Research Methods
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Research Method
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What is the positivist approach?
To view sociology as a science that uses the scientific method to study social facts from a macro perspective

What is the interpretivist approach?
To view sociology by focusing on the meanings, motivations and values individuals attach to their actions within cultural and social contexts
Bias
a lack of objectivity or inclination to favour a person or idea, regardless of the facts
Validity
whether the data being measured accurately depicts the real world
reliability
the ability to achieve the same procedure to get more consistent & confident results
Representativeness
describes how well a research sample mirrors the characteristics of a larger target population
Generalisability
The degree to which study findings from a sample can apply to a larger population or different contexts.
Quantitative data
information that can be measured, counted, and expressed with numbers
Qualitative Data
focuses on understanding the meanings, experiences, and behaviours of individuals and groups through non-numerical data
Objectivity
To not be influenced by opinion/experience in the findings of an experiment
Replicability
The ability to repeat an experiment/study with standardised conditions
Strengths of qualitative data
Detailed information
Provides context
Flexible and adaptable
Strengths of quantitative data
Reliable
Objective
Generalisable
Limitations of qualitative data
Lack of reliability- subjective
Difficulty generalising
Limitations of quantitative data
Lack of depth/context
Limited/misleading responses
operationalisation meaning
Finding ways to ask questions about, or to measure and observe, abstract concepts so that research can be carried out
hypothesis meaning
a tentative, testable statement that proposes a relationship between two or more variables
pilot studies meaning
A small preliminary test of a larger research project to identify and resolve potential issues before the full study begins
what are the different sampling techniques?
Stratified Random, Systematic, Snowball, Non-representative, Probability and Quota
what is probability sampling?
a method where every individual in a population has an equal chance of being selected for a study
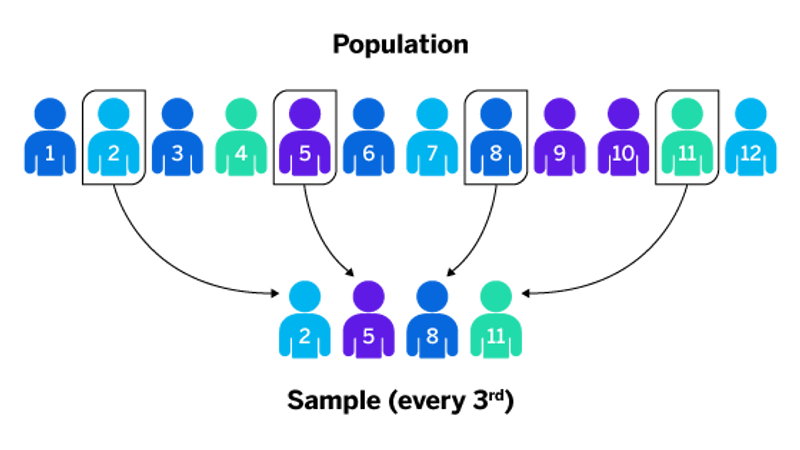
what is systematic sampling?
a method where every nth participant can be selected- this is done until the researcher has the desired number of participants
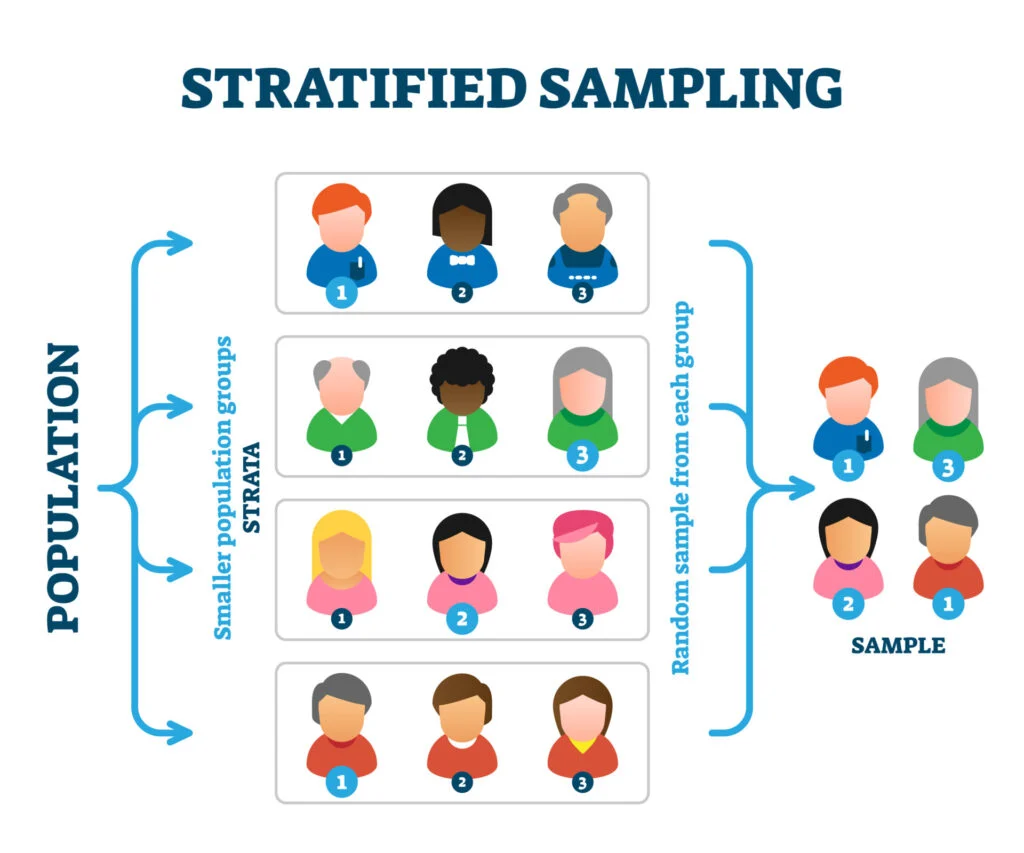
what is stratified sampling?
a method where a population is divided into subgroups (strata) based on shared characteristics like age, gender or race, and then a random sample is drawn from each subgroup
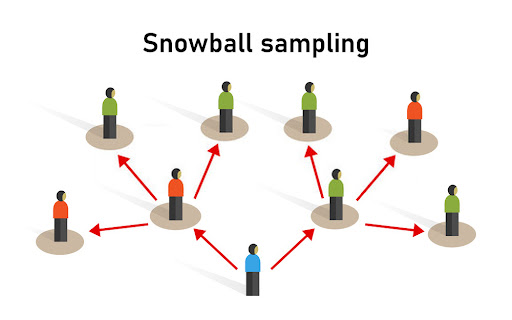
what is snowball sampling?
a method in sociology where no sampling frame is used and initial participants refer other people they know to be included in the study
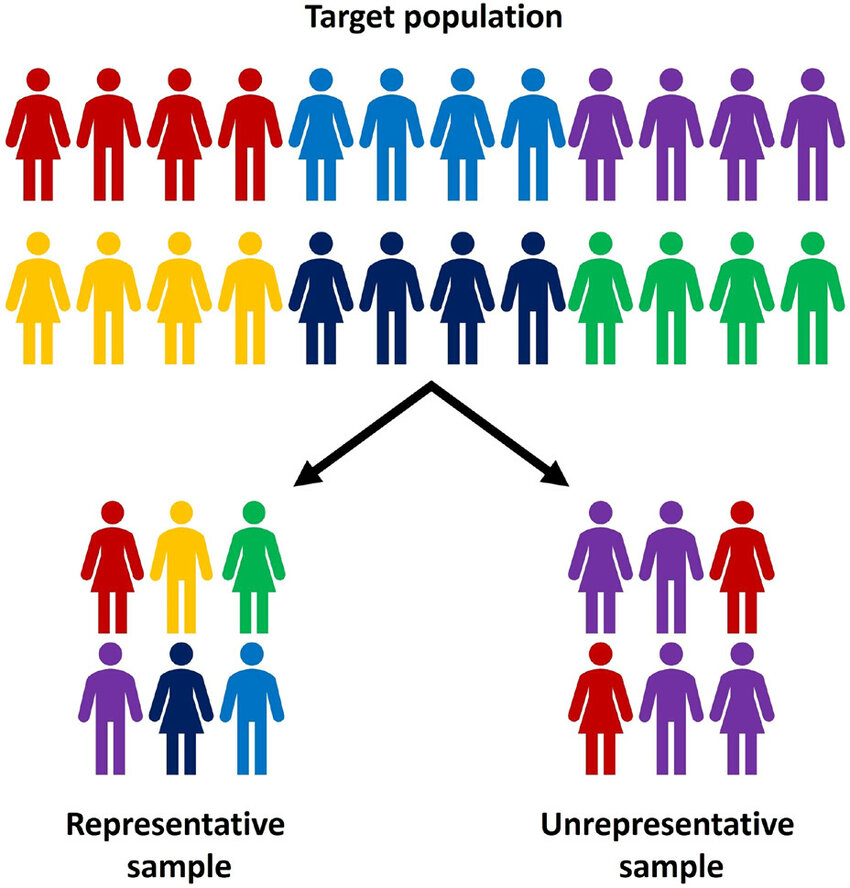
what is non-representative sampling?
a method where the sample selected for a study does not accurately reflect the characteristics of the larger population
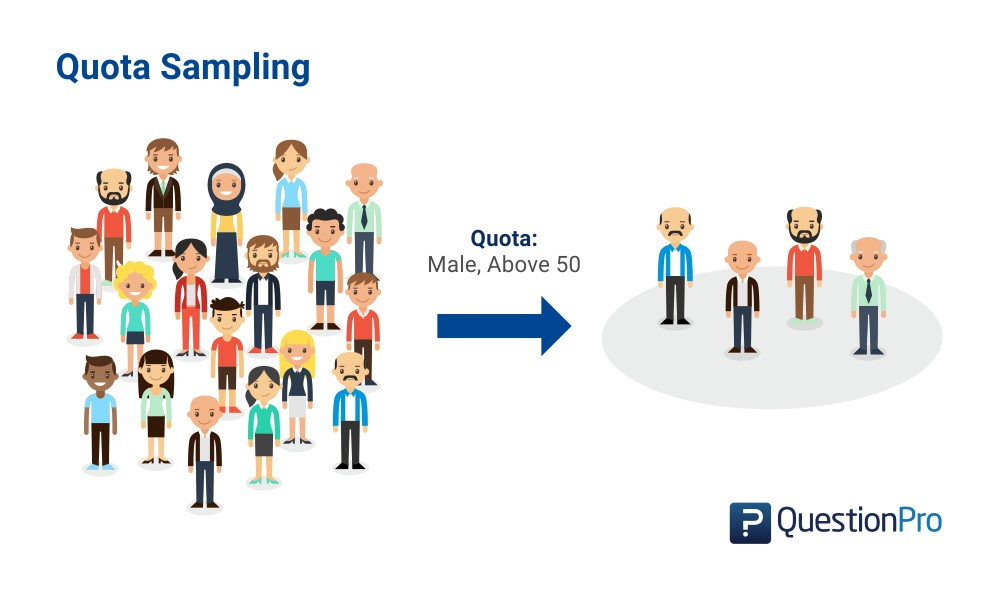
what is quota sampling?
a method that divides a population into subgroups based on specific characteristics, selecting a predetermined number of participants from each
what are the strengths of probability sampling?
reduces bias- eliminates investigator bias, simple to conduct
what are the limitations of probability sampling?
Time-consuming, a large sample size must be used to be effective, confounding results by chance
what are the strengths of systematic sampling?
simple, cost-effective, unbiased
what are the limitations of systematic sampling?
inherent bias- periodic traits may occur by chance
what are the strengths of stratified sampling?
representative, unbiased
what are the limitations of stratified sampling?
requires extensive prior knowledge
time-consuming
what are the strengths of snowball sampling?
valid data- gain access to hidden populations, less complicated, cost-effective
what are the limitations of snowball sampling?
not representative, sampling bias, time consuming- rapport
what are the strengths of quota sampling?
saves time- reduces load on investigators, cost-effective
what are the limitations of quota sampling?
lack of randomness is less reliable, researcher bias- individual choice is introduced
what are the strengths of non-representative sampling?
more in-depth data
what are the limitations of non-representative sampling?
not representative- can’t use it on other populations, cannot generalise

What is socialisation?
The life-long process where individuals learn norms, values, beliefs, and behaviours of their society and internalise it.
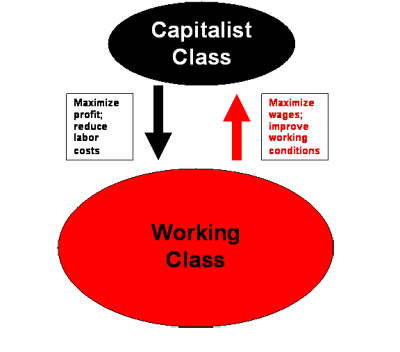
What is marxism?
A theoretical perspective that sees conflict between classes as the most important feature of society
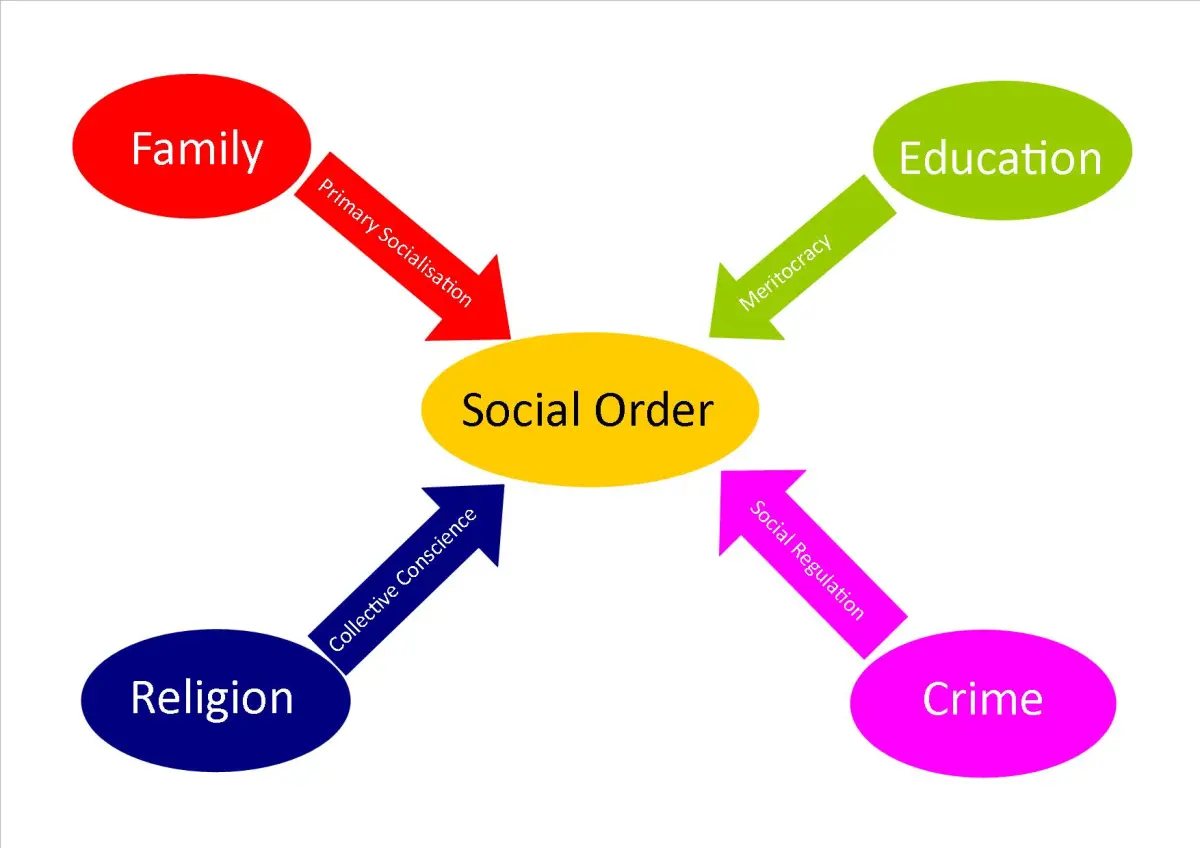
What is functionalism?
Society is likened to interconnected institutions that work together to maintain stability and order, similar to a human body.
What is feminism?
a theory that views society as patriarchal and based on gender inequality
What were the findings of James Patrick?
Social conditions led to the formation of a gang, which engaged in conflict situations that often did not result in actual fights.
what is a consensus?
agreement: a perspective on society which assumes that people generally share values
what is structuralism?
Sociological theory that says society is rooted in deep structures, shaping individual thoughts, actions, and cultural phenomena
what do positivists argue that behaviour is governed by?
social facts- laws, values, customs and other social rules in which individuals have no control
what is an empirical method?
one which allows us to objectively observe/measure some aspect of our behaviour and use the findings to develop existing theories or introduce new ones
value free research meaning
the ability of the researcher to keep their own values (personal, political and religious) from interfering with the research process + findings
what did durkheim conclude from his research?
the personal act of suicide is affected by the external social conditions- there is a relationship between the degree of integration/regulation in society and the suicide rate
why do positivists favour quantitative data?
it can be presented in numbers, so statistical tests can measure the strength of relationships between two or more factors
what is a casual relationship?
cause and effect- one factor causes another
what is a correlation?
a statistical link that indicates the extent to which two or more variables/ factors fluctuate in relation to each other
verstehen meaning
understanding the meaning of actions from the actor’s point of view
what is ecological validity?
it asks the question in whether the findings can be applied to other settings
what is historical validity?
it asks the question in whether the findings can be applied to different periods of time
what is the conflict approach?
A perspective that views society as unequal with conflict and social change arising from competition for limited resources like wealth, power, and status.
what does PERVRT stand for?
Practical, ethical, reliability, validity, representativeness, theoretical
what does it mean by ‘practical’ in PERVRT
Refers to factors like time, cost, and the availability of a sample.
what does it mean by ‘ethical’ in PERVRT
whether the research meets ethical guidelines, such as informed consent or anonymity
what does it mean by ‘theoretical’ in PERVRT
theoretical perspective (positivist or interpretivist) that informs the research method and the potential for researcher bias
Falsification definition
the process of testing a hypothesis or theory with the aim of refuting it
What are two features of functionalism
Biological analogy
socialisation
What are two features of marxism
Class struggle
Superstructure
Superstructure definition
Social institutions such as family, education, mass media and religion, which play a role in passing on the bourgeois ideology
Two features of feminism
Patriarchy
gender inequality