H. Chem- Unit 2 Quiz Review
1/50
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
energy levels of the electron, size of electron cloud
1st quantum number
sublevel of the electron, shape of e⁻ cloud
2nd quantum number
orbital on the sublevel
3rd quantum number
tells direction of electron's spin, can only be +1/2 or -1/2
4th quantum number
electrons in “s” sublevel
2
electrons in “p” sublevel
6
electrons in “d” sublevel
10
electrons in “f” sublevel
14
number of electrons in ALL atomic orbitals
2
Numbers possible for the second quantum number when the first quantum number is 1
0
Numbers possible for the second quantum number when the first quantum number is 2
0,1
Numbers possible for the second quantum number when the first quantum number is 3
0,1,2
Numbers possible for the second quantum number when the first quantum number is 4
0,1,2,3
Numbers possible for the second quantum number
n-1
or
(first quantum number) - 1
Numbers possible for the third quantum number when the second quantum number is 0
0
Numbers possible for the third quantum number when the second quantum number is 1
-1, 0, +1
Numbers possible for the third quantum number when the second quantum number is 2
-2, -1, 0, +1, +2
Numbers possible for the third quantum number when the second quantum number is 3
-3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3
How many electrons in each ring of Bohrs model
ring —> electron count
1 —> 2
2 —> 8
3 —> 18
4 —> 32
What is the ground state of atoms?
The lowest energy state of an atom
What is the excited state of atoms?
Atoms where the perfect amount of energy has been added so that the electrons can move to higher rings
Photons
The energy/light given off by electrons when they go back to ground state
When do atoms give off light
When electrons go back to ground state after being excited they give off photons, each element has their own unique light because they each have a different electron configuration
Valence electrons
The outermost electron (on the final shell)
Most amount of electrons in a shell
2n²
Number of orbitals in the S sublevel
1
Number of orbitals in the P sublevel
3
Number of orbitals in the D sublevel
5
Number of orbitals in the F sublevel
7
Doppler effect
as something moves away it redshifts and as something moves closer it blueshifts
Relationship between wavelength and energy
Shorter wavelength —> more energy
Longer wavelength —> less energy
Relationship between wavelength and frequency
Inverse relationship
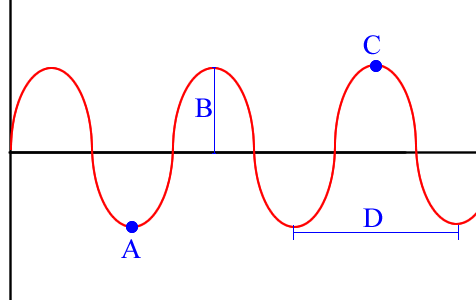
Term for A
trough
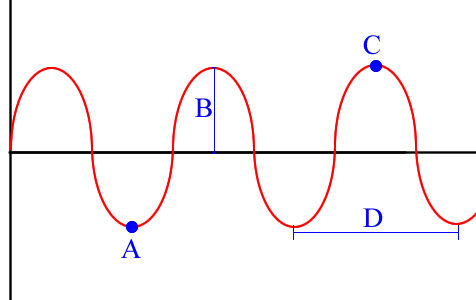
Term for B
amplitude
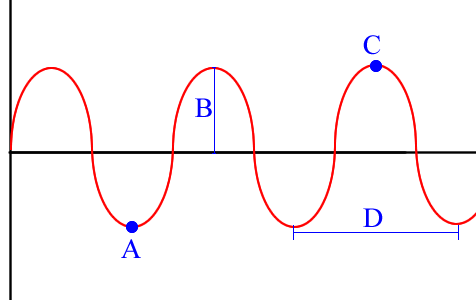
Term for C
crest
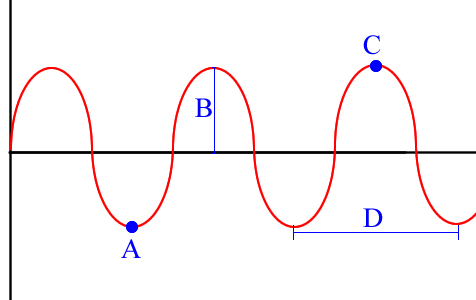
Term for D
wavelength

Spins are randomly oriented
Paramagnetic

Spins are aligned parallel
Ferromagnetic
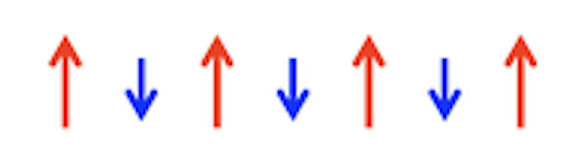
Spins are aligned antiparallel but do not cancel
Ferrimagnetic
Why can you not have more sublevels than shells?
You cannot not have more sublevels than shells because there is not enough room
4,3,2,1
invalid (1)
3,0,1,+1/2
invalid (1)
3,4,1,-1/2
invalid (4)
0,3,2,-1/2
invalid (0)
3,1,0,+1/2
valid
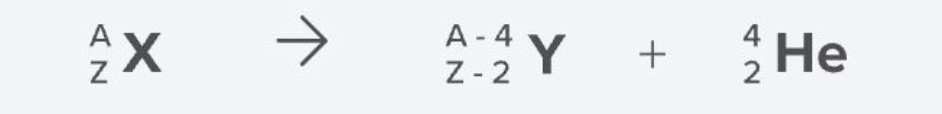
Alpha Decay
the element looses 2 protons and 4 from it’s mass —> result is a daughter and alpha particle

Beta Decay
the element gains a proton with no change to mass —> result is a daughter and an electron

Gamma Decay
the element has no change to mass or # of protons, however the starting (parent) element will have a “m” next to it’s mass amount because it is in an excited nuclear state —> result is a daughter and a gamma ray
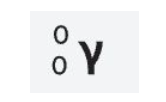
Template Alpha Decay equation
Template Beta Decay equation

Template Gamma Decay equation
