Art History Exam 2
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Model of Etruscan Temple, 6th century BCE, original temple found in Veii, Italy, created by Vulca

Veii Apollo, roof of the Portonaccio Temple, Veii, painted terracotta, c.510-500 BCE, created by Vulca

Sarcophagus with Reclining Couple, from Cerveteri, Italy, painted terracotta, c.520 BCE

Capitoline Wolf, from Rome, Italy, c.500- 540 BCE, artist unknown

Chimera, from Arezzo, Italy, first half of the 4th century BCE, artist unknown

Aule Metele (Arringdore), from Cortona, early first century BCE, unknow, Roman Republic era

Statue of Augustus, Prima Porta, Italy, early first century CE copy of a bronze original of c.20 BCE, Early Empire, artist unknown

Ara Pacis (Altar of Augustan Peace), Rome, 13-9 BCE, Early Empire

Equestrian Monument to Marcus Aurelius, 175CE, bronze

Monumental Head of Constantine (fragment), Rome, marble, 315-330 CE, Late Empire

South Frieze with Procession of the Imperial Family of Ara Pacis (Altar of Augustan Peace), Rome, 13-9 BCE, Early Empire

Apollodorus of Damascus: Trajan's Forum, Rome, dedicated 112 CE, High Empire

Basilica of Constantine (Basilica Nova), Rome, c.306-312 CE, Late Empire

Colosseum, Rome, 70-80 CE, Early Empire

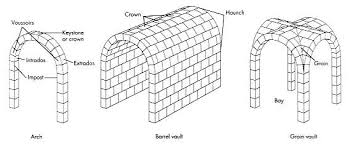
arch, barrel, and groin vaults
Arch of Titus, Rome, after 81CE, Early Empire

Arch of Constantine, Rome, 312-315 BCE, Late Empire


Pantheon, Rome, 118-125 CE, High Empire

Insula, Ostia, Italy, 2nd century CE, Early to High Empire

Pompeii
Pompeii was an ancient Roman city located near Naples in the Campania region of Italy. Pompeii, along with Herculaneum and many villas in the surrounding area was buried under 4 to 6m (13 to 20 ft) of volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 CE


Casa de Vettii (House of Vettii), Pompeii, Italy, Early Roman Empire, 62-79 BCE

House of the Mysteries, Pompeii, c.65 BCE, fourth style

Dionysiac (Bacchic) Frieze [2nd Style], Villa of the Mysteries, Pompeii, 65-50 BCE

Cubiculum M [2nd Style], Villa of Publius Fannius Synistor, located in Boscoreale, 50-40 BCE

Cubiculum15 [3rd Style], Villa of Agrippa Postumus, located in Boscotrecase, Pompeii, c.10 BCE image
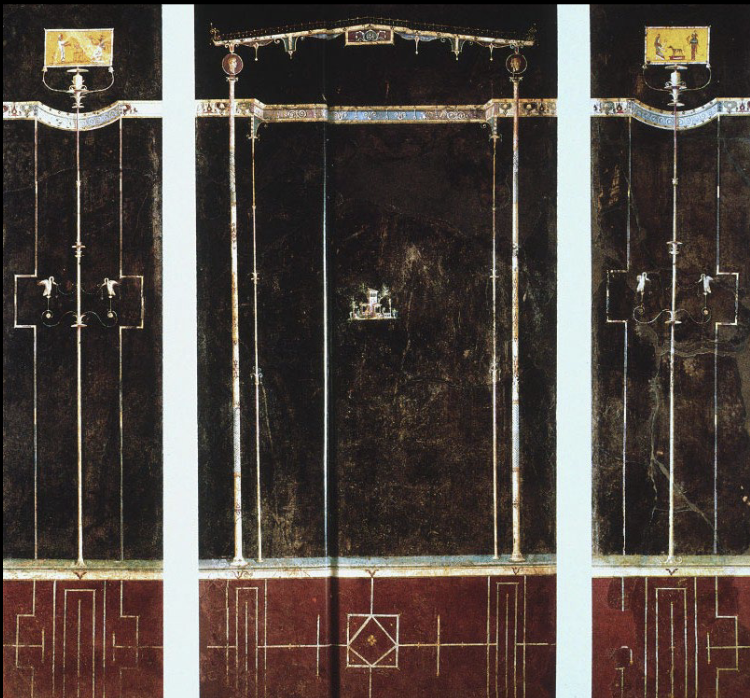

Ixion Room Fresco [4th Style], House
of the Vettii, Pompeii, 70-79 CE

Man with Portrait Busts of his Ancestors, late 1st century BCE, Republic Style, Rome

Head of a Old Man, located from Osimo, Italy, mid-first century BCE, Republic Style

Portrait bust of a Flavian Woman, from Rome, c.90 CE, Early Empire

Good Shepherd, first half of the 4th century, early Christian style, Vatican Museum, Rome

Greek Archaic Calf-Bearer, c.560BCE, Athens, early Christian style

Christ as the Good Shepherd, mosaic from the entrance wall of the Mausoleum of Galla Placidia, Ravenna, c.425, early Christian style

Basilica (and Martyrium) of Old St. Peter's, Rome, begun c.320 (reconstruction drawing), early Christian style


Mausoleum of Santa Costanza, Rome, c.337-51, early Christian style


Church of San Vitale, Ravenna, Italy, 526-547, Byzantine

Justinian Mosaic, mosaic from Church of San Vitale, Ravenna, c.547 CE Byzantine

Theodora and Attendants (mosaic, south wall), mosaic from Church of San Vitale, Ravenna, c.547 CE Byzantine


Hagia Sophia, Constantinople, 532-537 ce, architects:
Anthemius of Tralles & Isidorus of Miletus, Byzantine

Tufa
dark local limestone, cut into to create Etruscan tombs
Cupid
The Greek god Eros was the son of Aphrodite/Venus, representing a potent natural force of desire
Pax romana
Latin, “Roman Peace”
forum
the public square of an ancient Roman city
roman basilica
instead of temples serve as models for the first churches in Rome, including Old Saint Peter’s, which stood, like many other Early Christian
clerestory windows
primarily associated with the early Christian basilica, where they were used to let light into the nave and create a sense of divine presence. Early Christian churches were often modeled after Roman basilicas, which already featured a high nave and upper-level windows

arch
a curved structural member that spans an opening and is generally composed of wedge-shaped blocks (voussoirs) that transmit the downward pressure laterally.
barrel vault
Also called the tunnel vault, is an extension of a simple arch, creating a semicylindrical ceiling over parallel walls.

vault
A masonry roof or ceiling constructed on the arch principle, or a concrete roof of the same shape. A barrel (or tunnel) vault, semicylindrical in cross-section, is in effect a deep arch or an uninterrupted series of arches, one behind the other, over an oblong space. A quadrant vault is a half-barrel vault. A groin (or cross) vault is formed at the point at which two barrel vaults intersect at right angles. In a ribbed vault, there is a framework of ribs or arches under the intersections of the vaulting sections. A sexpartite vault is one whose ribs divide the vault into six compartments. A fan vault is a vault characteristic of English Perpendicular Gothic architecture, in which radiating ribs form a fanlike pattern.
groin vault
also known as cross vault, formed by the intersection at right angles of two barrel vaults of equal size

roman concrete
concrete construction revolutionized architectural design. Roman builders mixed concrete according to a changing recipe of lime mortar, volcanic sand, water, and small stones (caementa, from which the English word “cement” derives). After mixing the concrete, the builders poured it into wood frames and left it to dry. When the concrete hardened completely, they removed the wood molds, revealing a solid mass of great strength, though rough in appearance.
spolia
Latin, “spoils.” older statues and reliefs used in Late Antique monuments
rotunda
a circular building or room with a domed ceiling, a design popularized by ancient Greek tholi and famously emulated by the Roman Pantheon
dome
a hemispherical vault; theoretically, an arch rotated on its vertical axis. In Mycenaean architecture, domes are beehive-shaped
oculus
Latin “eye.” the round central opening of the dome
coffer
a sunken panel, often ornamental, in a vault or a ceiling
engaged (=half) column
a half-round column attached to a wall
insula
in roman architecture, a multistory apartment house, usually made of brick - faced concrete, also refers to an entire city block
mosaic
patterns or pictures made by embedding small pieces of stone or glass in cement on surfaces such as walls and floors, also the technique of making such works
atrium
the central reception room of a Roman domus that is partly open to the sky. Also, the open, colonnaded court in front of and attached to a Christian basilica.
cubiculum
a small cubicle or bedroom that opened onto the atrium of a Roman domus. also a chamber in an Early Christian catacomb that served as a mortuary chapel.
“picture window”
a style of Roman wall painting that flourished from approximately 80 B.C.E. to the end of the first century B.C.E. It is known as the "architectural style" because it used illusionistic paintings of architectural elements like columns, arches, and windows to make walls appear to open into imaginary landscapes and scenes. This style was the first to create a sense of depth and open up the space of a room by breaking from the flat, decorative surfaces of the previous style
illusionism
the representation of the threedimensional world on a two-dimensional surface in a manner that creates the illusion that the person, object, or place represented is three-dimensional.
trompe-l’oeil
meaning "to fool the eye," The technique became prominent in murals and ceiling paintings, creating illusions of depth, architecture, and open skies, often using perspective and foreshortening. Today, it continues in various forms, from architectural murals to modern sidewalk art. Frescoes in Pompeii show early examples of trompe l'oeil murals that made flat walls appear to open into other rooms or have false architectural elements
linear (=scientific) perspective
all the receding lines in a composition converge on a single vanishing point along the painting’s central axis to show depth and distance.
atmospheric perspective
the illusion of depth is achieved by the increasingly blurred appearance of objects in the distance
encaustic paint
a method using melted beeswax mixed with pigments, applied with heat to fuse layers together. Originating from the Greek word for "to heat," it was popular in ancient Roman and Egyptian art
Christian Basilica
a rectangular building adapted from the Roman civic basilica for use as a church, characterized by a high central nave, flanking side aisles, and an apse at one end
nave
the central area of an ancient Roman basilica of a church, demarcated from aisles by piers or columns
apse
a recess, usually semicircular, in the wall of a building, commonly found at the east end of a church.
aisle
the portion of a basilica flanking the nave and separated from it by a row of columns or piers.
transept
the part of a church with an axis that crosses the nave at a right angle
narthex
a porch or vestibule of a church, generally colonnaded or arcaded and preceding the nave
central-plan building
one with a layout organized around a central point, creating a symmetrical, often circular, octagonal, or square design. This type of plan was frequently used for tombs and later, for Christian churches, because the unified central space could be topped with a dome or large vault to symbolize grandeur and unity. Notable Roman examples include the Pantheon
mausoleum
a monumental tomb.
mosaic
patterns or pictures made by embedding small pieces of stone or glass in cement on surfaces such as walls and floors; also, the technique of making such works
tesserae
Greek, “cube.” a tiny stone or piece of glass cut to the desired shape and size for use in forming a mosaic
pendentive
a concave, triangular section of a hemisphere, four of which provide the transition from a square area to the circular base of a covering dome. Although pendentives appear to be hanging (pendant) from the dome, they in fact support it.
squinch
An architectural device used as a transition from a square to a polygonal or circular base for a dome. It may be composed of lintels, corbels, or arches.
arcade
a series of arches supported by piers or columns.
choir
The space reserved for the clergy and singers in the church, usually east of the transept but, in some instances, extending into the nave.