UAB BY 124 Exam 1
1/183
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
184 Terms
charophytes
(aquatic) green algae land plants evolved from
3 key traits land plants share with charophytes
1. rings of cellulose-synthesizing proteins embedded in plasma membrane
2. formation of a phragmoplast (helps form cell wall)
3. structure of flagellated sperm (not all will have this)
adaptations enabling plants' move to land: why?
1. CO2
2. sunlight
3. soil- nutrients
4. fewer predators/pathogens (never been seen before)
adaptations enabling plants' move to land: problems?
1. lack of structural support
2. scarcity of water
adaptations enabling plants' move to land: adaptations?
1. survive periods when not submerged
2. charophytes have a layer of durable polymer (sporopollenin) that prevents exposed zygotes from drying out
natural selection
can only act on traits present in population
phylogenetic tree of ancestral algae
a. red algae
b. chlorophytes
c. charophytes
d. embryophytes
4 derived traits (unique to) of plants
1. alteration of generations and multicellular, dependent embryos
2. walled spores produced in sporangia
3. multicellular gametangia
4. apical meristem
alteration of generations
n (gametophyte) <-> 2n (sporophyte)
multicellular, dependent embryos
supported by maternal tissue, placental transfer
walled spores produced in sporangia
adaptation
multicellular gametangia
through mitosis:
female (n) -> eggs (n)
male (n) -> sperm (n)
archegonia
female gametangia
antheridia
male gametangia
apical meristem
where growth occurs (up or down)
other derived traits of plants
5. cuticle (waxy covering of the epidermis)
6. stomata (open & close for gas exchange)
7. mycorrhizae (symbiotic relationship between fungi and land plants -> nutrients)
8. secondary compounds (deter herbivores and pathogens)
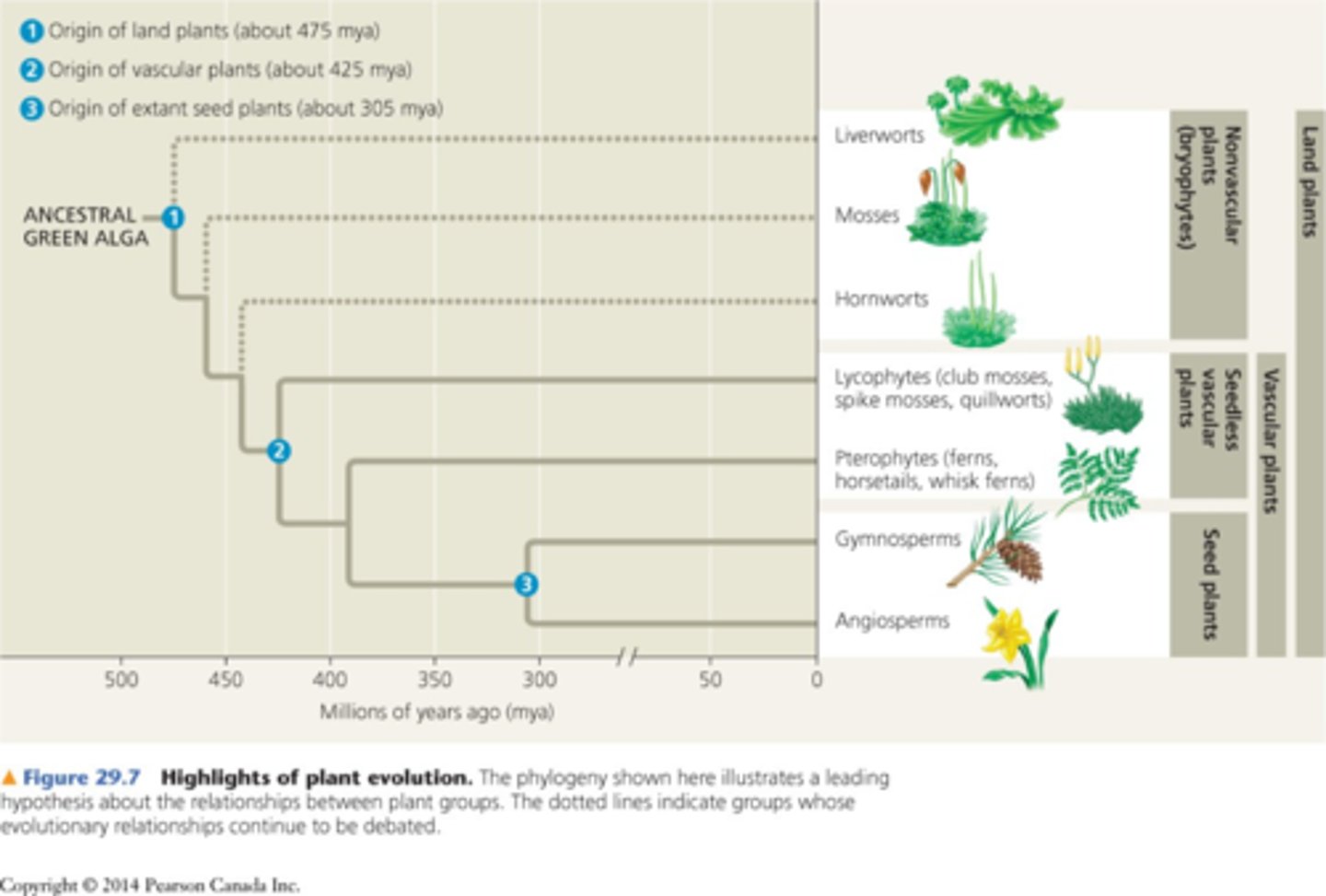
origin and diversification of plants
-evident in fossilized spores & sporophyte (2n) tissue
-see image for phylogenetic tree
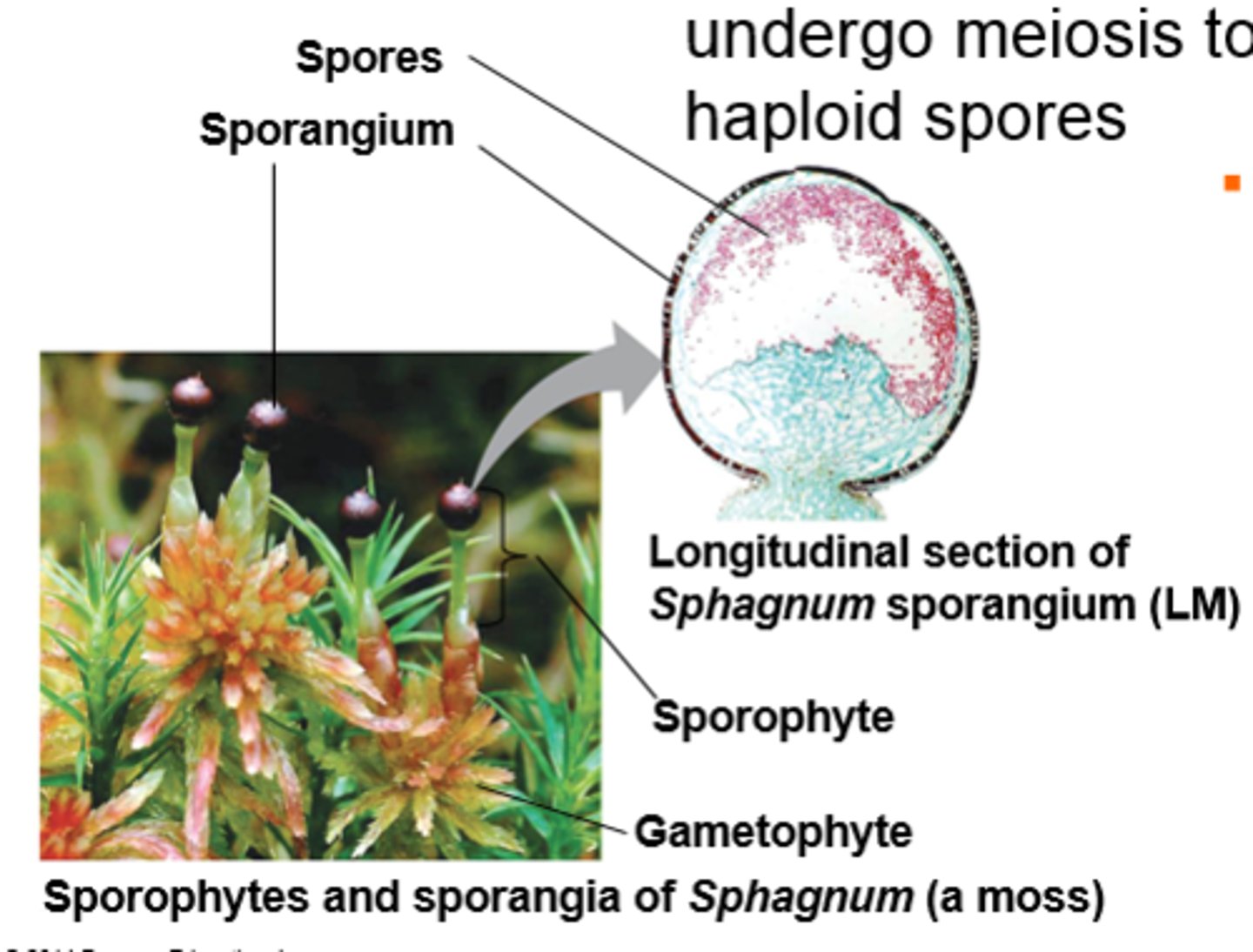
life cycles of mosses & other nonvascular plants: dominated by?
gametophytes (n)
3 phyla of byrophytes (small, herbaceous (non-woody) plants)
1. liverworts (Phylum Hepatophyta)
2. hornworts (Phylum Anthocerophyta)
3. mosses (Phylum Byrophyta)
location of gametophyte (n) & sporophyte (2n)
-can be in close proximity
-sporophyte arises from gametophyte
life cycle of moss
sporophyte (2n) -> meiosis -> spores (n) -> mitosis -> gametophytes (n) (male- sperm and female- egg) -> fertilization within archegonium (sperm has flagella and swims to egg) -> zygote (2n) -> embyro (2n) -> sporophyte (2n)
asexual reproduction in mosses
brood bodies
ecological and economical importance of mossess
1. peat -> fuel
2. acidity -> preservation of tissue
restrictions of mosses
1. moist environment necessary
2. unsubstantial root system
like carpet on the floor
1st plants to grow tall
ferns and other seedless vascular plants
1st (ancestral) vascular plant
Aglaophyton major
traits of living vascular plants
1. life cycles with dominant sporophytes (2n)
2. vascular tissues called xylem and phloem (plumbing system)
3. well-developed roots & leaves
xylem
(non-living) conducts water & minerals
1. trachieds
2. lignin
phloem
(living) distributes sugars, amino acids, and other organic compounds
life cycle of ferns
sporophyte (2n) (sorus underneath) -> sporangium -> meiosis -> spore (n) -> gametophyte (n) -> mitosis -> egg and sperm -> fertilization -> zygote (2n)n -> new sporophyte (grew from gametophyte)
evolution of roots
-organs that anchor vascular plants and absorb water and nutrients from soil
-tap root (pine trees) vs. fibrous root (oak trees)
evolution of leaves
1. microphylls (single vein)
2. megaphylls (highly branched) (more efficient)
sporophylls
modified leaves with sporangia
sori
clusters of sporangia of underside of sporophylls
strobili
cone-like structures formed from groups of sporophylls
homosporous spore production (most seedless vascular plants)
sporangium on sporophyll -> single type of spore -> typically bisexual gametophyte -> egg and sperm
heterosporous spore production (all seed plants and some seedless)
-megasporangium -> megaspore -> female gametophyte -> egg
-microsporangium -> microspore -> male gametophyte -> sperm
2 phyla of seedless vascular plants
1. Phylum Lycophyta (club mosses, spike mosses, and quillworts)
2. Phylum Monilophyta (ferns, horsetails, and whisk ferns and relatives)
distinguishing common name of mosses from mosses
height, roots, and chromosome number (haploid or diploid)
significance of seedless vascular plants
1. great heights during the Devonian and Carboniferous forming 1st forests
2. removed CO2 from atmosphere and may have contributed to global cooling at the end of Carboniferous (->carbon<-)
3. decaying plants of these Carboniferous forests -> coal
best adaptation of land plants
flowering plants (250,000 species)
key adaptations of plants for life on land
seed and pollen grains
common to all seed plants
1. reduced gametophytes (microscopic)
2. heterospory (distinct male- microspore and female- megaspore)
3. ovules (egg) (in gymnosperm, there's integument (2n), megaspore (n), and megasporangium (2n))
4. pollen (sperm) (water no longer needed for transportation)
5. seeds (survive better than unprotected spores, can be transported longer distances)
moses and other nonvascular plants
gametophyte: dominant
sporophyte: reduced, dependent
ferns and other seedless vascular plants
gametophyte: reduced, independent (photosynthetic and free-living)
sporophyte: dominant
seed plants
gametophyte: reduced (microscopic)
sporophyte: dominant
heterospory
-the rule among seed plants
-megaspore (female) -> egg
-microspore (male) -> sperm
development of female gametophyte within ovule (unfertilized)
1. megasporangium (2n)
2. megaspore (n)
3. 1 or more protective integuments (2n)
development of male gametophyte in pollen grain
1. microspores -> pollen with male gametophytes
2. pollination- transfer of pollen to part of seed plant containing ovule
fertilized ovule
1. female gametophyte (n)
2. egg nucleus (n)
3. discharged sperm nucleus (n)
4. pollen tube
5. inserted pollen grain/male gametophyte (n)
gymosperm seed
1. seed coat
2. spore wall
3. food supply (n)
4. embryo (2n)
evolutionary advantages of seeds over spores
1. may remain dormant for days to years until conditions are favorable for germination
2. supply of stored food
3. increased transportation by wind or animals
gymnosperms
-bear "naked seeds" typically on cones (formed by seeds exposed on sporophylls)
-4 phyla:
1. Cycadophyta (cycads)
2. Gingkophyta (1 living species= Ginko biloba)
3. Gnetophyta
4. Conifera
angiosperms
-seeds found in fruits (mature ovaries)
-single phylym: Anthophyta
-flowers & fruits- 2 key adaptations
life cycle of a pine
sporophyte (2n) -> a. microsporangia (2n) -> meiosis -> pollen and b. megasporangium (2n) -> meiosis -> megaspore -> egg <- pollen -> fertilization -> embryo (2n) -> seeds -> seedling (2n) -> sporophyte
angiosperm structure
1. sepal (leaf)
2. petal
3. carpel- stigma, style, and ovary
4. ovule
5. stamen- anther and filament
life cycle of angiosperm
sporophyte (2n) -> a. microsporangium -> meiosis -> microspore (n) -> pollen -> growing pollen tube and b. ovary -> meiosis -> megaspore (n) -> egg <- pollen -> fertilization -> zygote (2n) (nucleus of developing endosperm (food for egg) is 3n) -> seed -> germinating seed -> sporophyte
triploid endosperm
sperm fusing with egg and nucleus
angiosperm diversity
-more than 250,000 living species
-2 main groups:
1. monocot (1)- parallel veins, scattered vascular tissue, fibrous root, pollen with 1 opening, and flowers (3)
2. dicot (2)- netlike veins, ring-arranged vascular tissue, taproot, pollen with 2 openings, and flowers (4-5)
phylogenetic tree of angiosperms
evolution of flowering plants
(basal angiosperms)
1. amborella
evolution of vessel elements
2. water lillies
3. star anise
(core angiosperms- all connected)
1. magnolias
2. monocots
3. eudicots
types of taxon
1. monophyletic- includes a group of organisms who all arose from 1 common ancestor
2. polyphyletic- composed of unrelated organisms who arose from more than 1 ancestor
3. paraphyletic- includes most recent common ancestor but not all its descendents
human welfare greatly depends on seed plants: how/why?
1. most of our food comes from angiosperms
2. wood
3. medicines
4. fuel
5. animal diversity
selective breeding = artificial selection
humans have been doing it for years
(ex: corn)
genetic modification
leads to seeds with high-yielding crop but the seeds it produces can't reproduce
growth in plants
indeterminate (not predetermined) (but can still be ordered such as in broccoli)
basic hierarchy of plants
cell -> tissue -> organ
3 basic plant organs
1. roots
2. stems
3. leaves
2 types of systems in plants
1. root system (down)
2. shoot system (up)
roots can be modified: how?
to store energy (starch)
roots
-anchor
-absorb nutrients (because nutrients from the seed are used up fast)
function changes structure
specialized functions of roots
1. prop roots (corn)
2. storage roots (beet)
3. "strangeling" aerial roots (strangler fig)
4. pneumatophores (aquatic plants)
structures that have determine growth in plants
leaf blades, petioles, internodes, and flowers
stem
-bears leaves and buds
-elongates plant
specialized functions of stems
1. rhizomes (horizontal shoot) (ginger)
2. stolons (strawberry)
3. tubers (potato)
parts of leaf
1. leaf blade
2. petiole (joins leaf to stem)
types of leaves
1. simple
2. compound
3. double compound
4. wood-like
simple leaves
have single blade and petiole
compound leaves
have a blade divided into leaflets
double compound leaves
-have leaflets arranged along the middle vein
-large yet rarely damaged by wind or rain
needle-like leaves
characteristic of species adapted to extreme hot or cold temperatures
arrangements of leaves
1. alternate
2. opposite
3. whorled
4. rosette (upward staircase)
leaves: shade vs. sun?
-shade: larger leaves (more surface area) because of less sunlight
-sun: smaller leaves because of max sunlight
specialized functions of leaves
1. tendrils (climb)
2. spines (protect)
3. bulbs (storage) (onion)
4. reproductive
5. bracts (pollination) (poinsettias)
6. traps
3 types of tissues in plants
1. dermal (exterior)
2. vascular ("veins and arteries")
3. ground (the in-between)
dermal tissue system: in nonwoody plants
-has a single tissue called the epidermis
-the cuticle in stems and leaves helps prevent water loss
dermal tissue system: in woody plants
periderm replaces epidermis in older regions of stems and roots
dermal tissue system: trichomes
highly specialized epidermal cells
vascular tissue system: xylem
conducts water and dissolves minerals up
vascular tissue system: phloem
transports sugars and products of photosynthesis up and/or down (wherever needed)
vascular tissue of a stem or root: collectively called?
stele
ground tissue system: pith
ground tissue internal to vascular tissue
ground tissue system: cortex
ground tissue external to vascular tissue
ground tissue: includes?
-cells specialized for storage, photosynthesis, and support
-made up of: parenchyme, collenchyme, and sclerenchyme
major types of plant cells
1. parenchyma
2. collenchyma
3. sclerenchyma
4. water-conducting cells of xylem
5. sugar-conducting cells of phloem
parenchyma
(leaf)
-primary cell walls are thin and flexible
-perform most metabolic functions
-synthesize and store organic products
-where photosynthesis occurs (within chloroplasts)
-retain ability to divide and differentiate into other types of cells
collenchyma
(celery)
-thicker cell walls
-support young parts of the plant
-provide flexible support without restricting growth
-living and flexible when mature
sclerenchyma
(pear)
-function in support
-thick secondary cell walls with large amount of lignin
-mature cells can't elongate
-occur in regions where plant has stopped growing
trachieds/vessels
-in xylem of vascular tissue system
-nonliving
-move water up by cohesion and adhesition
siete tube/companion cells
-living
-provide nutrients (products of photosynthesis)
-in phloem of vascular tissue system
meristems: generate what?
cells for primary and secondary growth