Chapter 1 AP Econ
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
economics
how society makes the best choices under scarcity
scarcity
limited resources
everything is assumed to be scare
forces us to choose something over another
opportunity cost
what you give up to get something else
behavior
all actions are done with purpose
to increase utility (the satisfaction allowed from a g/s)
act in self interest but not selfishness
marginal analysis
= marginal benefits vs. marginal costs
marginal = extra
= (added benefits vs. added costs)
example of marginal analysis
buying a bigger engagement ring
marginal benefit = higher anticipated pleasure
marginal cost = higher cost than original
does obtaining the marginal benefits always come at a marginal cost of something else?
yes; since everything is scarce, obtaining the marginal benefit from something always comes at a marginal cost of something else
economic principles
generalization
ceteris paribus = assume other things equal → only one variable changes
positive economics
facts, cause/effect, subjective
normative economics
values, judgement, opinions, objective
budget line/ constraint
represents all possible combinations of consumption of 2 goods at fixed costs.
interior
attainable because you don’t have to use all of provided money but inefficient because you don’t maximize profit
anterior
unattainable because you don’t have enough money
4 factors of production
land
labor
capital
entrepreneurial ability
land
all natural resources
labor
physical and mental exertion in production of goods and services
cannot be forced labor → no cost on slavery
capital
assets used to be produce goods
capital goods = physical assets to produce other goods/services
not money → money is a means to buy capital goods, not a resource itself
capital goods = facilitate production of consumer goods
consumer goods = directly satisfy individual wages/needs
entrepreneurial ability
person combines [land, labor, and capital] into a business venture
takes risks, makes decisions
production possibilities model
PP table = shows different combinations of 2 products that can be produced with limited resources
PP curve/constraint/frontier = graph
what is the law of increasing opportunity cost
when the line gets steeper → giving up more of one product to produce another
describe the behavior of the points on the PPC
any point on the PPC is an efficient use of resources, in which there is a max employment
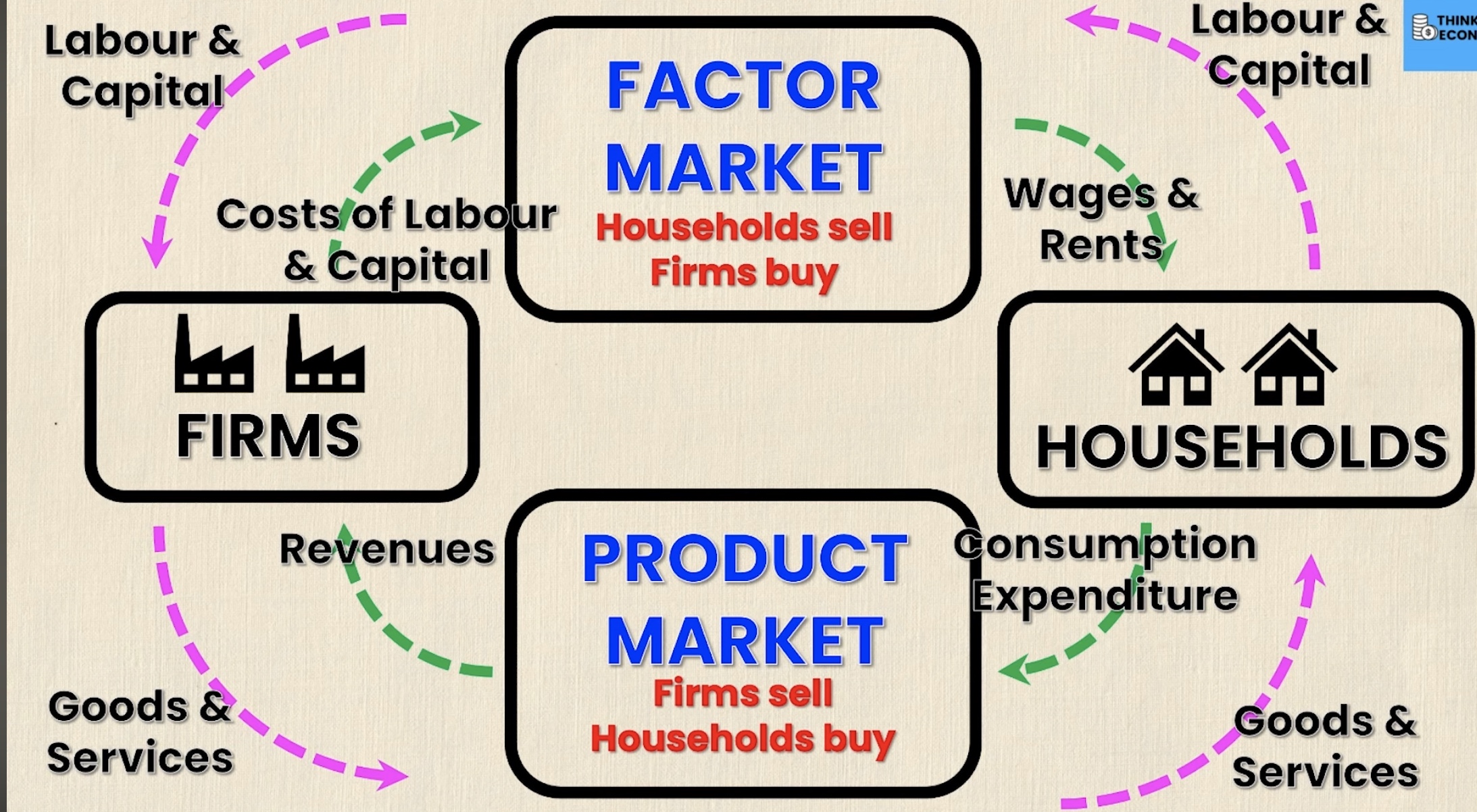
draw a circular flow model