PSYC102: CH7 - Memory
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Memory
Retention of information over time
Implicit Memory
Beneath level of conscious awareness (motor skills, object recognition)
Explicit Memory
Semantic facts, events, and knowledge
Memory Illusion
A false but subjectively compelling memory
DRM Paradigm
Sensory Memory
Brief storage of information before it is passed on to the short-term memory
Short-Term Memory
The capacity to hold a small amount of information in mind in an active readily available state for a short period of time
Brown Peterson Task
Test of duration of STM by asking participants to remember letters after a backwards counting task. For them to be able to measure duration of short term memory without rehearsing any information
Decay
Fading of information from memory over time
Interference
Loss of information from memory because of competition from additional information; often the stronger explanation
Proactive interference
Previously learned material interferes with the ability to acquire new information
Jen and Jill
Retroactive Interference
The acquisition of newer material interferes with the ability to retain older information
Jill and Jen
Chunking
Organizing information into meaningful groupings, which allows us to extend the span of STM
Rehearsal
Repeating information to extend the duration of retention in short-term memory and promote the likelihood of transfer to long-term memory
Maintenance Rehearsal
Repeating information in their original form; no meaningful connections
Elaborative Rehearsal
Linking information together in a meaningful way
Levels of Processing
The depth of rehearsal, or how we transform the information, influences how well we remember it
Long-term Memory
Enduring retention of information, including facts, experiences, and skills
Priming
Our ability to identify a stimulus more easily or more quickly after we’ve encountered similar stimuli
Word Stem Tasks:
BA____
Encoding
The process of getting information into our memory stores
Attention plays a crucial role
Mnemonics
Mnemonic Devices
An active, strategic learning device or method that enhances recall
Rely on internal mental strategies during encodes to help recall info later on
Method of Loci
Uses known locations as cues for memory items
Pegword Method
A pre-memorized set of words serves as a sequence of mental “pegs” onto which the to-be-remembered material can be “hung”
Storage
The process of keeping information in memory
Storage
The process of keeping information in memory
Schemas
Organized knowledge structures or mental models that we’ve stored in memory
Scripts: a procedure for a set order of events
Retrieval
The reactivation or reconstruction of information or experiences from our memory stores
Retrieval Cues
Pieces of information that serve to help us retrieve information
Recall
People have to generate previously learned information
Recognition
People have to select previously learned information from a set of options
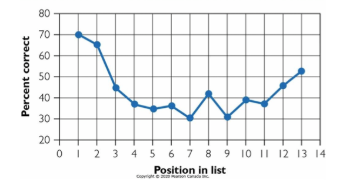
Serial Position Curve
Primacy Effects: Better memory for items in the early positions of the list
LTM
Recency Effects: Better memory for items at the end positions of the list
STM
Relearning
Reacquiring knowledge that has previously been learned, but has been forgotten overtime
Ebbinghaus studied _______ using nonsense syllables
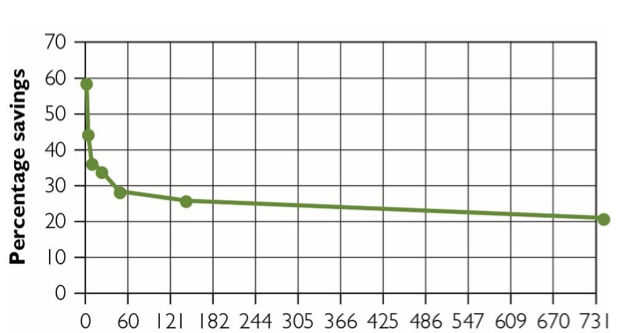
Savings Score
The reduction in the number of trials necessary for relearning a list, compared to the original learning of the list
Distributed Practice
Learning in small amounts over time
Massed Practice
Learning a lot at once
Encoding Specificity
We will better remember some information when the conditions under which we retrieve the information are similar to the conditions under which we encoded that information
Context-Dependent
State-Dependent
Context-Dependent Learning
Superior retrieval of memories when the external context of the original memories matches the retrieval context
State-Dependent Learning
Superior retrieval of memories when the organism is in the same physiological or psychological state as it was during encoding
Long-Term Potentiation
A long-lasting strengthening of the connections between two neurons after synchronous activation
Long-Term Depression
A long-lasting weakening of the connections between two neurons after low patterns of activation
Overconfidence in Memory
Certainty in the accuracy of memory
Source memory: Memory of the exact source of the information
Processing Fluency: The ease with which something comes to mind
Flashbulb Memory
Emotional memories that are vivid and detailed
Source Monitoring
The ability to accurately remember the source of a memory, including whether it is something encountered in the real world or something imagined
Source Monitoring Failure
Remember the content of the information but cannot attribute it to a particular source
Cryptomnesia
A person unconsciously plagiarizes something they have heard or read before, but because they have forgotten the source, mistakenly think that it is a new idea that they thought of
Amnesia
Loss of memory or memory abilities due to brain damage or disease
Retrograde Amnesia
Loss of memory of events before the injury
Ribbot’s Law: temporal gradient in ___________
Anterograde Amnesia
Loss of memory of events after the injury
Patient K.C.
Episodic memory processes were disrupted, but semantic memory processes were intact.
Patient H.M.
Unable to transfer new information to LTM, but able to retrieve already stored memories from LTM.