable region
Form the antigen binding site
Sequence variability concentrated in certain segment of the v region
HYPER- why?
There are many variables
Variation
Because there are many variants to recognize many antigens
3 regions
HV1, HV2, HV3
Complementary-determining region (complementary to the antigen surface)
hypervariable immunoglobin (Ig) domains that confine specific antibody binding
CDR1, CDR2, CDR3
Where antibody binding site at
Variable framework region
Fr1, Fr2, Fr3, fr4
Supporting part of antibody
Not part determining what antigen can bind
What is an epitope?
Structure (segment of antigen) recognized by an antibody
Draw and explain the structure of a t-cell receptor
T-cell receptor
Composed of 2 transmembrane glycoprotein alpha and beta chains
extracellular portion of each chain consists of two domains
Draw and label various components of MHC molecules (class I and class II)
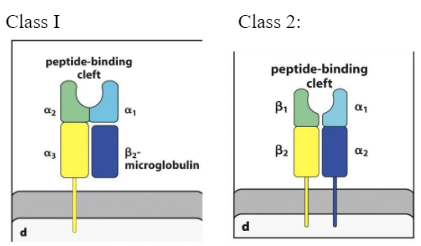
Describe the function of MHC molecules
Function:
to bind peptide fragments derived from pathogens and display them on the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T cells
MHC class I
The T-cell receptor binds to the top of the: peptide: MHC class I complex.
Cytotoxic
Cd 8
MHC class II
Recognized by Cd 4
What MHC properties made it difficult for pathogens to evade immune response?
The function of MHC molecules is to bind peptide fragment derived from pathogens and display them on the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T-cells
Two separate properties of the MHC make it difficult for pathogens to evade immune responses:
Polygenic: it contains several different MHC class I and class II genes
That alone adds variation
Highly polymorphic: there are multiple variants of each gene within the population as whole.
Describe the different distribution of MHC class I and class II
MHC I
present peptides from pathogens commonly viruses, to CD8 cytotoxic T-cells.
T-cells, B cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, epithelial cells of the thymus, neutrophils, hepatocytes
Kidney, brain
MHC II
found on B lymphocytes, dendritic cells and macrophages (APC: Antigen presenting Cells)
T-cells, B-cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, epithelial cells of thymus
Mainly found on antigen presenting cells
Describe the different cellular locations that MHC class I and II obtain peptides
Peptides from the cytosol are bound to MHC class I molecules and are recognized by CD8 T-cells, whereas
Peptides generated in intracellular vesicles are bound to MHC class II molecules and recognized by CD4 T-cells.
What are ABC proteins and what do they do?
ABC proteins mediate the ATP-dependent transport of ions, sugars, amino acids and peptides across membranes in many types of cells, including bacteria.
The two ABC proteins normally associated with the Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane are called:
Transporters Associated with Antigen Processing-1 and 2 (TAP-1 and TAP-2)
TAP1 and TAP2 form a peptide transporter in the Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane
Why is sending peptides to the ER?
MHC I is at
MHC can’t leave until bind to peptide
How does protein get degraded in cytosol?
degraded are introduced into the core of the proteasome. and there are broken down into short peptides, which are then released
The PA28 proteasome activator binds to either end of the proteasome
Proteasome found in cytosol
What are the immunoevasin produced by virus?
Immune Evasion- process of blocking peptide from entering ER
Through TAP or MHC
From activating
Not have response for MHC class I
Dislocate MHC
Overall- blockage
Result of blockage
By blocking entrance to going to er
Interfere with binding = no presentation of peptide
Infected cells won’t be able to present to lymphocyte= won’t know about it
Infection will continue
E19, us6, icp47
Describe the generation of MHC II bound peptide
Generated in Acidified Endocytic Vesicles
Antigen is taken to the apc cell then takes endosome activates ….
Steps
Antigen is taken up form the extracellular space into intracellular vesicles
In early endosome of neutral ph, endosomal proteases are infective
Acidification of vesicles activates protease to degrade antigen into peptide fragments
Vesicles containing peptide fuse with vesicles containing MHC class II molecules
pH= activates protease
Describe what invariant chain protein is and its function on MHC II is?
The Invariant Chain Directs newly synthesized MHC class II Molecules to Acidified intracellular Vesicles
forms trimers, with each subunit binding noncovalently to an MHC class II : heterodimer
The Invariant Chain is cleaved to leave a peptide fragment, CLIP, bound to the MHC class II molecule
Cleaved so it can’t bind other peptides=
What is HLA-DM and what is its function?
What it is:
HLA-DM is vital to the proper loading and presentation of peptides in macrophages, immature dendritic cells, B cells, and other antigen presenting cells(APC).
Function
Facilitates the Loading of Antigenic Peptides onto MHC class II molecules
The class II molecule, HLA-DM, binds to MHC class II: CLIP complexes, catalyzing the release of CLIP and the binding of antigenic peptides
Make binding site available
Its in the endoplasm ER
Explain why t-cell recognition of antigen is MHC restricted?
The co-recognition of a foreign peptide and MHC molecule is known as MHC restriction because the MHC molecule is said to restrict the ability of the T-cell to recognize antigen
The antigen-specific T-cell receptor (TCR) recognizes a complex of an antigenic peptide and a self MHC molecule.
T cell receptors binds to peptide + MHC
Peptide MHC needs to be specific for T cell receptors- can’t bind to just any
Different variant of MHC
Expressed in many versions - able to recognize wide
Describe what superantigens are
bind independently to MHC class II molecules and to T-cell receptors, binding to the V domain of the T-cell receptor (TCR), away from the complementarity-determining regions, and to the outer faces of the MHC class II molecule, outside the peptide-binding site
Binds to the side
This mode of stimulation DOES NOT prime an adaptive immune response specific for the pathogen.
It causes a massive production of cytokines by CD4 T-cells
The cytokines have two effects on the host:
1. Systemic toxicity
2. Suppression of the adaptive immune response
Describe the various functional classes of effector cells
CD4TH1 and CD4TH2 cells
contribute to humoral immunity by stimulating the production of Antibodies and inducing class switching. All classes of Antibodies contribute to humoral immunity, which is directed at extracellular pathogens.
Stimulate production of antibodies + induce class switching
CD4TH17
recruit neutrophils to sites of infection
TFH
cells contribute to humoral immunity by stimulating the production of Antibodies by B-cells, induce class switching and produce cytokines characteristics of either TH1 or TH2.
Suppress
CD4 regulatory T-cells
tend to suppress the adaptive immune response and are important in preventing immune responses from becoming uncontrolled and in preventing autoimmunity.
How do lymphocytes gain entrance to lymph node from blood?
3 distinct stages:
Adhesion molecules
Involved:
selectins, integrins, members of the immunoglobulin superfamily and some mucin-like molecules
After adhesion, the T-cells follow gradients of chemokines to pass through the HEV wall into the paracortical region of the lymph node
initial Rolling of lymphocytes along the endothelial surface, Activation of integrins, firm Adhesion and transmigration (Diapedesis) across the endothelial layer into the paracortical areas, the T-cell zones.
Chemokines
Chemokines receptors
Describe the mechanisms that dendritic cells uptake antigens into their endocytic system
Uptake of Antigens into the endocytic system, either by receptor-mediated phagocytosis or by macropinocytosis, is considered to be the major route for delivering peptides to MHC class II molecules for presentation to CD4 T-cells
Phagocytosis
Macropinocytosis
Small amount of
Describe the T-cell mediated cytotoxicity.
cytotoxic T-cells can recycle to kill multiple targets, but each killing require the same series of steps, including receptor binding and the directed release of cytotoxic proteins stored in granules.
Early in apoptosis the chromatin becomes condensed (red) and there is a necrotic cell.
In the late stages of apoptosis, panel c: the cell nucleus is very condensed and the cell has lost much of its cytoplasm and membrane
what is the mechanism of cytotoxic T cell?
The principal mechanism of cytotoxic T-cell action is the calcium-dependent release of specialized cytotoxic granules upon recognition of antigen on the surface of a target cell.
Cytotoxic granules are modified lysosomes that contain at least three distinct classes of cytotoxic effector proteinsthat are expressed specifically in cytotoxic T-cells
What signals do APCs have for clonal expansion and differentiation for naïve T-cells?
1) Binding of the foreign-peptide: self-MHC complex by the T-cell receptor and in this example, a CD4 co-receptor, transmits a signal to the T-cell that an antigen has been encounter.
2) Effective activation of naïve T-cells requires a second signal, the co-stimulatory signal, to be delivered by the same antigen-presenting cell (APC) in this example CD28 on the T-cell encountering B7 molecules on the antigen presenting cell, whose net effect is the increase survival and proliferation of the T-cell that has received signal 1.
3) Cytokines in general are involved in directing this signal, differentiation