Ch. 13: Skin, Hair, & Nails
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Largest organ of the body?
Skin
Layers of the skin?
Epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous (fat) layer
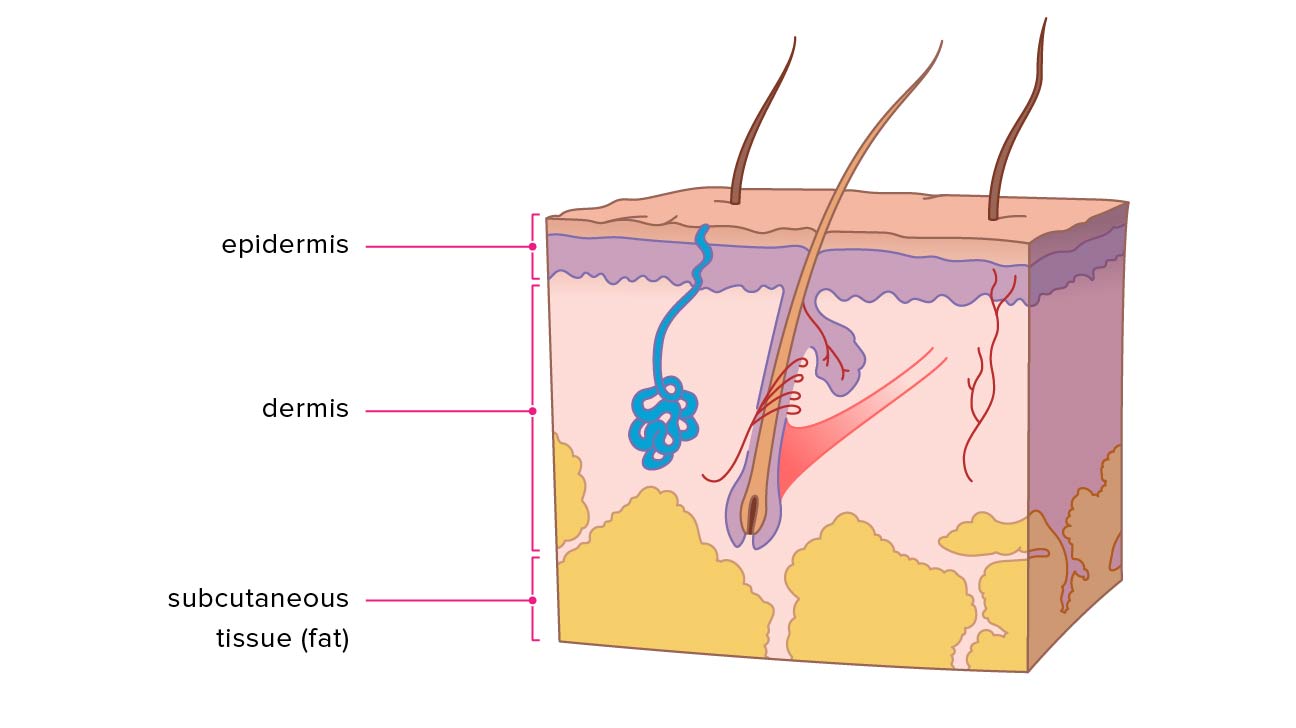
Epidermis
thin but tough. Its cells are bound tightly together into sheets that form a rugged protective barrier; major ingredient is protein keratin; produce the pigment melanin
dermis
inner supportive layer consisting mostly of connective tissue, or collagen (resists skin tearing); resilient elastic tissue that allows the skin to stretch with body movements. The nerves, sensory receptors, blood vessels, and lymphatics lie in the dermis; hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands are embedded in the dermis.
vellus hair
Fine, faint hair; covers most of the body
terminal hair
darker, thicker hair that grows on the scalp and eyebrows and, after puberty, on the axillae, the pubic area, and the face and chest in the male.
vernix caseosa
thick, white, cheesy substance made up of sebum and shed epithelial cells; present at birth
Aging adult skin
looses elasticity, epidermis thins and flattens, wrinkles, loss of collagen and subcutaneous fat, reduction in muscle tone
senile purpura
Bruises; minor trauma may produce dark red discolored areas
aging adult hair
hair loss, functioning melanocytes decreases = gray hair, hair thins
Keloids
raised scars that form at a wound site and grow beyond the normal boundaries of the wound; common among Black peoples
hyperpigmentation
dark spots after common acne has resolved
hypopigmentation
light spots after common acne has resolved
Melasma
“mask of pregnancy,” is a patchy tan-to-dark brown discoloration of the face; common among black peoples
Measles
measles virus is one of the most highly contagious pathogens known among all groups of people
Seborrhea & Xerosis
oily; dry
Pruritus
itchy skin
Alopecia
significant hair loss
Hirsutism
shaggy or excessive hair; excess body hair in females. This forms a male pattern on the face, chest, and back and indicates an increase in androgen hormones
Physiologic jaundice
present on day 3 or 4
Pathologic jaundice
present on day 1
vitiligo
absence of melanin pigment in patchy areas of white or light skin on the face, neck, hands, feet, and body folds and around orifices; occurs in all people, although dark-skinned people are more severely affected
Nevus
Mole; a clump of melanocytes (tan/brown color); 6 mm or less in size
ABCDEF (mnemonic)
used to assess abnormal characteristics of pigmented lesions
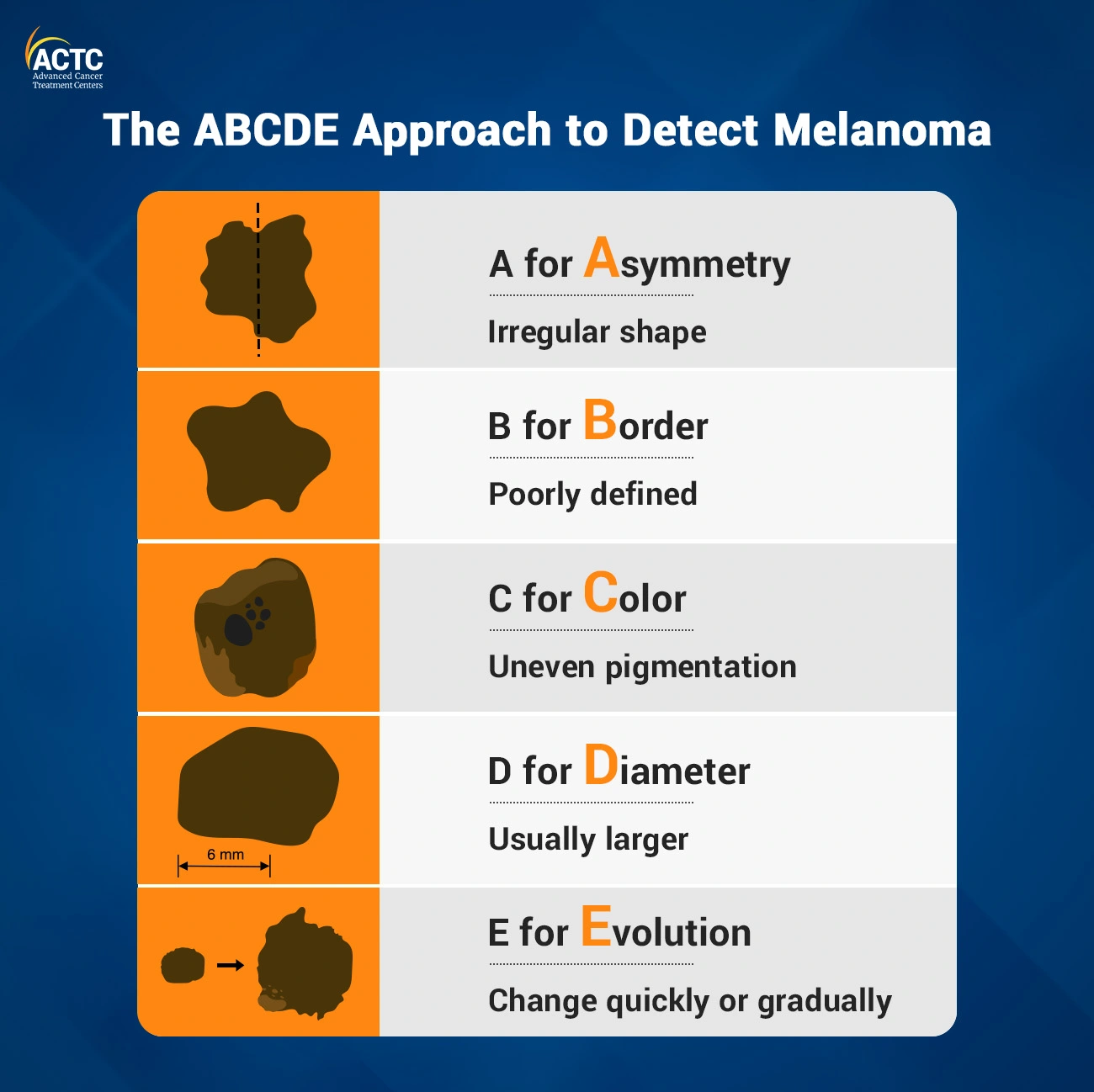
Funny looking (refers to the “ugly duckling” sign, in which the suspicious lesion stands out as looking different compared with its neighboring nevi
Pallor
paleness; whitish color to skin; presents with rapid pulse rate, oliguria, apprehension, and restlessness.
Cyanosis
blue/purple tint to the skin; easily seen where the skin is thin, such as the lips, mouth, earlobes and fingernails; decreased oxygen in the bloodstream; indicates hypoxemia and occurs with shock, cardiac arrest, heart failure, chronic bronchitis, and congenital heart disease.
Erythema
redness of the skin; caused by increased blood flow (hyperemia); occurs with polycythemia, venous stasis, carbon monoxide poisoning, and the extravascular presence of red blood cells
Jaundice
yellow skin color indicates rising amounts of bilirubin in the blood; occurs with hepatitis, cirrhosis, sickle-cell disease, transfusion reaction, and hemolytic disease of the newborn.
Chronic iron deficiency anemia
“spoon” nails, with a concave shape. Fatigue, exertional dyspnea, rapid pulse, dizziness, and impaired mental function accompany most severe anemias.
Chronic cigarette smoking causes what to skin temperature?
causes vasoconstriction, noted in cool, pale hands.
Hypothermia
Generalized coolness; accompanies shock, cardiac arrest.
Localized hypothermia occurs in peripheral arterial insufficiency and Raynaud disease.
Hyperthermia
warm, moist skin; increased metabolic rate such as in fever or after heavy exercise.
Diaphoresis
profuse perspiration/sweating; occurs with thyrotoxicosis, heart attack, anxiety, or pain.
How does dehydration affect moisture?
With dehydration, mucous membranes are dry, and lips look parched and cracked. With extreme dryness the skin is fissured, resembling cracks in a dry lake bed.
atrophic
very thin, shiny skin
Edema
fluid accumulating in the interstitial spaces; it is not present normally affects mobility;
Cherry (senile) angiomas
small smooth, slightly raised bright red dots that commonly appear on the trunk in all adults older than 30 years
Primary lesions
when a lesion develops on previously unaltered skin
Secondary lesions
when a lesion changes over time or changes because of scratching or infection
what to note on lesions?
Color
elevation
patter/shape
size
location
exudate
dermatoscope
medical tool used for closer inspection of a lesion
The Profile Sign
the angle made by the nail as it exits the proximal nailfold; 160 degrees
Clubbing of nails
occurs with congenital cyanotic heart disease, lung cancer, and pulmonary diseases
leukonychia
white hairline linear markings from trauma or picking at the cuticle
café au lait spot
large round or oval patch of light brown pigmentation (thus the name coffee with milk), which is usually present at birth
Acrocyanosisa
bluish color around the lips, hands and fingernails, and feet and toenails. This may last for a few hours and disappear with warming. NEWBORNS
Striae
jagged linear “stretch marks” of silver-to-pink color that appear during the 2nd trimester on the abdomen, breasts, and sometimes thighs
linea nigra
a brownish-black line down the midline of a pregnant woman stomach
Vascular spiders (spider angioma)
These lesions have tiny red centers with radiating branches and occur on the face, neck, upper chest, and arms; common in pregnancy
lentigines
“Liver spots”; common; clusters of melanocytes due to chronic sun exposure
Acrochordons
skin tags; overgrowths of normal skin that form a stalk and are polyp-like
Pressure Injuries (PI)
appear on the skin over a bony prominence when circulation is impaired, e.g., when confined to bed or immobilized.
Pressure Injury Stages
Stage 1: intact red skin but unbroken
stage 2: loss of epidermis and exposed dermis
stage 3: full thickness skin loss; extends into subcutaneous layer
stage 4: full thickness skin/tissue loss; muscle is exposed
Deep Tissue Pressure Injury (DTPI)
Localized, non-blanchable color change to deep red, maroon, purple in intact or nonintact skin. Preceded by pain and temperature change. Begins in the muscle closest to the bone
Telangiectasia
spider veins; visible small linear red blood vessels (broken capillaries)
Spider Telangiectasia
fiery red, star-shaped marking with a solid circular center.
Contusion
Bruise;
1) red-blue or purple immediately after or within 24 hours of trauma and generally progresses to
(2) blue to purple
(3) blue-green
(4) yellow
(5) brown to disappearing
Diaper Dermatitis
Diaper rash; Inflammatory disease caused by skin irritation from ammonia, heat, moisture, occlusive diapers.
Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)
chronic inflammatory skin lesion caused by overstimulated immune system, strong genetic component, and environmental triggers.
Chickenpox (Varicella)
Shiny vesicles; Small, tight vesicles
German Measles (Rubella)
Pink, papular rash (similar to measles but paler) first appears on face, then spreads. Distinguished from measles by presence of neck lymphadenopathy and absence of Koplik spots. Prevention of rubella occurs with two spaced doses of the MMR vaccine.
Primary Contact Dermatitis
Local inflammatory reaction to an irritant in the environment or an allergy
Tinea Corporis
(Ringworm of the Body)
Tinea Pedis
(Ringworm of the Foot); athletes foot
Psoriasis
immune-mediated, chronic, inflammatory skin disease with environmental triggers (trauma, stress, infections, medications) and genetic factors. Note the sharp margins. Chronic plaque psoriasis is a raised, scaly, erythematous patch, with silvery scales that are pruritic and painful.
Herpes Zoster (Shingles)
Small, grouped vesicles emerge along route of cutaneous sensory nerve, then pustules, then crusts.
Erythema Migrans of Lyme Disease
distinctive bull’s-eye, red macular or papular rash
Basal Cell Carcinoma
start as a small, pink or red papule then develops rounded, pearly borders with central red ulcer or looks like large open pore with central yellowing; Most common form of skin cancer; All must be removed.
Malignant Melanoma
transformation of melanocytes
Toxic Alopecia
Patchy, asymmetric balding that accompanies severe illness or use of chemotherapy
Tinea Capitis (Scalp Ringworm)
Rounded, patchy hair loss on scalp, leaving broken-off hairs, pustules, and scales on skin. Caused by fungal infection
Traction Alopecia
frontal or temporal hairline, where the hair is in constant tension, but loss can occur in any scalp area. Trauma is from tight braiding, tight ponytail, barrettes, cornrows, hair weaves, dreadlocks, and use of chemical relaxation.