lecture 9: reasoning - metacognition
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
metacognition
-something which refers to or reflects on the original concept
-thinking about thinking
-when you reflect on the contents of your mind
metacognitive judgements
-perceptions of your own mental state, including:
confidence
awareness
Fuocco, 1996 - example of metacognitive failure
-McArthur Wheeler robbed two banks with no visible attempt at disguise
-arrested and when questioned said he “wore the juice” → he thought that rubbing his face with lemon juice rendered it invisible to videotape cameras
confirmation bias
-a preference for seeking information that can only confirm your existing beliefs, rather than contradict it
-about active search for information, not just whether you believe information when you encounter it
Wason’s selection task
-four cards that all have:
a letter on one side
a number on the other side
four cards are: E, X, 1, 6
-rule is that all cards with a vowel on one side have an even number on the other side
-which card would you turn over to determine if the statement is true?
-confirmation bias is that most people turn over E and 6, when E and 1 test the rule
Wason task - controls
-things that don’t help:
motivation/reward
changing the wording
university education
-something that does help is making the task less abstract
Wason’s selection task - social rule version
-four people in a pub, each has a drink:
have the age on one side
other side has the drink
rule is that all people with an alcoholic drink must be older than 18
-which people do you need to inspect to decide if the rule is being broken?
most errors are two errors
making the wrong choice
thinking you’ve made the right choice
→ error + metacognitive error
choosing affected by misattribution
-The Mere Exposure Effect
-Mental contamination
-misattribution is making errors in identifying the cause of something
The Mere Exposure Effect (MEE)
-the idea that having already encountered something encourages future preference
-typically found after brief, repeated exposures with low levels of attention and involvement
-often used in advertising
Stafford & Grimes (2012) - recognition memory and MME
-recognition memory may support MME
-230 students exposed to 10 novel brand logos
-10 logos were paired with 10 unseen novel logo
-10 pairs of logos, one target and one distractor in the test phase
-found that recognition, whether correct or mistaken will enhance (rather than inhibit) the likelihood of preference
explanation of recognition and MME
-fluency
-exposure means that stimuli is processed with ease (fluency) and this ease can be interpreted as being pleasing
misattribution based on fluency
-preference judgements are quick heuristic process with a systematic bias in preferring things that are easily processed → don’t have access to full memory and so can’t remember everything
-recognition and preference are based on fluency → memory judgements correlate with preference judgements
misattribution
-participants say they recognise something when it is novel (meta memory error)
-thinking that you have seen something before when you haven’t is a metacognitive process and misattribution is a metacognitive error
mental contamination
-Wilson & Brekke (1994)
-the process whereby a person has an unwanted response because of mental processing that is unconscious or uncontrollable
Dutton & Aron 1974 (mental contamination)
-450ft Capilano Suspension Bridge
-has many arousal-inducing features:
tendency to tilt, sway and wobble
very low handrails of wire cable
creates the impression that one is about to fall off
-evidence for heightened sexual attraction under conditions of high anxiety
Dutton & Aron 1974 - results (mental contamination)
-male participants approached by female researcher on Capilano Suspension Bridge or non-fear arousing bridge
-greater tendency for those on the fear arousing bridge to contact the female researcher afterwards than those on the non-fear arousing bridge
-misattribution and source confusion of fear arousal to sexual arousal/attraction
misattribution summary
-don’t have access to all causes of thoughts and feelings
-use metacognitive processes of asking ourselves:
is that memory reliable?
where did that feeling come from?
-attribution is a continuous metacognitive process → but can have metacognitive errors
illusion of explanatory depth (IoED)
-Rozenblit & Keil (2002)
-most people feel they understand the world with far greater detail, coherence and depth than they really do
-thinking you understand something more than you do is a metacognitive error
stages of Rozenblit & Keil (2002)
-instructions and training
-first rating of belief of understanding the concept
-generate explanation
-second rating of belief of understanding the concept
-answer diagnostic question
-third rating of belief of understanding the concept
-read expert explanation
-fourth rating of belief of understanding the concept (initial knowledge relative to expert explanation)
-fifth rating of belief of understanding the concept (current knowledge after reading expert explanation)
Rozenblit & Keil (2002) - results
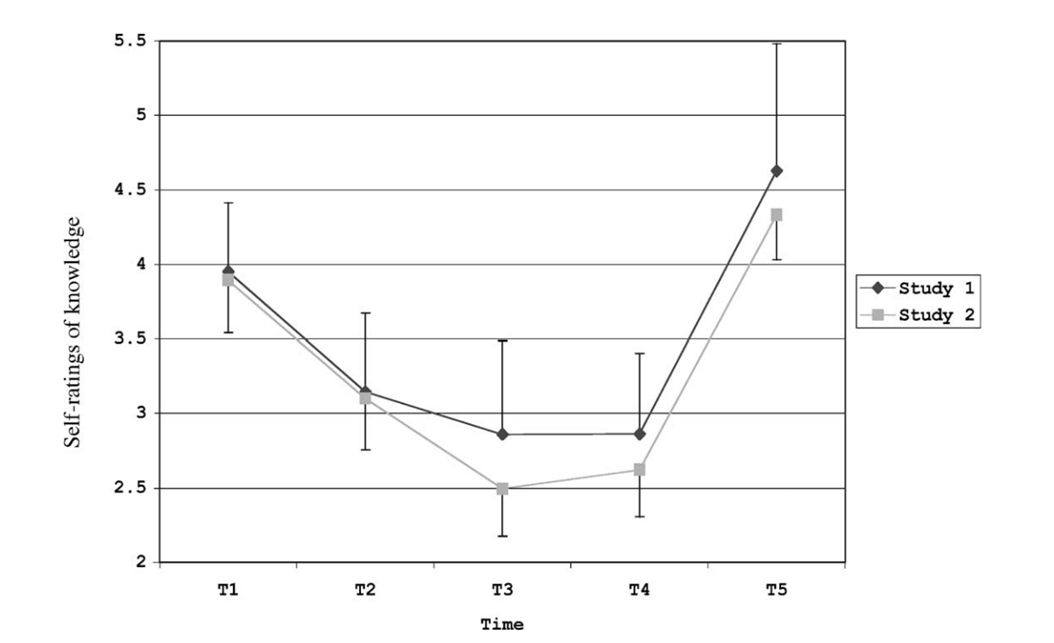
-second, third and fourth ratings after being asked to calibrate their understanding and self rating goes down
-realise they do not understand as well as they originally believed they did (first rating)
-fifth rating higher than before as they sense they understand after going through the different processes
reason of IoED
-rate our level of understanding higher than we have
-because we misattribute expertise based on familiarity
Ferncach et al (2013) - using IoED to change minds
-people often hold extreme political views, yet may know less about complex policies than they think
-asked participants to rate 6 political policies
-asked to explain how the policy would work and its effect
-having to explain policies moderated attitudes towards the policy
explanation undermines the illusion of understanding
can adjust our thinking to correct errors
Dunning-Kruger effect
-not always aware of errors in judgement
-high confidence in belief is metacognition
-so high confidence in a false belief is a metacognitive error
domains tested (Dunning-Kruger effect)
self rated belief in ability compared to others
tested the ability using an objective measure
-found that those in the lowest quartile perceived themselves as being more skilled than they actually were
-whereas the most skilled underestimated their skill
the dual burden theory (mechanism of Dunning-Kruger effect)
-performance and metacognition of the performance (ability to judge how good you are) are both based on the skill
-high skill = perform well and understand the skill so can judge your ability
-low skill = low performance but lack knowledge to make accurate metacognitive judgements
-incompetent individuals lack the metacognitive skills necessary for accurate self-assessment
criticism of Dunning-Kruger effect
-McIntosh and Della Sala questioned the validity and reliability of findings to support the effect
-referred to regression to the mean as accounting for the findings
-suggest that information against the effect is often ignored in favour of the causal idea rather than accept a statistical explanation for the pattern → a cognitive bias
-Dunning-Kruger effect has been weaponsied as a way to dismiss others’ views
metacognition and heuristics
-metacognitive errors can result from basing judgement on wrong information
-metacognition employs heuristics due to lack of information
-use heuristics to understand ourselves and the world
-metacognitive errors can result from heuristics