Northern Renaissance/Reformation
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms


Martin Luther’s 95 Theses



Humanism
An intellectual movement during the Renaissance that emphasized the value of human beings, individualism, and the study of classical texts.
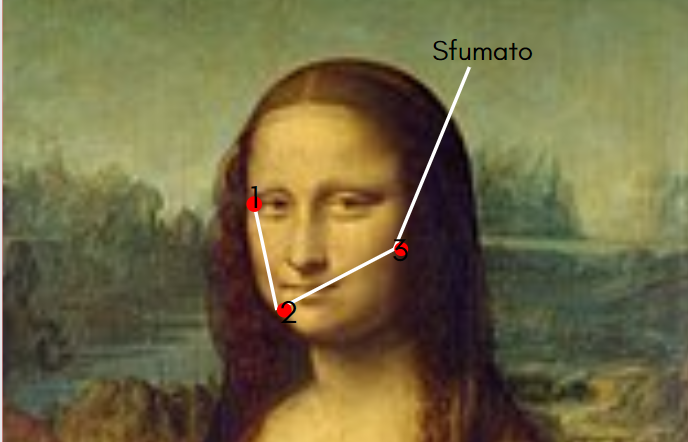

Sfumato
A painting technique used to create soft transitions between colors and tones, often to depict atmospheric effects.

Chiaroscuro
A technique used in painting to represent light and shadow in a way that adds depth to the artwork.
Perspective
An artistic technique used to represent three-dimensional objects on a two-dimensional surface, creating an illusion of depth.
Fresco
A mural painting technique where pigments are applied on wet plaster, allowing the colors to become an integral part of the wall.
Rhetoric
The art of persuasive speaking or writing, emphasized during the Renaissance as a key component of education.
Patronage
Support given by wealthy individuals or institutions to artists, allowing them to create and disseminate their works.
Baroque Art
An artistic style that emerged after the Renaissance, characterized by dramatic use of light, bold colors, and emotional intensity.
Realism
An artistic movement that aims to depict subjects as they are, without embellishment or interpretation.
Naturalism
A style of art that seeks to represent objects and figures as they appear in nature, emphasizing realism and accuracy.

Flemish Painting
A style of painting that originated in Flanders during the Renaissance, characterized by detailed realism and vibrant color.
Mannerism
An artistic style that emerged after the High Renaissance, characterized by elongated forms and exaggerated poses.
Baroque Music
A style of music from the late Renaissance to the early 18th century, marked by expressive melodies and the use of ornamentation.
Renaissance Architecture
A style of architecture that emerged during the Renaissance, combining elements from classical Roman and Greek architecture.

Leonardo da Vinci
An Italian polymath of the Renaissance known for masterpieces like 'Mona Lisa' and 'The Last Supper' and contributions to science and engineering.
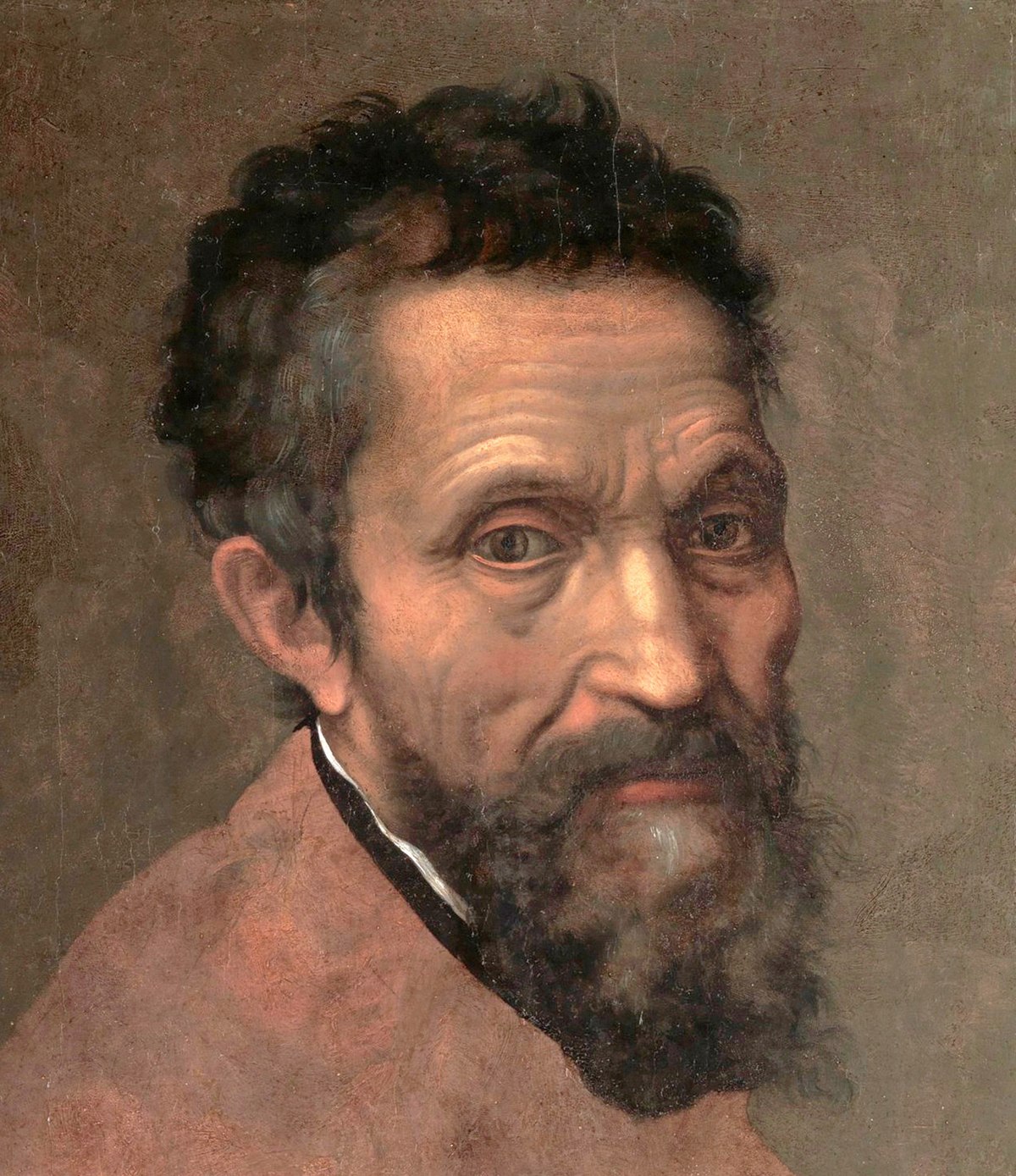

Michelangelo
An Italian sculptor, painter, and architect of the Renaissance, noted for works such as the Sistine Chapel ceiling and the statue of David.

Raphael
An Italian painter and architect known for his depictions of human figures and harmonious compositions, famous for works like 'The School of Athens'.
Counter-Reformation
A movement within the Catholic Church in response to the Protestant Reformation, aimed at reforming church practices and reaffirming doctrines.
Council of Trent
A ecumenical council held in the 16th century to address issues raised by the Protestant Reformation and to implement internal church reforms.
Symbolism in Art
The use of symbols to represent ideas or qualities, often seen in Renaissance artwork to convey deeper meanings and narratives.