Superpowers
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Defining Superpowers
A superpower is a country that can prject its power and ideas globally, and influence other countries using its economic, political, military and cultural strengths
Geopolitical power
Refers to the influence of geographical factors (economy, population size, military strength) on the actions of countries towards others: their foreign policy, agreements and alliances, and conflicts
Geopolitical heirachy
Hyper-power
Complete global dominance, no rivals
USA
Superpower
Globally dominant, but more than one can exist at one time
EU
Emerging power
Globally influential, but only in certain areas of influence
Russia, China, Brazil, India
Regional power
Leads on a continental, but not global scale
Japan, Mexico, Nigeria
Sources of power
Economic
A large total GDP gives countries the wealth needed to be a global player
Political
Leading, rather than following, within global organisations such as the UN, IMF and WTO
Military
Nuclear weapons, a large air force and navy are required to threaten or force a country’s will on others
Natural resources
Fossil fuels, land for farming, mineral wealth and water resources increase self-sufficiency
Cultural
Having ideas, art, music, food and fashion that others find appealing is a source of power
USA as a global Superpower
Economic
Worlds largest GDP of $25 trillion 2022
Vast domestic market
TNCs (29% worlds 2000 largest TNCs)
Political
UN headquarters in NY
NATO
Military
Largest navy
Leading nuclear power (1750 active nuclear witharheads)
Largest operator of military bases globally (bases on every continent)
Natural resources
Abundant supplies of fossil fuels (gas and coal)
Arable land
2nd leading country in natural resources value (after Russia)
Cultural
Hollywood
English speaking
Hard Power
Soft Power
Hard Power
Using military and economic influence (trade deals, sanctions) to force a country to act in a particular way
Can get results, but it is expensive and risky
Others may view military action as unnecessary or illegal, so the aggressor may lose allies and moral authority (e.g. Russia's 2014 invasion of the Crimea)
Soft Power
More subtle persuasion of countries to act in a particular way, on the basis that the persuader is respected and appealing
Includes political persuasion (diplomacy) and cultural influence
Relies on a country having respected culture, values and politics, which may be enough to persuade some countries but not others
If applied well, is low cost and, because it is about creating alliances and friendly relations, may spread to other countries
Smart Power
Joseph Nye argues that in the 21st century the most successful countries are those that combine hard and soft power, forming smart power
Hard and soft power
USA vs UK
USA hard power
1991 organised and led the coalition to expel Iraqi forces that had invaded Kuwait in the First Gulf War
2003 invaded Iraq in the Second Gulf War when economic sanctions (softer power) failed to persuade President Saddam Hussein to change policy
UK soft power
5th largest economy, attractive market and source of TNC FDI
One of the largest networks of diplomats and embassies in the world
BBC World Service is more neutral and reliable than many government broadcasters
Films (Pride and Prejudice), television (Downton Abbey) and literature (Harry Potter)
City of London (and New York) dominate international finance, banking and law, setting standards and values
Mackiner’s ‘Heartland’ theory
Persuaded the USA, UK and other European countries that Russia needed to be ‘contained’ i.e. prevented from spreading outward by taking over new areas close by
Reinforced the idea that control over physical resources was important
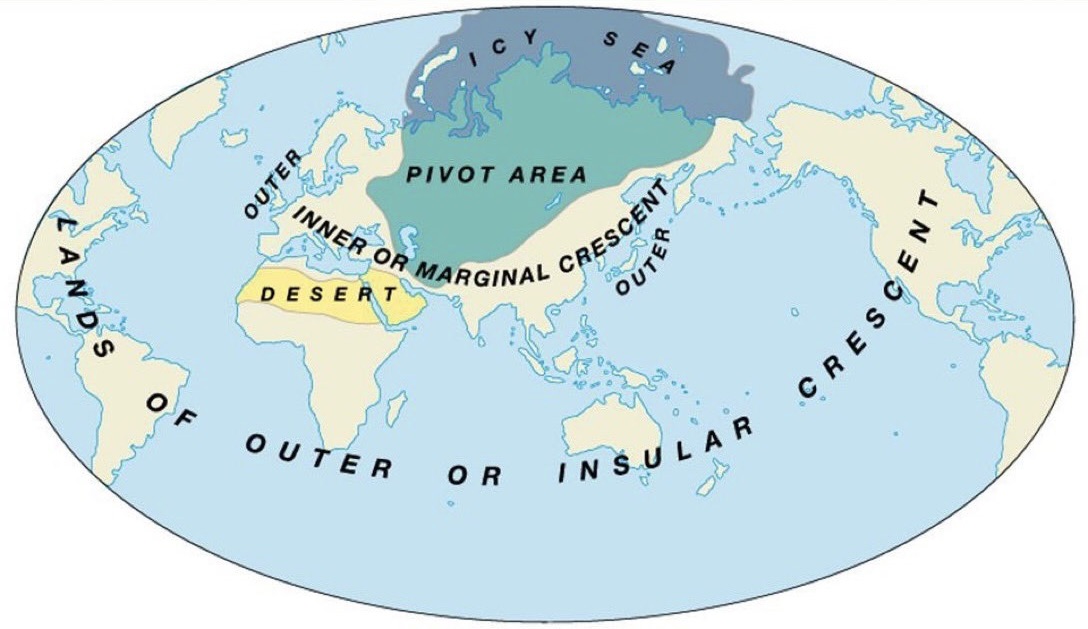
Patterns of power