AP Bio - Chapter 6-8 Unit Quiz: Cell Energetics
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cell Energy, Cell Respiration, Photosynthesis
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
The cellular process of breaking down large molecules into smaller ones is defined as
catabolism
The cellular process of synthesizing large molecules from smaller ones is defined as
anabolism
Anabolic pathways usually share which characteristics?
They consume energy to synthesize polymers from monomers
Which of the following descriptions would be an example of potential energy?
the chemical bonds in a molecule of sucrose
Which of the following is the most comprehensive definition of metabolism in living organisms?
Metabolism consists of all the energy transformation reactions in an organism
Which of the following reactions releases energy?
Hydrolysis Reactions
Which of the following statements is true for all exergonic reactions?
The reaction proceeds with a net release of free energy
What reaction tends to require an input of energy?
Dehydration
Which of the descriptions below is an example of an exergonic reaction?
hydrolysis of glycogen to release glucose monomers
Which of the following processes would be an example of a catabolic pathway?
providing energy that can be used to drive cellular work
Which of the following is an example of an anabolic pathway?
A set of coupled reactions that are exergonic
When chemical, transport, or mechanical work is performed by an organism, what happens to the heat that is generated?
It is released to the environment
Hydrolysis of ATP releases energy, which ultimately results in the production of ADP and inorganic phosphate. What is commonly the immediate fate of the phosphate released by ATP hydrolysis in the cell?
It is attached to a substrate to form a phosphorylated intermediate
Which of the following statements about enzyme-catalyzed reactions is true?
The rate of reaction is greater than when the same reaction occurs in the absence if an enzyme
In most exergonic reactions, before products can be formed, the reactants must first overcome a thermodynamic barrier known as the:
Activation Energy of the reaction
Which of the following statements regarding enzymes is true?
Enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering the activation energy barrier
The active site of an enzyme is the region that
binds substrates for the enzyme
Which of the following statements best describes the induced fit model of enzyme activity?
The binding of substrate changes the conformation of the active site to bind the substrate more tightly.
A mutation that results in a single amino acid substitution in the active site of an enzyme may have which of the following consequences?
It may change the substrate specificity of the enzyme
Zinc, an essential trace element for most organisms, is required in the active site of the enzyme carboxylpeptidase in order for the enzyme to function properly. The zinc most likely functions as a(n)
cofactor necessary for enzyme activity
Why might a severe fever result in death if it is not brought under control?
It may alter the tertiary and quaternary structures of cellular enzymes
A noncompetitive inhibitor decreases the rate of an enzymatic reaction by
Changing the shape of the enzyme active site
Cooperactivity is a form of allosteric activation in which
Binding of a substrate molecule to one active site in a multisubunit enzyme stimulates the binding of substrate molecules to the active sites of other subunits
The mechanism by which the end product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an enzyme that catalyzes an earlier step in the pathway is most precisely described as
Feedback inhibition
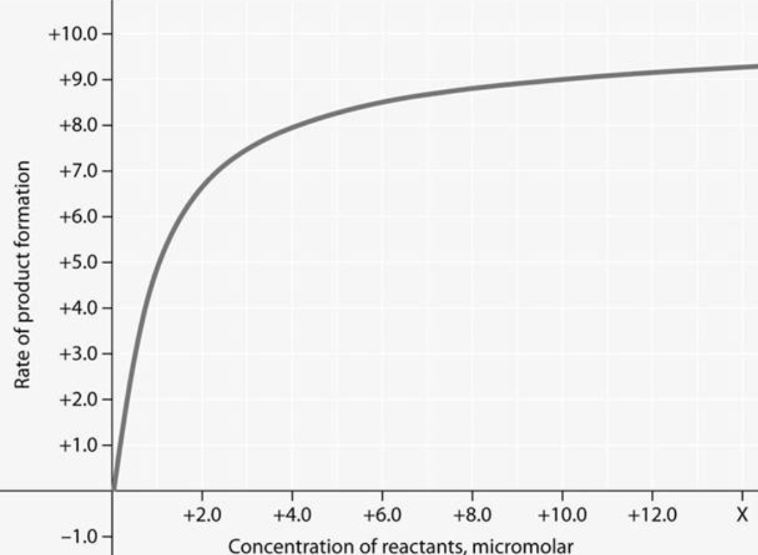
For the enzyme-catalyzed reaction shown in figure 6.2, which of these treatments will cause the greatest increase in the rate of the reaction if the initial concentration is 1.0 micromolar?
Doubling the enzyme concentration
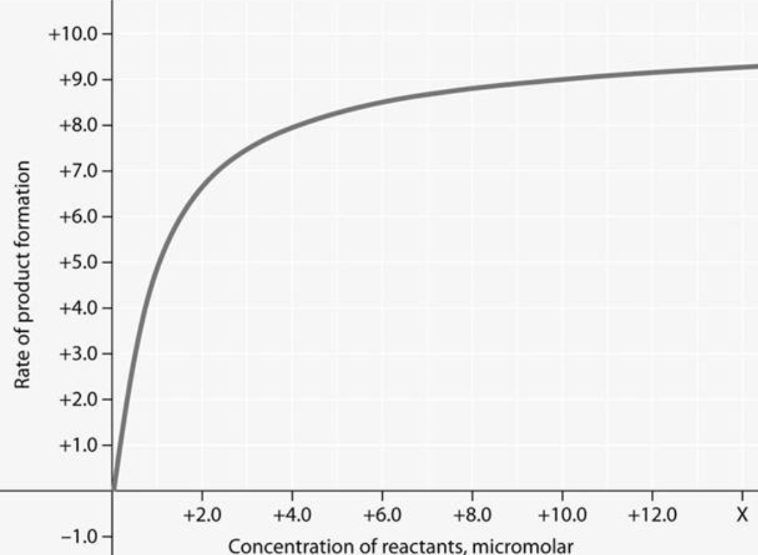
In figure 6.2, why does the reaction rate plateau at higher reactant concentrations?
Most enzyme molecules are occupied by substrate at high reactant concentrations
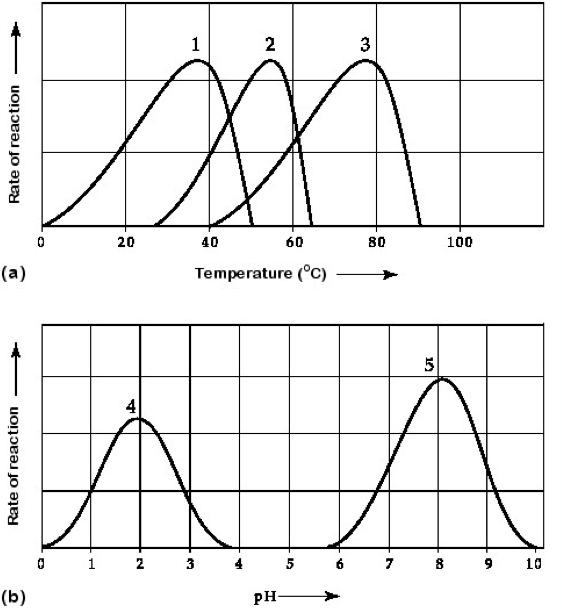
Which curves on the graphs in figure 6.3 may represent the temperature and pH profiles of an enzyme taken from a bacterium that lives in a mildly alkaline hot spring at temperatures of 70C or higher?
Curves 3 and 5
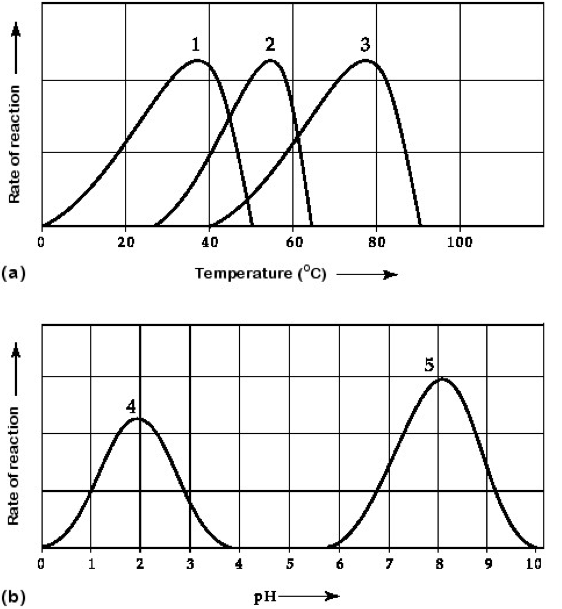
Which temperature and pH profile curves on the graphs in figure 6.3 were most likely generated from analysis of an enzyme from a human stomach, where conditions are strongly acidic?
Curves 1 and 4
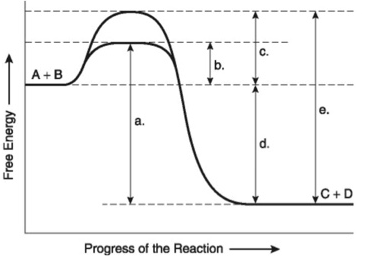
Figure 6.4 illustrates various aspects of the free-energy change (∆G) for the reaction A+B → C+D. Which of the following best describes the forward reaction?
Exergonic, ∆G<0
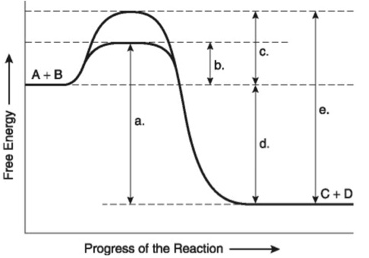
Figure 6.4 illustrates various aspects of the free-energy change (∆G) for the reaction A+B → C+D. Which of the following changes in free-energy represents the overall ∆G for the reaction?
D
Which of the following terms describes metabolic pathways that break down complex molecules to release stored energy?
Catabolic Pathways
In an oxidation-reduction reaction, how is the reducing agent changed?
It loses electrons and loses potential energy
As a result of an oxidation-reduction reaction, how is the oxidizing agent changed?
It gains electrons and gains potential energy
Why does the oxidation of organic compounds by molecular oxygen to produce CC2 and water release free energy?
Electrons are moved from atoms that have a lower affinity for electrons (such as C) to atoms with a higher affinity for electrons such as (such as O)
The complete reactions of cellular respiration in the presence of oxygen (C6H12O6 + 6O2 - 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy) result in which of the following?
oxidation of C6H12O6 and reduction of O2
When a glucose molecule loses a hydrogen atom as the result of an oxidation-reduction reaction, the glucose molecule becomes
oxidized
Which of the following about NAD+ is true?
NAD+ is reduced to NADH during glycolysis
Where does glycolysis occur in animal cells?
Cytosol
Which chemical process generates the ATP produced in glycolysis?
substrate-level phosphorylation
Which chemical process generates the ATP produced in the citric acid cycle?
substrate-level phosphorylation
The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event?
Accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain
Which of the following indicates a primary path by which electrons travel downhill energetically during aerobic respiration?
glucose → NADH → electron transport chain → oxygen
Which of the following sequences represents the correct order in which metabolic reactions occur during the complete oxidation of glucose through aerobic respiration?
glucose → glycolysis → pyruvate oxidation → citric acid cycle → electron transport chain
How many molecules of oxygen (O2) are consumed by the complete oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) to carbon dioxide and water in aerobic respiration?
6
Which of the following metabolic processes in eukaryotic cells will proceed manually whether oxygen (O2) is present or absent?
glycolysis
Which of the following correctly lists all of the energy-containing molecules produced by the catabolism of one molecule of glucose in glycolysis?
2 NADH, 2 Pyruvate, and 2 ATP
Carbon Dioxide (CO2) is released during which of the following states of cellular respiration?
Oxidation of pyruvate to Acetyl CoA and the citric acid cycle
Where are the proteins of the Electron transport chain located in a eukaryotic cell?
inner mitochondrial membrane
Which of the following molecules donates electrons directly to the electron transport chain at the LOWEST level?
FADH2
Which of the following molecules donates electrons directly to the electron transport chain at the HIGHEST level?
NADH
What is the primary role of oxygen in cellular respiration?
To serve as an acceptor for electrons and protons, forming water
Inside an active mitochondrion, most electrons follow which of the following pathways?
citric acid cycle → FADH2 → electron transport chain → ATP
In chemiosmosis, what is the most direct source of energy that is used to convert ADP + inorganic phosphate to ATP?
energy released from movement of protons down their electrochemical gradient through ATP synthase
Where in the mitochondria is the enzyme ATP synthase located?
inner membrane
Energy released by the electron transport chain is used to pump H+ into which location in eukaryotic cells?
mitochondrial intermembrane space
Which of the following metabolic processes produces the most ATP when glucose (C6H12O6) is completely oxidized to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water?
oxidative phosphorylation (chemiosmosis)
The complete oxidation of two molecules of glucose (C6H12O6) in cellular respiration produces how many molecules of ATP?
60-64
Which of the following metabolic pathways occur(s) in the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells?
Glycolysis and Fermentation
Which of the following metabolic pathways is common to both aerobic cellular respiration band anaerobic fermentation?
Glycolysis
Yeast cells grown anaerobically can obtain energy by fermentation, which results in the production of
ATP, CO2, and ethanol
Which statement best supports the hypothesis that glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway that originated before that last universal common ancestor of life on earth?
Glycolysis is widespread and is found in the domains Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya
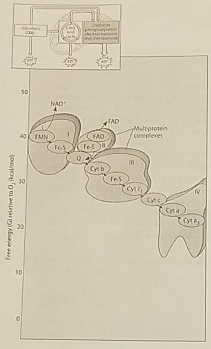
Figure 7.2 illustrates the electron transport chain. Which of the following is initially added to the chain with the highest free energy?
NADH
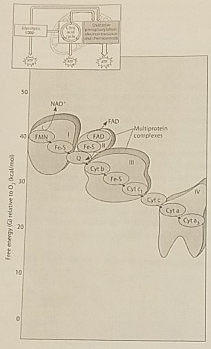
Which of the following is an accurate description of the events that occur along the electron transport chain depicted in Figure 7.2?
Each electron transfer between carriers results in oxidation of one carrier and reduction of another
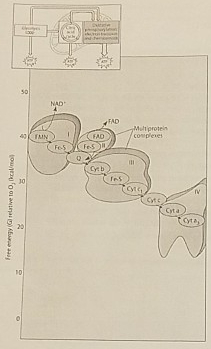
Which of the protein complexes labeled with Roman Numerals in Figure 7.2 transfers electrons to O2?
Complex IV
Which of the following molecules are products of the light reactions of photosynthesis that are utilized in the Calvin Cycle?
ATP and NADPH
Where does the Calvin Cycle take place?
Stroma of the Chloroplast
Which of the following reactions produces the oxygen released by photosynthesis
Splitting of water molecules
The leaves of a plant with a unique photosynthetic pigment appear orange in sunlight. What wavelengths of visible light are most likely to be absorbed by this unique pigment?
Blue and Violet
Which of the following events occurs in the light reactions of photosynthesis?
Light is absorbed and high energy electrons are transferred to reaction-center chlorophyll
Which of the following statements correctly describes an activity directly associated with photosystem I?
It receives electrons from the electron transport chain associated with thylakoid membranes
The pH of the inner thylakoid space has been measured, as have the pH of the stroma and of the cytosol of a particular plant cell. Which of the following relationship relationships would you expect to find when the cell is examined in the light?
The pH of the stroma is lower than that of either the thylakoid space or the cytosol
Which of the following reactions reduce(s) oxygen to form water?
Cellular respiration only
What are the products of linear electron flow?
ATP and NADPH
What is the primary function of cyclic electron flow?
to produce additional NADPH
Where are ATP synthase complexes located in a plant cell?
Thylakoid membranes and inner mitochondrial membranes
Which of the following statements about the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration is correct?
Cellular respiration is catabolic and photosynthesis is anabolic
Photophosphorylation in photosynthesis is most similar to which of the following processes associated with cellular respiration?
oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria
What is the primary function of the calvin cycle?
to produce simple sugars from carbon dioxide
What compound provides the reducing power for the Calvin Cycle reactions?
NADPH
Which of the following metabolic pathways produce(s) reduced soluble electron carriers?
both the light reactions of photosynthesis and the citric acid cycle
how would you predict that doubling the atmospheric CO2 concentration would affect the C3 plants?
They will experience increased rates of photosynthesis and growth
Where do enzymatic reactions of the calvin cycle take places?
Stroma of the chloroplast
An early step in the process of carbon fixation combines three molecules of CO2 with three molecules of RUBP to produce three 6-carbon molecules, which are immediately converted into six 3-carbon molecules. These six molecules are phosphorylated and reduced to produce glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate (G3P). What additional events occur to complete the Calvin cycle?
release of one G3P to make sugars and regeneration of RuBP
Which of the following metabolic processes consume(s) CO2?
the Calvin Cycle only
CAM plants keep stomata closed in daytime, thus reducing loss of water. They can do this because they
fix CO2 into organic acids during the night when temperatures are cooler
Theodor W. Engelmann illuminated a filament of algae with light that passed through a prism, thus exposing different segments of algae to different wavelengths of light. He added aerobic bacteria and then noted in which areas the bacteria congregated. He found that the largest groups were found in areas illuminated by the red and blue light. What did Engelmann conclude about the congregation of bacteria in the red and blue areas?
bacteria congregated in these areas because they were the areas where the most oxygen was released by the algae
Theodor W. Engelmann illuminated a filament of algae with light that passed through a prism, thus exposing different segments of algae to different wavelengths of light. He added aerobic bacteria and then noted in which areas the bacteria congregated. He found that the largest groups were found in areas illuminated by the red and blue light. This experiment helped to determine the relationship between which of the following parameters?
wavelengths of light and the rate of photosynthesis
Theodor W. Engelmann illuminated a filament of algae with light that passed through a prism, thus exposing different segments of algae to different wavelengths of light. He added aerobic bacteria and then noted in which areas the bacteria congregated. He found that the largest groups were found in areas illuminated by the red and blue light. What would you predict would happen if you ran the same experiment without passing light through a prism?
The bacteria would be relatively evenly distributed along the algal filament
A spaceship designed to support human life for a multiyear voyage to the outer planets of the solar system will include plants to provide oxygen and consume carbon dioxide. Because the spaceship will have limited exposure to the Sun for extensive periods, an artificial light source will be needed to support photosynthesis. What wavelengths of light should be used to maximize plant growth with a minimum expenditure of energy?
a combination of blue and red light
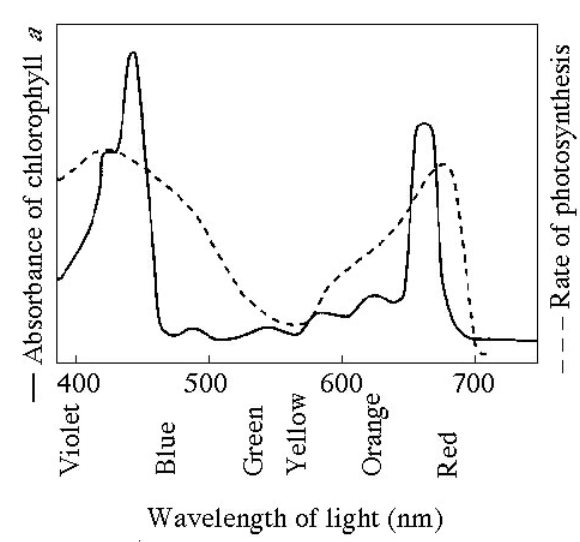
Figure 8.1 shows the absorption spectrum for chlorophyll an and the action spectrum for photsynthesis. Why are they different?
Other pigments absorb light in addition to chlorophyll a
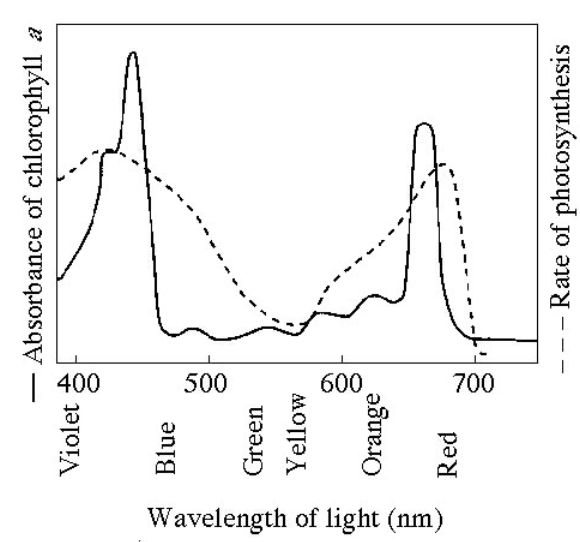
Figure 8.1 shows the absorption spectrum for chlorophyll a and the action spectrum for photosynthesis. What wavelength of light is most effective in driving photosynthesis?
420nm
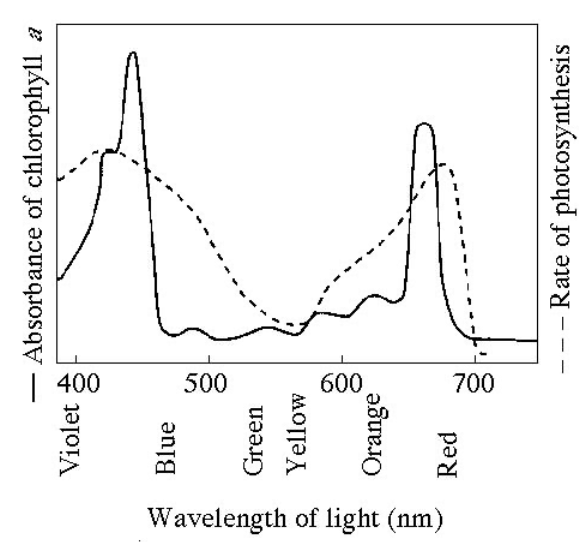
Figure 8.1 shows the absorption spectrum for chlorophyll a and the action spectrum for photosynthesis. What colors of light are least effective in driving photosynthesis?
Green-Yellow
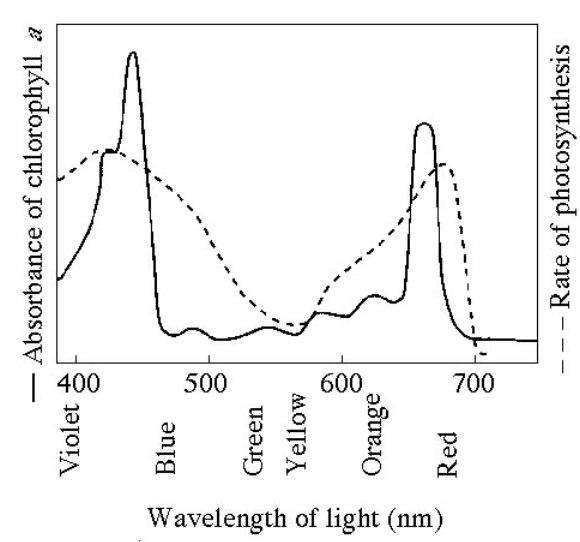
figure 8.1 shows the absorption spectrum for chlorophyll a and the action spectrum for photosynthesis. Halobacterium has a photosynthetic membrane that appears purple. It’s photosynthetic action spectrum is the inverse of the action spectrum for green plants. What wavelengths of light do the halobacterium photosynthetic pigments absorb?
Green and Yellow