General Biology 1115 Ch 2
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Organisms are composed of matter. What is matter?
Anything that occupies space and has mass.
Matter is composed of chemical elements. What are chemical elements?
Substances that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reactions.
What is the smallest unit of matter that still retains properties of an element?
An atom.
What are the 3 subatomic particles that make up an atom? What are their charges?
Protons: 1 positive charge
Neutrons: no charge
Electrons: 1 negative charge
Which subatomic particles have the ability to change in number? Which don't?
Only the number of neutrons and electrons can change. The number of protons is consistent for a given element.
What does the atomic number represent?
The number of protons.
What makes up the mass number?
The number of protons + the number of neutrons.
What is the mass of 1 proton/neutron?
1 Da (dalton) or amu (atomic mass unit).
What is an isotope?
Atoms with the same number of protons, but different number of neutrons.
What is a valence electron?
Electrons that belong to the outermost shell, otherwise known as the valence shell.
What do atoms with incomplete valence shells tend to be?
Chemically reactive.
What do atoms with complete valence shells tend to be?
Chemically inert.
What can atoms with incomplete valence shells do to obtain stability?
Share or completely transfer valence electrons with others.
What are the 3 types of chemical bonds?
1. Covalent
2. Ionic
3. Hydrogen
What is a covalent bond?
It is when 2 atoms share an electron.
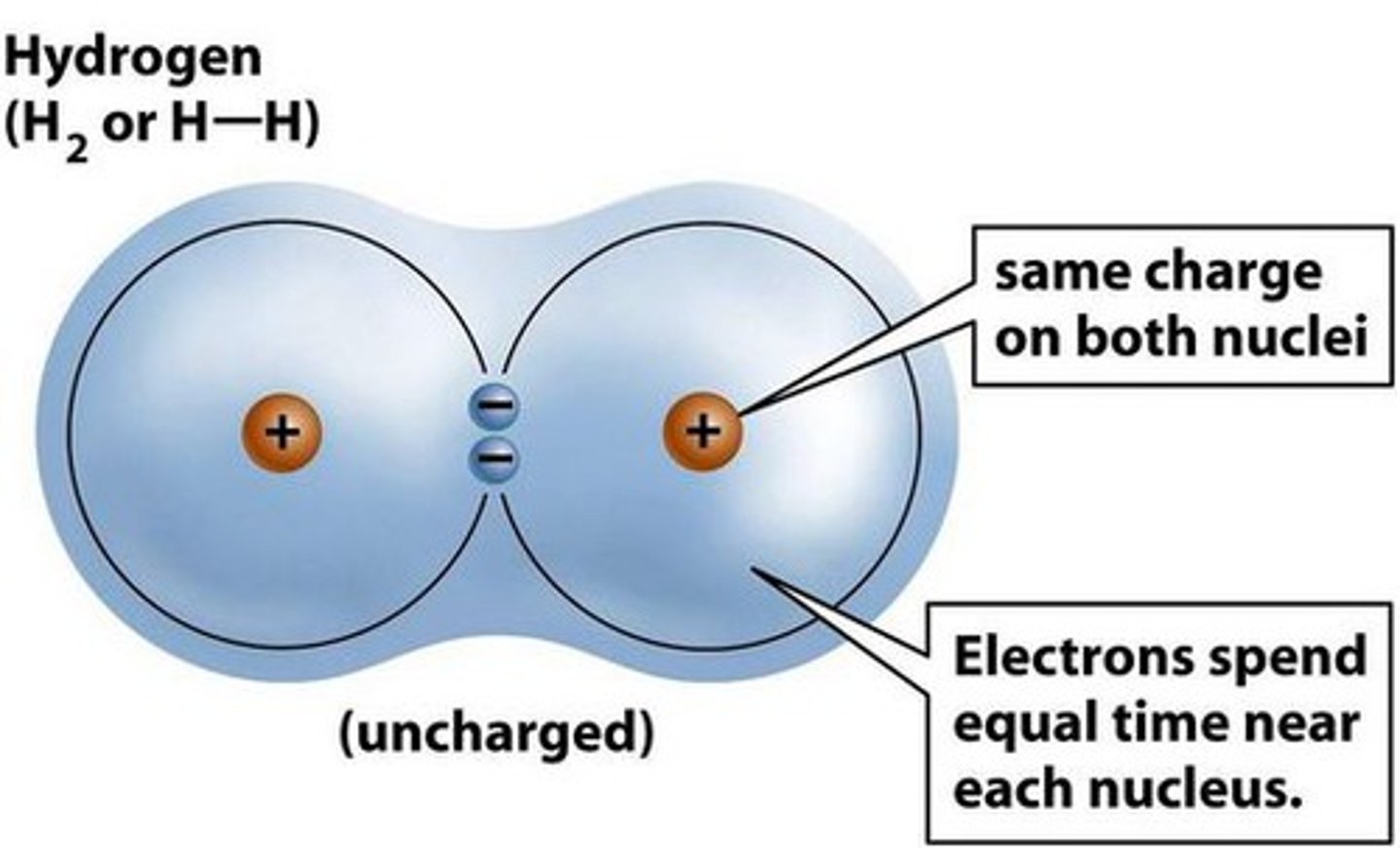
When atoms are held together by covalent bonds, what do they form?
Molecules.
What is electronegativity?
An atom's attraction to electrons that determines the type of bond that forms.
What 2 factors determine electronegativity?
1. Proximity of electrons to the nucleus
2. The number of electrons required to fill the valence shell
What are the 2 types of covalent bonds?
1. Non-polar covalent
2. Polar covalent
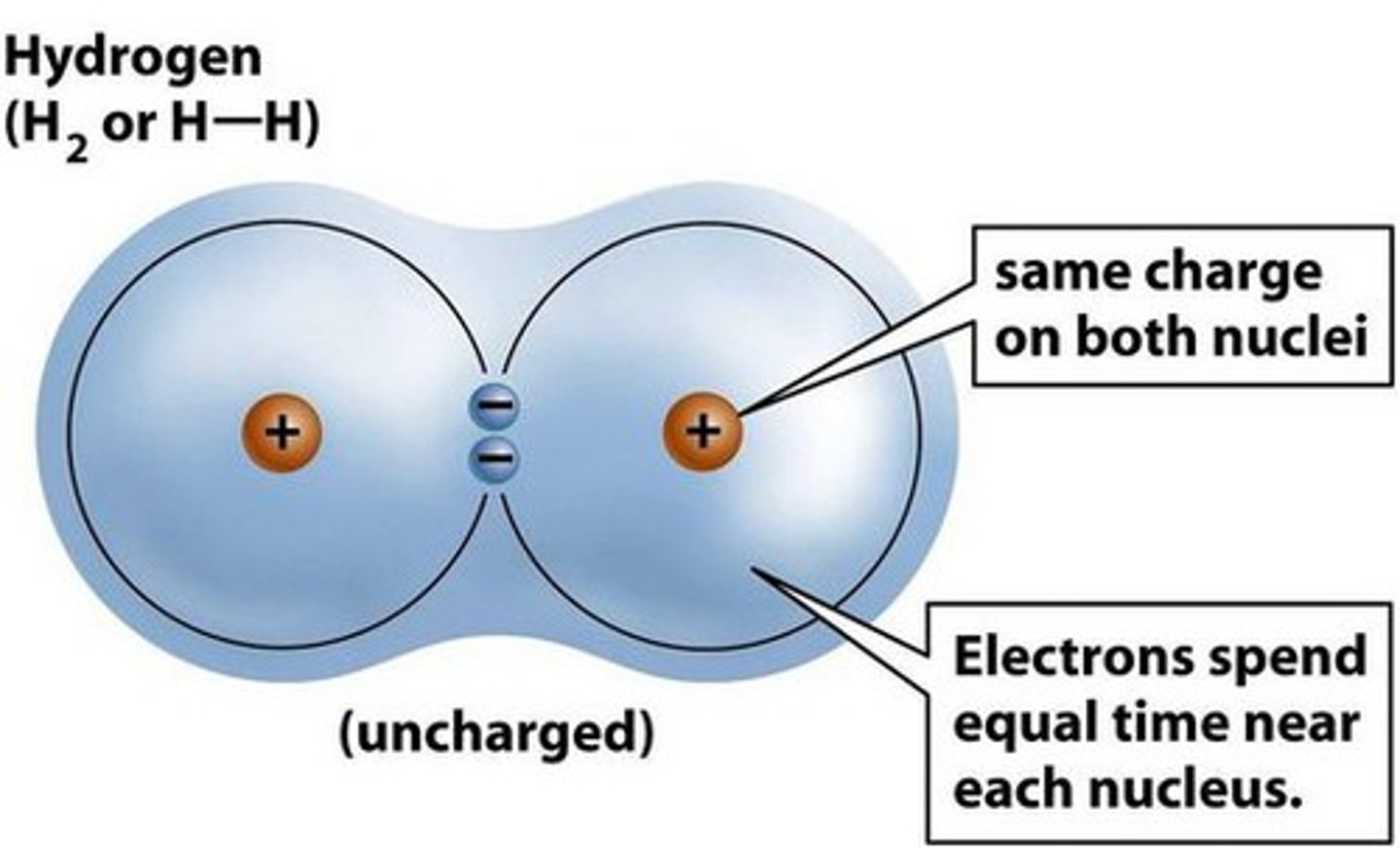
When is a covalent bond non-polar?
When electrons are shared equally.
When is a covalent bond polar?
When shared electrons are pulled closer to the more electronegative atom, making it partially negative and the other atom partially positive (hence POLAR).
E.g. H2O - O is more electronegative than H so partial charges exist on the O and H atoms.
Which of these 4 elements share similar electronegativity with another? Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen.
Carbon and Hydrogen
Oxygen and Nitrogen
Which pair of elements is more electronegative than the other?
Carbon and Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen
Oxygen and Nitrogen are more electronegative than Carbon and Hydrogen.
After a complete electron transfer occurs between two atoms, what term do we now call the atom?
An ion.
What are the names of the positively and negatively charged ion?
Anion: negative
Cation: positive
How do ions form?
When the electronegativity between atoms is very different and a complete electron transfer occurs.
What is an ionic bond?
An attraction between ions of OPPOSITE charges.
What is a chemical compound?
A substance made up of 2 or more elements in which atoms are bonded together in a set ratio.
Which bonds can compounds be held together by?
Ionic or covalent bonds.
Which type of compound IS NOT considered a molecule?
Ionic compounds.
Which type of compound IS considered a molecule?
Covalent compounds.
Why aren't all molecules considered compounds?
Because molecules can be made up of two atoms of the same kind.
E.g. H2, O2
Which type of compound is less stable than the other when it comes to biological systems?
Ionic compounds are less stable than covalent compounds.
What are hydrogen bonds?
A weak bond between polar covalent molecules as a result of attraction between opposite partial charges.
Which elements are most often associated with hydrogen bonding in biological systems?
Most often HYDROGEN with a partial POSITIVE charge bonding with either an OXYGEN or NITROGEN with a partial negative charge.
What characteristics do hydrogen bonds have because of their weak strength?
They can form, break, and reform easily.
What is the difference between a hydrogen bond and a polar covalent bond?
Both bonds are a result of partial positive and partial negative charges coming together to form a bond. The difference is that hydrogen bonds happen at a molecular level whereas polar covalent bonds happen at an atomic level.
E.g. Hydrogen bond = H2O (molecule) bonds with another H2O (molecule)
Polar covalent bond = H (atom) bonds with another H (atom)
How are water molecules held together? How do water molecules interact with one another?
Water molecules are held together intramolecularly by polar covalent bonds. Water molecules interact with other water molecules intermolecularly through hydrogen bonds.
What makes water so important for life?
Water is a versatile solvent. Life's chemical reactions are more available to react when they are dissolved in water.
What is a solution?
Liquid that is a homogenous mixture of substances.
What is a solvent?
A dissolving agent of the solution.
What is a solute?
A substance that is dissolved.
What type of compound and molecule does water's polarity allow it to dissolve?
Ionic compounds and polar molecules.
Define hydrophilic.
"Water-loving" substances that stay in solution because they interact with water's partial charges.
Define hydrophobic.
"Water-fearing" molecules that are uncharged/non-polar, and do not dissolve in water.
Why don't hydrophobic molecules dissolve in water?
Because water molecules will instead interact with themselves via hydrogen bonds.
What three properties does water display due to its polar nature?
Cohesion: water molecules interact with one another through hydrogen bonds
Adhesion: water molecules interact with and "stick" to polar/charged surfaces
Surface tension: hydrogen bonds between water molecules at the surface of the liquid resist stretching or breaking of that surface.
What happens to water when it is frozen?
Water expands. Specifically, more hydrogen bonds form between water molecules. These bonds are highly ordered and produce an open hexagonal structure that pushes molecules away from one another.
If "solid water" or ice has the same mass as liquid water but takes up more space, what does that mean for its density?
"Solid water" or ice is less dense than liquid water. (This is why ice floats on the surface of liquid water)
What is a chemical reaction?
The making and breaking of chemical bonds, and the rearrangement of atoms to form new substances.
Define reactant.
The starting substances.
Define product.
The resulting substances.
When can reactants and products switch?
In reversible reactions, depending on certain conditions.
What is dynamic equilibrium?
When the rate of dissociation is equal to the rate of reformation.
E.g. Water in an aqueous solution
H2O <=> H+ + OH-
What is an acid?
A chemical compound that donated H+ ions to solutions. More acidity, higher H+ concentration.
What is a base?
A compound that binds to H+ ions and removes them from solution. More basic/alkaline, lower H+ concentration.
In an aqueous solution at 25 degrees Celsius, what is the product of [H+][OH-]?
10^-14 mol/L
*1 mol = 6.02x10^23 molecules
What formula can you use to calculate the pH of a solution when [H+] is known?
pH = -log[H+]
What is the range of the pH scale? At what pH is a solution basic? Neutral? Acidic?
0-14
0 = most acidic
7 = neutral
14 = most basic
What do strong acids do in water?
They dissociate completely and irreversibly in water, releasing a large number of H+ ions.
E.g. HCl
What do strong bases do in water?
They dissociate completely and irreversibly in water, releasing a large number of OH- ions that bind to H+ ions and remove them from the solution.
E.g. NaOH
If strong acids/bases bind and release H+ or OH- ions irreversibly, what does that mean for weak acids/bases?
Weak acids and bases bind and release H+ or OH- ions reversibly.
E.g. Acetic acid, ammonia (base)
What is a buffer?
A compound that minimizes changes in pH by binding to or releasing ions depending on how much of that ion is already in solution.
What are most buffer systems composed of?
A weak acid and the corresponding weak base. They reversibly work by either donating H+ or accepting H+.
E.g. carbonic acid (H2CO3) and bicarbonate ion (HCO3-) contributes to pH stability in human blood
Define energy.
A system's ability to do work/capacity to cause change.
What are the two types of energy?
Potential and kinetic.
What is potential energy?
Energy stored in a molecule/system due to its position.
E.g. chemical energy stored in molecular bonds
Ep = mgh where h= height
What is kinetic energy?
Energy that a molecule/system possesses due to its motion.
E.g. heat, light
*Ek = 1/2mv^2 where v = velocity
What do we call the potential energy of molecules?
Chemical energy.
What is chemical energy?
The position of the shared electrons in covalent bonds. If shared electrons are far from the nuclei, bonds are long and weak. If shared electrons are close to one or both nuclei, bonds are shorter and stronger.
Describe potential energy in molecules.
The potential for that molecule to form stronger bonds through chemical reactions.
Heat is a form of kinetic energy. What is heat? What is temperature?
Heat: the total amount of kinetic energy in a system due to its molecular motion. As molecules move, they "bounce" off one another and transfer kinetic energy.
Temperature: average intensity of heat due to kinetic energy of molecules.
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
The energy of the universe is constant; energy can be transferred or transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
Energy transfer = energy moves from one location to another
Energy transformation = energy changes from one form to another
What is the second law of thermodynamics?
Every energy transformation increases the entropy (disorder) of the universe; during every transfer or transformation, some energy is converted to heat.
What makes a reaction spontaneous?
Reactions will be spontaneous when the product molecules are less ordered than the reactant molecules. (Entropy increases). If the products have lower potential energy than the reactants, the reaction will be spontaneous. That means the shared electrons in the products are held more tightly than those in the reactants.
What is an organic molecule?
Molecules that contain both carbon and hydrogen atoms.
What do you call an organic molecule that ONLY contains carbon and hydrogen?
Hydrocarbons.
Why is life's molecular diversity based on carbon?
Because carbon has a valence shell with 4 empty spots. This means it is able to make 4 covalent bonds with other atoms.
What shapes can carbon form due to its ability to make 4 covalent bonds?
A variety of chains and rings.
What does carbon most commonly bond with?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen (and occasionally phosphorus and sulphur).
What is a functional group?
A group of atoms commonly attached to the carbon skeleton of organic molecules, and involved in chemical reactions.
What are the 6 types of functional groups?
Carbonyl, carboxyl, phosphate, hydroxyl, sulfhydryl, and amino.
What does a carbonyl group do?
Reacts with certain other compounds to produce large molecules.
What does a carboxyl group do?
They tend to release a proton, act as a weak acid.
What does a phosphate group do?
Bonds between phosphate groups are weak and unstable, and store a large amount of chemical energy.
What does a hydroxyl group do?
They are highly polar, can release proton to act as a weak acid.
What does a sulfhydryl group do?
They may covalently bond to one another to form disulfide bridges.
What does an amino group do?
They tend to attract protons, act as a weak base.