MCAT Biology - The Digestive System
1/134
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
Digestive System
take complex foods composed of polysaccharides, fats, and proteins and large macromolecules into smaller, simpler monosaccharides, fatty acids, and amino acids and then absorb them into the bloodstream; requires a complex system of mechanical and chemical agents; specialized sections with different functional roles
intracellular digestion
involves the oxidation of glucose and fatty acids for energy
metabolism
set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms
the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes
the conversion of food to building blocks of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates
the elimination of metabolic wastes
alimentary canal
runs from the mouth to the anus and is sectioned off by sphincters; where extracellular digestion occurs
extracellular digestion
the process by which these nutrients are obtained from food occurs within the lumen of the alimentary canal
sphincters
circular smooth muscles around the canal that can contract to allow compartmentalization of function
Digestion
involves the breakdown of food into its constituent organic molecules: starches and other carbohydrates into monosaccharides, lipids (fats) into free fatty acids and glycerol, and proteins into amino acids
Mechanical digestion
the physical breakdown of large food particles into smaller food particles
Chemical digestion
the enzymatic cleavage of chemical bonds, such as the peptide bonds of proteins or the glycosidic bonds of starches
Absorption
involves the transport of products of digestion from the digestive tract into the circulatory system for distribution to the body’s tissues and cells
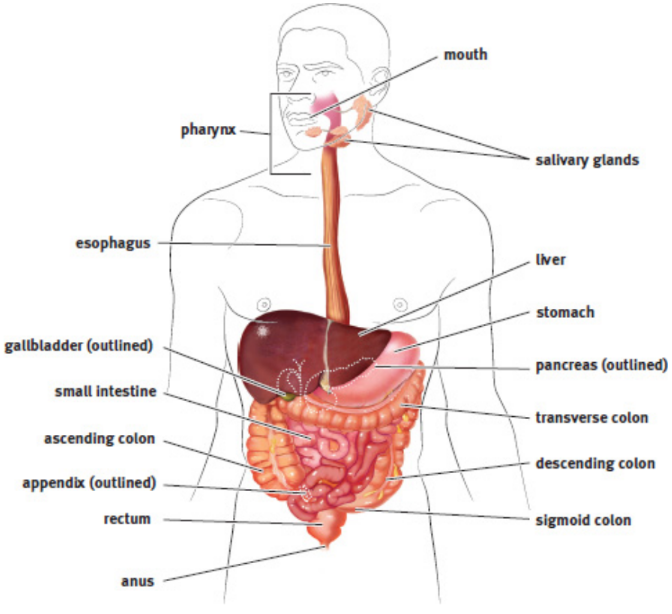
oral cavity / mouth
First portion of the alimentary canal that receives food; plays a role in both mechanical and chemical digestion of food
pharynx
a shared pathway for both food entering the digestive system and air entering the respiratory system
esophagus
receives food from the pharynx and transports it to the stomach; top third is composed of skeletal muscle (voluntary), the bottom third is composed of smooth muscle (involuntary), and the middle third is a mix of both
stomach
highly muscular organ with a capacity of approximately two liters; upper left quadrant of the abdominal cavity, underneath the diaphragm; Chemical breakdown of food takes place by means of secreted digestive enzymes and gastric hydrochloric acid; thick mucosa to avoid autodigestion
small intestine
follows stomach; seven meters; three segments: the duodenum, the jejunum, and the ileum
large intestine
rectum
feces are stored until an appropriate time of release
salivary glands
pancreas
endocrine function: the release of insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin
exocrine function: pancreatic juices
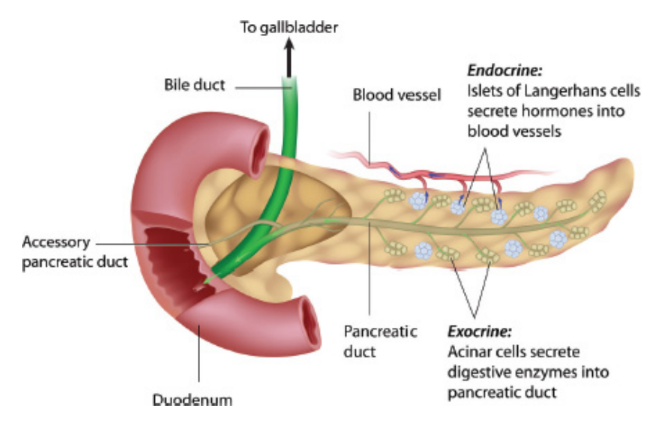
liver
located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen; makes bile and processes nutrient-rich blood; detoxifies both endogenous and exogenous compounds
gallbladder
located just beneath the liver; stores and concentrates bile; contracts and pushes bile out into the biliary tree when activated by CCK
enteric nervous system
collection of one hundred million neurons in the walls of the digestive tract that govern the function of the gastrointestinal system and trigger peristalsis; function independently of the brain and spinal cord, although it is heavily regulated by the autonomic nervous system
peristalsis
rhythmic contractions of the gut tube in order to move materials through the system
food coma
feeling sleepy and lethargic after eating a big meal due to parasympathetic activity
ingest
Consumption of a substance by an organism; accomplished by taking in a substance through the mouth into the gastrointestinal tract, such as through eating or drinking
thirst
need for water; encouraging the behavior of fluid consumption
triggered by ADH and aldosterone
glucagon
secreted by the pancreas; stimulate feelings of hunger
ghrelin
secreted by the stomach and pancreas; stimulate feelings of hunger
Leptin
made by adipocytes; stimulating feelings of satiety
mastication / chewing
breaking up of large food particles into smaller particles using the teeth, tongue, and lips; increase the surface area-to-volume ratio of the food, creating more surface area for enzymatic digestion as it passes through the gut tube; moderates the size of food particles entering the lumen of the alimentary canal
saliva
liquid with enzymes produced in the salivary galns; aids mechanical digestion by moistening and lubricating food
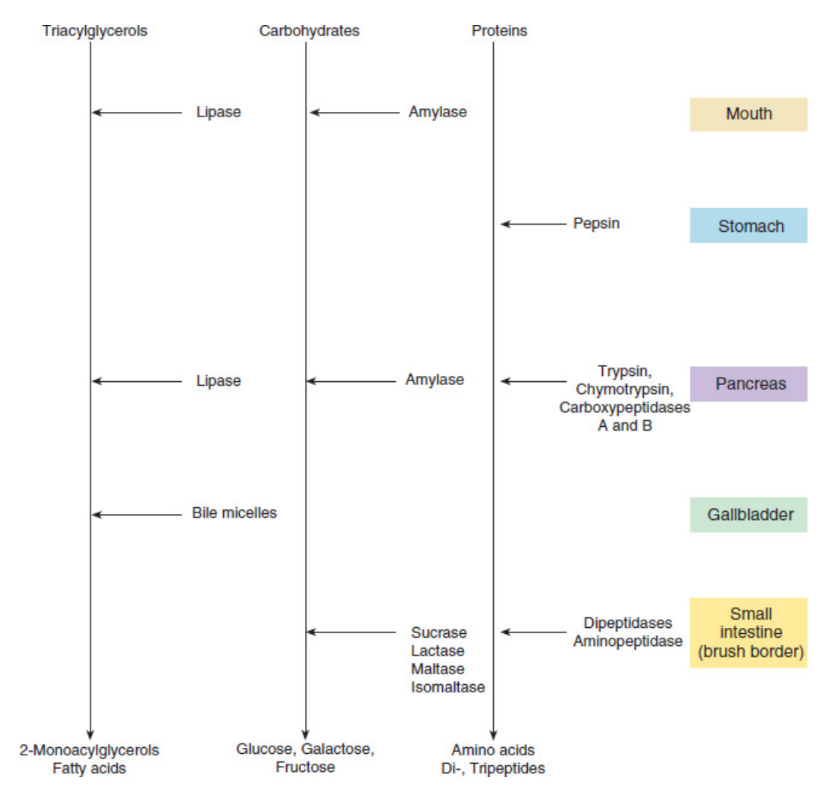
Salivary amylase
capable of hydrolyzing starch into smaller sugars (maltose and dextrins)
lipase
catalyzes the hydrolysis of lipids
bolus
ball of food formed by the tongue to be forced back to the pharynx and swallowed
emesis / vomiting
reversal of peristalsis due to exposure to chemicals, infectious agents, physical stimulation in the posterior pharynx, and even cognitive stimulation
upper esophageal sphincter
muscles of the oropharynx that initiated swallowing
lower esophageal (cardiac) sphincter
relaxes and opens to allow the passage of food into the stomach at the end of the esophagus
gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
classic heartburn symptoms after eating; weakness in the lower esophageal sphincter; acid reflux irritates the less-protected mucosa, stimulating general burning pain
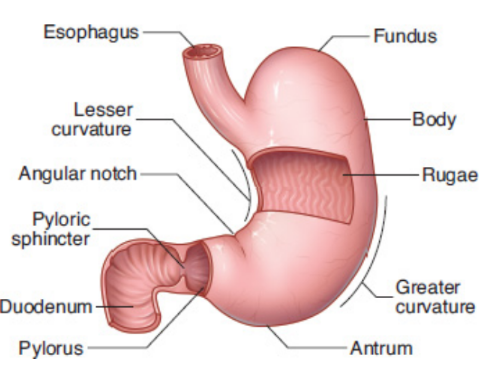
fundus
upper curved part; contain mostly gastric glands
body of stomach
main, central region of the stomach; contain mostly gastric glands
antrum
lowest part of stomach; contain mostly pyloric glands.
pylorus
part of the stomach leading into small intestine; contain mostly pyloric glands
lesser curvature
internal curvature of the stomach
greater curvature
external curvature of the stomach
rugae
lining of the stomach is thrown into folds
gastric glands
respond to signals from the vagus nerve
vagus nerve
parasympathetic nervous system; activated by the brain in response to the sight, taste, and smell of food
Mucous cells
produce the bicarbonate-rich mucus that protects the muscular wall from the harshly acidic (pH = 2) and proteolytic environment of the stomach
Gastric juice
combination of secretions from chief cells and parietal cells.
chief cells
secrete pepsinogen
zymogen
inactive form of an enzyme
pepsinogen
zymogen form of pepsin; cleaved into pepsin by hydrogen ions
Pepsin
digests proteins by cleaving peptide bonds near aromatic amino acids, resulting in short peptide fragments
activated by acidic environment
parietal cells
secrete hydrochloric acid
Helicobacter pylori
bacteria that can survive acidic stomach environment; infection is usually asymptomatic but can cause inflammation, ulcers, and even certain gastric cancers
intrinsic factor
glycoprotein involved in the proper absorption of vitamin B12; secreted by parietal cells
pyloric glands
contain G-cells
G-cells
secrete gastrin
Gastrin
peptide hormone; induces the parietal cells in the stomach to secrete more HCl and signals the stomach to contract, mixing its contents
chyme
acidic, semifluid mixture from the digestion of solid food in the stomach; significant increase in the surface area
few substances that are absorbed directly from the stomach
alcohol and aspirin
Zollinger–Ellison syndrome
rare disease resulting from a gastrin-secreting tumor (gastrinoma) causing excessive HCl production; sign: excessive HCl production
duodenum
responsible for the majority of chemical digestion; minor involvement in absorption; secretes brush border enzymes, enteropeptidase, secretin, cholecystokinin (CCK)
pyloric sphincter
where food leaves the stomach and enters the duodenum
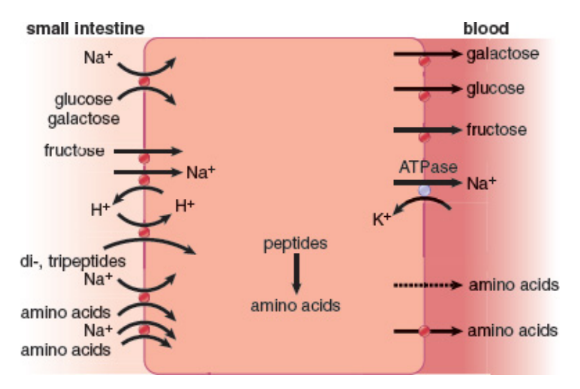
Brush-border enzymes
present on the luminal surface of cells lining the duodenum and break down dimers and trimers of biomolecules into absorbable monomers
ex. disaccharidases
enteropeptidase
involved in the activation of other digestive enzymes from the accessory organs of digestion
disaccharidases
digest disaccharides
Maltase
digests maltose
isomaltase
digests isomaltose
lactase
digests lactose
sucrase
digests sucrose
Peptidases
break down proteins or peptides
Aminopeptidase
removes the N-terminal amino acid from a peptide
Dipeptidases
cleave the peptide bonds of dipeptides to release free amino acids
Celiac disease
immune reaction against gluten, a protein found in grains, especially wheat; immune system develops antibodies against certain components of gluten; cross-react with elements of the small intestine, causing damage to the mucosa; not true allergies
symptoms: diarrhea, discomfort, malabsorptive syndromes
Enteropeptidase / enterokinase
enzyme critical for the activation of trypsinogen to trypsin and procarboxypeptidases A and B
trypsinogen
zymogen pancreatic protease
trypsin
pancreatic protease; initiates an activation cascade
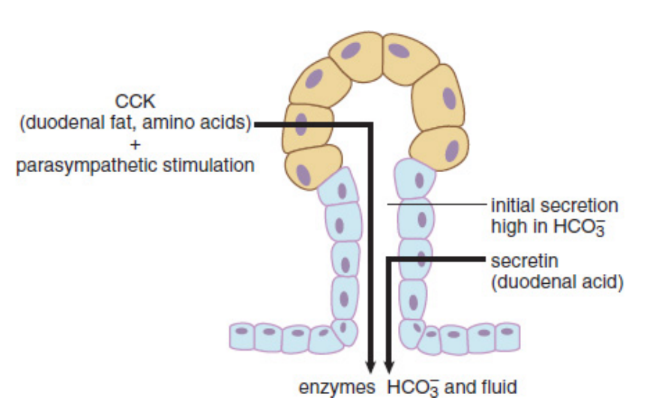
Secretin
peptide hormone that causes pancreatic enzymes to be released into the duodenum; regulates the pH of the digestive tract by reducing HCl secretion from parietal cells and increasing bicarbonate secretion from the pancreas
enterogastrone
hormone that slows motility through the digestive tract to allow digestive enzymes to act on chyme, especially fats
cholecystokinin (CCK)
synthesized and secreted by enteroendocrine cells in the duodenum in response to the entry of amino acids and fat in chyme into the duodenum; stimulates the release of both bile and pancreatic juices; acts in the brain, where it promotes satiety.
Bile
complex fluid composed of bile salts, pigments, and cholesterol
Bile salts
derived from cholesterol; important role in the mechanical digestion of fats; have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions, allowing them to serve as a bridge between aqueous and lipid environments
emulsify
mix two or more liquids that are normally immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation
micelles
an aggregate with the hydrophilic "head" regions in contact with surrounding solvent, sequestering the hydrophobic single-tail regions in the centre
Pancreatic juices
complex mixture of several enzymes in a bicarbonate-rich alkaline solution; helps to neutralize acidic chyme, as well as provide an ideal working environment for the digestive enzymes; pH ~8.5
accessory organs of digestion
outgrowths of endoderm from the gut tube during development that aid in the release of enzymes
acinar cells
exocrine cells that produce pancreatic juices
Pancreatic amylase
breaks down large polysaccharides into small disaccharides and is therefore responsible for carbohydrate digestion
chymotrypsinogen
zymogen; responsible for protein digestion
carboxypeptidases A and B
zymogen pancreatic proteases
pancreatic lipase
capable of breaking down fats into free fatty acids and glycerol
Pancreatitis
inflammation of the pancreas from premature activation of pancreatic enzymes and autodigestion of the pancreatic tissue; may result in a long hospital stay and long-term consequences such as diabetes and the reduced digestion of proteins and fats
usually caused by gallstones or excessive consumption of alcohol
major / minor duodenal papillae
where pancreatic ducts empty into the duodenum
bile ducts
connect the liver with both the gallbladder for storage and small intestine to emulsify chyme
hepatic portal vein
receives all blood draining from the abdominal portion of the digestive tract for processing before draining into the inferior vena cava on its way to the right side of the heart
glycogen
storage form of glucose
triacylglycerols
storage form of fat
glycogenolysis
produces glucose from glycogen
gluconeogenesis
produces glucose from other biomolecules