Embryo Cardio Development (Drop Box)
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
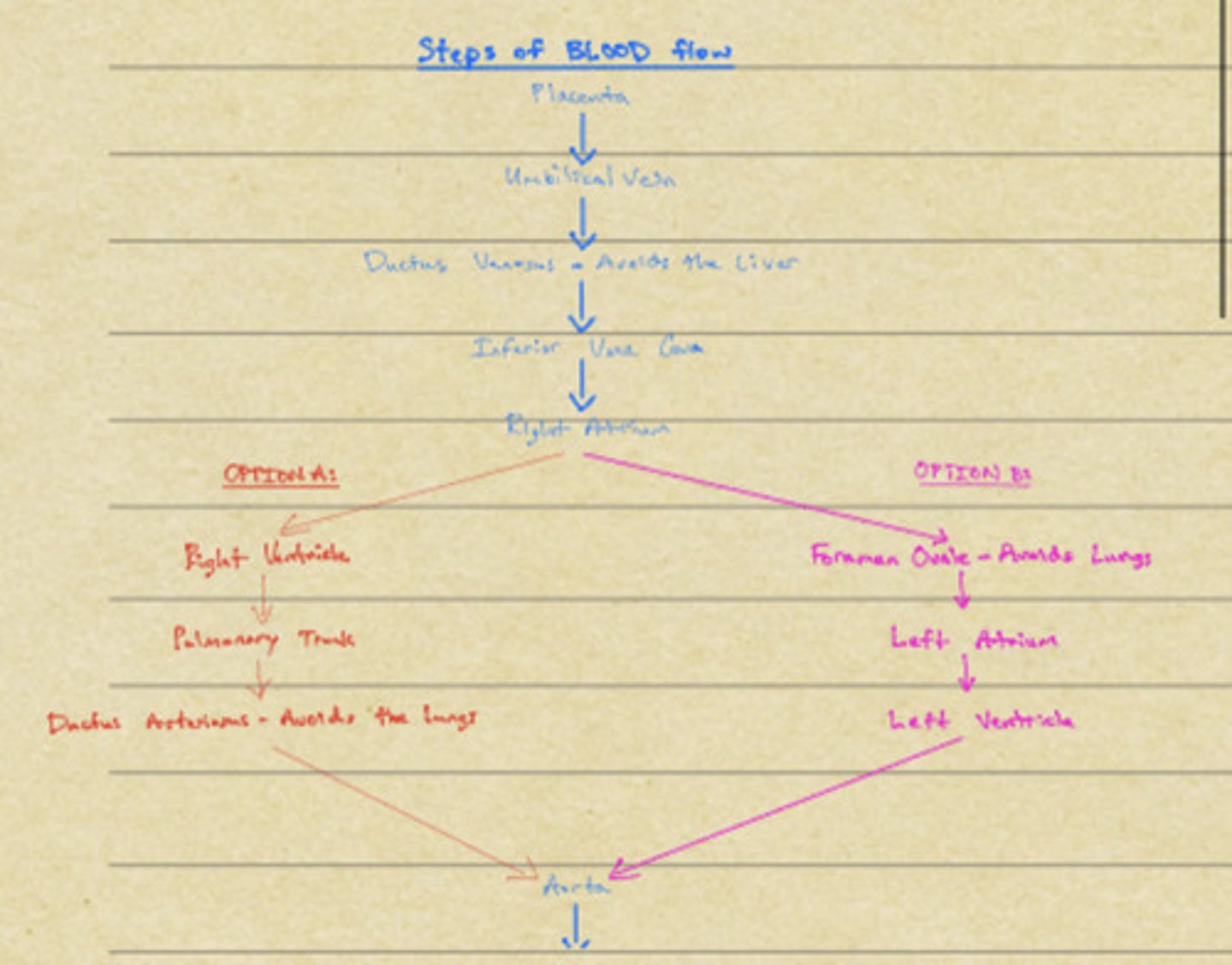
Umbilical artery
The medial umbilical ligament represents the embryonic ___________
Kidney
The subcardinal vein develops because of the development of the ___________
Portal vein, hepatocardiac part, IVC and Hepatic veins
All the following develop from the Vitelline veins:
Aortic arch I
The maxillary artery develops from the ___________________
Yolk sac
The vitelline arteries are blood supply to the ___________ in the embryo
Septum primum
The ostium secundum is found in the _______________
Interatrial septum
The left venous valve forms the __________________
Bulbus cordis
The membranous interventricular septum develops from the _____________
Valve of the IVC
The sinoatrial swellings give rise to the ________________ in the adult
Embryonic atrium
Pectinate muscle develops from the ______________
Splanchnic
The proximal bulbar swellings develop from the ____________ mesoderm
Sinus venosus
The smoothed wall portion of the right atrium develops from the ______________
Nothing
The superior right venous valve develops into ____________
Embryonic ventricle
The muscular interventricular septum develops from the ___________________
Pulmonary artery, aorta
The ductus arteriosus connects the _________ to the __________
Hyoid artery; Stapedial artery
Aortic arch II develops into the ________________
Subcardinal vein, sacrocardinal vein, and vitelline vein
The inferior vena cava is formed from all the following:
Umbilical vein, inferior vena cava
The ductus venosus connects the ______________ to the _____________
Umbilical artery
The medial umbilical ligament forms from the _____________
Septum primum
The ostium secundum forms in the _______________
Embryonic ventricle, bulbus cordis
The proximal bulbar swellings are found between the _______________ and the _______________
Left posterior cardinal vein, right umbilical vein and left anterior cardinal vein
During the shift to the right, all the following disappear:
Embryonic ventricle
Papillary muscle develops from the __________________
Sinus venosus; one of the two sinus horns
The coronary sinus develops from the ____________________ or ____________________
Embryonic ventricle
Papillary muscle develops from the _________________
VI (left)
The ductus arteriosus develops from aortic arch ______
(GI tract... single, midline structures)
Superior mesenteric artery, inferior mesenteric artery and celiac artery
The vitelline artery gives rise to all the following:
Round ligament of the liver
After birth the umbilical vein becomes the _____________________
Subcardinal vein
The renal vein forms from the _______________
Splanchnic
The heart develops from the ________________ mesoderm
Right venous valve
The valve of the inferior vena cava develops from the _________________________
Aortic arch II
The stapedial artery develops from
A
The inferior vena cava is formed by all the following except:
A. Supracardinal veins
B. Subcardinal veins
C. Vitelline veins
D. Sacrocardinal veins
Vitelline veins
The hepatic veins are formed from the ____________
B
All the following lead to changes in the circulatory system at the time of birth except:
A. Increased pressure in the right atrium
B. Bradykinin secretion
C. Environmental changes for the baby
D. Trauma of the birth process
III
The internal carotid artery forms from aortic arch:
Septum primum
The ostium secundum is found in the:
Umbilical vein, IVC
The ductus venosus connects the ____________ and _______________
Embryonic atrium
Pectinate muscle develops from the ________________
Left sinus horn
The coronary sinus develops from the ______________
Right venous valve
The valve of the coronary sinus develops from the _____________
Maxillary artery
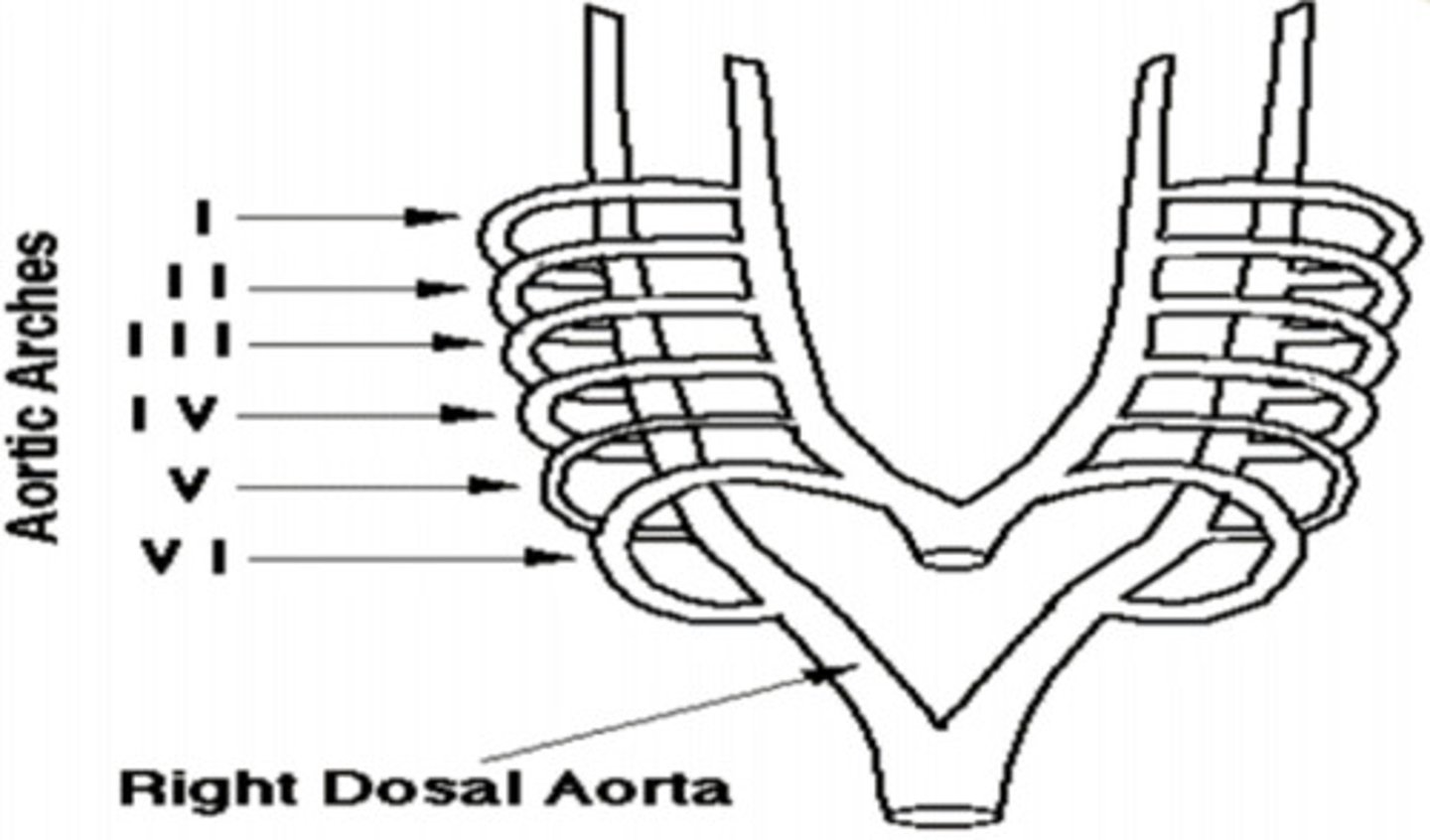
Aortic Arch I ——>
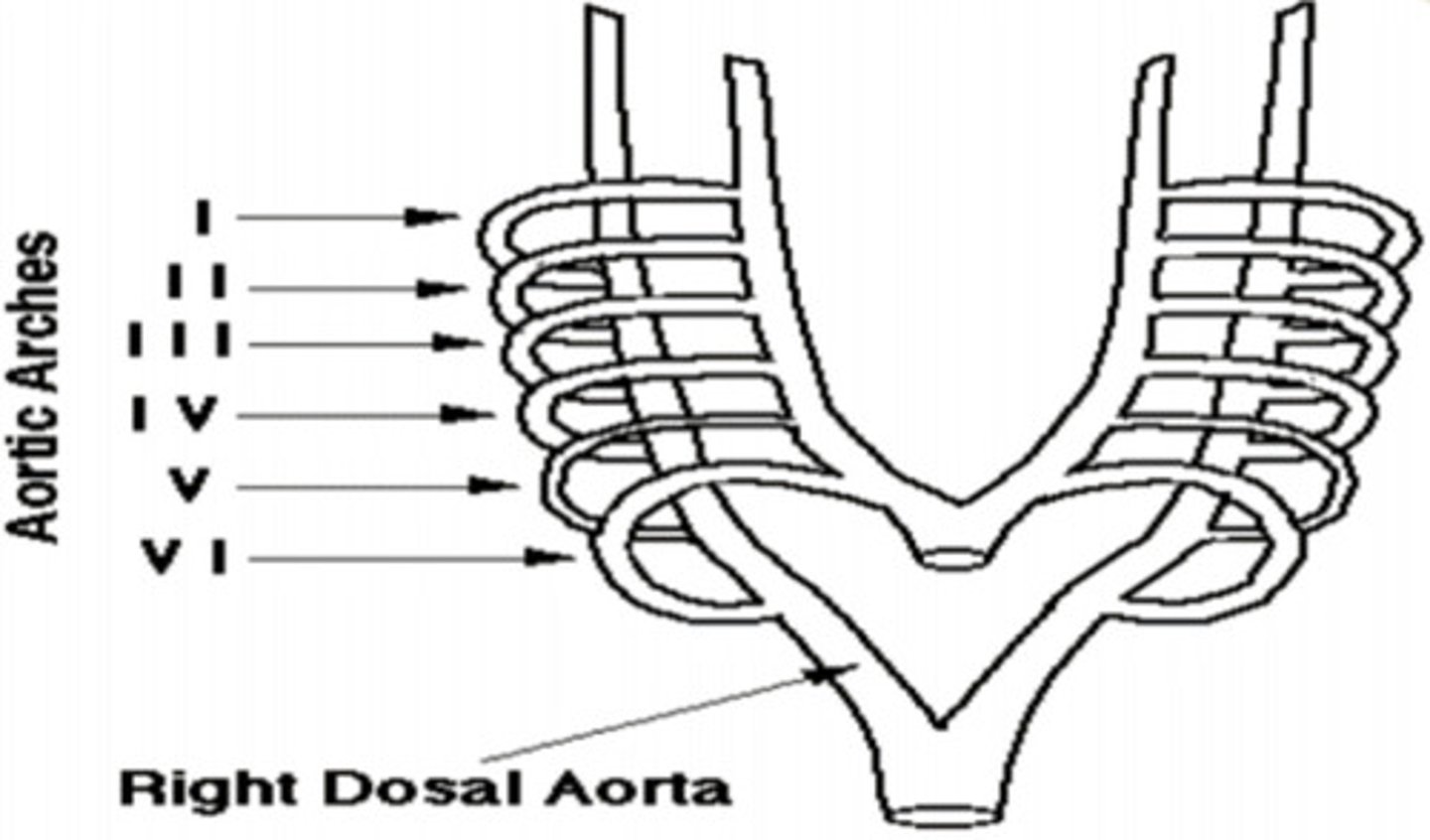
Hyoid and Stapedial (into the ear) Artery
Aortic Arch II ——>
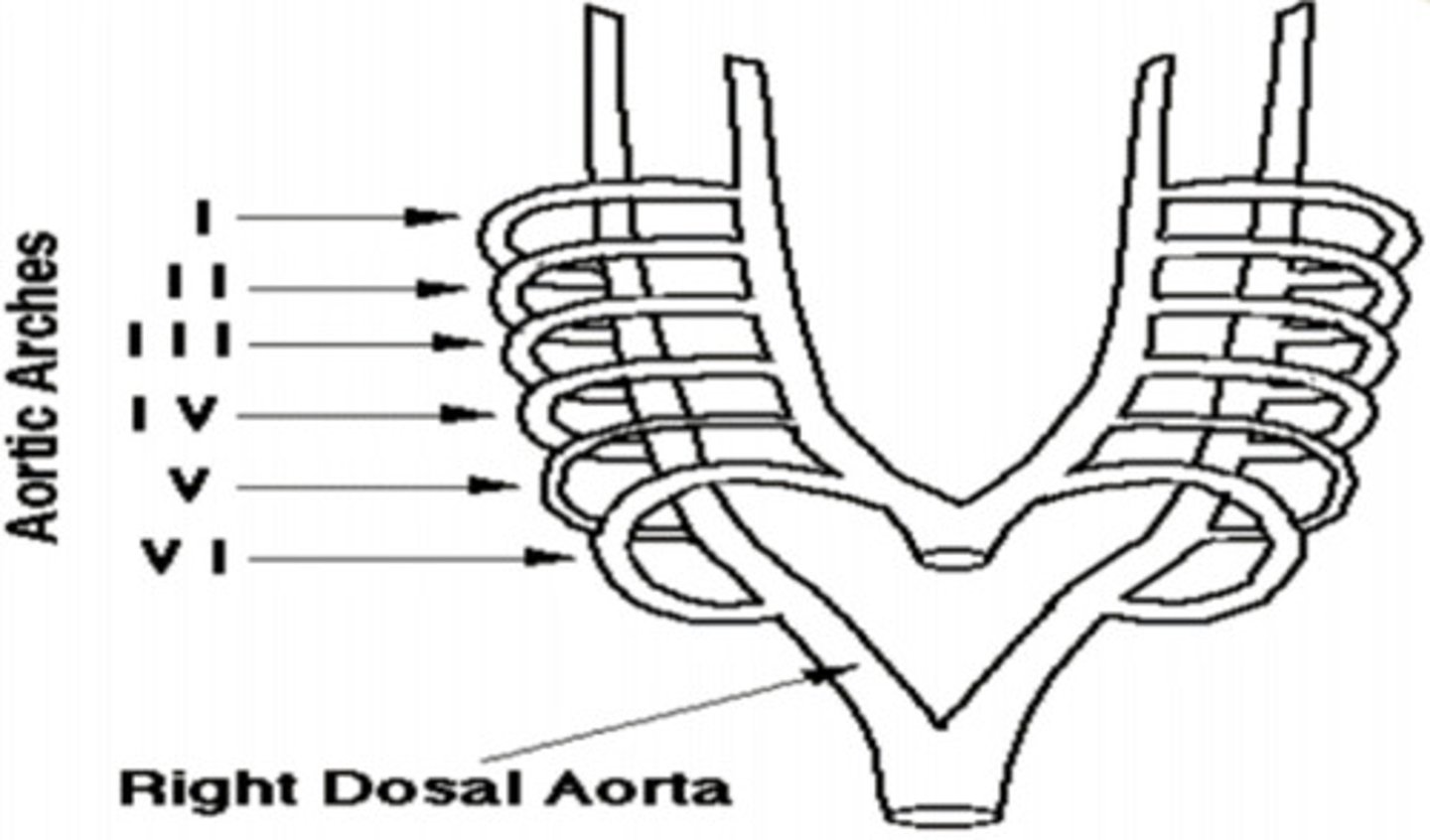
Common and Internal Carotid Artery (neck area)
Aortic Arch III ——>
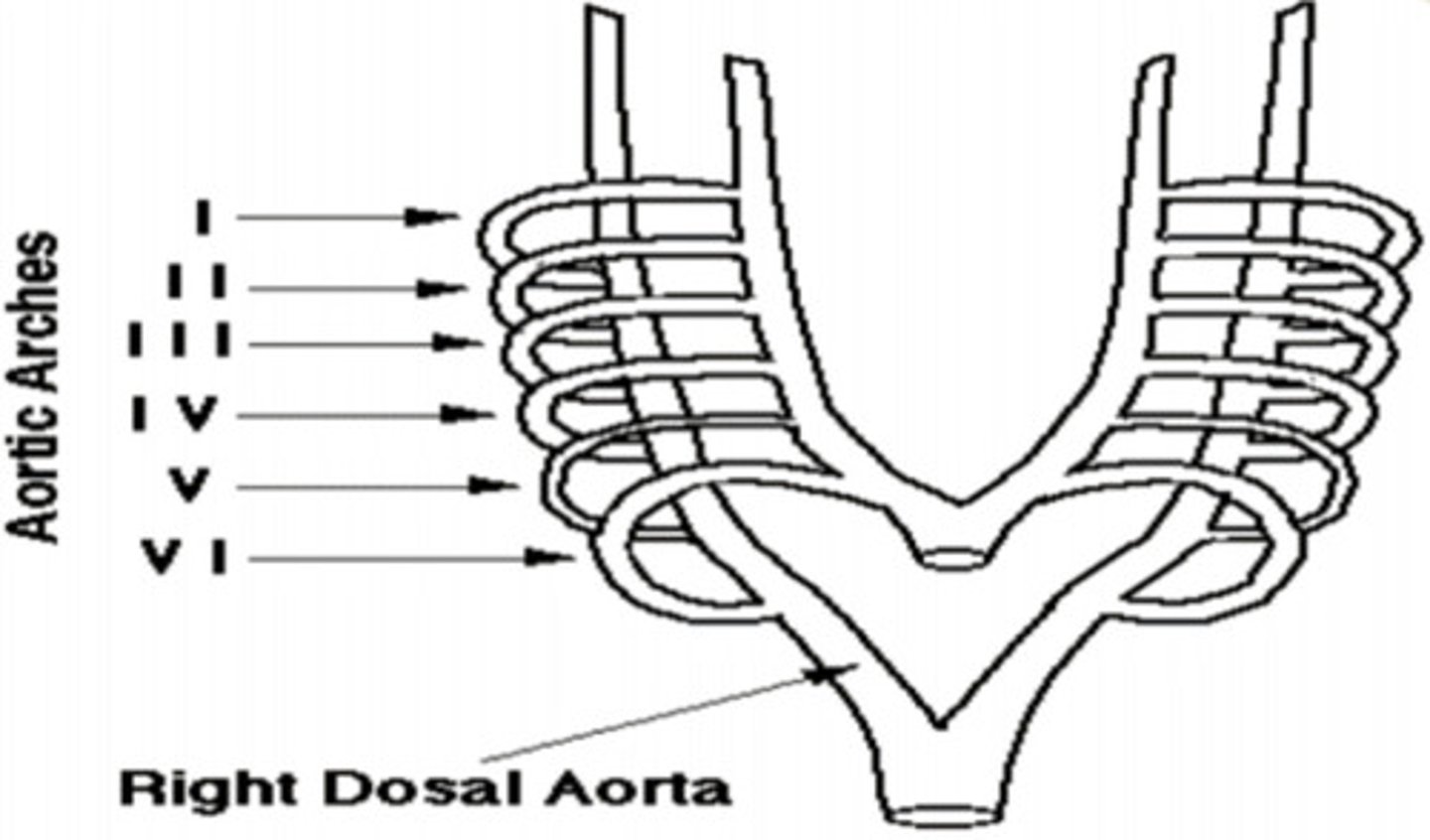
Arch of Aorta
Aortic Arch IV Left ——>

Right Subclavian Artery
Aortic Arch IV Right ——>
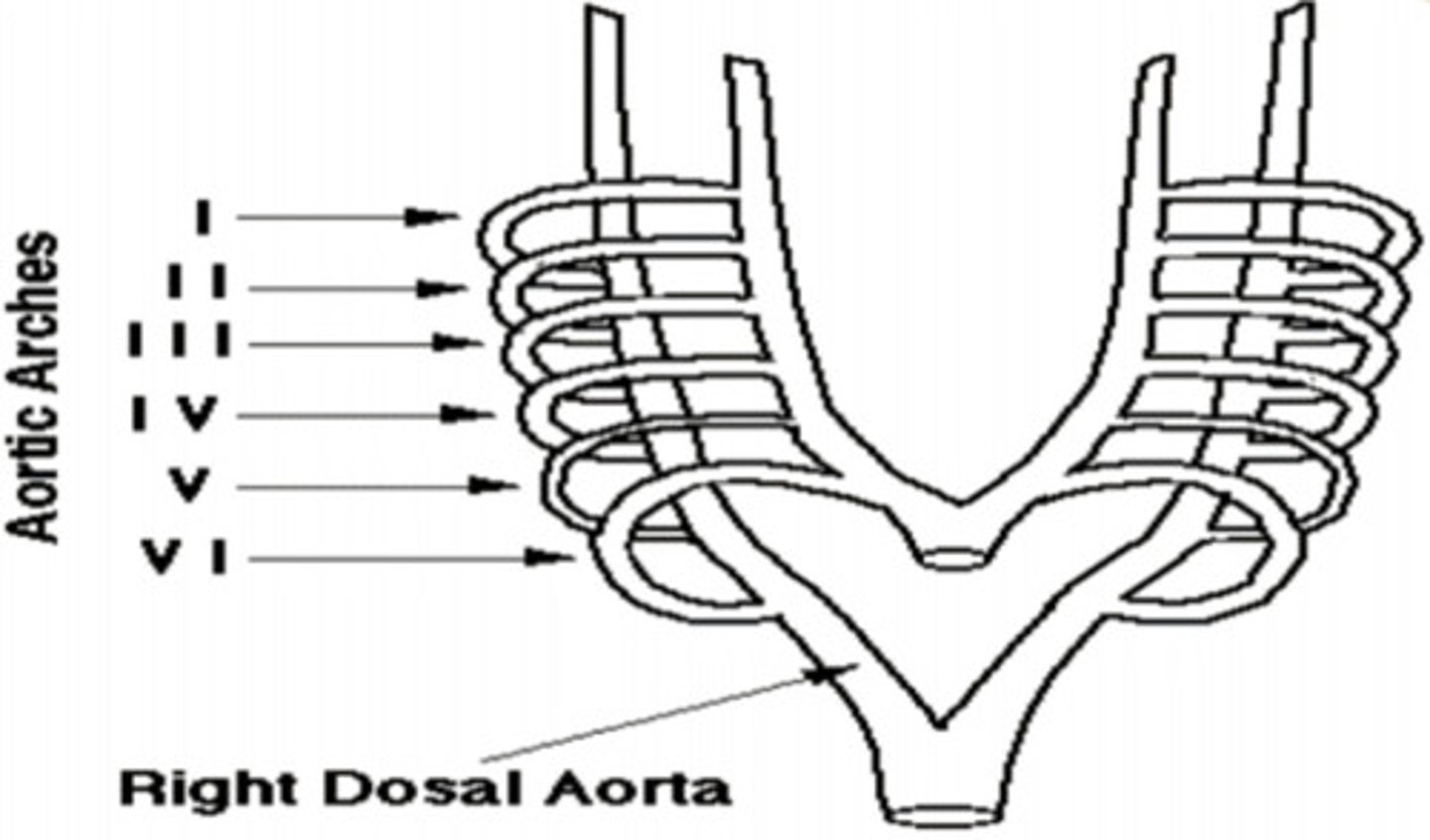
Develops Quickly and disappears (no adult derivatives)
Aortic Arch V ——>
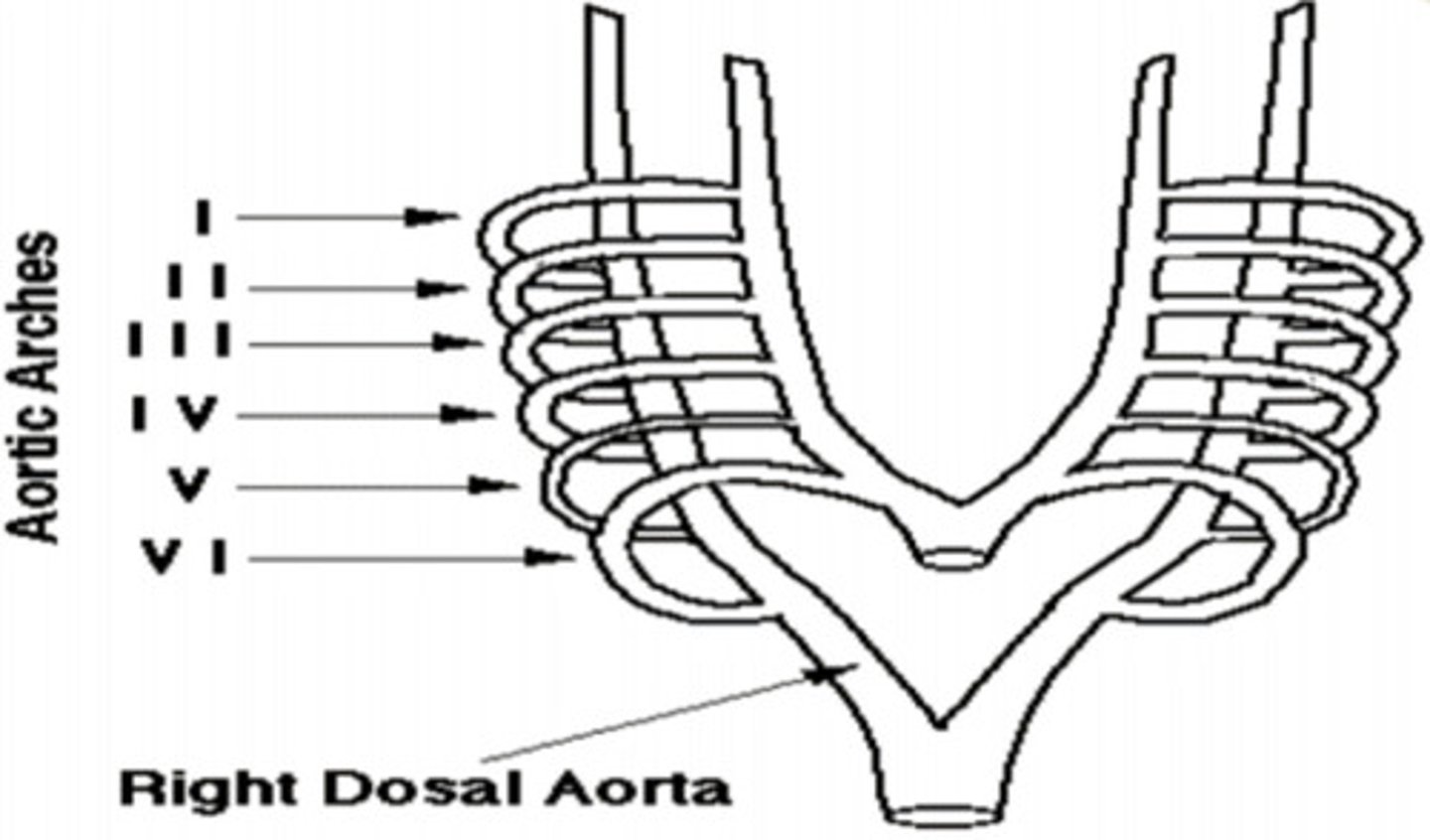
Left Pulmonary Artery; Ductus Arteriosus (shunt between ventricles... pulmonary trunk -> aorta, due to path of least resistance)
Aortic Arch VI Left ——> __________________ ——> Then through the _________________
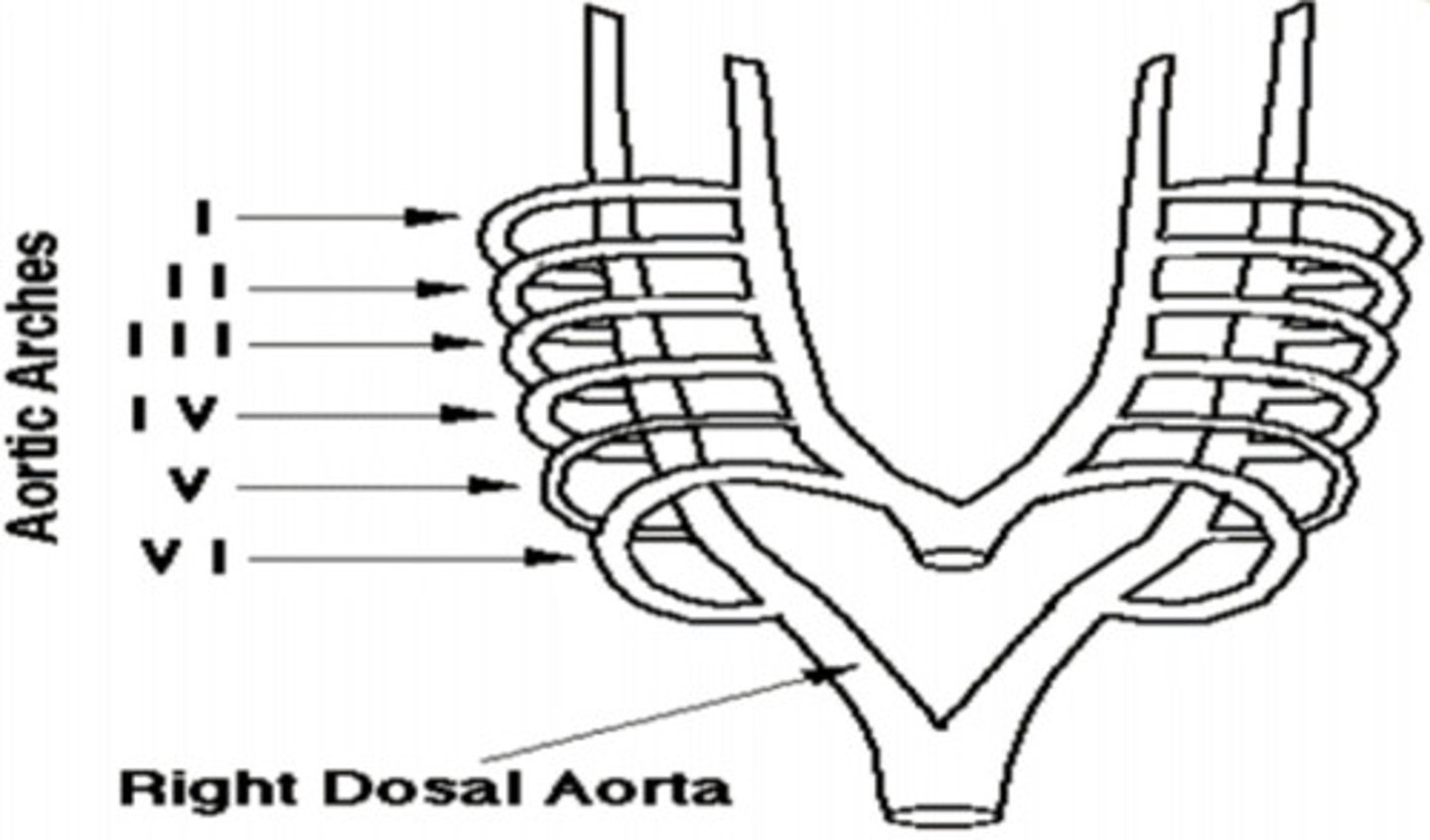
Right Pulmonary Artery
Aortic Arch VI Right ——>
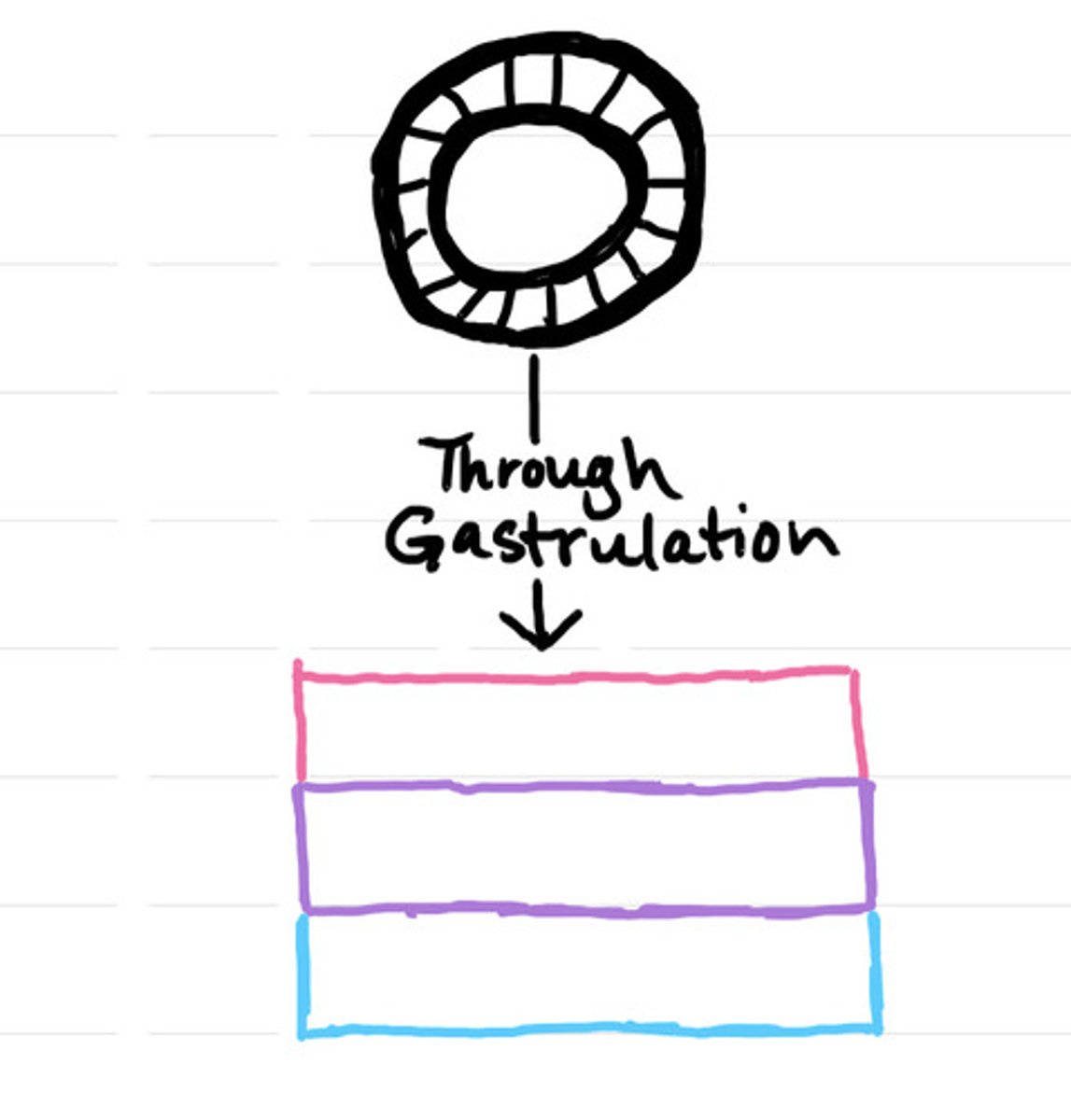
Ectoderm (pink), mesoderm (purple), endoderm (blue)
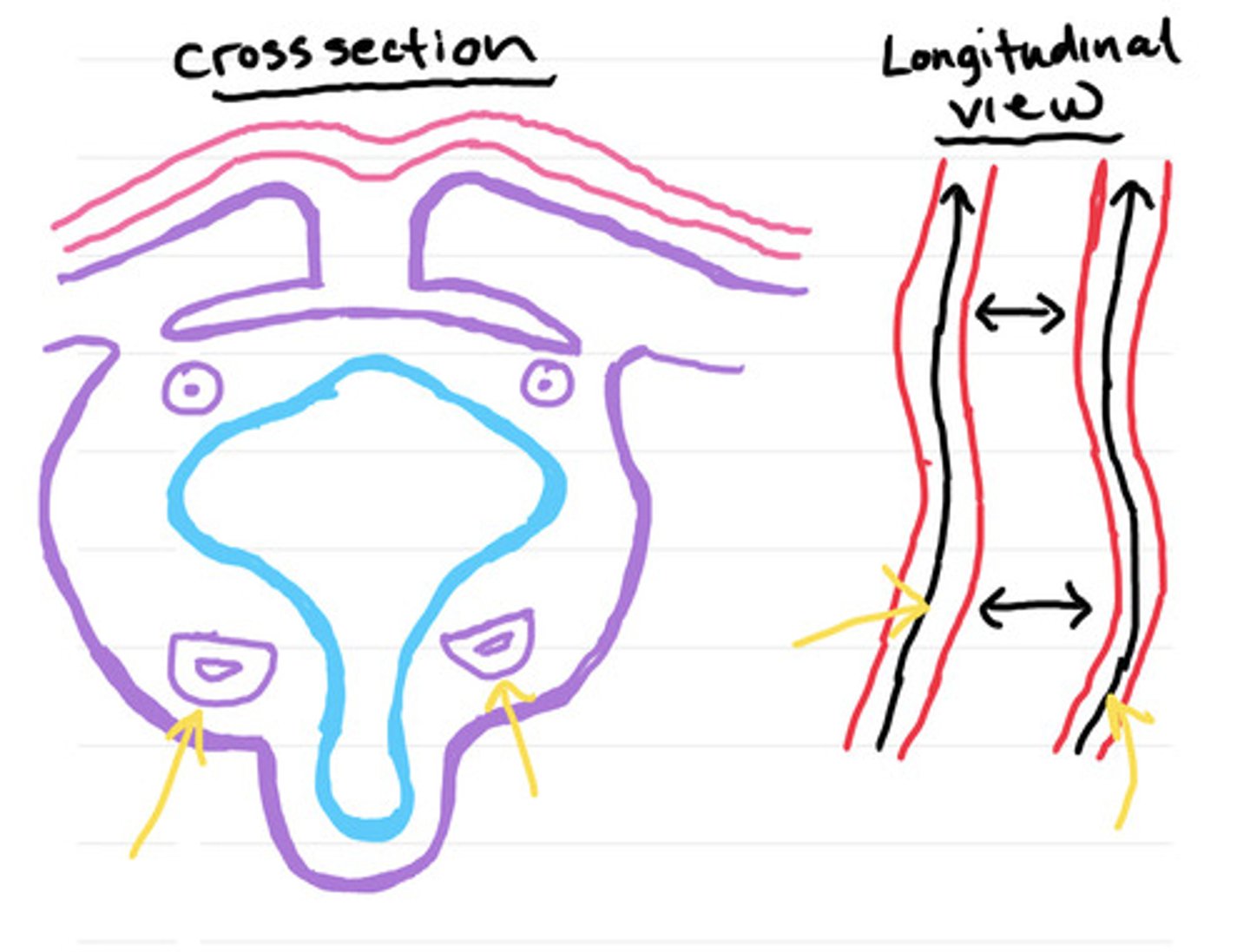
1. Intermediate Mesoderm, 2. Paraxial Mesoderm, 3. Somatic Mesoderm, 4. Splanchnic Mesoderm (becomes heart)

Endothelial Tubes
(Day 18)
Identify the Yellow Arrows
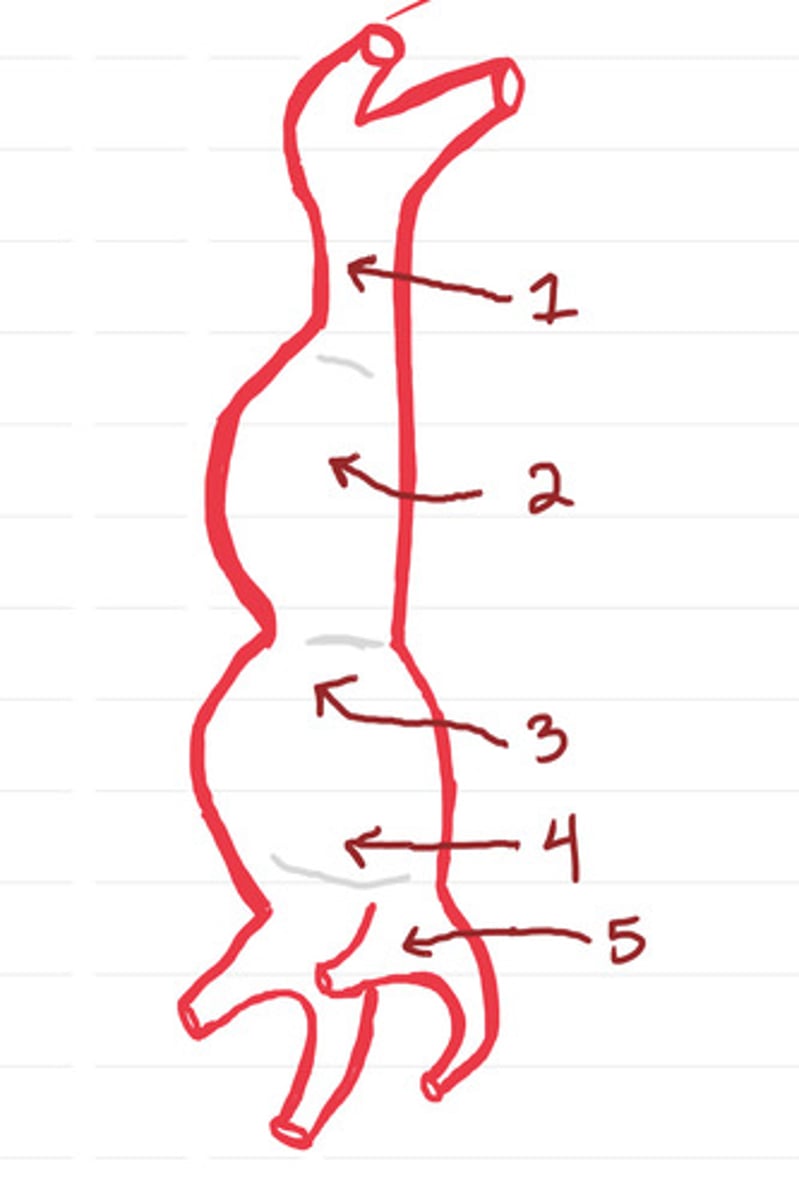
1. Truncus Arteriosus, 2. Bulbus Cordis, 3. Primitive Ventricle, 4. Primitive Atrium, 5. Sinus Venosus
(Day 20)
1. Truncus arteriosus, 2. Bulbus cordis, 3. Primitive Atrium, 4. Primitive Ventricle, 5. Endothelial Tubes
(Day 22)
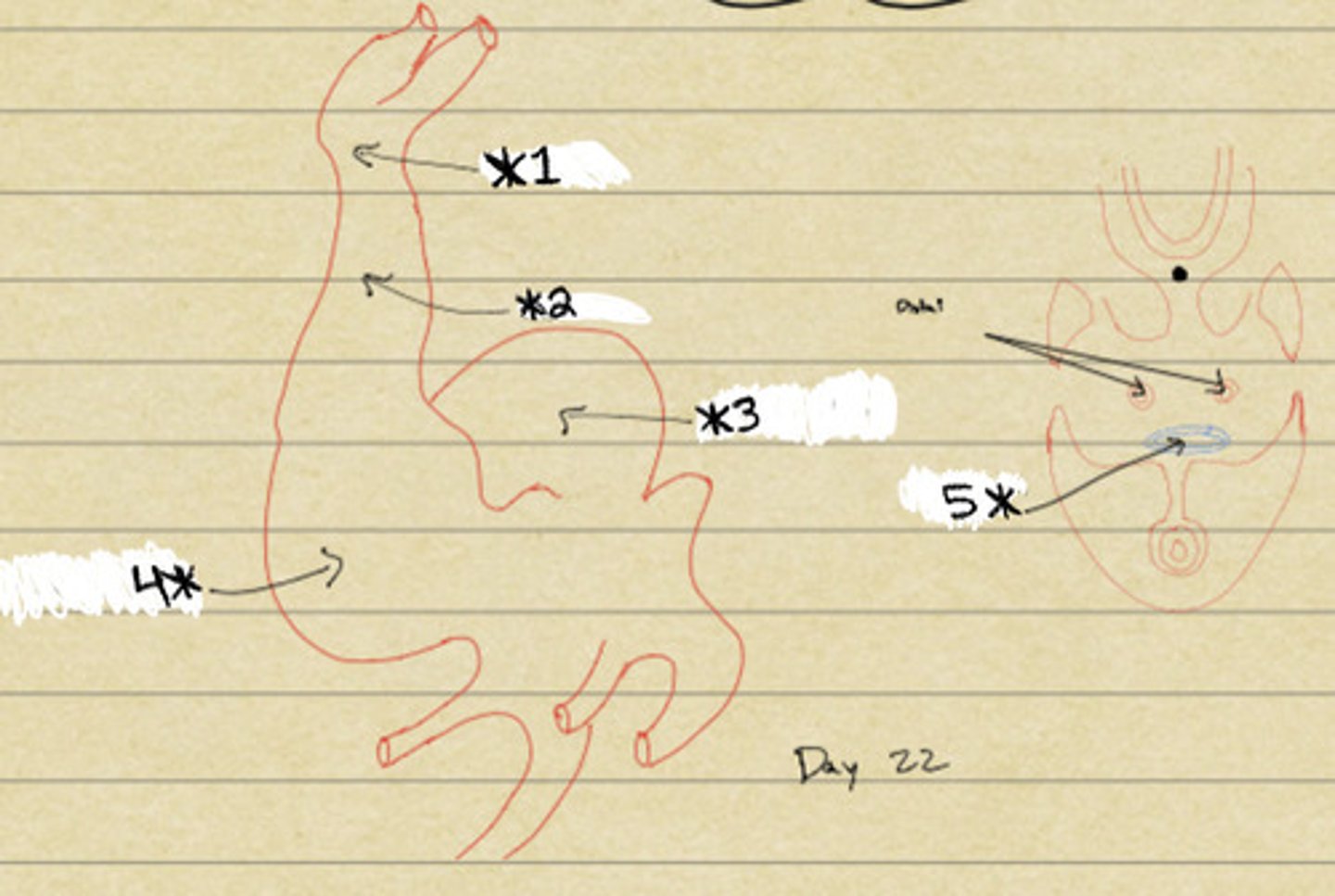
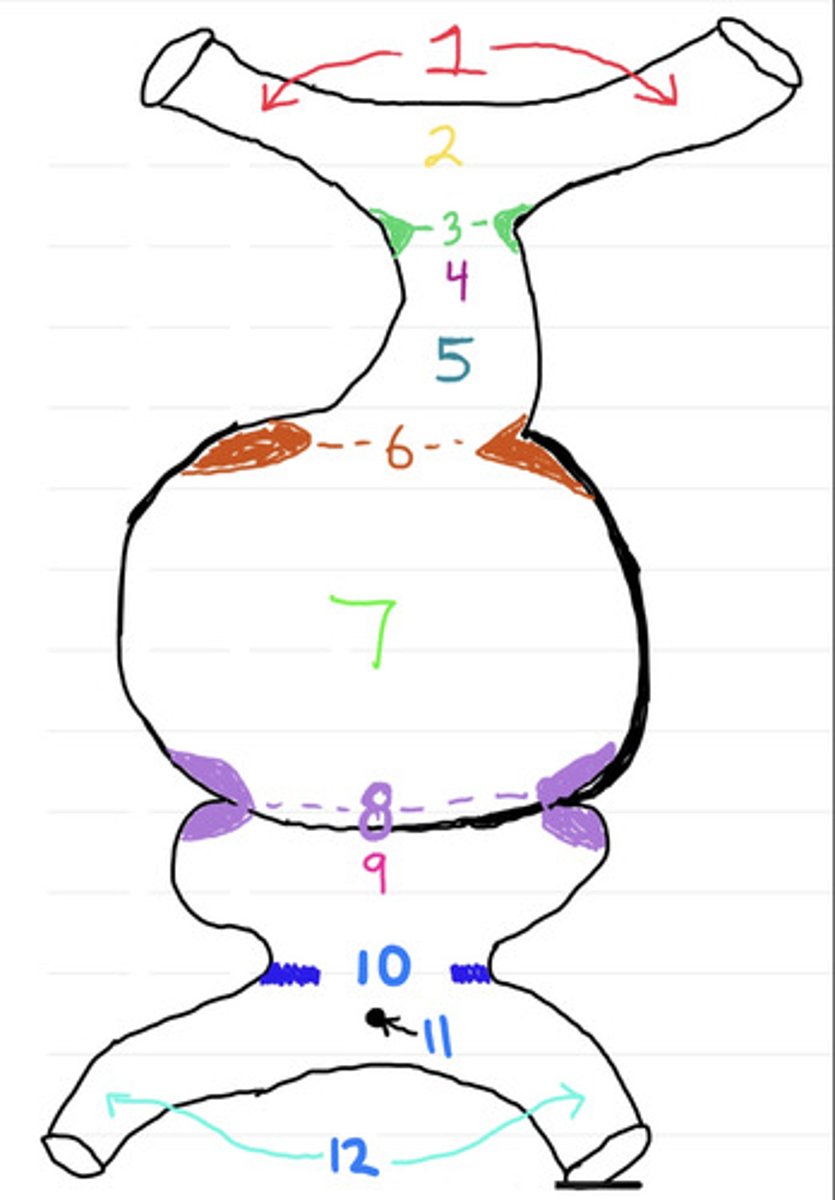
1. Arteries, 2. Aortic Arch, 3. Distal Bulbar Swellings, 4. Truncus Arteriosus, 5. Bulbus Cordis, 6. Proximal Bulbar swellings, 7. Primitive Ventricle, 8. Atrio-ventricular Swellings, 9. Primitive Atrium, 10. Sino-atrial swellings, 11. Sinus Venosus, 12. Veins
Linear heart
24
What Day?
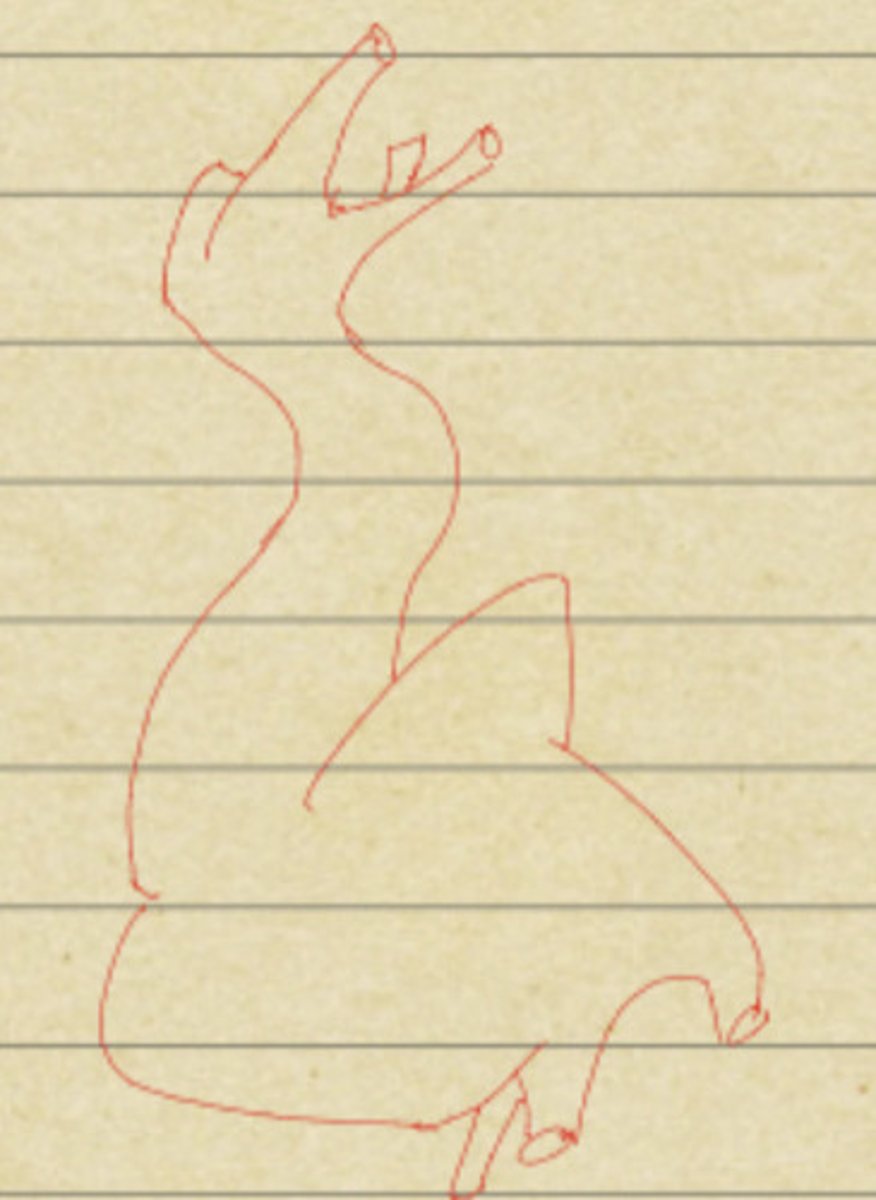

28
What day?
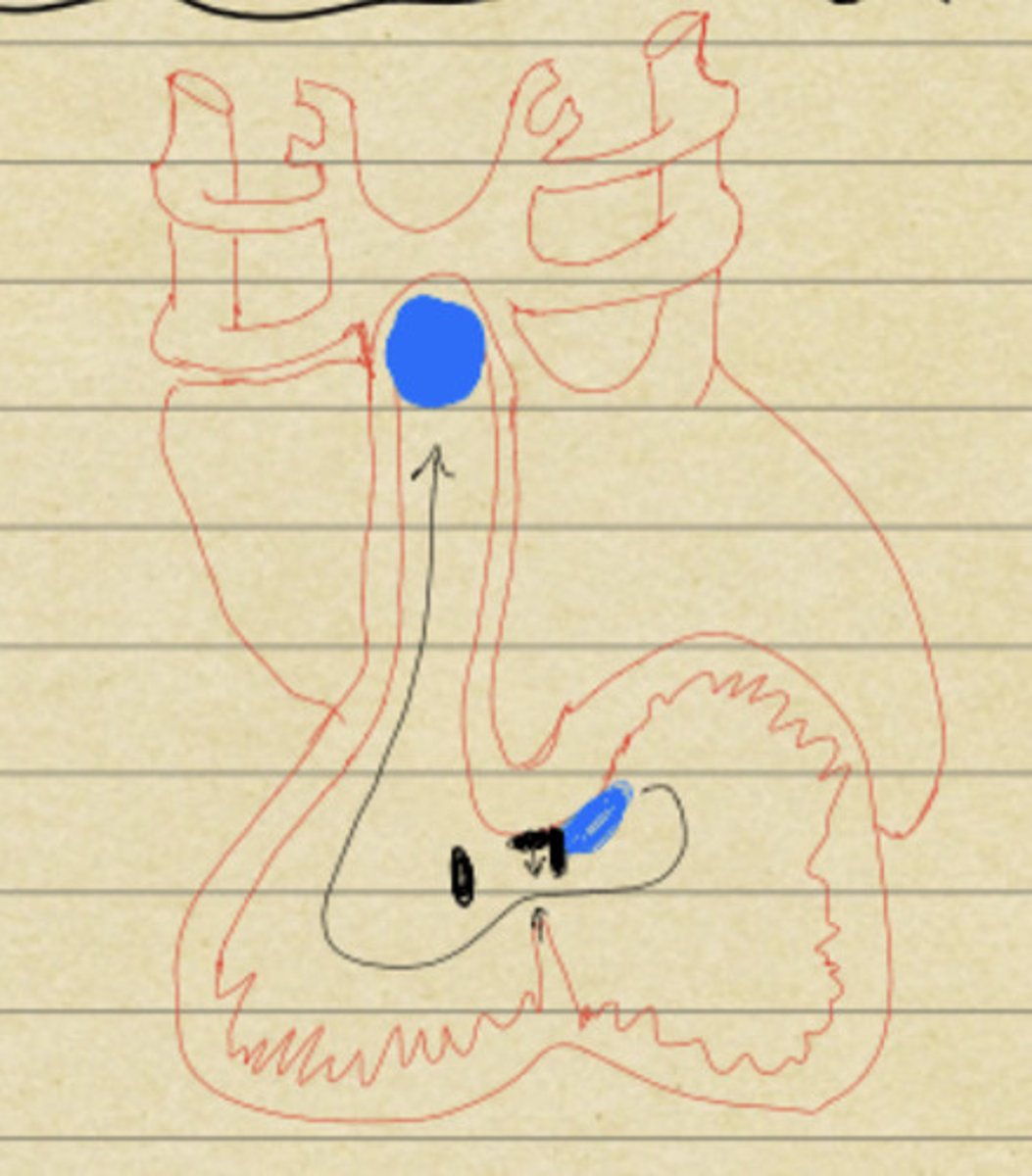
30
What day?
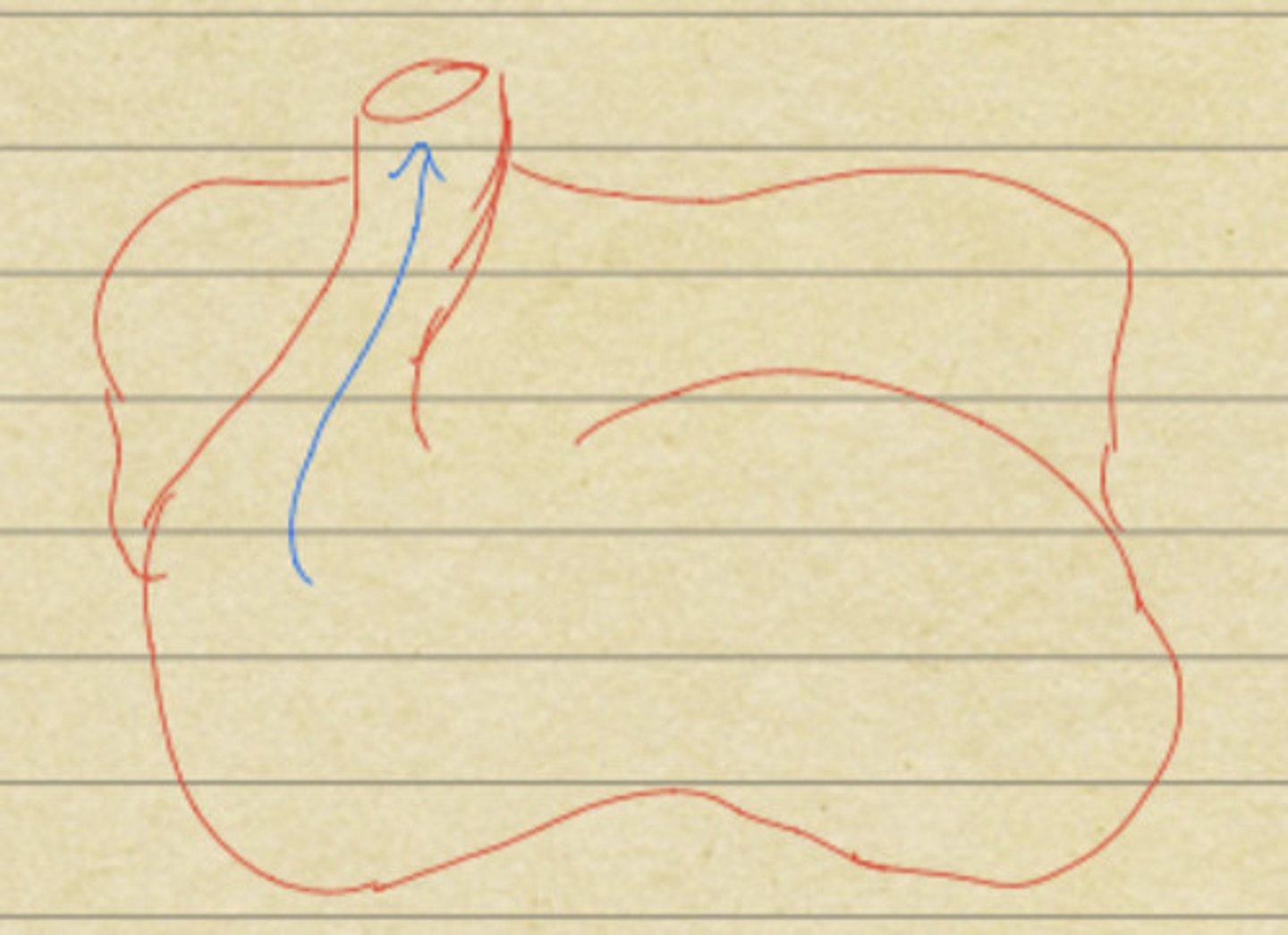
Artery
vessels that carry blood away from the embryo's heart (oxygenation of blood doesn't matter at this point)
Umbilical artery
Supplies blood to the placenta
Cranial (Truncus Arteriosus)
Arteries come out of _________ aspect
6
How many pharyngeal arches form?
Aortic
For each pharyngeal arches there will be one _______ arch
Lower head and neck
Pharyngeal arches supply :
After baby's first breath
Ductus arteriosus closes when?
Common iliac, internal iliac arteries, pelvis
Descending Aorta divides into ___________, which divides into external (not important for embryo but supplies lower extremities) and _______________ which supplies the __________
Umbilical arteries
Internal iliac arteries lead into
medial umbilical ligaments (can be traced all the way back to internal iliac arteries)
When the baby is born, the umbilical arteries will clamp down & form
Veins
vessels that carry blood toward the embryo's heart (oxygenation of blood doesn't matter at this point)
Liver
Vitelline Veins & Umbilical veins develop because of the __________