Chapter 1 & 2: Introduction to the Science Life, Chemistry of Life
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
What are the 7 characteristics of life?
1. order 2. cells 3. growth & development 4. energy utilization 5. Response to the Environment (Stimulus)
6. Reproduction 7. Evolution

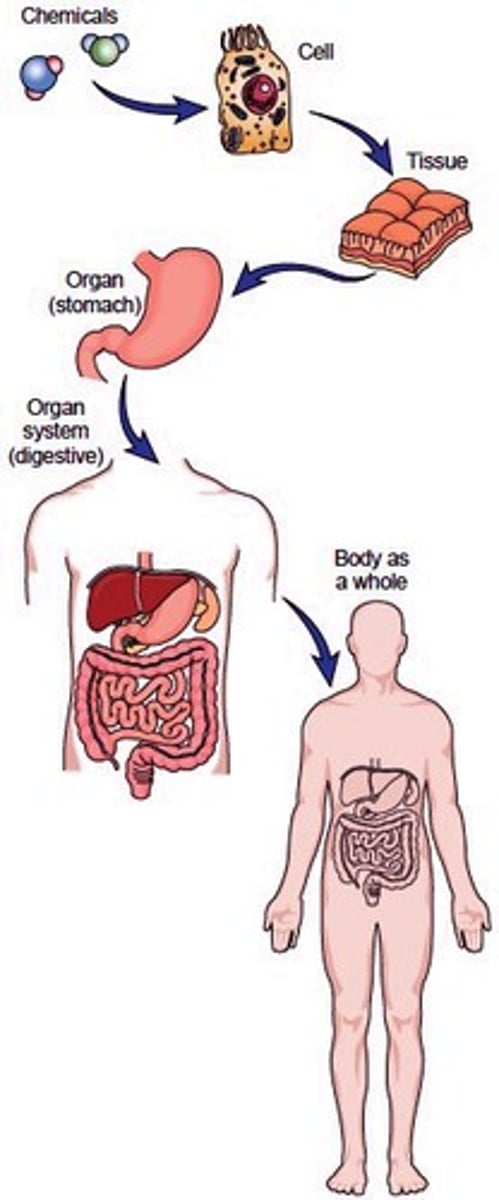
Levels of organization
cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
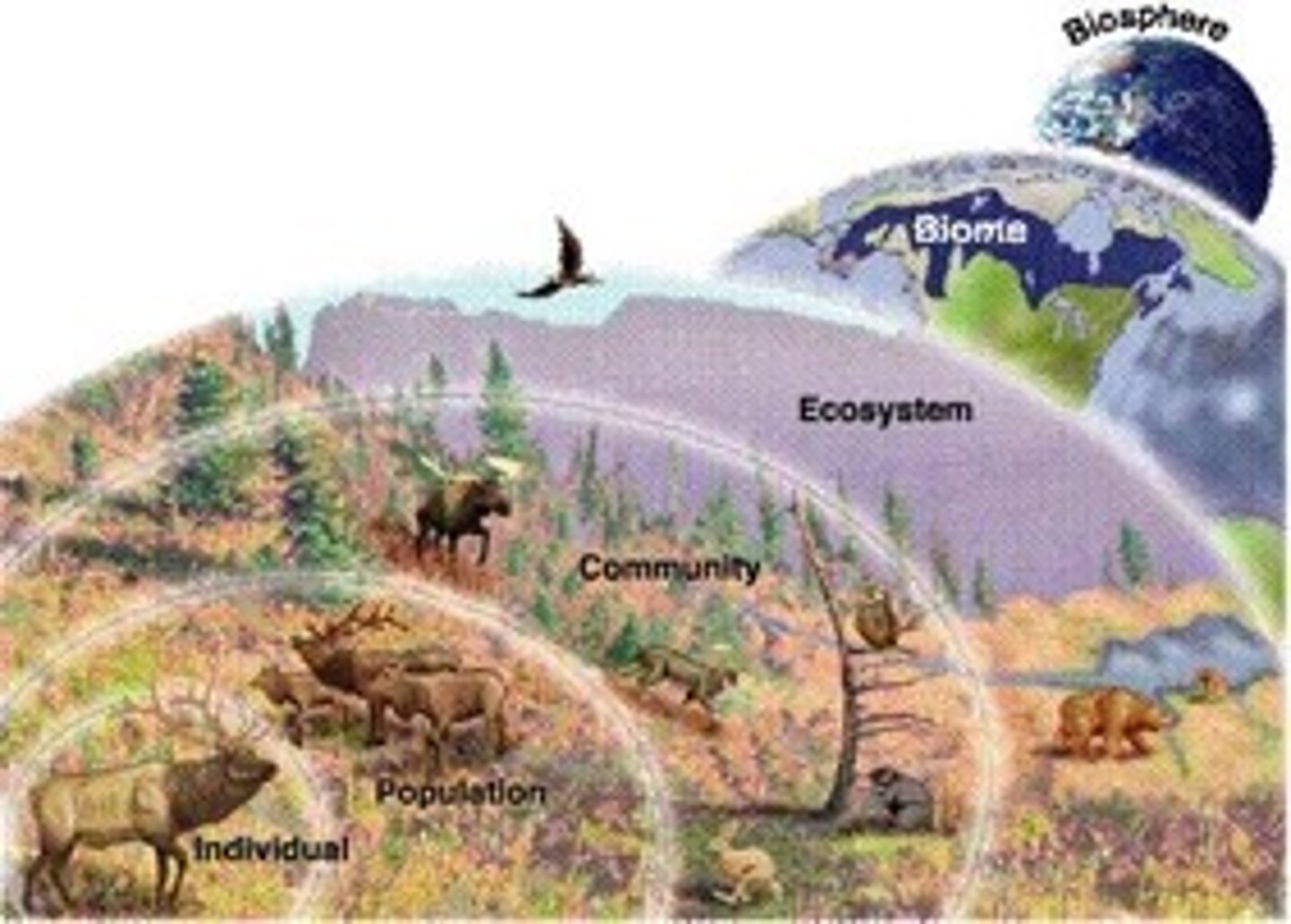
ecological organization
organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere
What is the scientific method?
is a "recipe for discovery" used across all sciences.
Four components of the scientific method
1. Observation
2. Hypothesis
3. Experimentation
4. Analysis/Conclusion

What is a hypothesis?
A hypothesis is an "if-then" statement that must be specific and testable.

What is a theory?
a well-substantiated, comprehensive explanation, and is much broader in scope than a hypothesis.
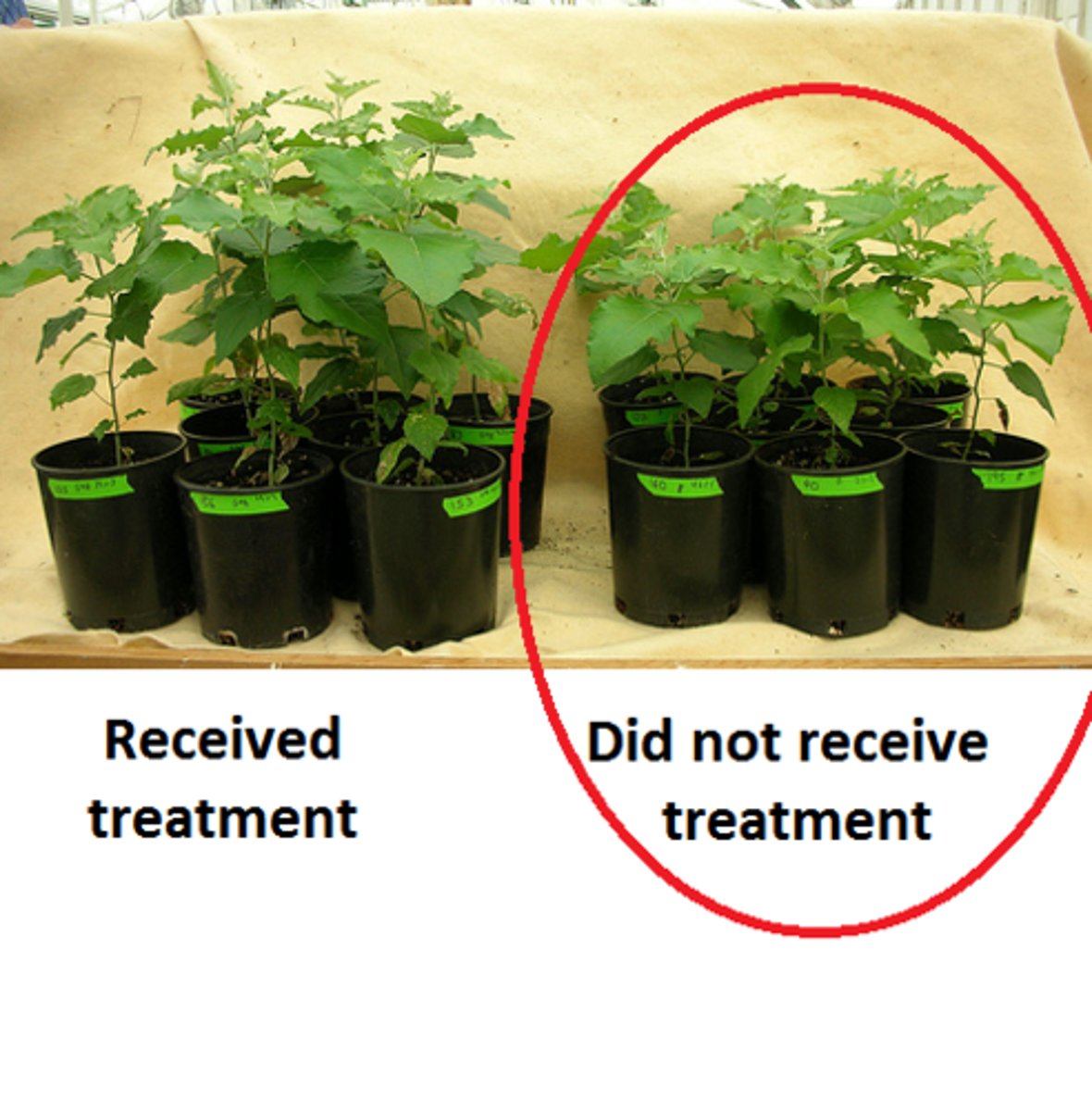
A controlled experiment is one that
consists of two parallel tests comparing the experimental sample against a control sample.
experimental group vs. control group
EXPERIMENTAL GROUP is the group receiving the independent variable
CONTROL GROUP does not receive anything, in order to act as a comparison

independent variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied.

dependent variable
The outcome factor; the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable.

Controlled variables
remain constant across experiments

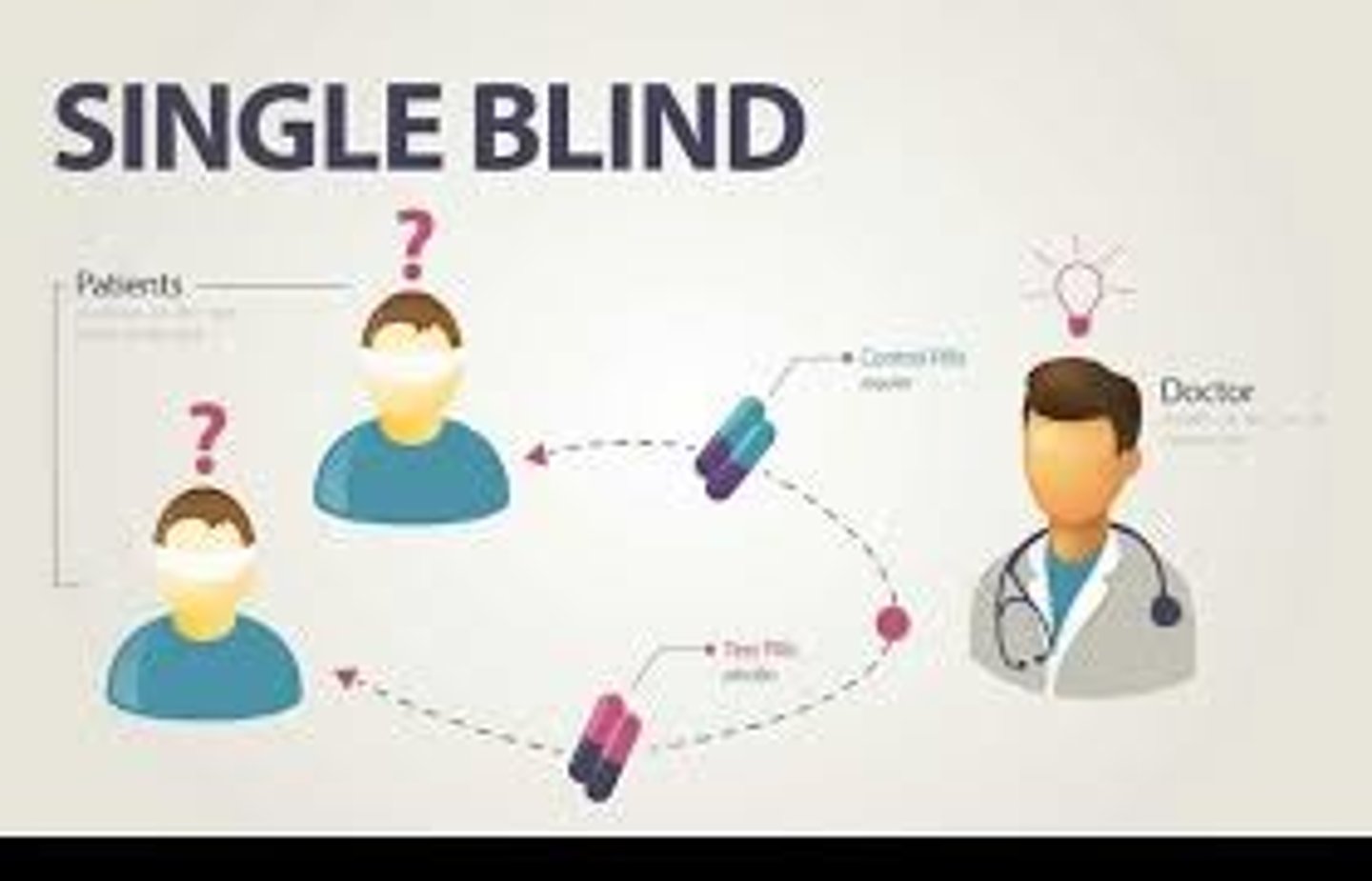
single-blind study
study in which the subjects do not know if they are in the experimental or the control group
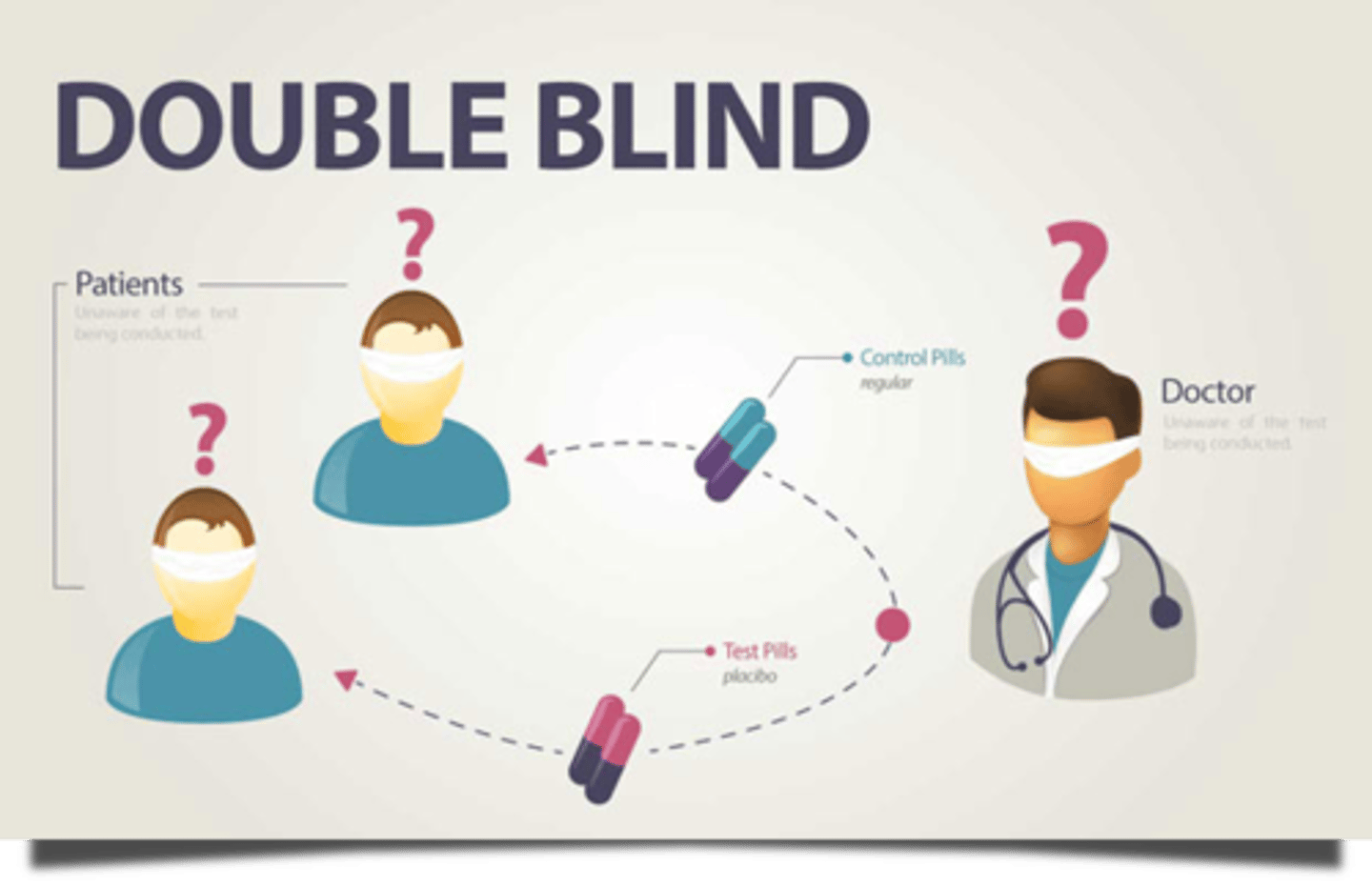
double-blind study
study in which neither the experimenter nor the subjects know if the subjects are in the experimental or control group
placebo effect
substance or treatment with no therapeutic effect

Pseudoscience
is falsely represented as having a scientific basis
Ex: Astrology, Fortune Telling, Etc.

peer review
A process that maintains scientific integrity must be reviewed by other scientists

Matter
anything that has mass and takes up space
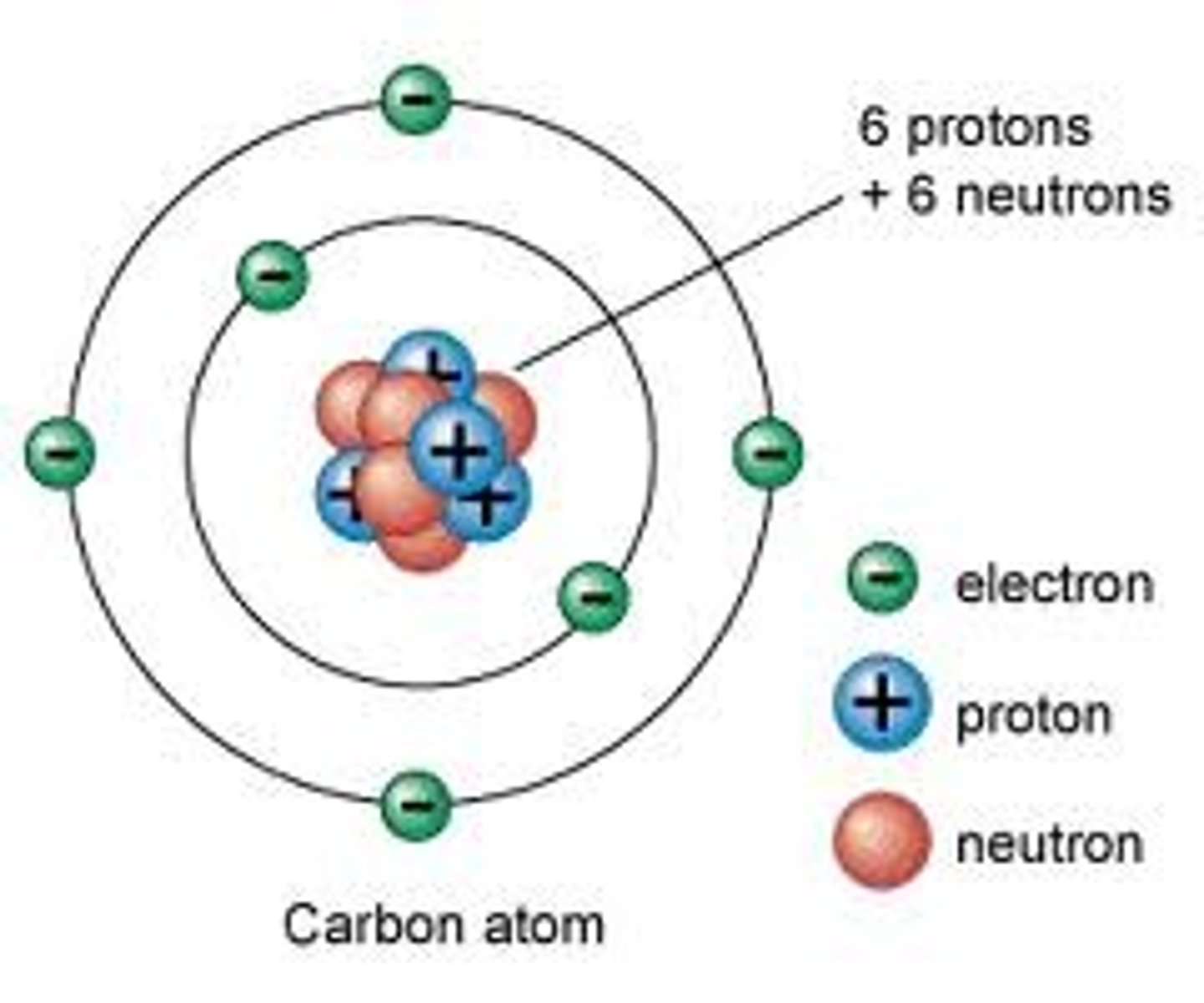
Atom
the smallest unit of matter
Molecules
two or more atoms joined together
What are the 6 essential elements of life?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur (CHONPS)
3 major subatomic particles
protons, neutrons, electrons

Protons
Positively charged particles
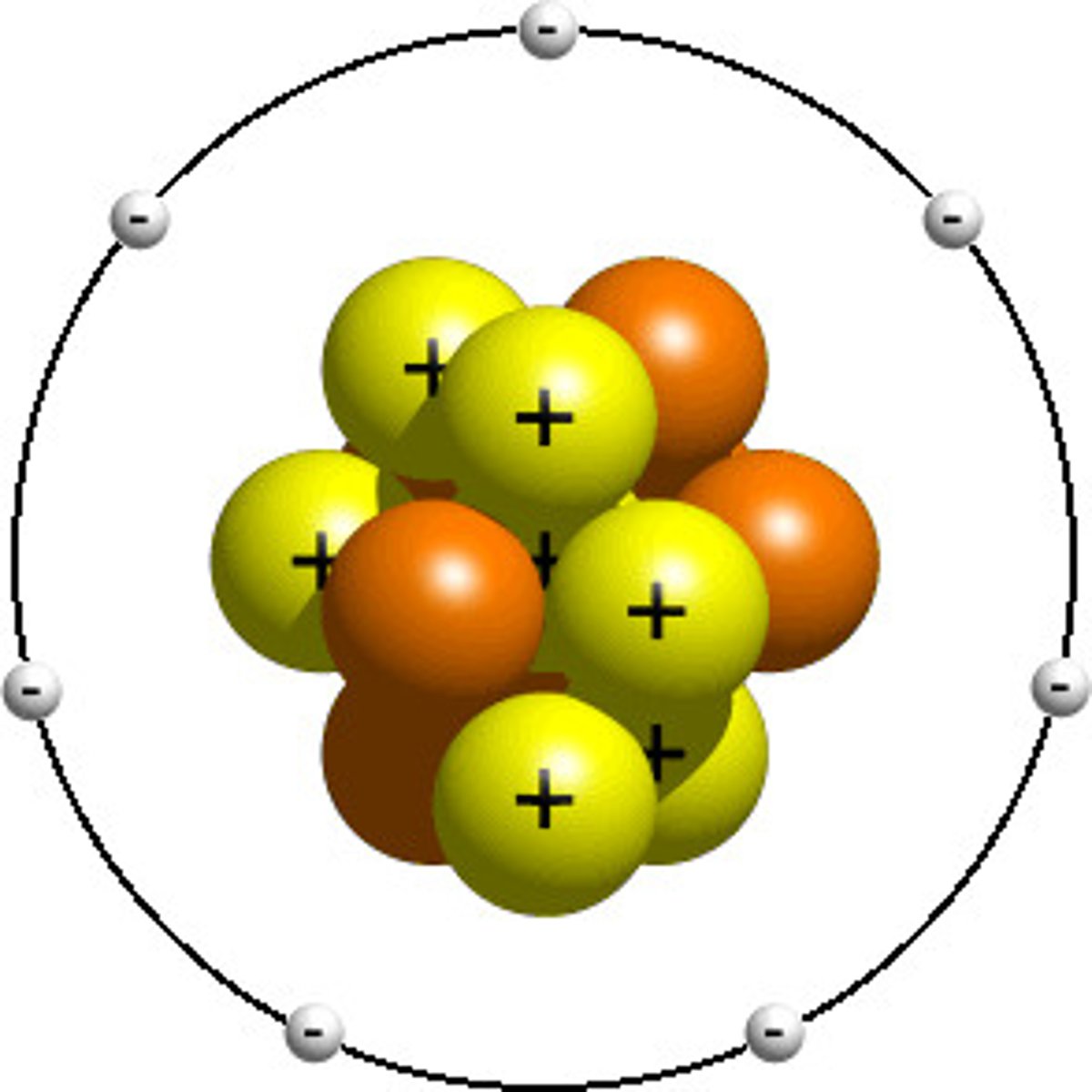
Neutrons
no charge
Electrons
Negatively charged particles
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
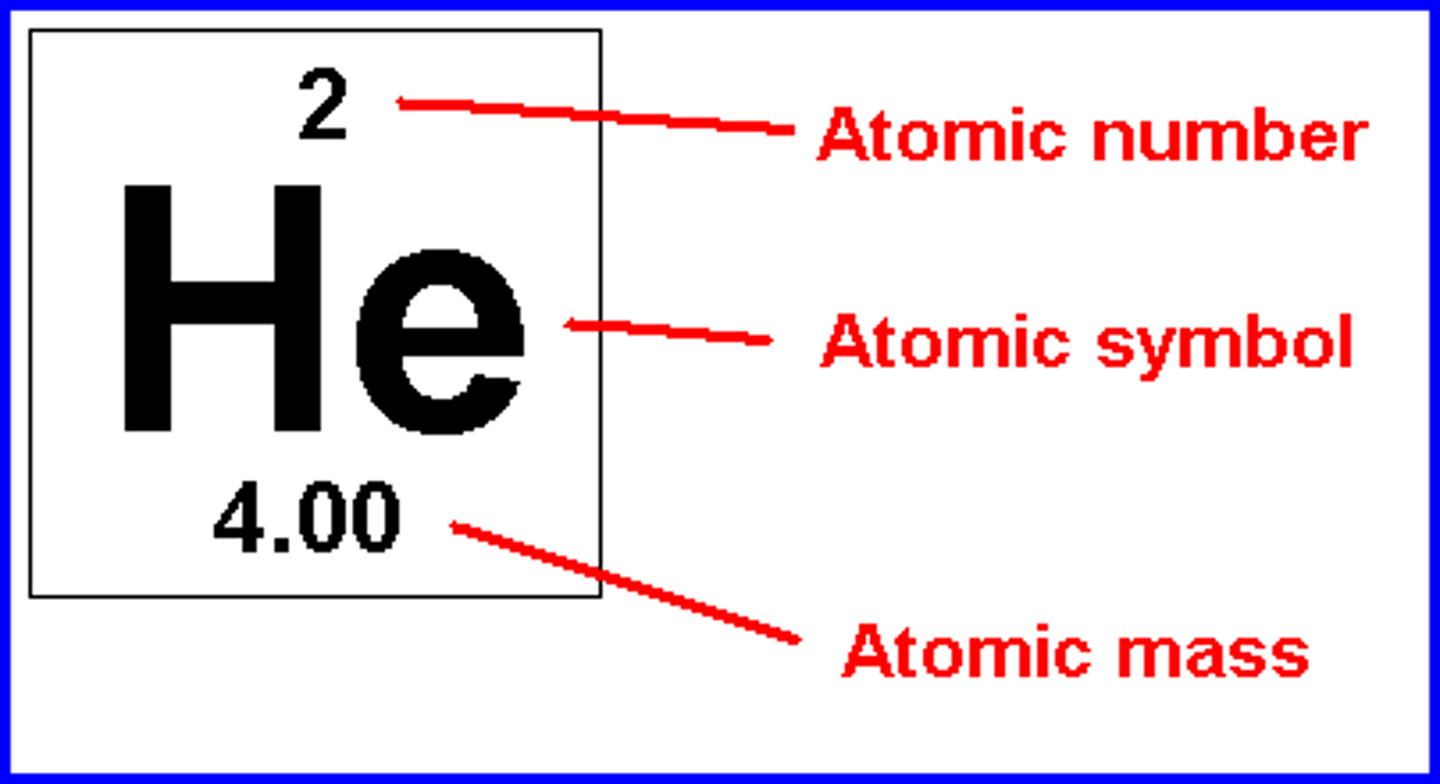
atomic mass
Number of protons and neutrons
K shell orbital
Holds 2 electrons
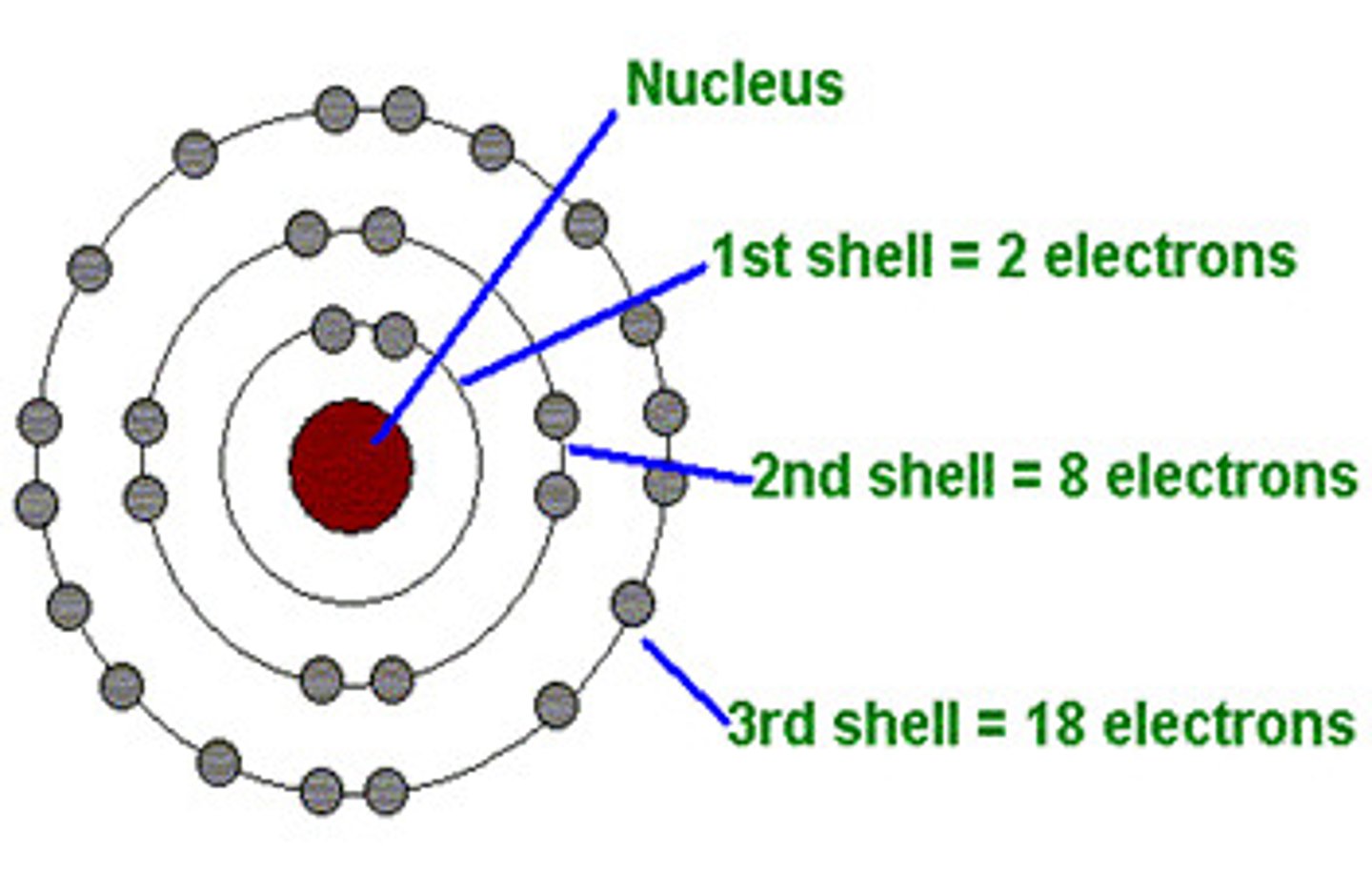
The ( L&M) shells hold...
8 electrons
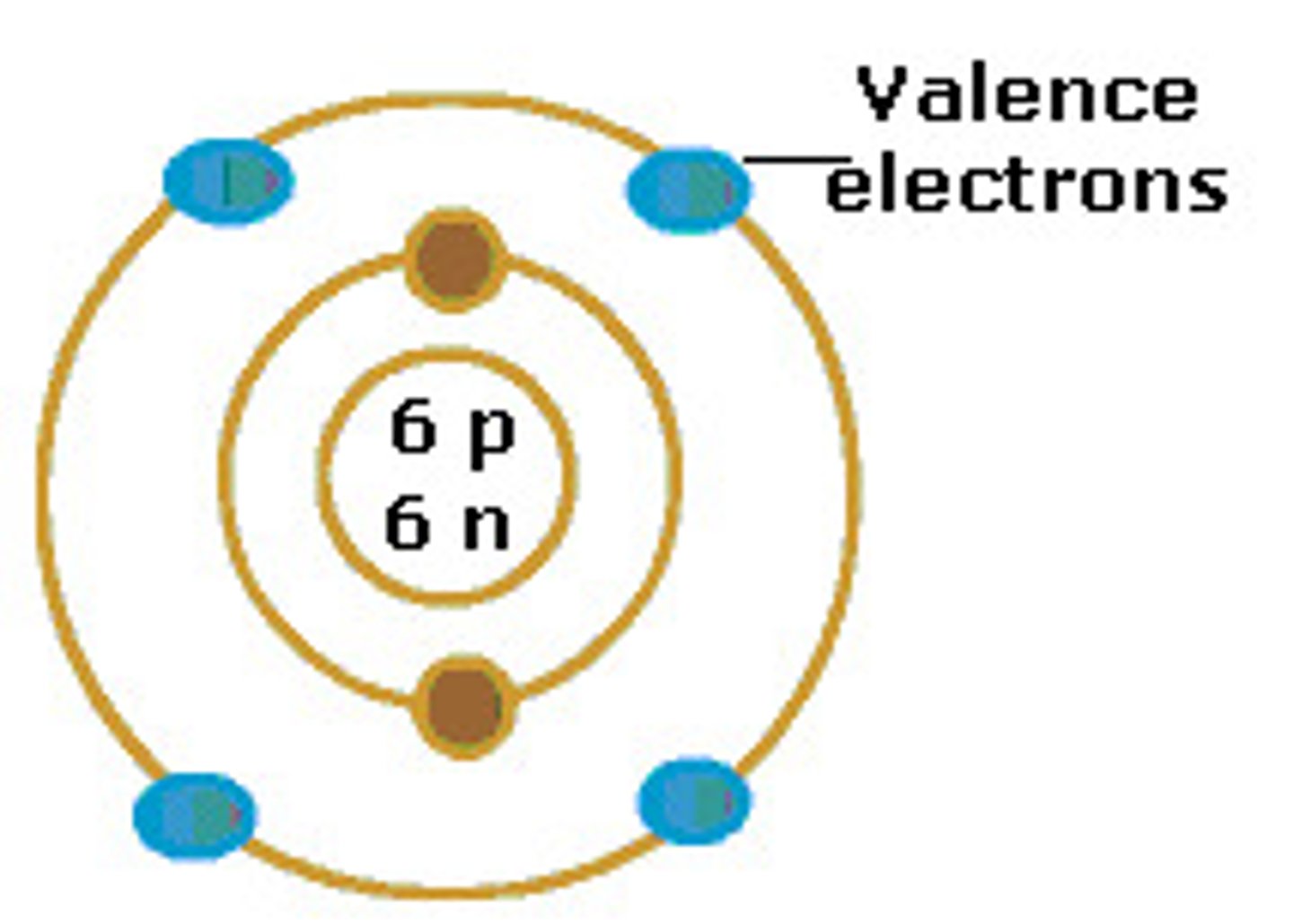
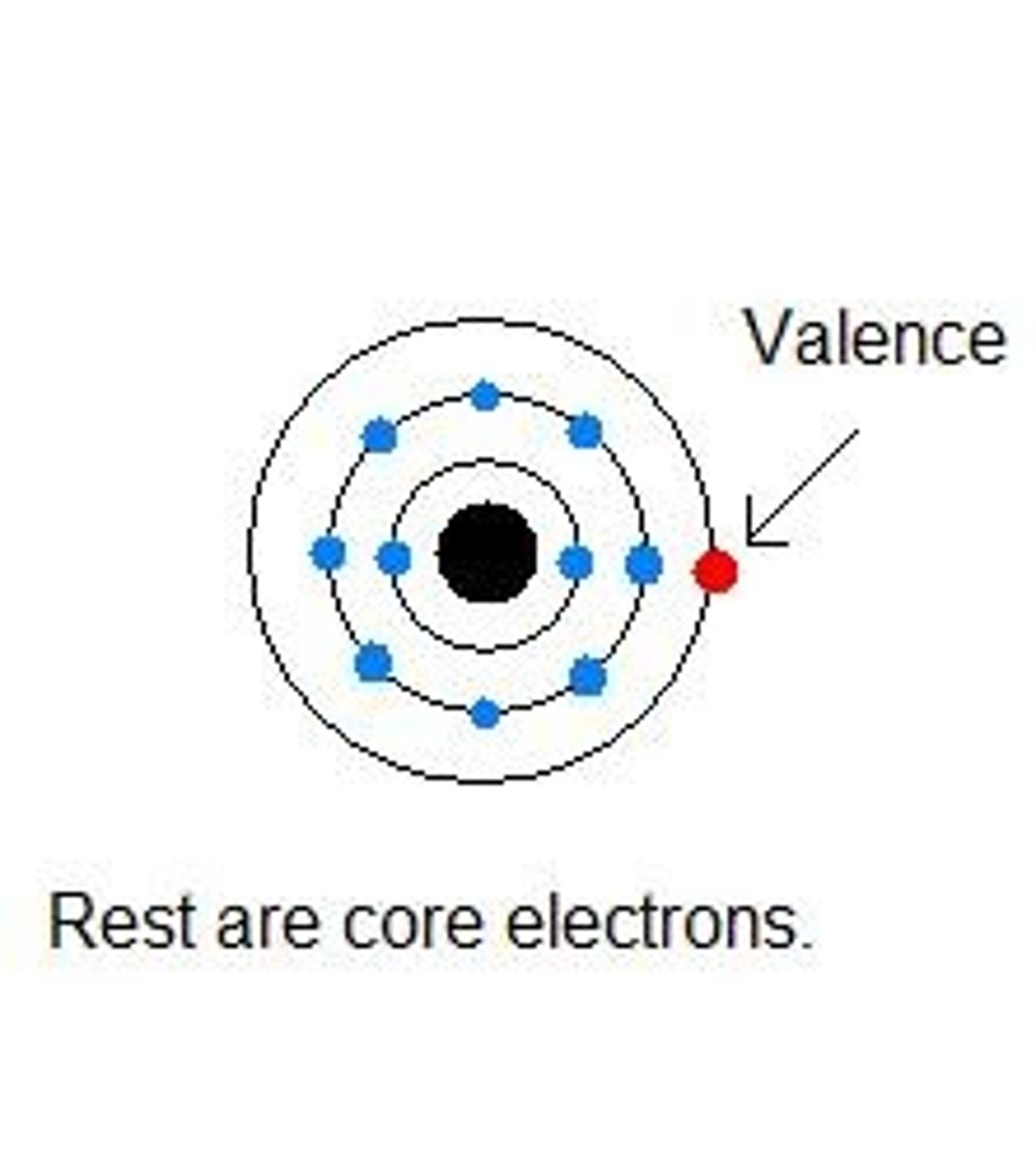
valence electrons
Electrons on the outermost energy level of an atom
When are atoms the most stable?
when all of the electron orbitals in the valence shell are filled
What are the 4 major types of chemical bonds?
- Ionic
- Polar Covalent
- Non-Polar Covalent
- Hydrogen
Ionic Bonds
Electrons are transferred from one atom to another.
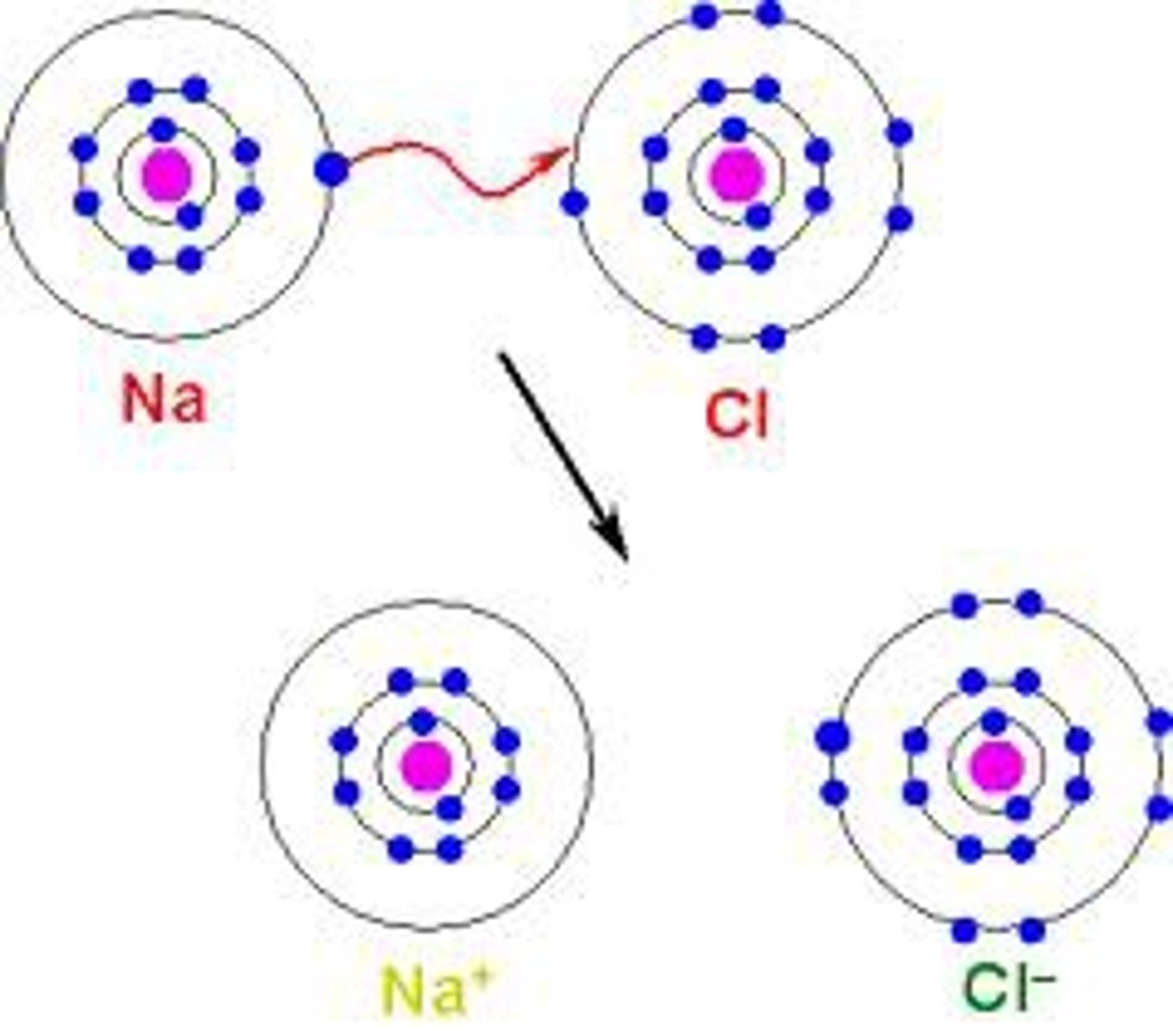
Ions
are charged atoms that have gained or lost electrons
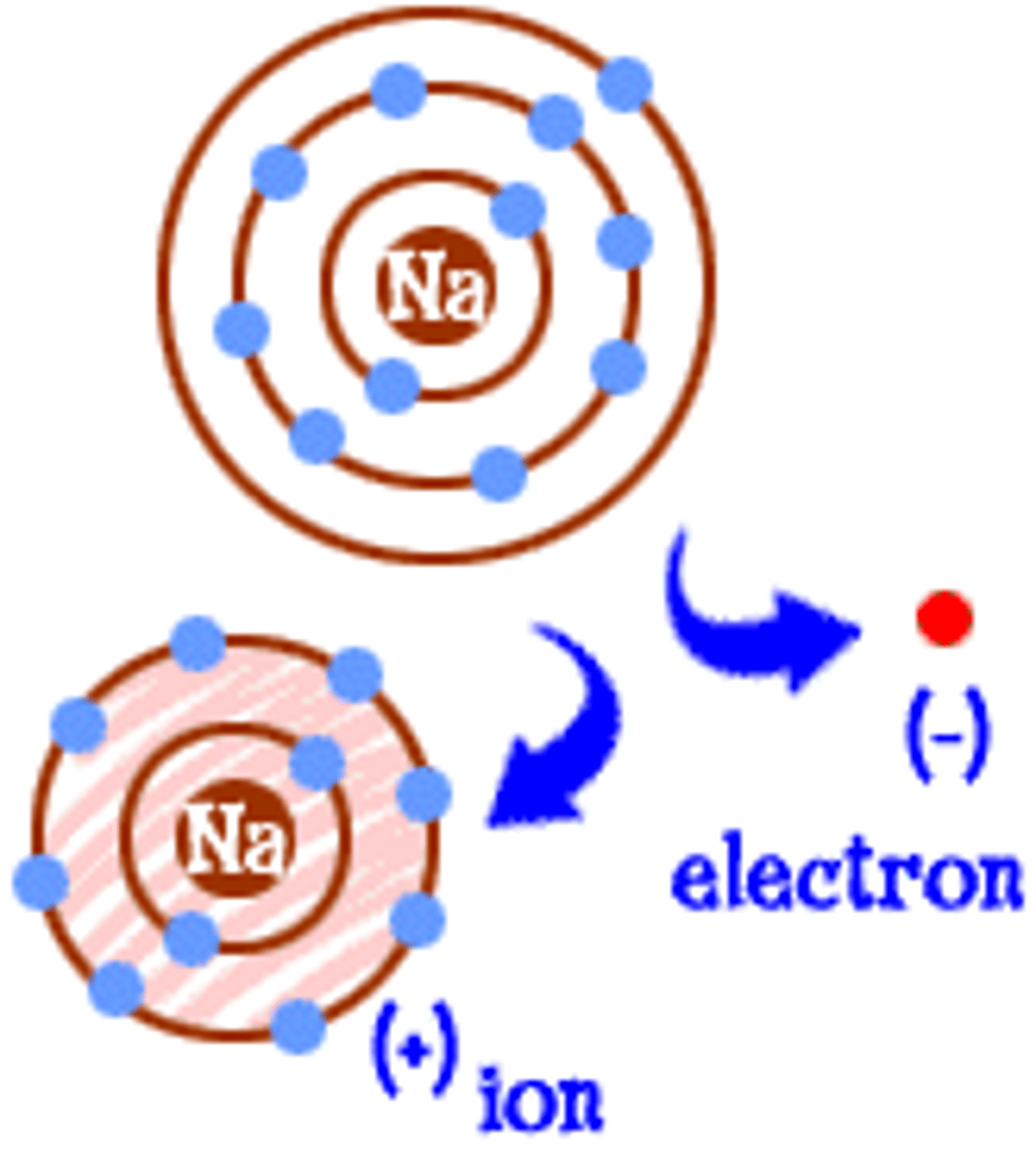
Cations
positively charged ions, when you lose electrons

Anions
negatively charged ions, gaining of electrons
Covalent bonds
Bonds created by sharing electrons with other atoms. Strongest bonds
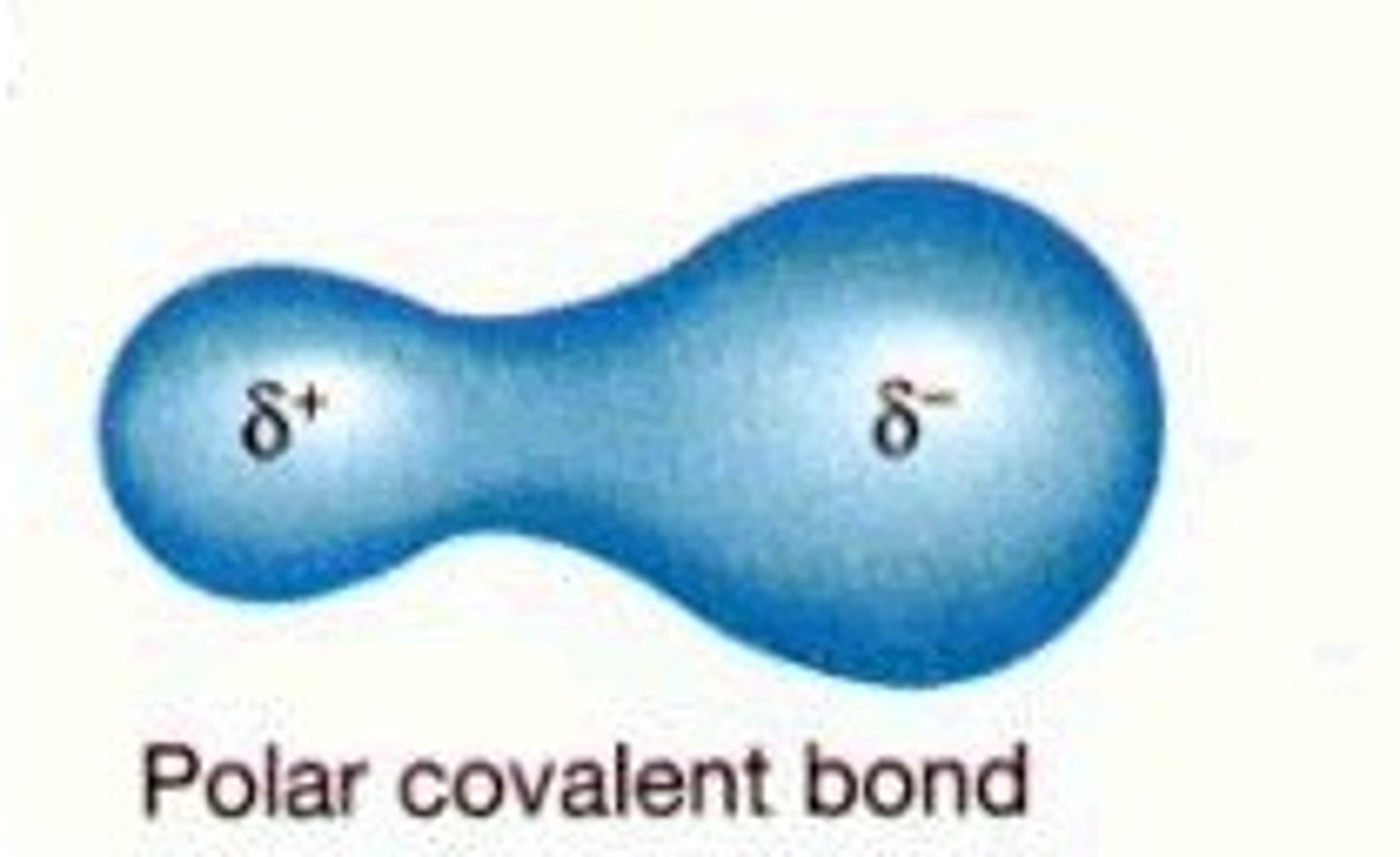
Polar covalent bonds
Bonds in which electrons are not shared equally between atoms of different elements in a compound
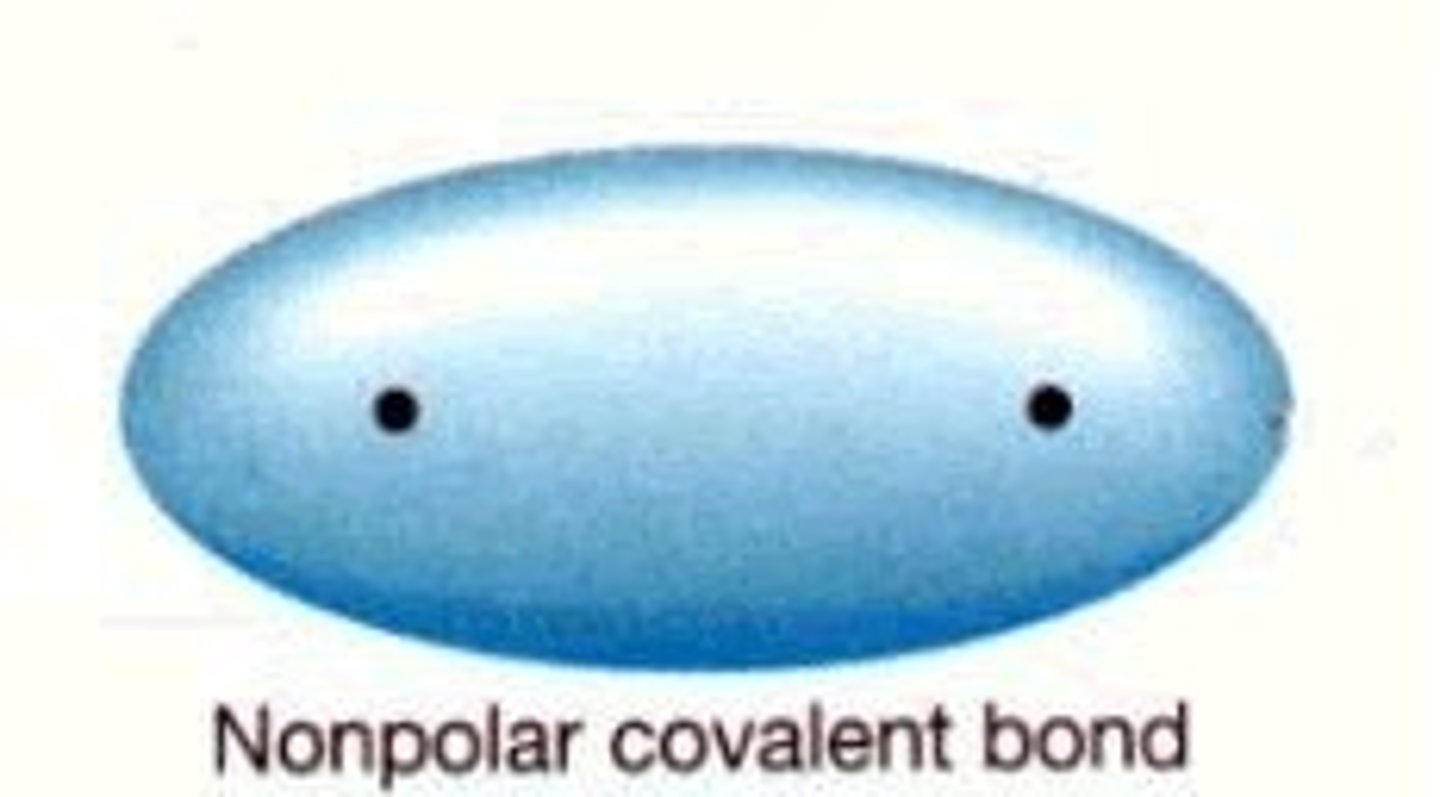
nonpolar covalent bond
a covalent bond in which the electrons are shared equally by the two atoms
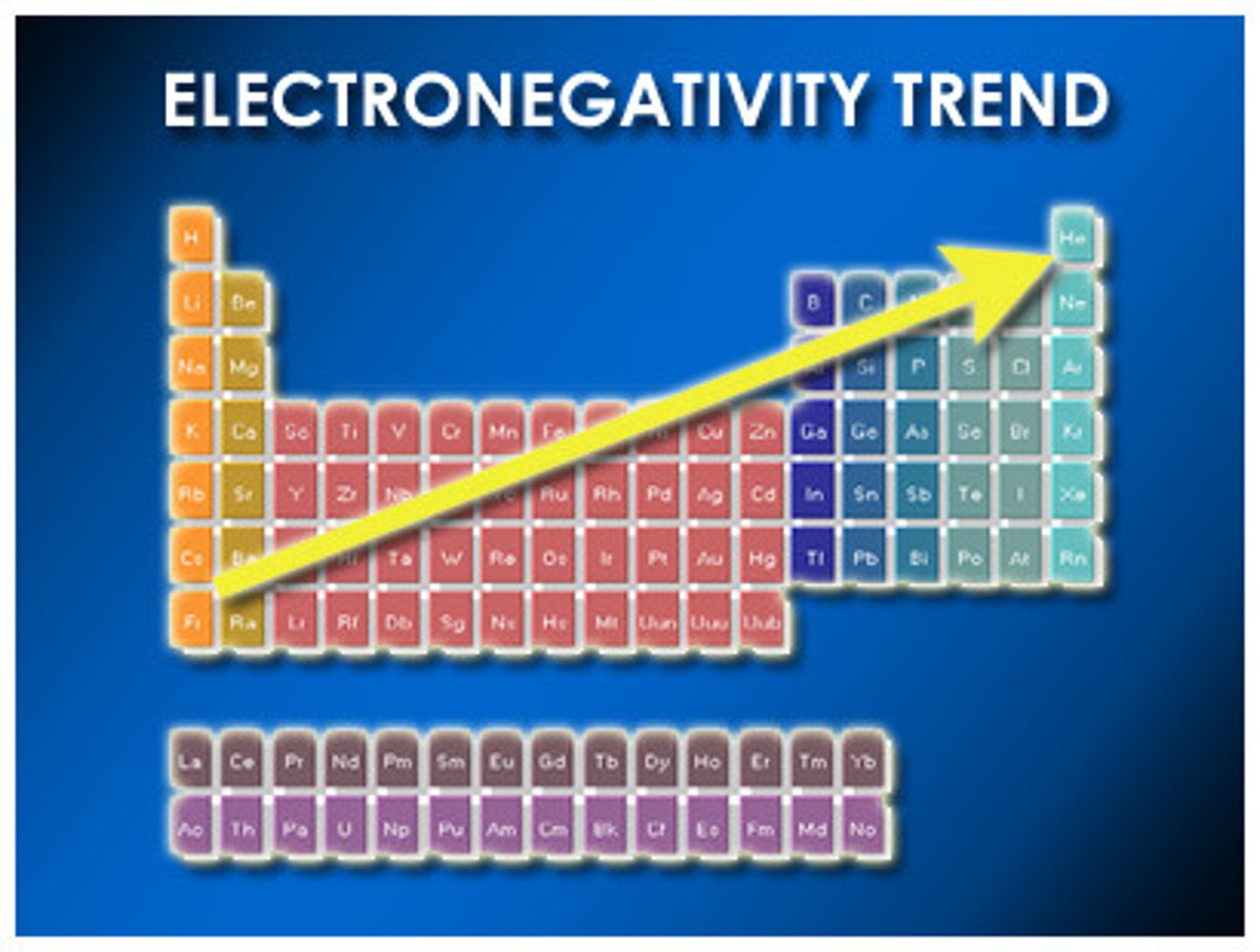
Polarity is determined by
difference in electronegativity
What are important polar molecules?
water

Non-polar molecules are _______ in water
insoluble
Polar molecules are _______ in water
soluble
Hydrogen bonding
form between a hydrogen atom and an atom that is negatively charges. WEAKEST BOND!
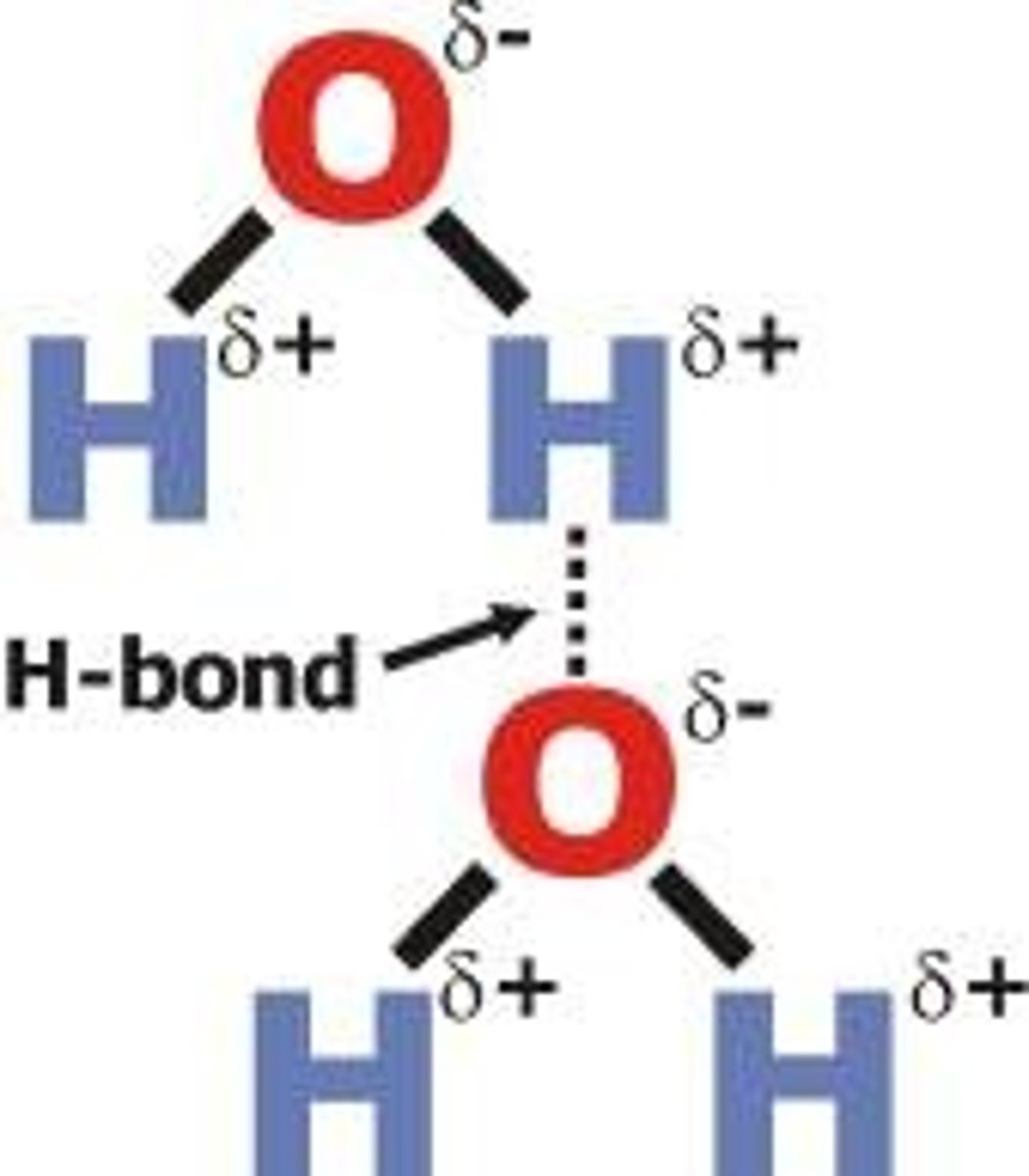
7 special properties of water
- High specific heat
- High surface tension
- High Boiling Point
- Cohesion
- Adhesion
- Higher density as a liquid than a solid
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
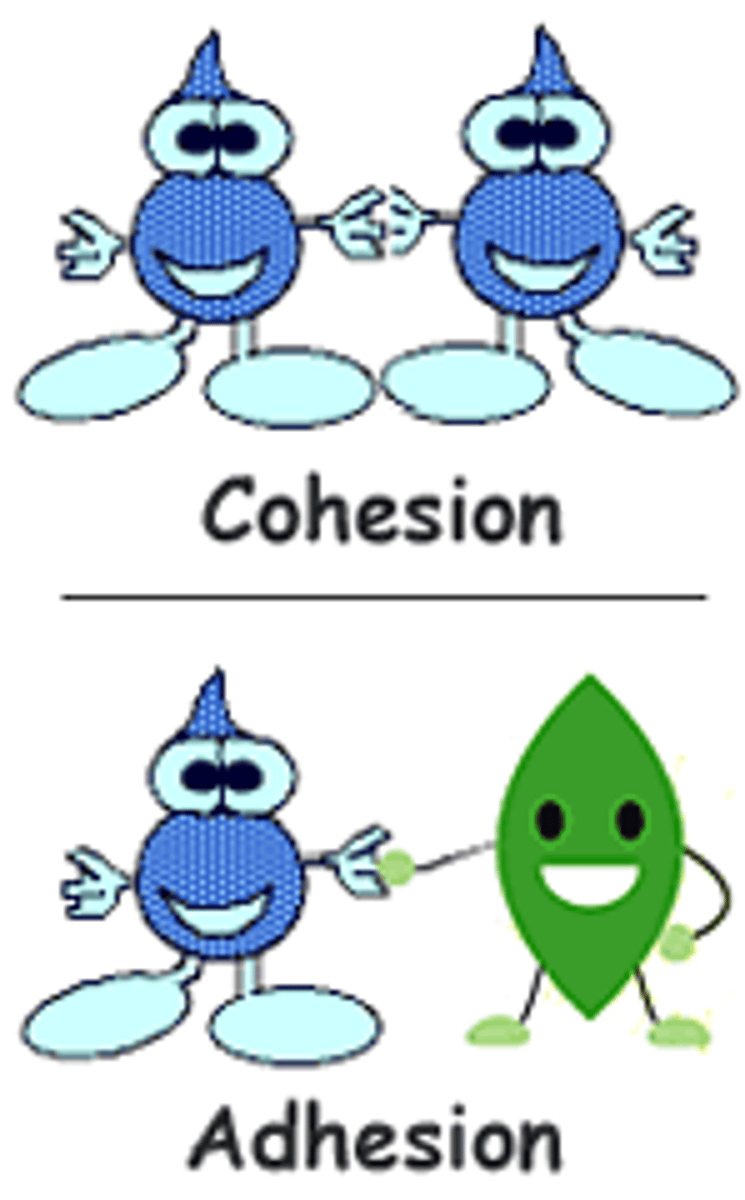
Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances

Solvent
the dissolving agent in a solution

Solute
The thing getting dissolved
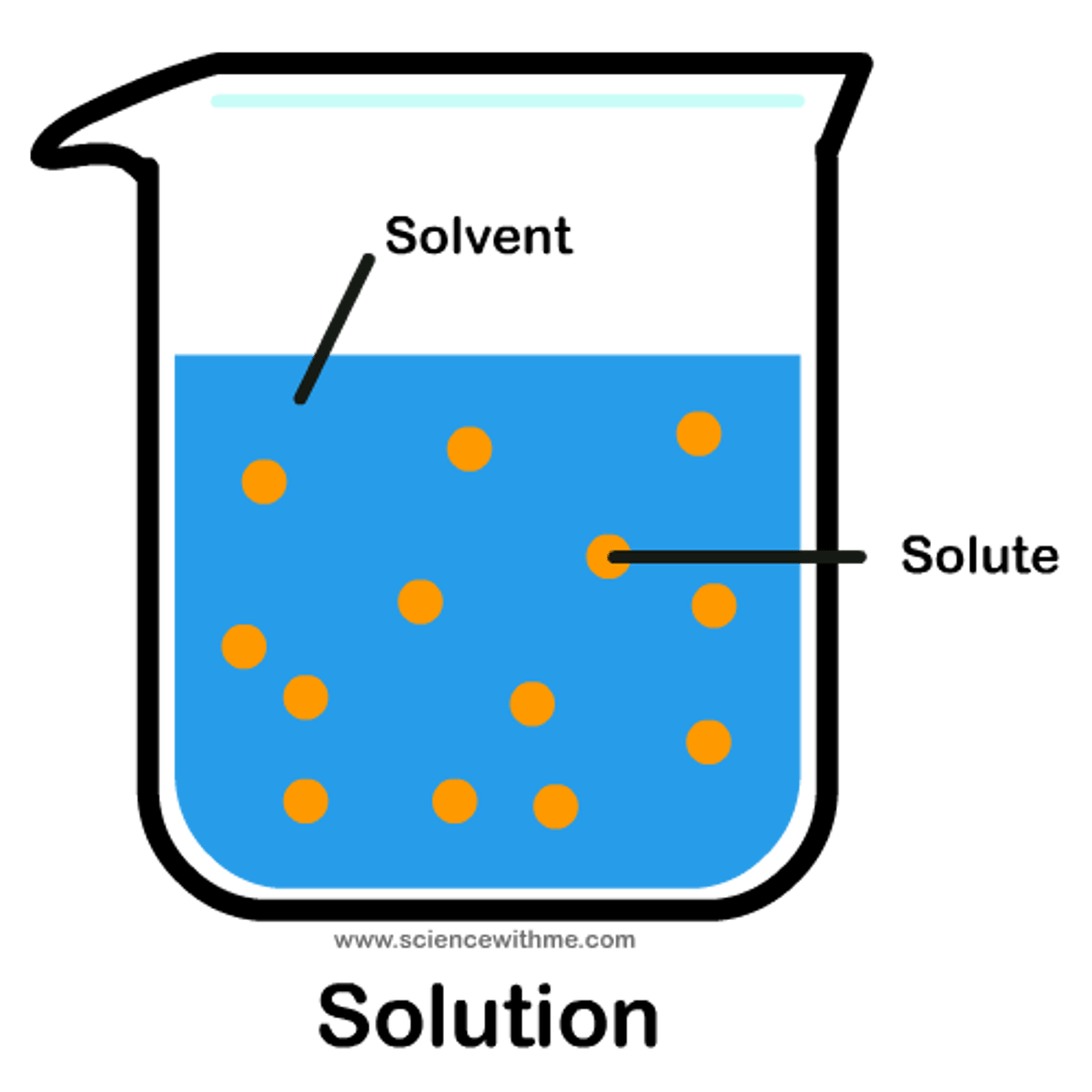
Solution
solute + solvent: final product

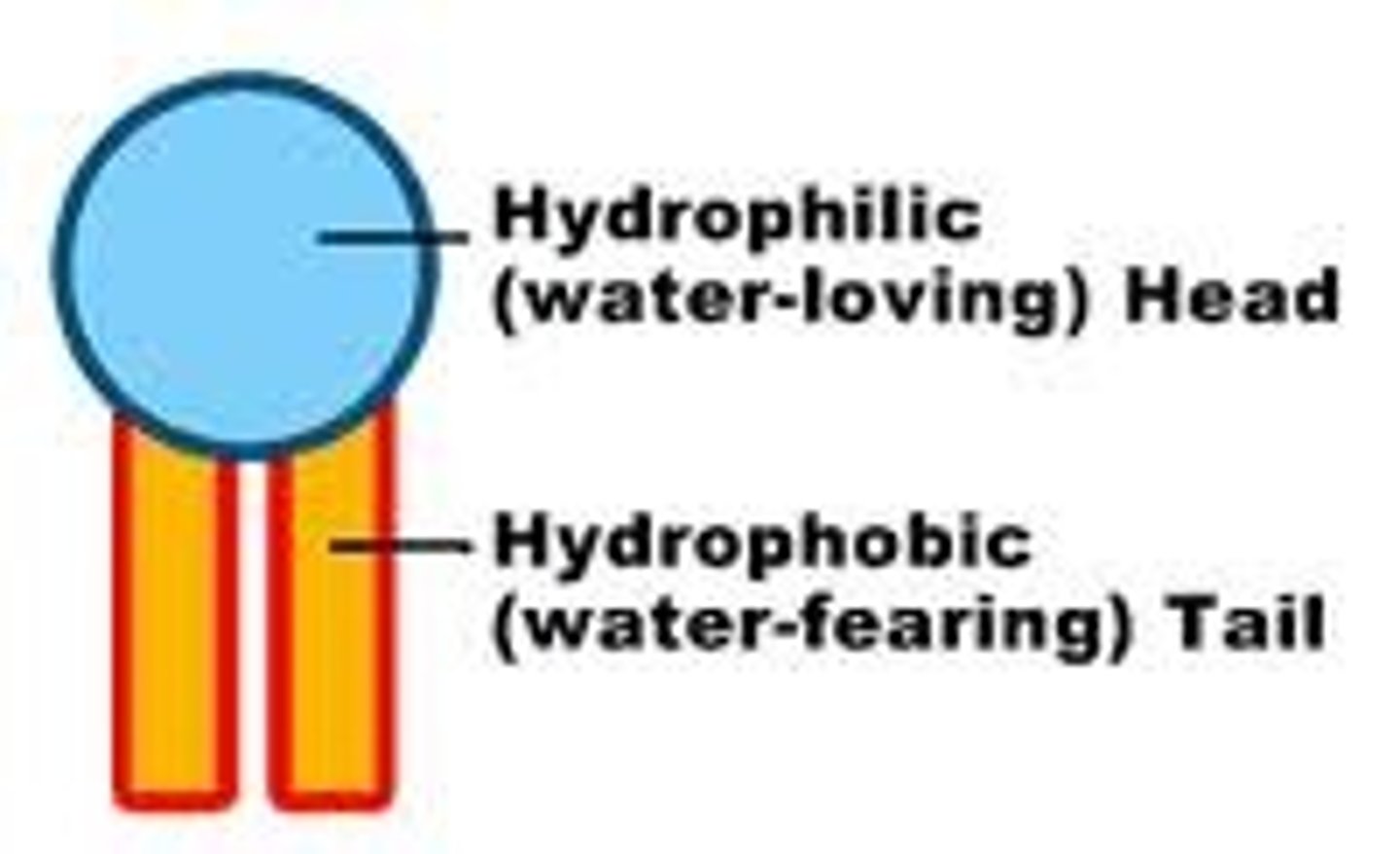
Hydrophilic
water loving
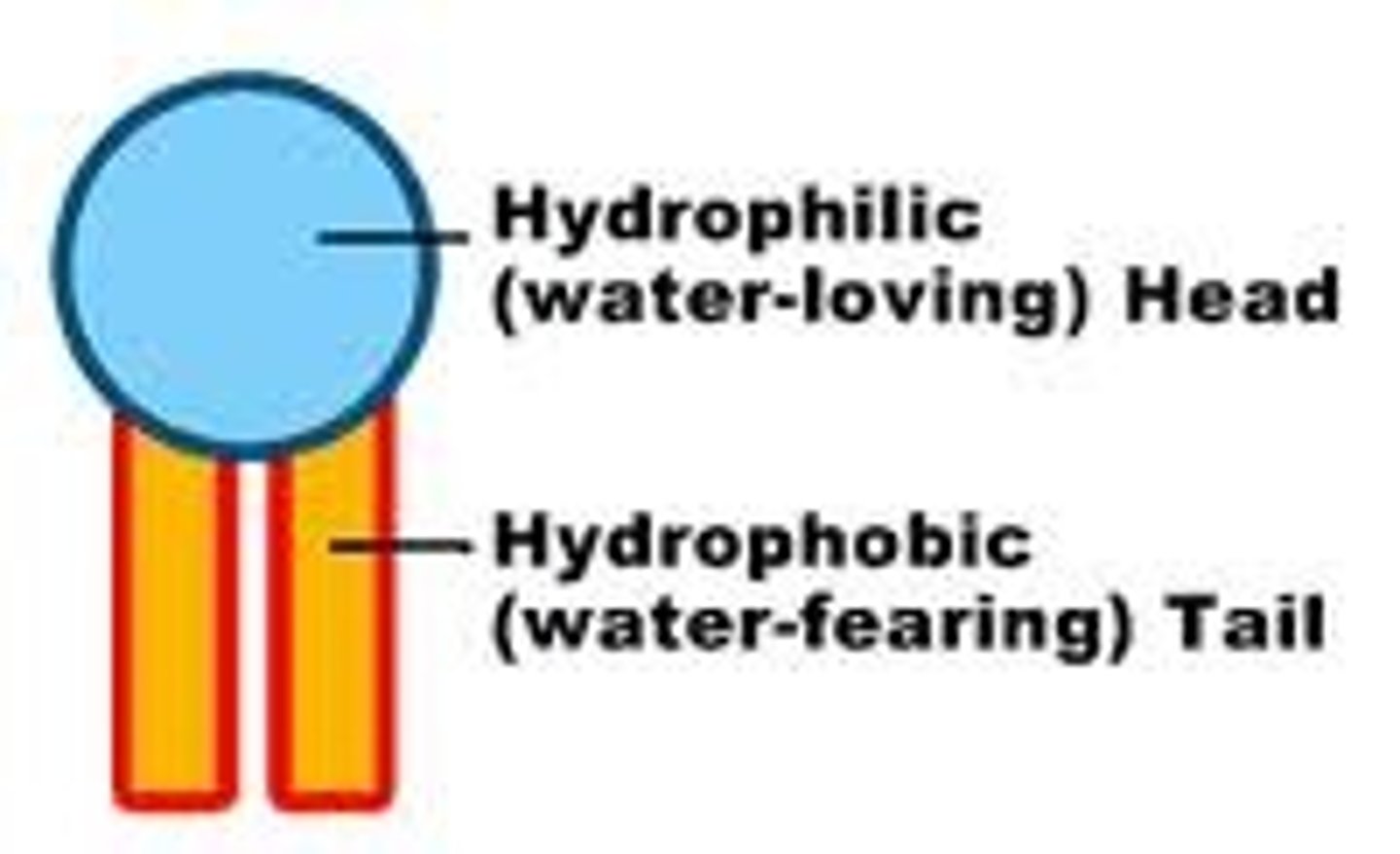
Hydrophobic
Water fearing (oils)
pH scale
scale with values from 0 to 14, used to measure the concentration of H+ ions in a solution; a pH of 0 to 7 is acidic, a pH of 7 is neutral, and a pH of 7 to 14 is basic
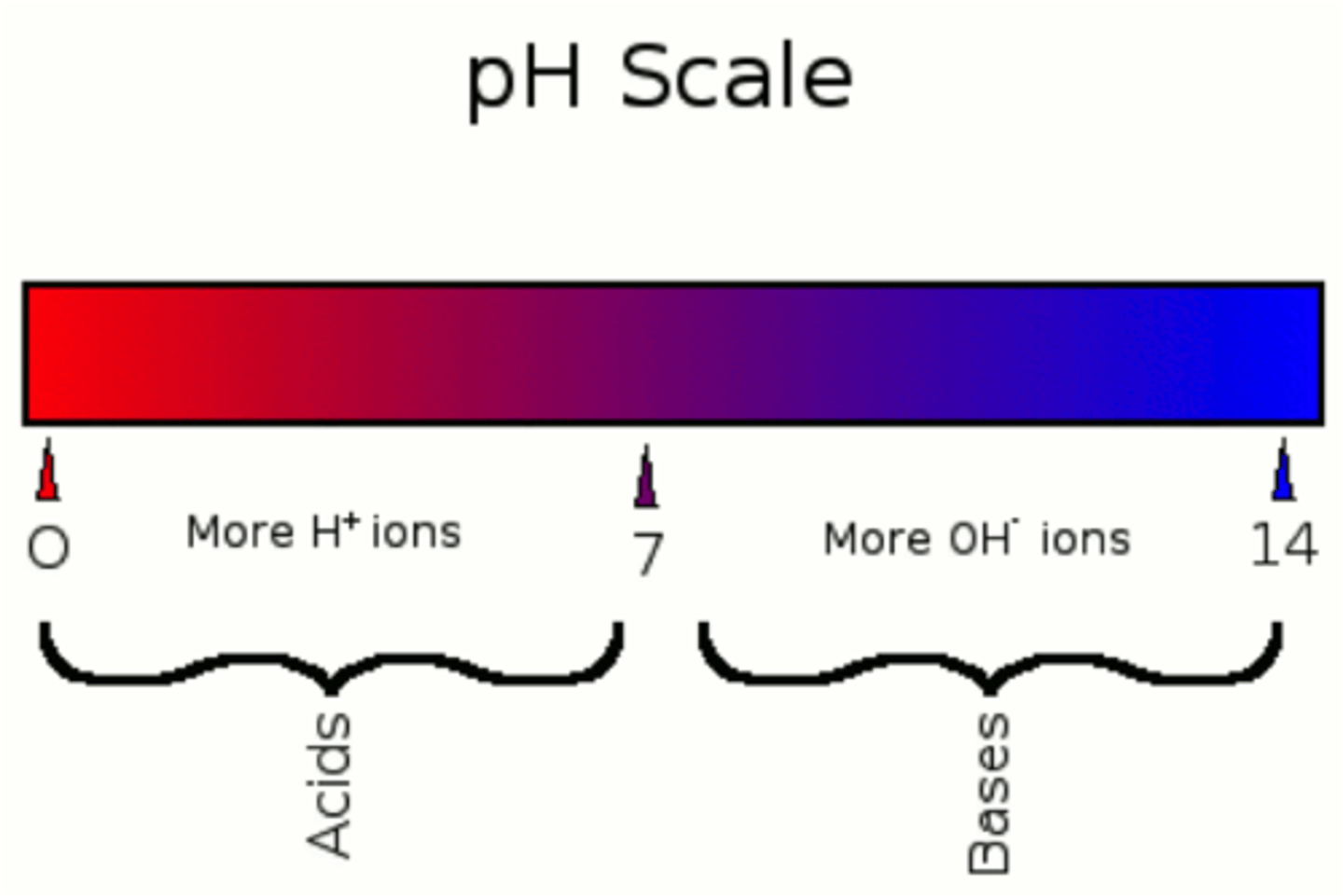
pH is measured on a scale of
10 log
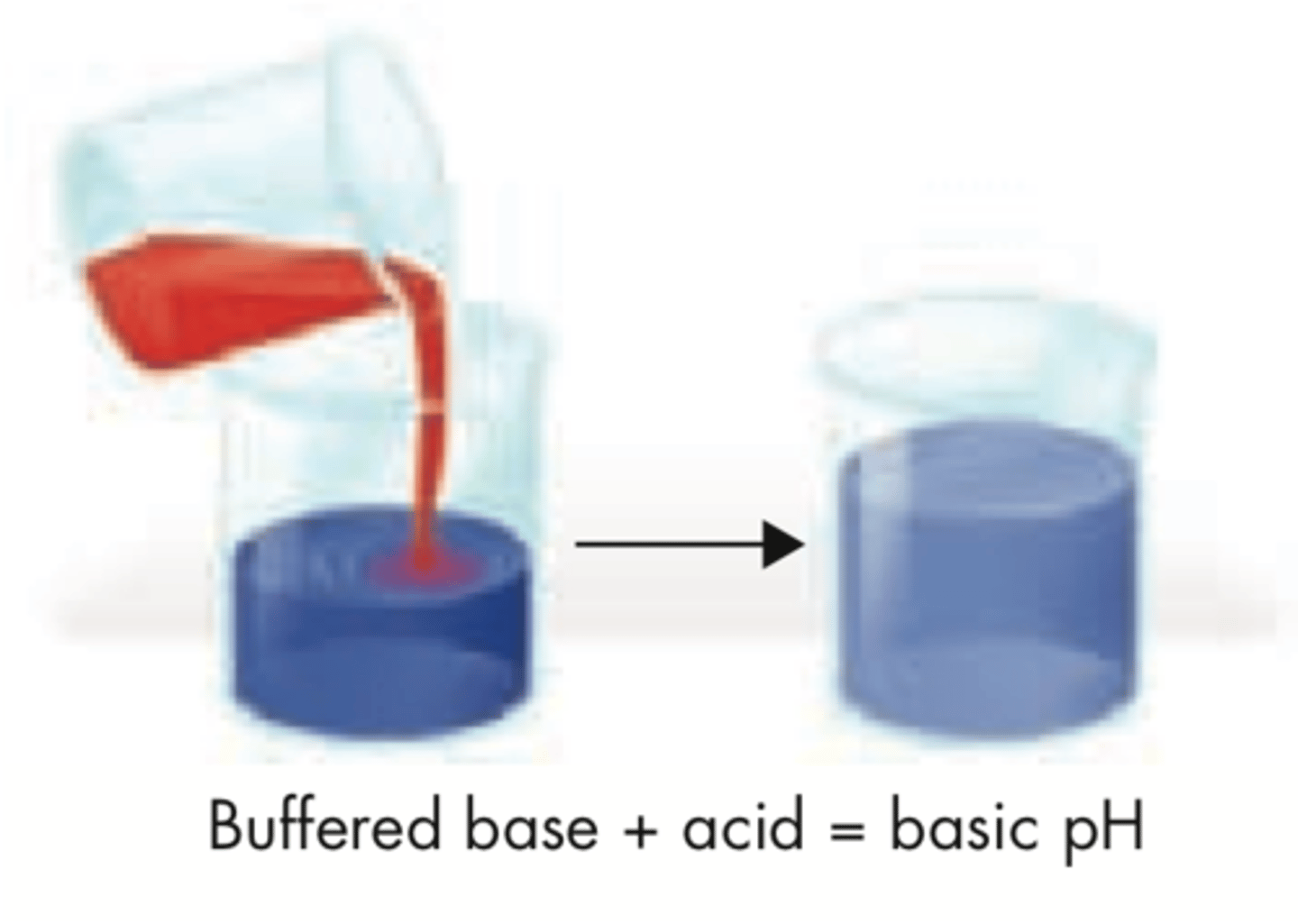
Buffers
chemical substance that resists changes in pH ( can either accept or donate hydrogen ions)