Unit 7 - Sampling Distributions
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
parameter
# that describes some characteristic of the population
statistic
# that describes some characteristic of a sample (taken from a sample)
symbols for statistics (proportion, mean, SD)
p̂, x̄, s
symbol for parameters (proportion, mean, SD)
p, μ, σ
!!! sampling variability: the value of a statistic varies in a repeated random sampling
Population must be 10x larger or more than sample (10% Condition)
NEVER ASSUME NORMALITY -> always check 10% (can find SD) and large counts condition (can use approx. Normal distribution and find probability) for sample proportion/sample mean (LCC is np ≥ 10 and n(1-p) ≥ 10 for sample proportion; n ≥ 30 for sample mean)
Interpret answer by using context
usually give statistic + sample, look at bigger picture to find parameter + population
p̂ = X/n (sample proportion = count of successes in sample over sample size) (proportion is the proportion of successes out of a sample. Think fraction or decimal)
statistic likely to be off from parameter if n is low/small
sampling distribution
the distribution of values of a statistic of all possible samples of the same size from the same pop.
^difficult to do, so a simulation is appropriate ex: 30 samples of size n
^each point is a statistic collected from a sample of the same size. take statistic from EACH SAMPLE for many many samples. shows all possible values that the statistic can take and how often it occurs
population distribution
gives the values (data points) of the variable for all the individuals in the pop. (data/numbers of population)
^ex: every U.S. income; the U.S. Census (info abt every citizen)
distribution of sample data
shows the values of the variable for all the individuals in the sample (data/numbers from sample)
^ex: the incomes from the sample of 200 Americans
unbiased estimator
a statistic used to estimate a parameter
-IF the mean of its sampling distribution equals the true value of the parameter being estimated (ex: sample mean, sample proportion, SD; NOT median) (aka if in many samples, the values of the statistic are centered at the value of the parameter)
-ex: can use x̄ if the expected value of the sampling distribution (mean of many means of many samples) equals μ
variability of a statistic
described by the spread of its sampling distribution
^incr sample size, decr variability/spread of distribution of statistic (decr variability in sample)
^larger sample -> more data/info abt population -> more precise estimates (+less variability of the sample statistic)
bias
variability
aim is off consistently
how scattered/close it is (similar results or not?)
!best estimate → want low/no bias (close to actual parameter), low variability (data close tgt & less spread out)!
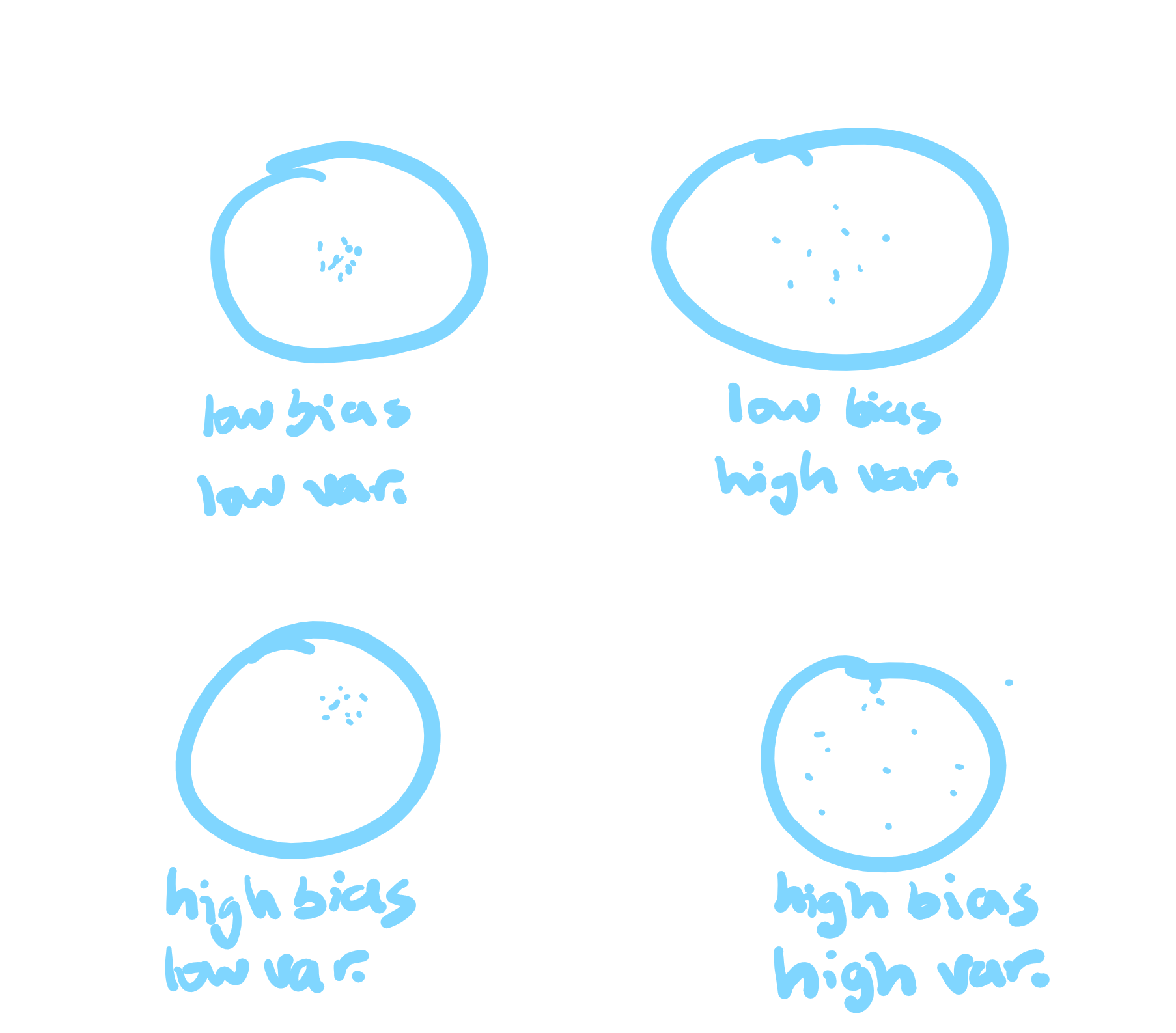
about sample proportion distributions
SHAPE: can be approx normal (depends on n sample size and p population proportion, large counts condition)
CENTER: μp̂ = p (b/c p̂ is an unbiased estimator of p)
SPREAD: incr n (sample size), decr σp̂ (sample spread) (σp̂ depends on n and p)
*n changes, variability changes (don’t look at N)
Sampling distribution of a sample proportion (choose SRS of size n from population size N w/ proportion p of success, let p̂ be the sample proportion of successes)
μp̂ = p
10% condition before find SD → n ≤ 1/10*N (use words if given n but not N (can assume N is large))
σp̂ = √ [p(1-p)/n]
check large counts condition: np ≥ 10 and n(1-p) ≥ 10 → then can find probability and use normal curve shape
*state the # of ppl needed to assume the SD
^as n incr, sampling distrib. becomes approx normal
as n changes, what happens to shape, center, and spread? (for sample proportion & sample mean)
shape approx same (normal) (decr n slightly less normal, incr n appears to look more normal)
same center
SD changes
incr n, decr SD
decr n, incr SD
SAMPLE PROPORTION: find factor from OG size n to final size n (ex: times 1/6). the factor that SD changes by is the reciprocal of that then sqr root. (ex: 1/6 → √6)
SAMPLE MEAN: find factor from OG size n to final size n (ex: times 2). the factor that SD changes by is 1 over the sqr root of the OG factor (ex: 2 → 1/√2)
!!! ask for parameters/statistics -> make sure to give #s and use symbols! ^parameter from population, statistics from sample
avoid absolutes (prob wrong if says 'exactly Normal')
good estimator → see if sampling distrib. mean of the statistic matches parameter (ex: sampling distrib. mean of mean temperatures matches parameter mean temp.)
^what is it centered around?
^find mean by adding all values (ticks, make sure to include if multiple of the same #) then dividing by the # of dots
^n is the sample size!!!
-
SAMPLING DISTRIB OF MEAN
-SD will decr if sample size incr
-SD is a measure of the variability of the sample mean among repeated samples
-sample mean is an unbiased estimator of the true population mean (also, sample proportion is unbiased estimator of the true population proportion)
-sampling distribution show how the sample mean will vary in repeated samples
Sampling distribution of a sample mean (suppose x̄ is the mean of an SRS of size n drawn from a large population with mean μ and SD σ)
μx̄ = μ
10% condition before find SD → n ≤ 1/10*N (use words if given n but not N (can assume N is large)) (overlook independence violation)a
σx̄ = σ/√n
if shape of population distribution is normal, then shape of sampling distribution of x̄ is also normal (no matter the size of n) → can find probability
if shape of pop. distrib. is NOT normal, then shape of sampling distribution of x̄ is normal if n ≥ 30 → can find probability
central limit theorem
when n is large (n ≥ 30), sampling distribution of the sample mean x̄ is approx normal
^no matter the shape of the population distribution (even if shape is not normal!)
*incr n, incr shape look normal (think incr n, decr SD, data closer tgt and more centered)
*given population has a finite SD