BIO 181 Module 4
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
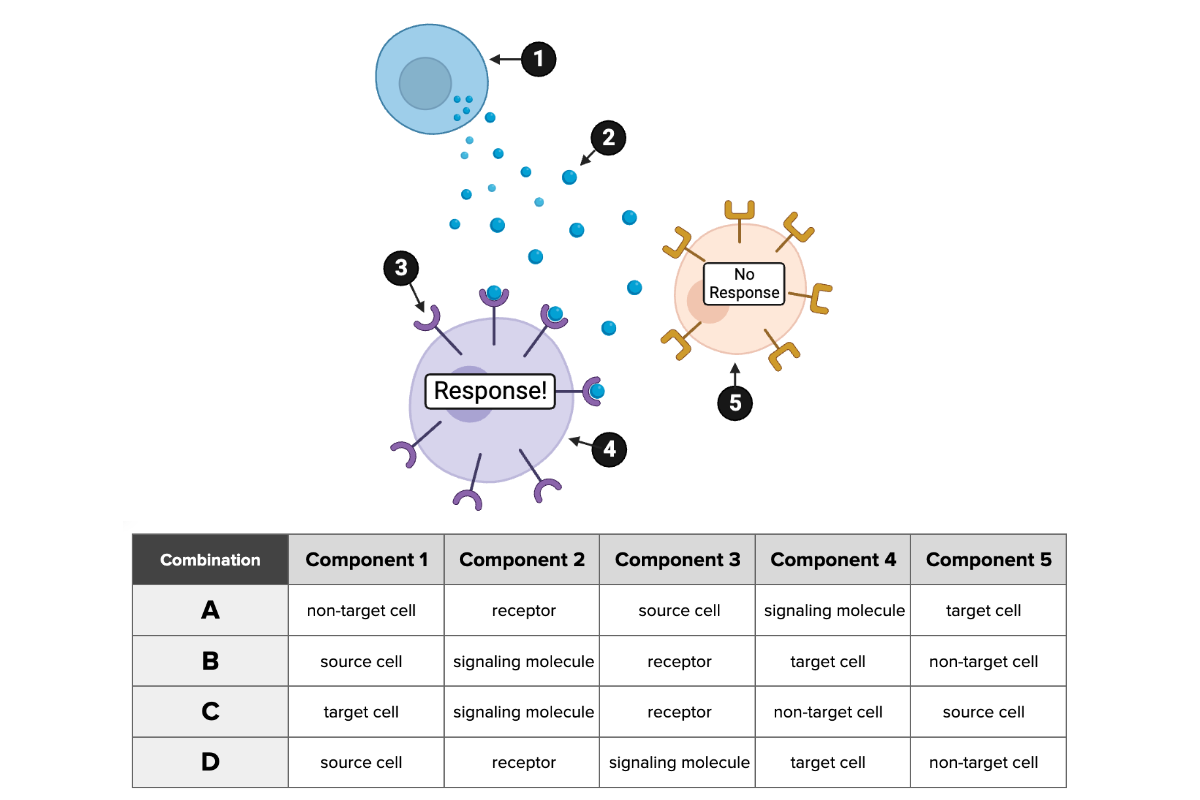
Which combination of labels accurately describes the five components of the cellular communication system?
a. Combination A
b. Combination B
c. Combination C
d. Combination D
b. Combination B
Which statements accurately describe hormones? Select all that apply.
a. Hormones are signaling molecules.
b. Hormones travel to target cells through the bloodstream.
c. Hormones trigger a response in a target cell.
d. Hormones can affect the function of any cell with the appropriate receptors.
a. Hormones are signaling molecules.
b. Hormones travel to target cells through the bloodstream.
c. Hormones trigger a response in a target cell.
d. Hormones can affect the function of any cell with the appropriate receptors.
Which statements accurately describe hydrophilic signaling molecules? Select all that apply.
a. Hydrophilic signaling molecules have polar or charged regions.
b. Hydrophilic signaling molecules require carrier proteins to travel through the bloodstream in high concentration.
c. Hydrophilic signaling molecules are unlikely to diffuse through the phospholipid bilayer of a cell membrane.
d. Hydrophilic signaling molecules are smaller than hydrophobic signaling molecules.
a. Hydrophilic signaling molecules have polar or charged regions.
c. Hydrophilic signaling molecules are unlikely to diffuse through the phospholipid bilayer of a cell membrane.
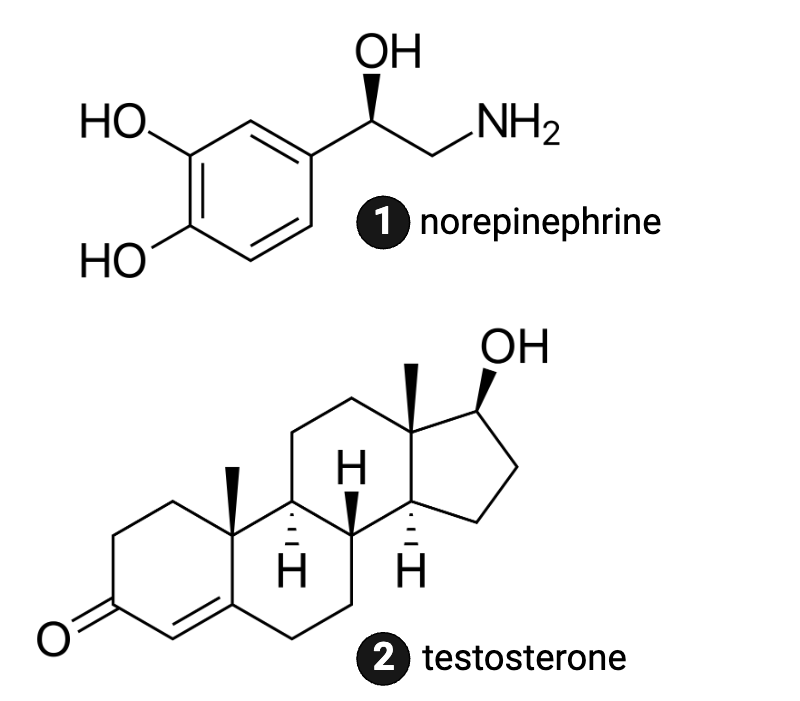
Which molecule is more hydrophilic?
a. norepinephrine
b. testosterone
a. norepinephrine
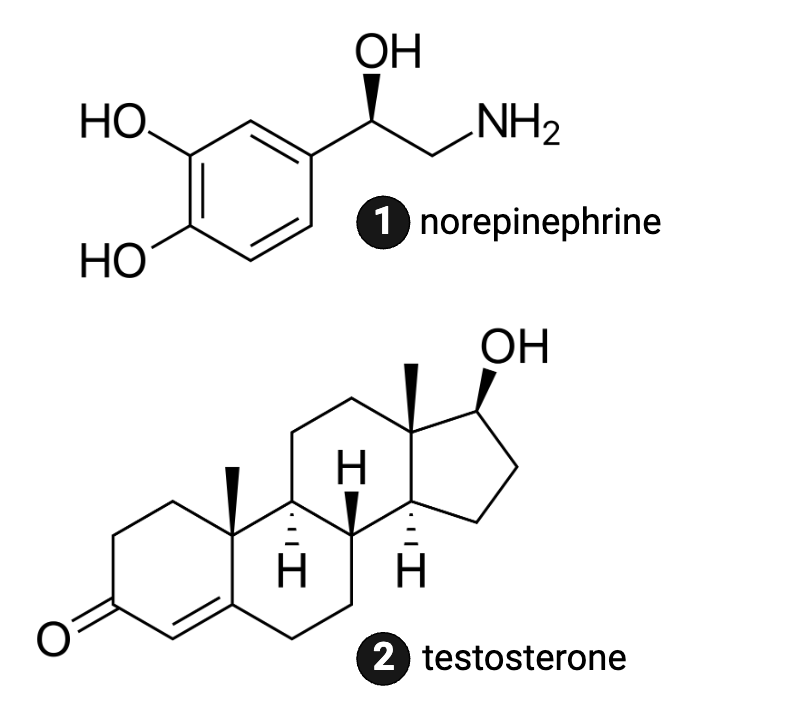
Which molecule is more likely to be bound to a protein when traveling in the blood?
a. norepinephrine
b. testosterone
b. testosterone
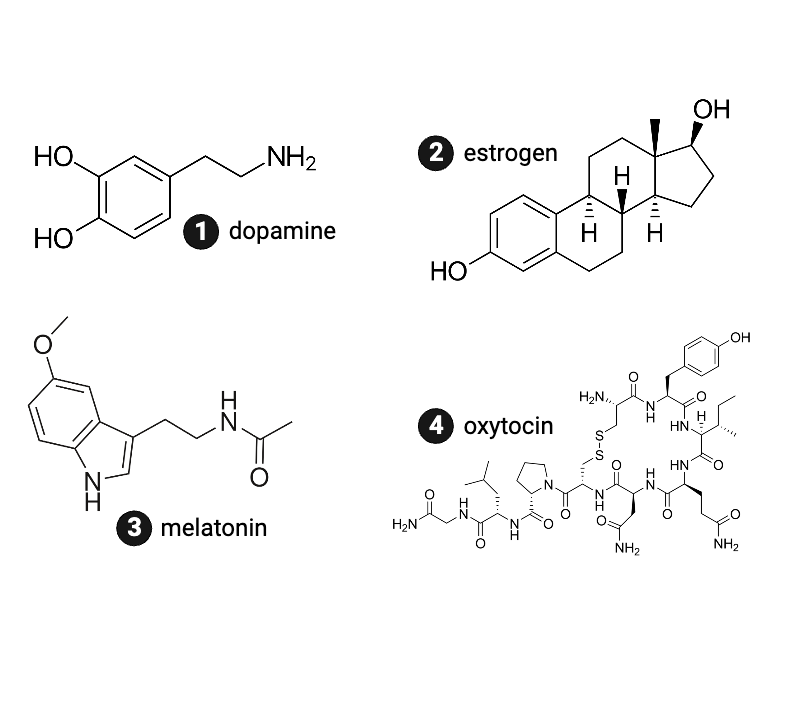
Which hormone is the most hydrophobic?
a. dopamine
b. estrogen
c. melatonin
d. oxytocin
b. estrogen
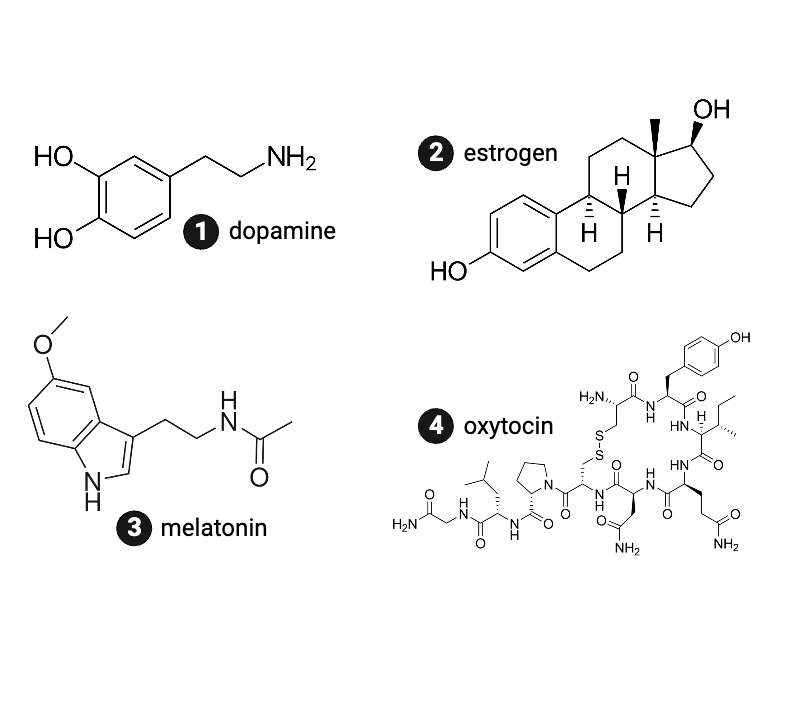
Which hormone is most hydrophilic?
a. dopamine
b. estrogen
c. melatonin
d. oxytocin
d. oxytocin
Which statement accurately describes a receptor? Select all that apply.
a. A receptor binds specific molecules.
b. A receptor adds a phosphate group to a signaling molecule.
c. A receptor transports specific molecules through the cell membrane.
d. A receptor can be found on the exterior or the interior of a cell.
a. A receptor binds specific molecules.
d. A receptor can be found on the exterior or the interior of a cell.
Which term refers to the process of adding a phosphate group to a molecule?
a. phosphorylation
b. phosphatase
c. dephosphorylation
d. gene expression
e. integration
a. phosphorylation
Which term refers to an enzyme that adds a phosphate group to another molecule?
a. kinase
b. phosphatase
c. receptor
a. kinase
Which type of enzyme removes a phosphate group from a molecule?
a. kinase
b. phosphatase
c. receptor
b. phosphatase
Which term refers to the process of removing a phosphate group from a molecule?
a. phosphorylation
b. phosphatase
c. dephosphorylation
d. gene expression
c. dephosphorylation
Which term refers to the process of using genetic information to produce new proteins?
a. phosphorylation
b. gene expression
c. cellular response
b. gene expression
When receptors bind signaling molecules, which type of cellular response will require the most time to occur?
a. activating existing proteins
b. deactivating existing proteins
c. producing new proteins
c. producing new proteins
Which response can result from phosphorylation of a receptor?
a. activation of the receptor
b. inhibition of the receptor
c. either activation or inhibition of a receptor
c. either activation or inhibition of a receptor
Dephosphorylation of a receptor can result in which of the following?
a. activation of the receptor
b. inhibition of the receptor
c. either activation or inhibition of the receptor
c. either activation or inhibition of the receptor
Which sequence accurately describes the steps of signaling by a hydrophilic hormone?
a. Sequence A
b. Sequence B
c. Sequence C
c. Sequence C
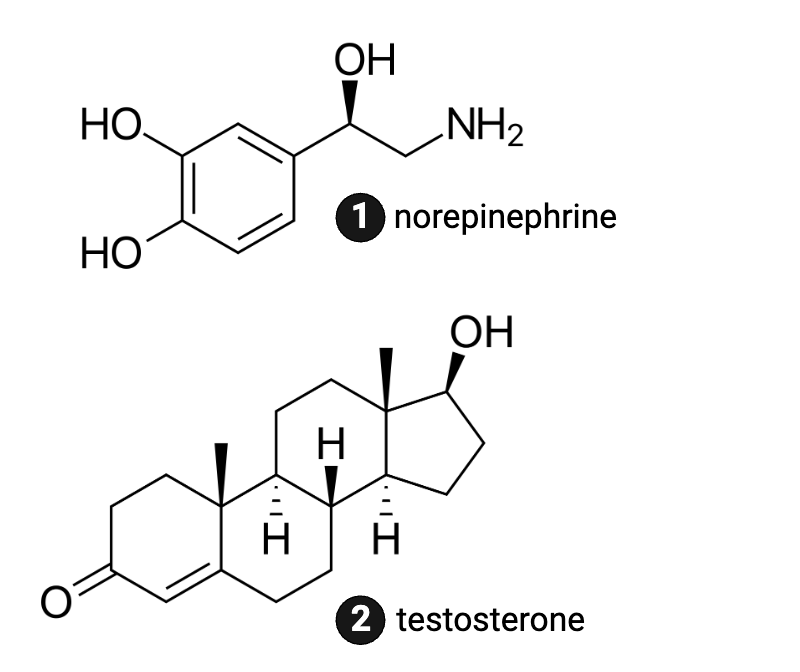
Which molecule is more likely to diffuse through a phospholipid bilayer?
a. norepinephrine
b. testosterone
b. testosterone
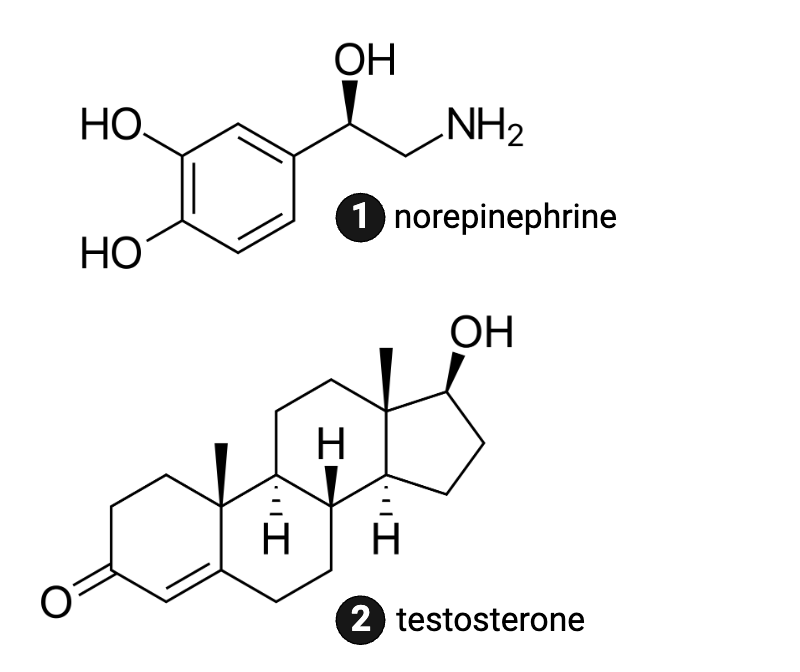
Which molecule is more likely to bind to a membrane receptor?
a. norepinephrine
b. testosterone
a. norepinephrine
A nonpolar signaling molecule is likely to bind to a _________ receptor.
a. intracellular
b. membrane
a. intracellular
A hydrophilic signaling molecule is likely to bind to a __________ receptor.
a. intracellular
b. membrane
b. membrane
A signaling molecule that directly regulates gene expression is likely to bind to a _________ receptor.
a. intracellular
b. membrane
a. intracellular
Which process is typically the first step of a signaling pathway?
a. An enzyme degrades the signaling molecule.
b. A hydrophobic interaction occurs between the signaling molecule and the receptor.
c. An enzyme phosphorylates the receptor.
d. A signaling molecule binds to a receptor.
d. A signaling molecule binds to a receptor.
Which statements accurately describe the binding of a signaling molecule to a receptor? Select all that apply.
a. Binding can be transient, enabling the signaling molecule to dissociate quickly from the receptor.
b. Binding can be prolonged, creating a stable complex consisting of the signaling molecule and receptor.
c. Binding can cause the protein to change shape.
d. Binding occurs only with specific types of receptors.
a. Binding can be transient, enabling the signaling molecule to dissociate quickly from the receptor.
b. Binding can be prolonged, creating a stable complex consisting of the signaling molecule and receptor.
c. Binding can cause the protein to change shape.
d. Binding occurs only with specific types of receptors.
Which statements about signaling molecules are accurate? Select all that apply.
a. A signaling molecule with a high affinity for a receptor is less likely to bind.
b. A signaling molecule with a high affinity for a receptor is more likely to bind.
c. A signaling molecule will bind to any receptor.
d. A signaling molecule will bind only to a receptor with a certain structure.
b. A signaling molecule with a high affinity for a receptor is more likely to bind.
d. A signaling molecule will bind only to a receptor with a certain structure.
Which statements about the affinity between a signaling molecule and its receptor are accurate? Select all that apply.
a. Affinity depends on the polarity or charge of the receptor's binding site.
b. Affinity depends on how well the signaling molecule fits into the receptor's binding site.
c. Affinity is a measure of how quickly a signaling molecule binds to its receptor
d. Affinity is a measure of the strength of binding of a signaling molecule to its receptor.
a. Affinity depends on the polarity or charge of the receptor's binding site.
b. Affinity depends on how well the signaling molecule fits into the receptor's binding site.
d. Affinity is a measure of the strength of binding of a signaling molecule to its receptor.
True or false? Upon binding a signaling molecule, an intracellular receptor can only activate existing proteins in the intracellular fluid.
a. true
b. false
b. false
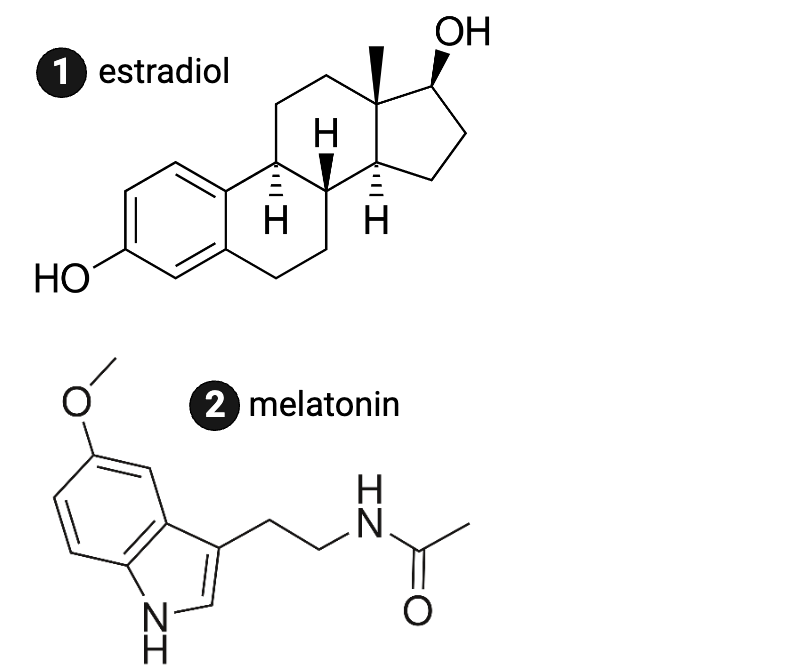
Which molecule is more likely to diffuse through a phospholipid bilayer?
a. estrogen
b. melatonin
a. estrogen
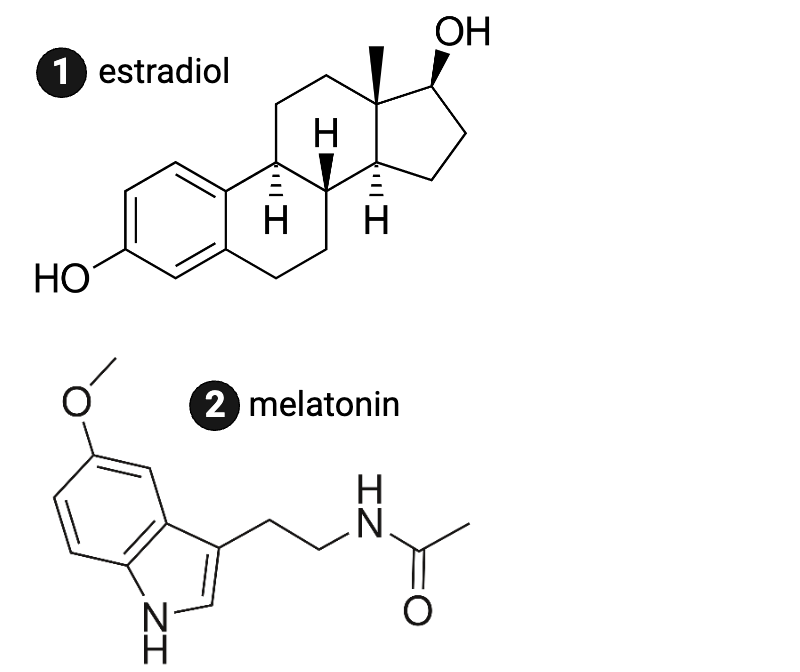
Which molecule is more likely to bind to an intracellular receptor?
a. estrogen
b. melatonin
a. estrogen
A polar signaling molecule is likely to bind to a _________ receptor.
a. intracellular
b. membrane
b. membrane
An intracellular receptor is likely to bind a __________ signaling molecule.
a. hydrophobic
b. hydrophilic
a. hydrophobic
A signaling molecule that binds to an intracellular receptor is likely part of a cell signaling pathway that _______.
a. directly affects gene expression
b. activates existing proteins in the cell
a. directly affects gene expression
Upon binding a signaling molecule, an intracellular receptor likely initiates a _____ response
a. rapid (e.g., a change in protein activity)
b. slow (e.g., regulation of gene expression)
b. slow (e.g., regulation of gene expression)
Which of the following events would be most likely to initiate a cell signaling pathway?
a. A large, polar signaling molecule binds to a membrane receptor.
b. A small, nonpolar signaling molecule binds to a membrane receptor.
c. A large, nonpolar signaling molecule binds to a membrane receptor.
d. A large, polar signaling molecule binds to an intracellular receptor.
e. A small, nonpolar signaling molecule binds to an intracellular receptor.
a. A large, polar signaling molecule binds to a membrane receptor.
Which statement accurately describes the process of signal transduction?
a. Signal transduction is the conversion of an extracellular signal into an intracellular response.
b. Signal transduction is the transport of signaling molecules in the bloodstream.
c. Signal transduction is the degradation of a signaling molecule by an enzyme.
d. Signal transduction is the termination of a signaling pathway in a cell.
a. Signal transduction is the conversion of an extracellular signal into an intracellular response.
What is the function of secondary messengers in signal transduction?
a. Secondary messengers degrade signaling molecules.
b. Secondary messengers degrade receptors.
c. Secondary messengers spread a signal within a cell.
d. Secondary messengers terminate a signaling pathway.
c. Secondary messengers spread a signal within a cell.
Which statement about amplification is accurate?
a. Amplification increases the number of signaling molecules in the extracellular environment.
b. Amplification increases the number of activated proteins in the intracellular fluid.
c. Amplification is the result of the increase in duration of a cellular response.
d. Amplification leads to the degradation of secondary messengers that is regulated by negative feedback.
b. Amplification increases the number of activated proteins in the intracellular fluid.
True or false? Amplification decreases the magnitude of a cell's response to signaling molecules.
a. true
b. false
b. false
Which statements about amplification are accurate? Select all that apply.
a. Amplification enables a few signaling molecules to affect the activity of many proteins.
b. Amplification ensures the termination of a signaling pathway.
c. Amplification promotes negative feedback in a signaling pathway.
a. Amplification enables a few signaling molecules to affect the activity of many proteins.
Which statements about termination are accurate? Select all that apply.
a. Termination converts a signaling molecule to a secondary messenger.
b. Termination enables a few signaling molecules to affect the activity of many proteins.
c. Termination enables a cell to deactivate the proteins in a signaling pathway after responding to signaling molecules.
d. Termination occurs when the product of one step in a signaling pathway inhibits a previous step.
a. Termination converts a signaling molecule to a secondary messenger.
c. Termination enables a cell to deactivate the proteins in a signaling pathway after responding to signaling molecules.
d. Termination occurs when the product of one step in a signaling pathway inhibits a previous step.
Which mechanisms would terminate a signaling pathway? Select all that apply.
a. Enzymes inside the cell break down signaling molecules.
b. Enzymes inside the cell break down receptors and activate secondary messengers.
c. Proteins activated in a signaling pathway inhibit the activity of receptors.
d. Receptors activate secondary messengers.
a. Enzymes inside the cell break down signaling molecules.
c. Proteins activated in a signaling pathway inhibit the activity of receptors.
Which sequence accurately describes a signaling pathway?
a. Reception of the signal → Transduction of the signal → Amplification of the signal → Termination of the signal → Cellular Response
b. Reception of the signal → Transduction of the signal → Amplification of the signal → Cellular Response → Termination of the signal
c. Reception of the signal → Amplification of the signal → Transduction of the signal → Cellular Response → Termination of the signal
d. Reception of the signal → Amplification of the signal → Transduction of the signal → Termination of the signal → Cellular Response
b. Reception of the signal → Transduction of the signal → Amplification of the signal → Cellular Response → Termination of the signal
Which functions are performed by a secondary messenger? Select all that apply.
a. amplifying a signal
b. transmitting a signal to the nucleus
c. activating proteins inside a cell
d. converting a signal from one molecular form to another
a. amplifying a signal
b. transmitting a signal to the nucleus
c. activating proteins inside a cell
d. converting a signal from one molecular form to another
Which processes are examples of amplification in a signaling pathway? Select all that apply.
a. The phosphorylation of multiple proteins by a single kinase
b. The degradation of multiple signaling molecules by a single enzyme
c. The activation of multiple kinases by a single receptor.
d. The inhibition of multiple receptors through negative feedback.
a. The phosphorylation of multiple proteins by a single kinase
c. The activation of multiple kinases by a single receptor.
Which processes can occur during signal transduction? Select all that apply.
a. The receptor is phosphorylated.
b. The receptor changes conformation.
c. Enzymes are activated.
d. Secondary messengers are activated.
e. The receptor is degraded.
f. Proteins enter the nucleus to affect gene expression.
a. The receptor is phosphorylated.
b. The receptor changes conformation.
c. Enzymes are activated.
d. Secondary messengers are activated.
f. Proteins enter the nucleus to affect gene expression.
Which statement accurately describes how phosphorylation can facilitate signal transduction?
a. An enzyme adds a hydrophobic molecule to a receptor.
b. A signaling molecule binds to a receptor.
c. A receptor adds a phosphate group to a protein inside the cell.
d. A hydrophilic molecule is converted to a hydrophobic molecule.
c. A receptor adds a phosphate group to a protein inside the cell.
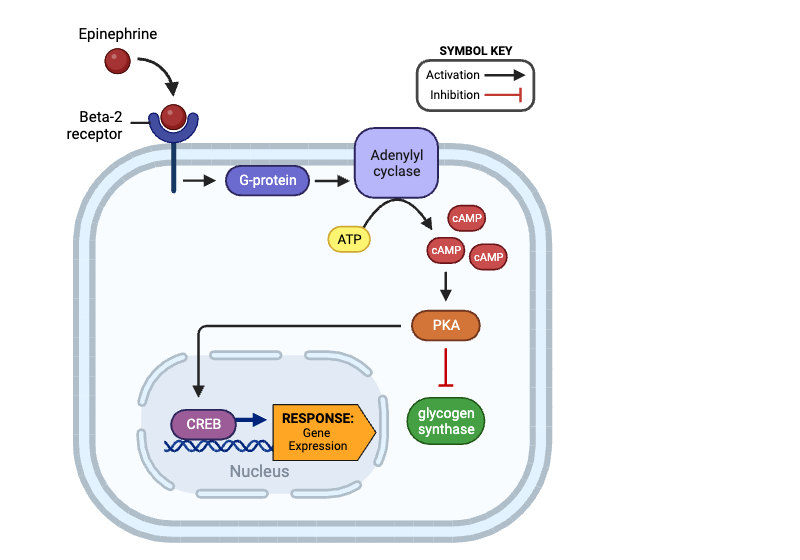
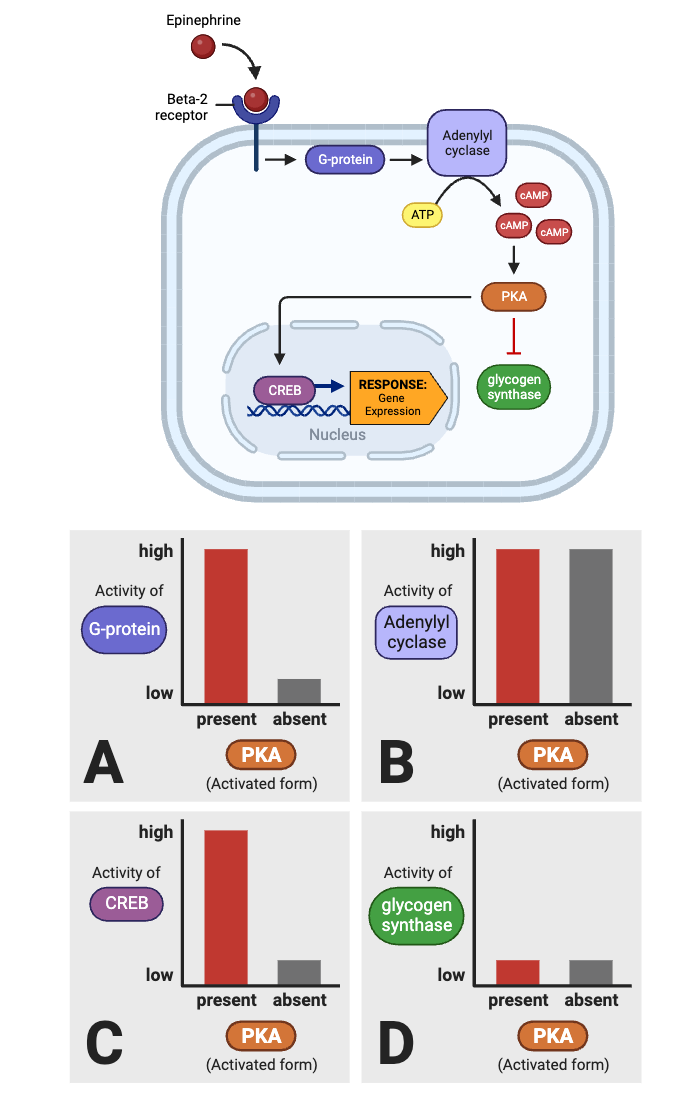
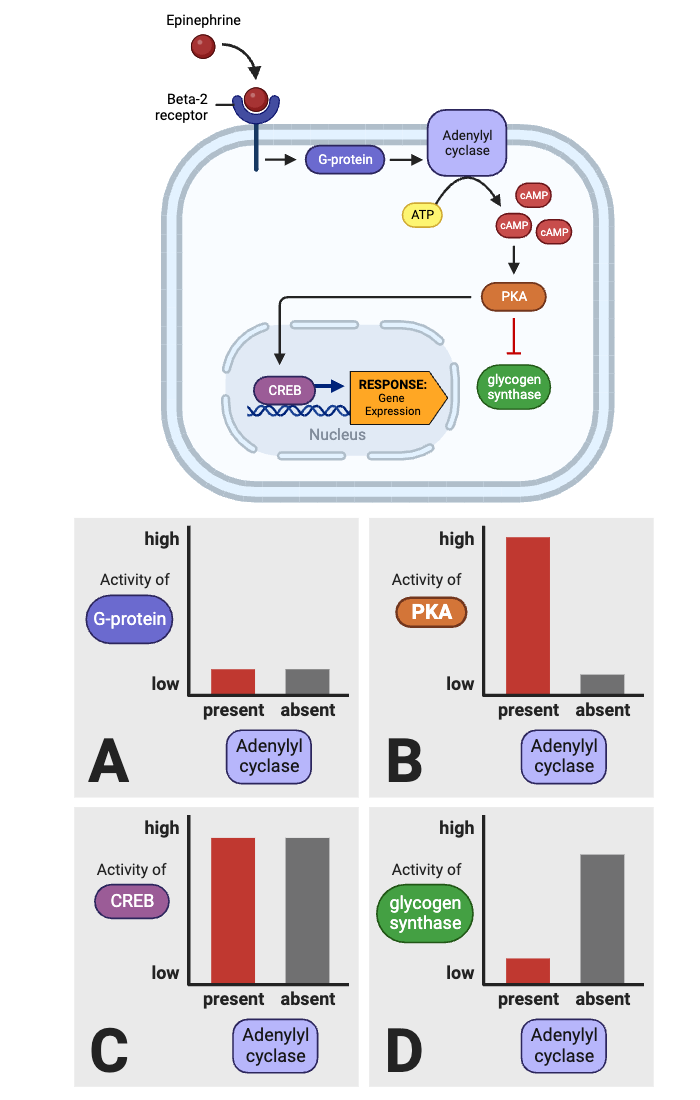
True or false? After binding epinephrine, a beta-2 receptor can activate a G-protein.
true
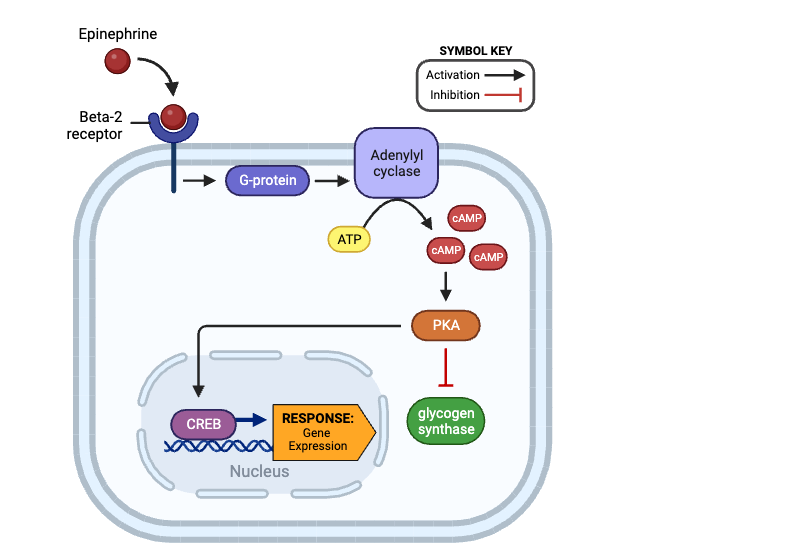
True or false? Once activated, a G-protein can directly inhibit the activity of adenylyl cyclase.
false
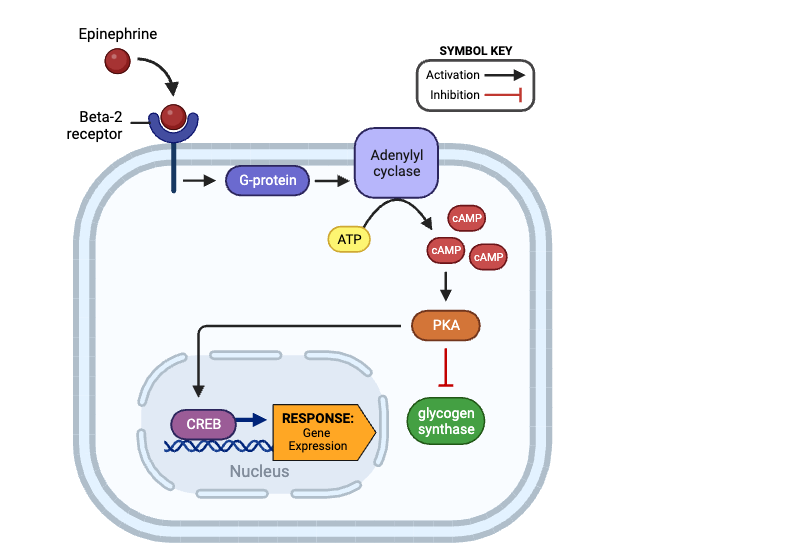
True or false? An activated adenylyl cyclase can produce Cyclic AMP (cAMP).
true
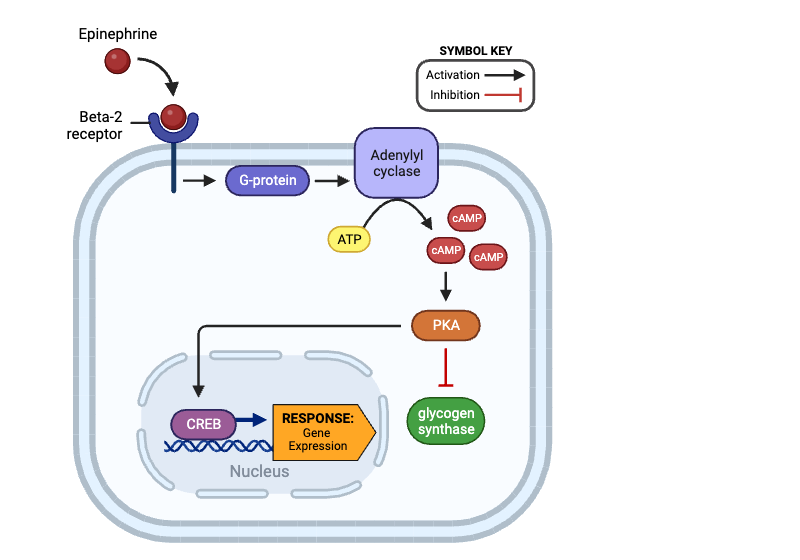
True or false? An activated PKA can activate a G-protein.
false
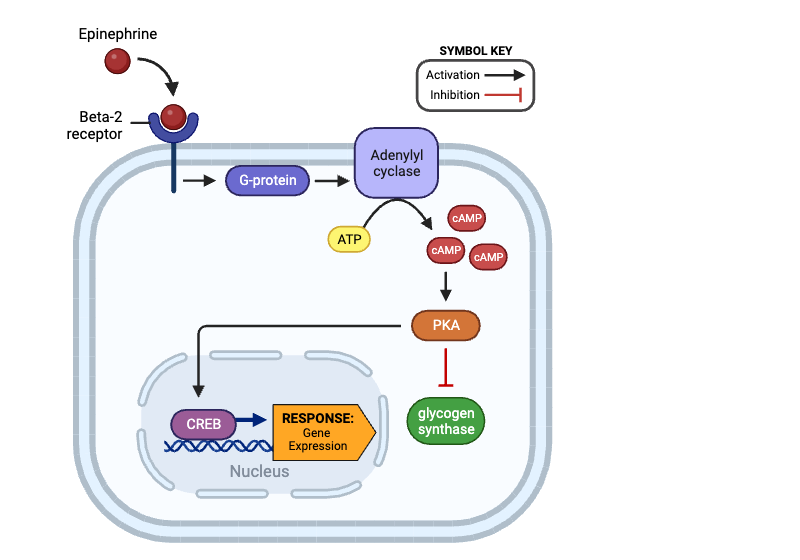
True or false? Once activated, PKA can directly activate glycogen synthase.
false
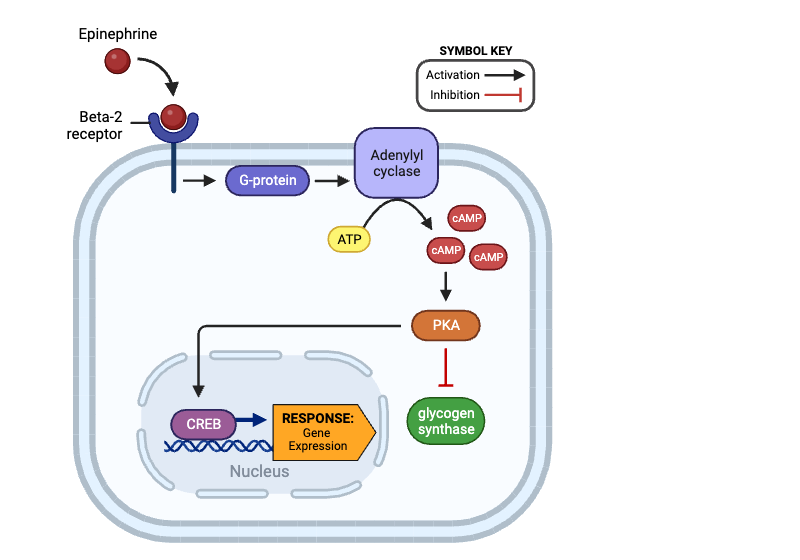
True or false? Once activated, PKA can directly activate CREB.
true
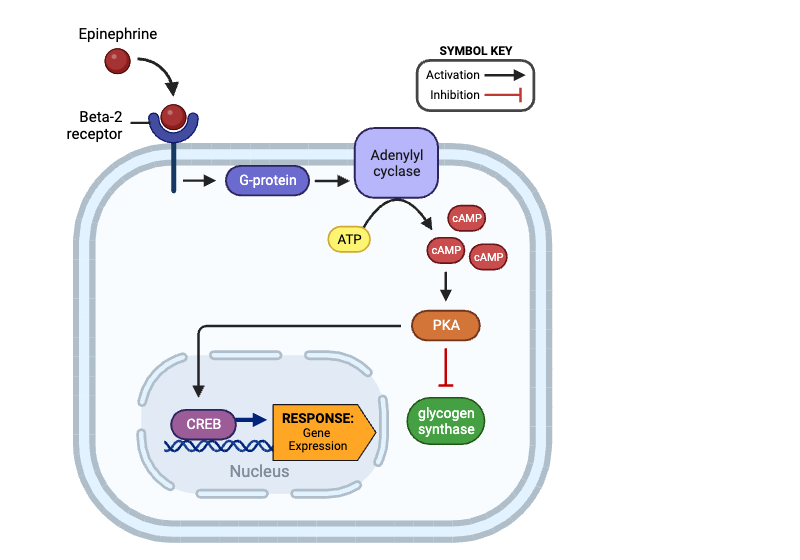
True or false? The production of cAMP by adenylyl cyclase amplifies the signal within a cell.
true
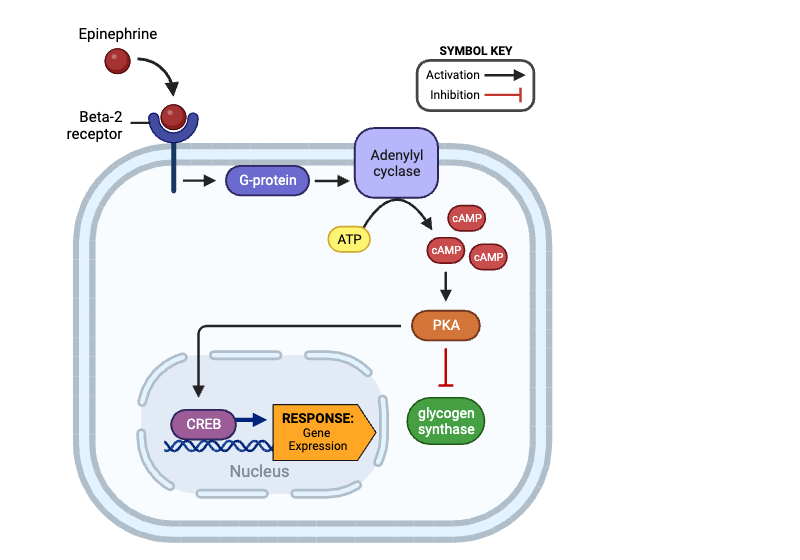
True or false? Once activated, CREB can affect gene expression.
true
Which molecule directly activates adenylyl cyclase?
a. beta-2 receptor
b. G-protein
c. cAMP
d. PKA
e. glycogen synthase
f. CREB
b. G-protein
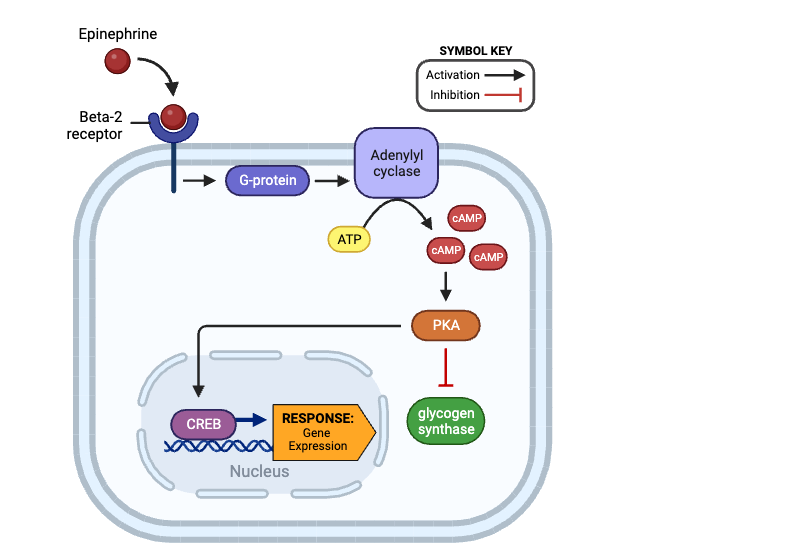
Which molecules indirectly activate adenylyl cyclase? Select all that apply.
a. beta-2 receptor
b. G-protein
c. cAMP
d. PKA
e. glycogen synthase
f. CREB
a. beta-2 receptor
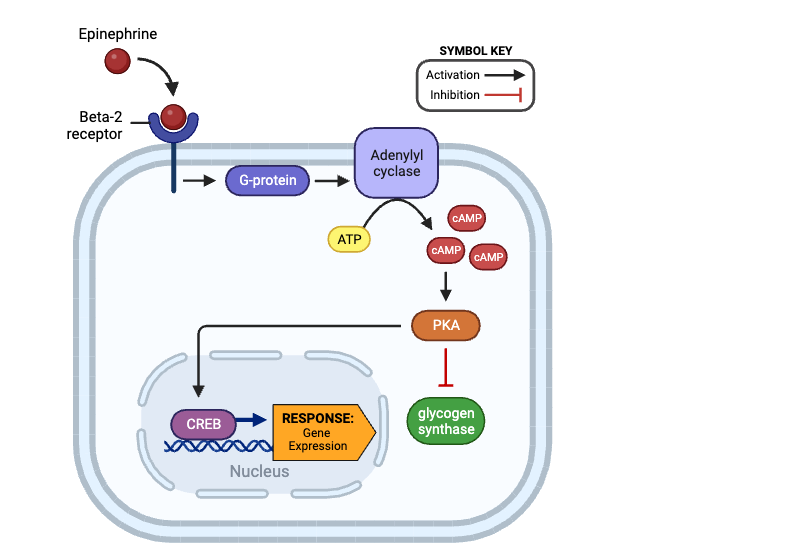
Which molecule directly activates PKA?
a. beta-2 receptor
b. G-protein
c. adenylyl cyclase
d. cAMP
e. glycogen synthase
f. CREB
d. cAMP
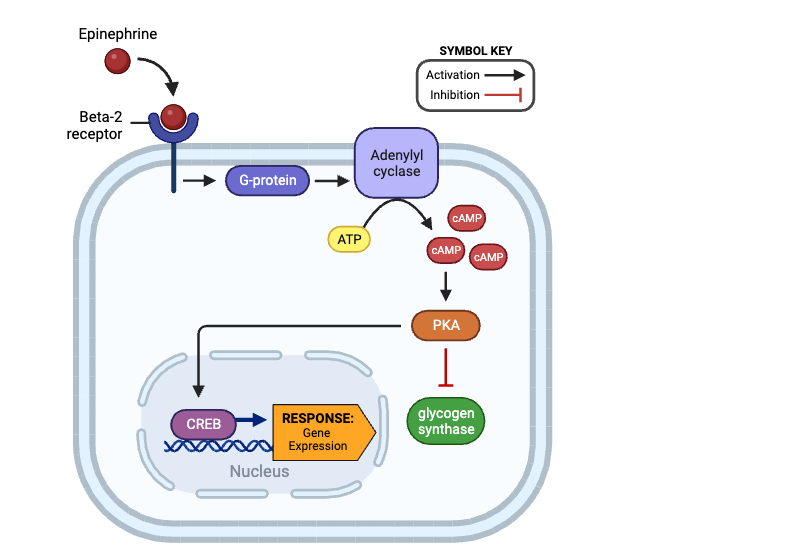
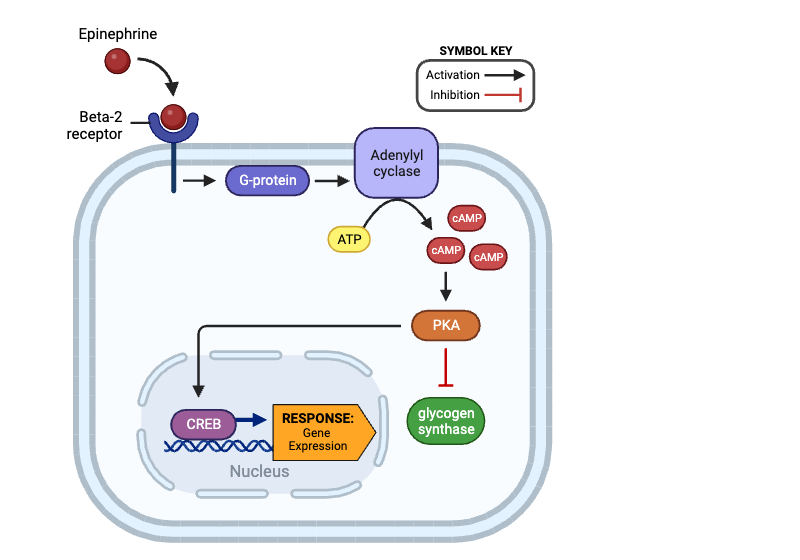
Which molecules indirectly activate PKA? Select all that apply.
a. beta-2 receptor
b. G-protein
c. adenylyl cyclase
d. cAMP
e. glycogen synthase
f. CREB
a. beta-2 receptor
b. G-protein
c. adenylyl cyclase
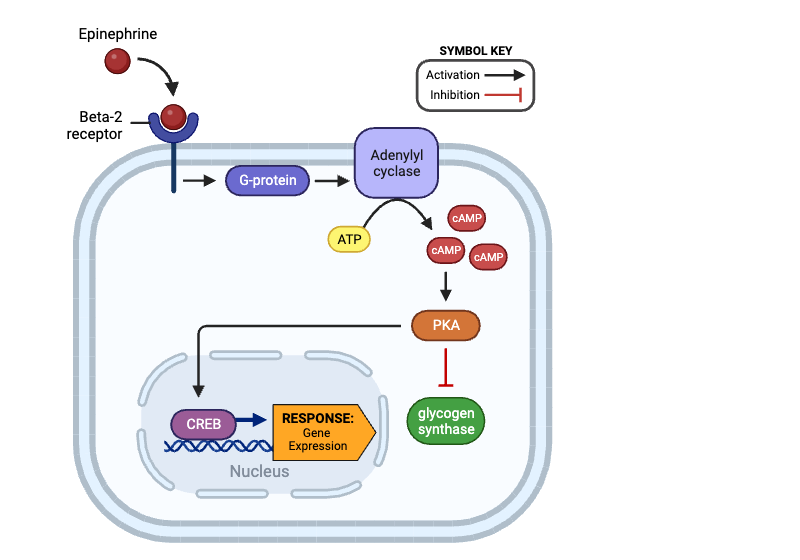
Which molecules indirectly inhibit glycogen synthase? Select all that apply.
a. beta-2 receptor
b. G-protein
c. adenylyl cyclase
d. cAMP
e. PKA
f. CREB
a. beta-2 receptor
b. G-protein
c. adenylyl cyclase
d. cAMP
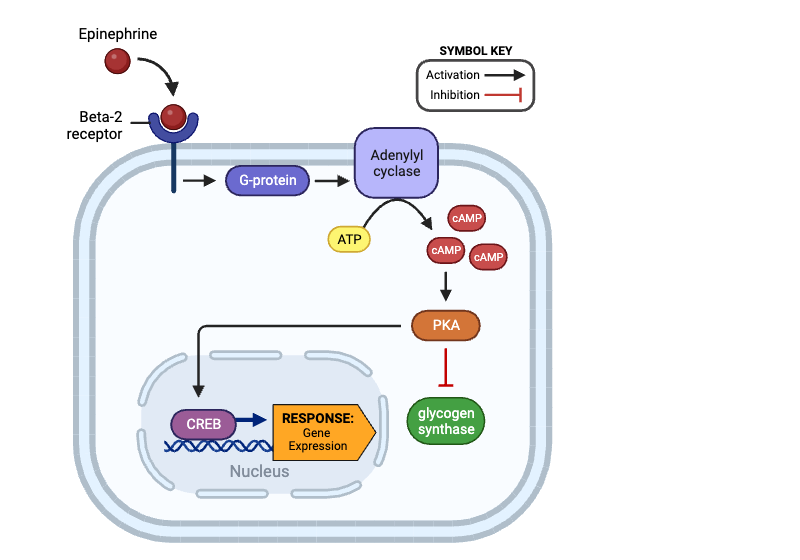
Which molecule directly inhibits glycogen synthase?
a. beta-2 receptor
b. G-protein
c. adenylyl cyclase
d. cAMP
e. PKA
f. CREB
e. PKA
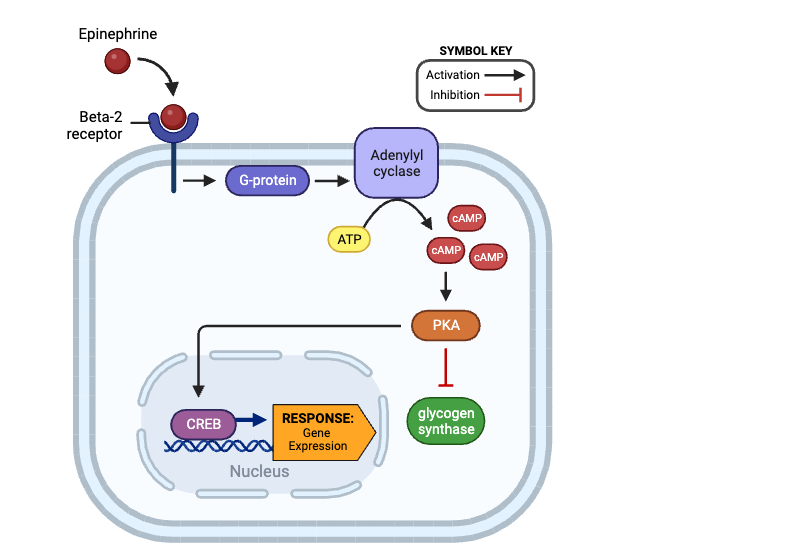
Which molecules are indirectly activated by a beta-2 receptor? Select all that apply.
a. G-protein
b. adenylyl cyclase
c. cAMP
d. PKA
e. glycogen synthase
f. CREB
b. adenylyl cyclase
c. cAMP
d. PKA
f. CREB
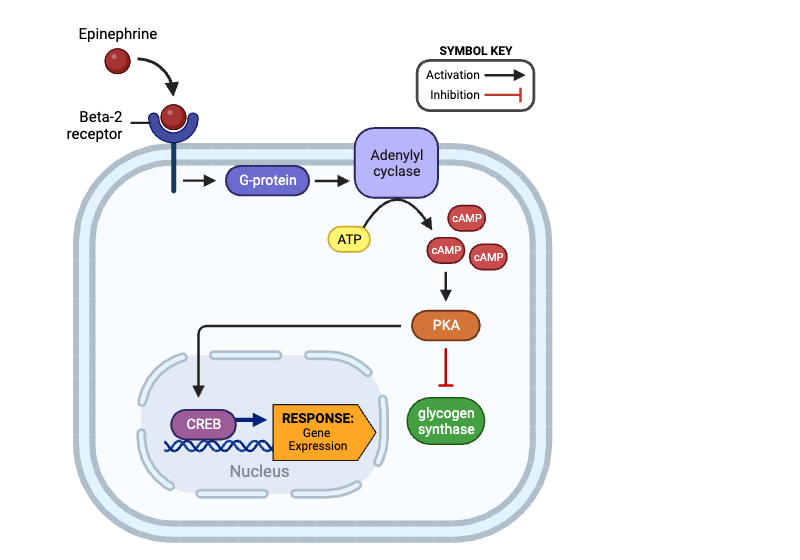
Which molecule enters the nucleus and affects gene expression?
a. beta-2 receptor
b. G-protein
c. adenylyl cyclase
d. cAMP
e. PKA
f. glycogen synthase
g. CREB
e. PKA
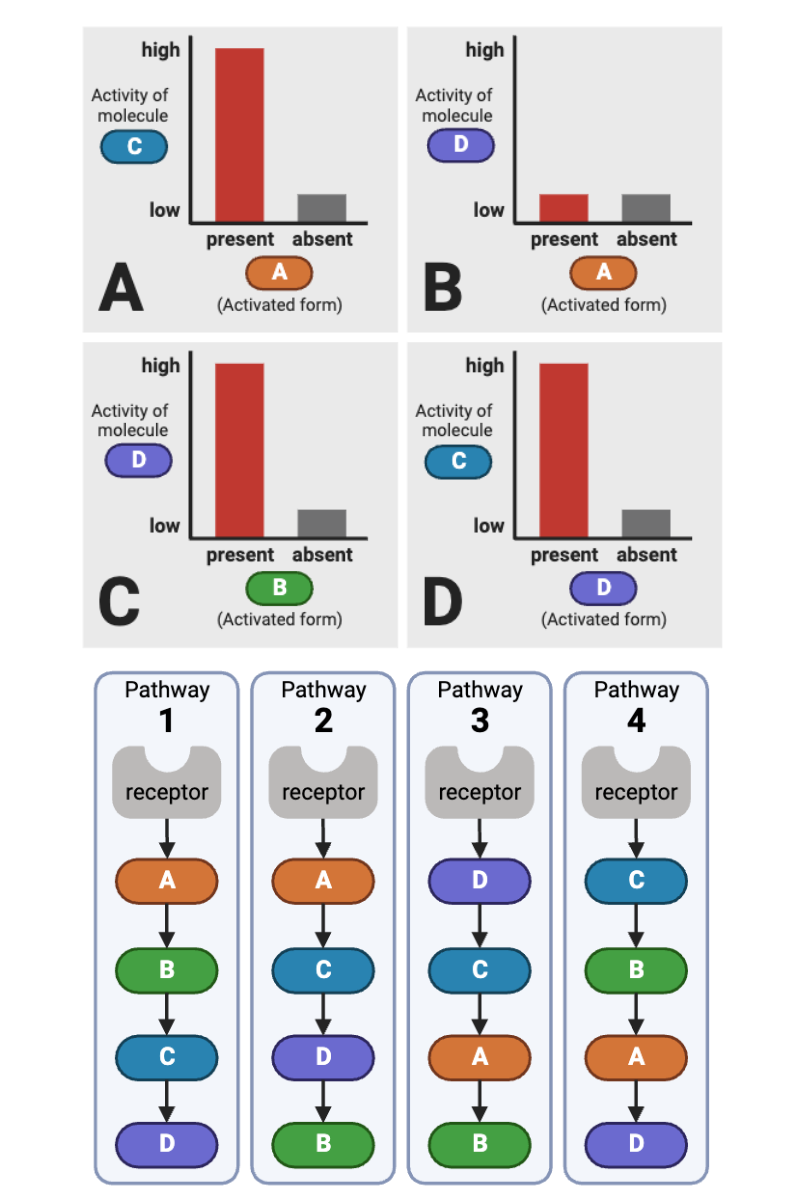
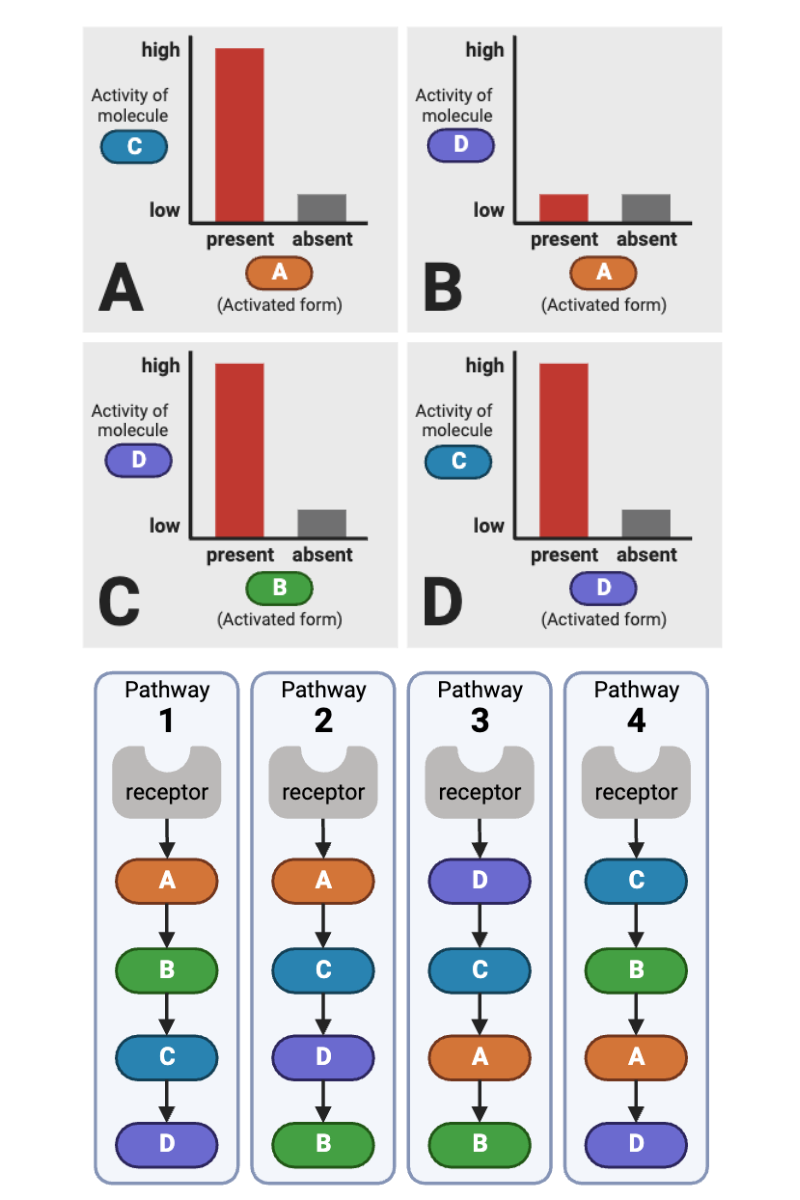
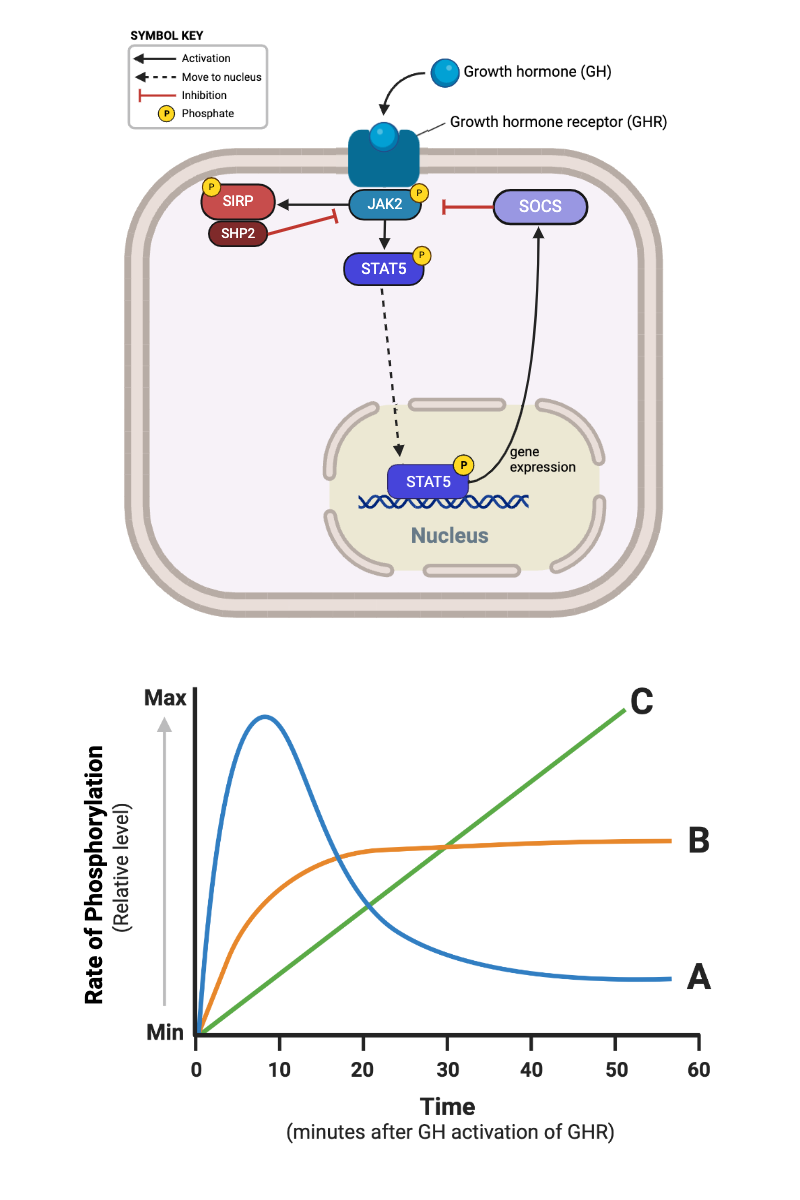
Which signaling pathways (1 through 4) in the bottom figure are consistent with the data in Plot A (upper left plot) of the top figure? Select all that apply.
a. Pathway 1 (Receptor → A → B → C → D)
b. Pathway 2 (Receptor → A → C → D → B)
c. Pathway 3 (Receptor → D → C → A → B)
d. Pathway 4 (Receptor → C → B → A → D)
a. Pathway 1 (Receptor → A → B → C → D)
b. Pathway 2 (Receptor → A → C → D → B)
Which signaling pathways (1 through 4) are consistent with the data in Plot B (upper right plot) of the top figure? Select all that apply.
a. Pathway 1 (Receptor → A → B → C → D)
b. Pathway 2 (Receptor → A → C → D → B)
c. Pathway 3 (Receptor → D → C → A → B)
d. Pathway 4 (Receptor → C → B → A → D)
c. Pathway 3 (Receptor → D → C → A → B)
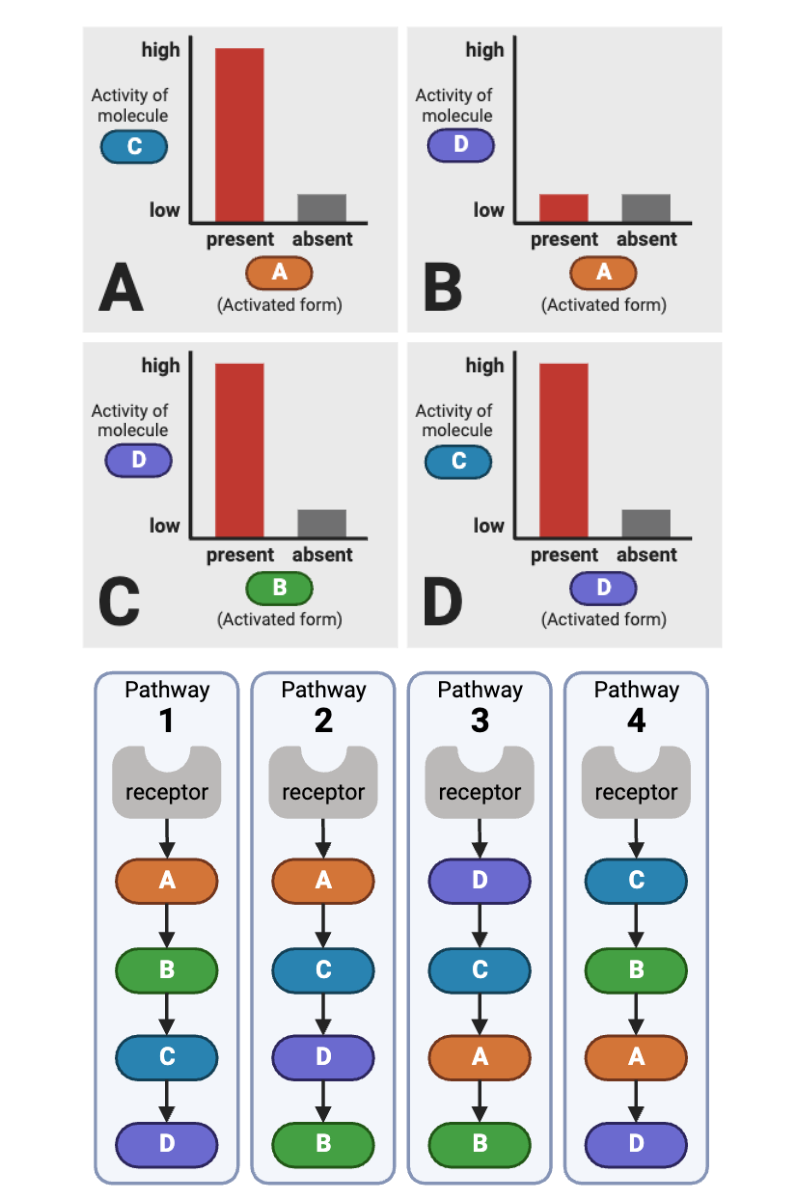
Which signaling pathways (1 through 4) are consistent with the data in Plot C (lower left plot) of the top figure? Select all that apply.
a. Pathway 1 (Receptor → A → B → C → D)
b. Pathway 2 (Receptor → A → C → D → B)
c. Pathway 3 (Receptor → D → C → A → B)
d. Pathway 4 (Receptor → C → B → A → D)
a. Pathway 1 (Receptor → A → B → C → D)
d. Pathway 4 (Receptor → C → B → A → D)
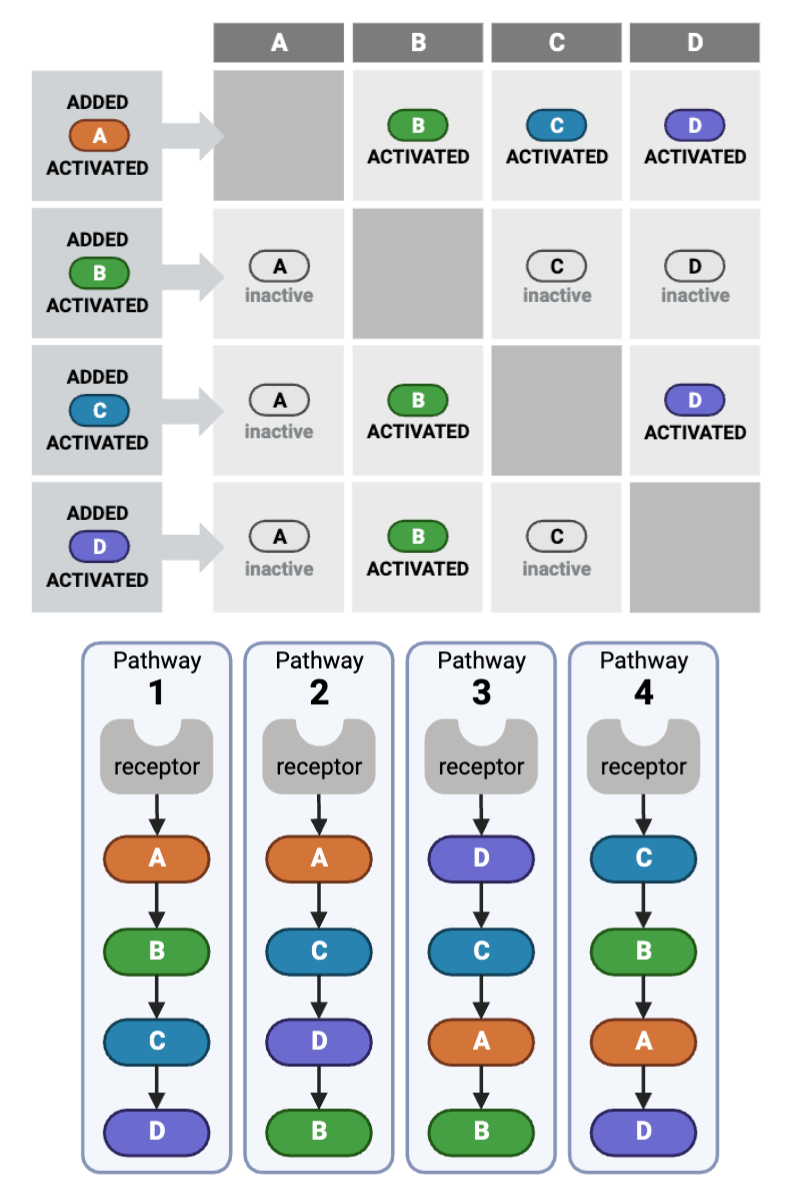
Which signaling pathways (1 through 4) are consistent with the data in Plot D (lower right plot) of the top figure? Select all that apply.
a. Pathway 1 (Receptor → A → B → C → D)
b. Pathway 2 (Receptor → A → C → D → B)
c. Pathway 3 (Receptor → D → C → A → B)
d. Pathway 4 (Receptor → C → B → A → D)
c. Pathway 3 (Receptor → D → C → A → B)
Which signaling pathway (1 through 4) is consistent with the data in the top figure?
a. Pathway 1 (Receptor → A → B → C → D)
b. Pathway 2 (Receptor → A → C → D → B)
c. Pathway 3 (Receptor → D → C → A → B)
d. Pathway 4 (Receptor → C → B → A → D)
b. Pathway 2 (Receptor → A → C → D → B)
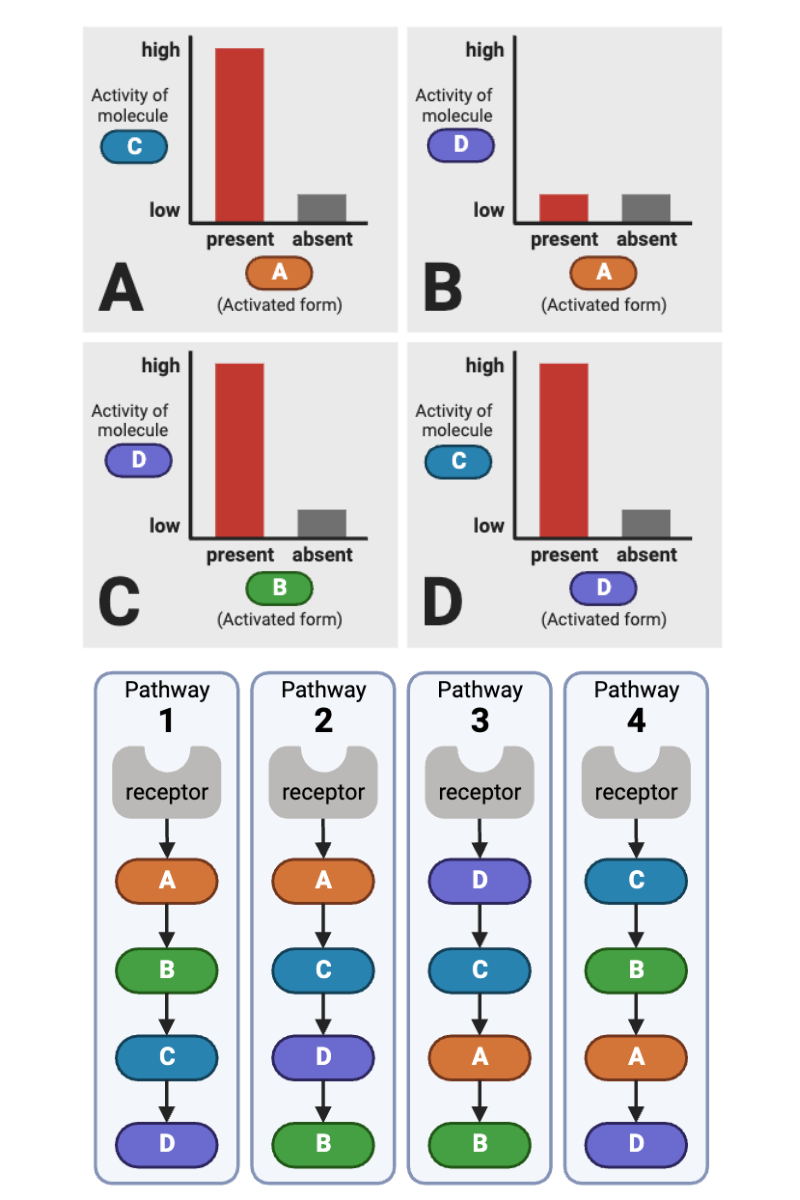
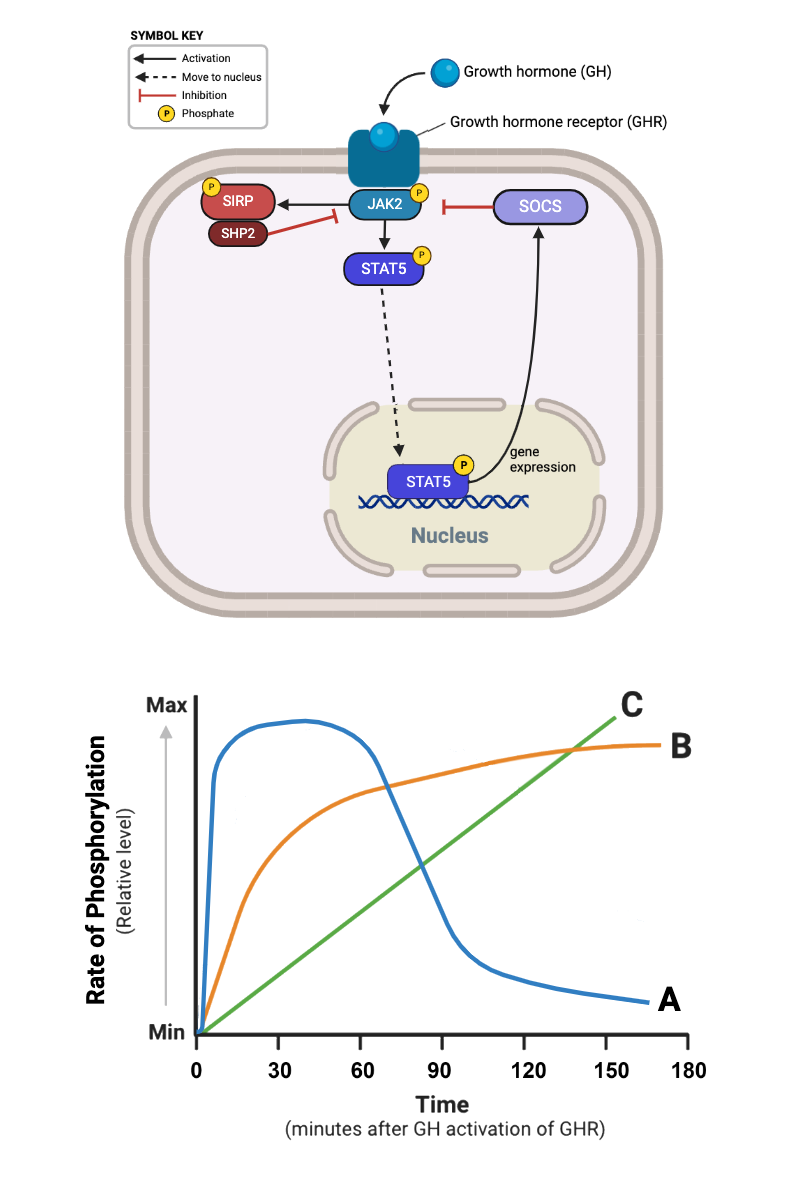
Which plots (A through D) in the bottom figure are consistent with the model of the signaling pathway in the top figure? Select all that apply.
a. Plot A
b. Plot B
c. Plot C
d. Plot D
b. Plot B
c. Plot C
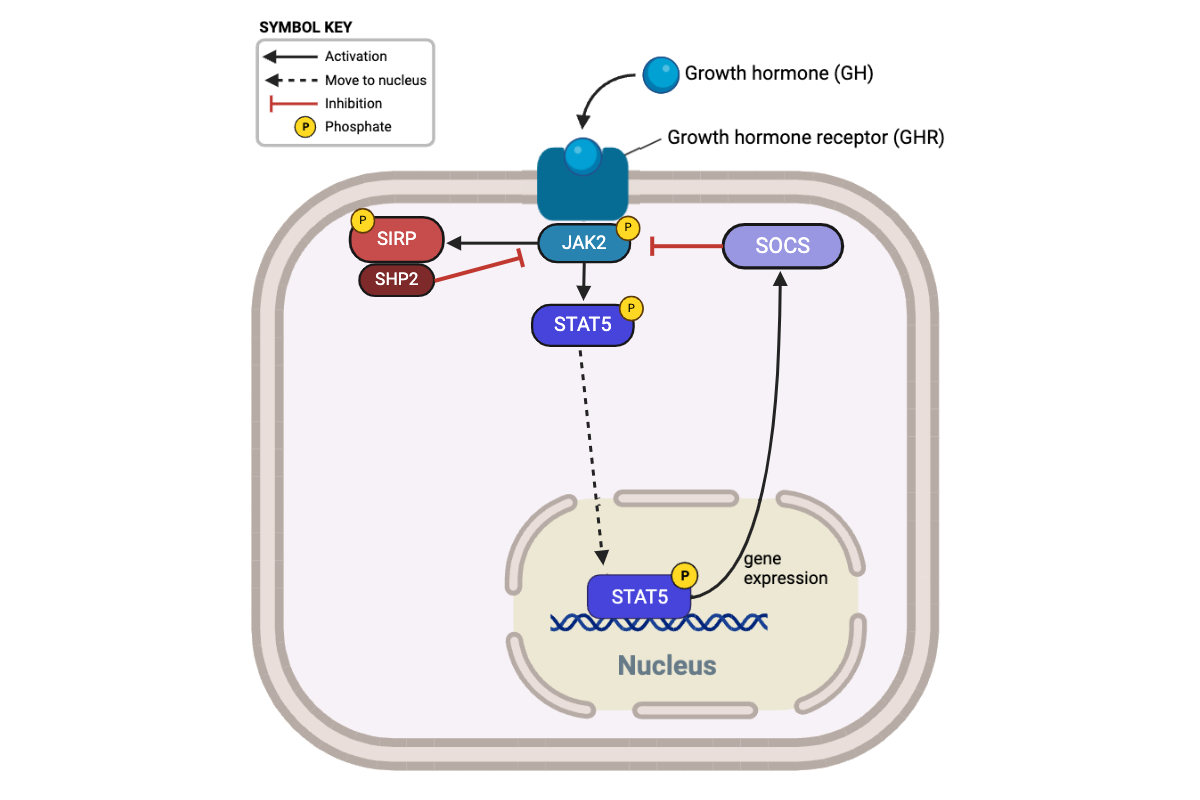
Which plots (A through D) in the bottom figure are consistent with the model of the signaling pathway in the top figure? Select all that apply.
a. Plot A
b. Plot B
c. Plot C
d. Plot D
b. Plot B
d. Plot D
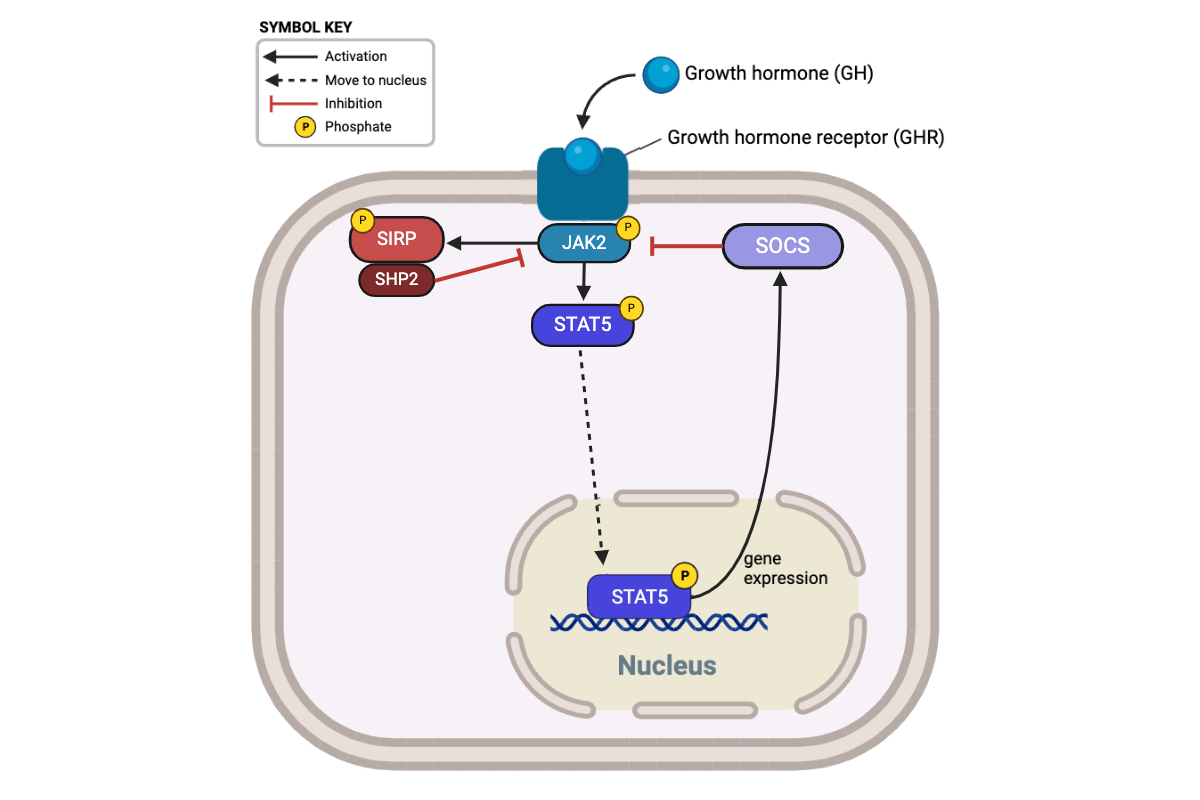
Which proteins directly terminate this signaling pathway by inhibiting JAK2? Select all that apply.
a. GHR
b. SIRP
c. SOCS
d. STAT5
e. SHP2
c. SOCS
e. SHP2
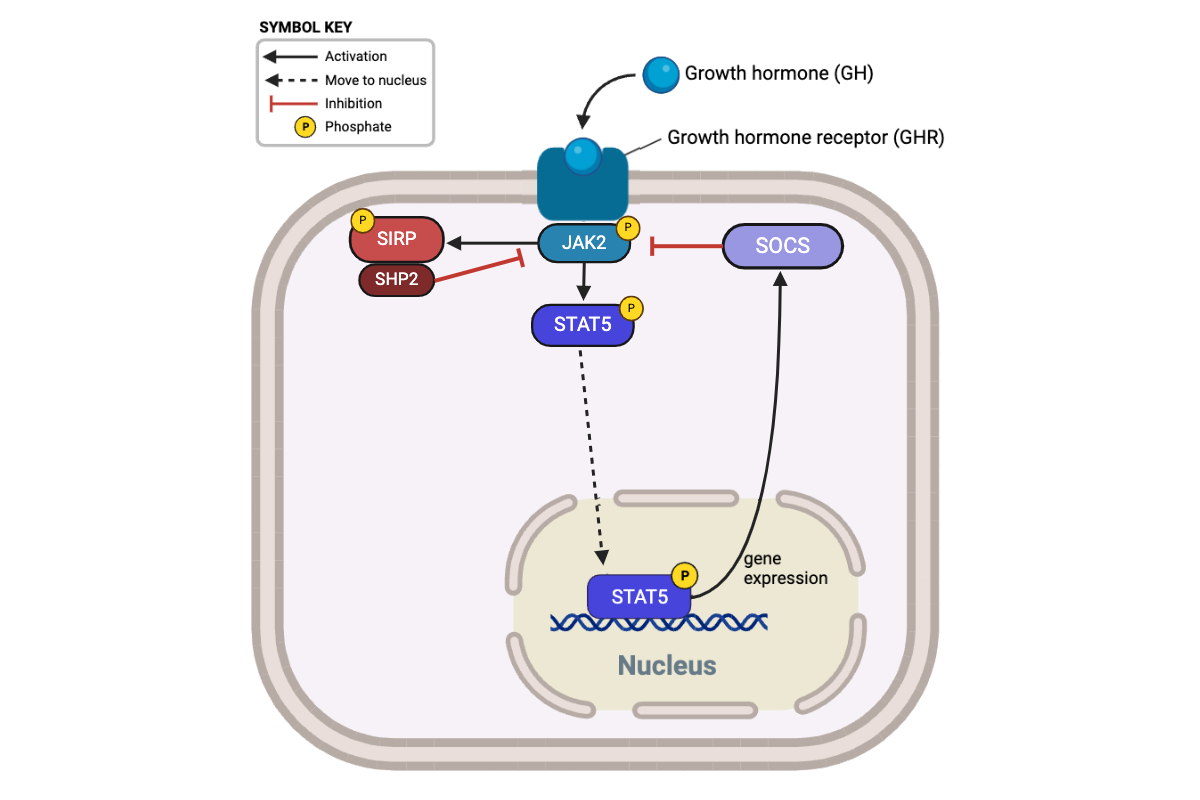
Which processes directly reduce the activity of proteins in this signaling pathway? Select all that apply.
a. binding of growth hormone by a receptor
b. phosphorylation of JAK2 by a growth-hormone receptor
c. phosphorylation of STAT5 by JAK2
d. dephosphorylation of JAK2 by SHP2
e. inhibition of JAK2 by SOCS
d. dephosphorylation of JAK2 by SHP2
e. inhibition of JAK2 by SOCS
True or false? When a signaling molecule activates a growth-hormone receptor, SOCS immediately inhibits the activity of JAK2.
False
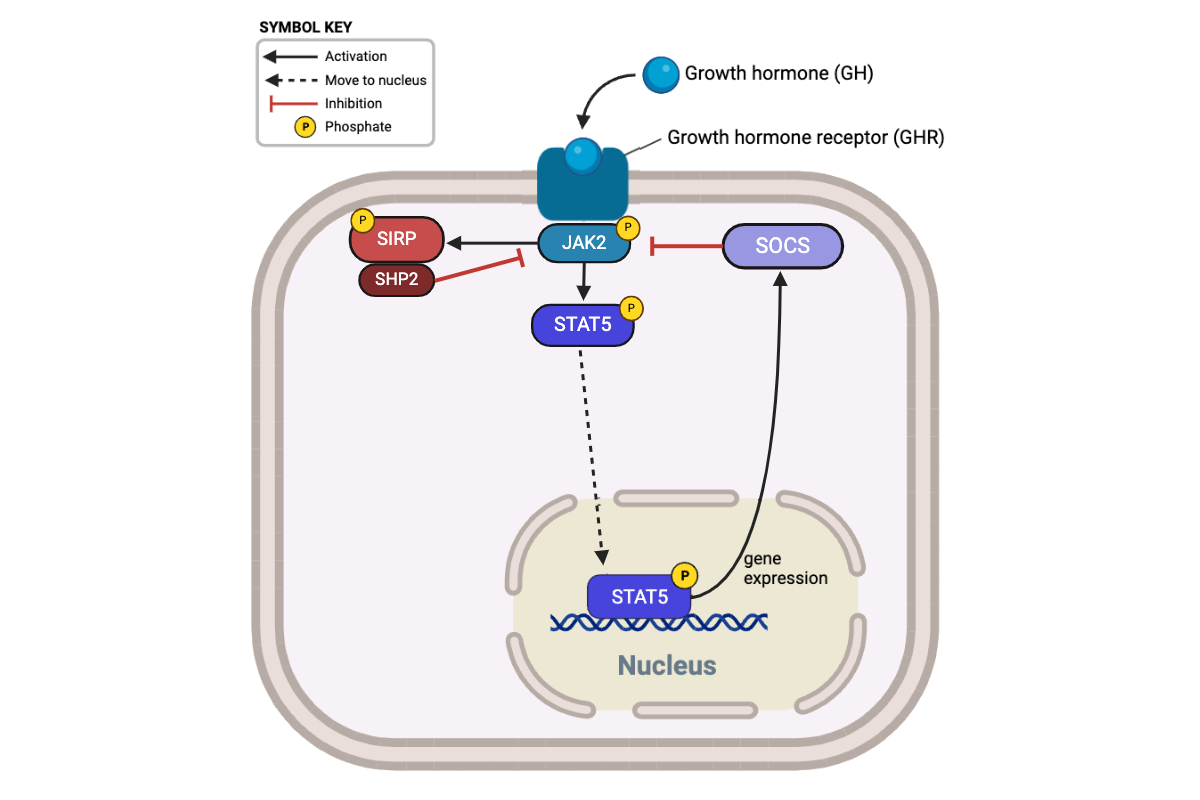
True or false? SHP2 indirectly increases the abundance of phosphorylated STAT5 in the presence of growth hormone.
False
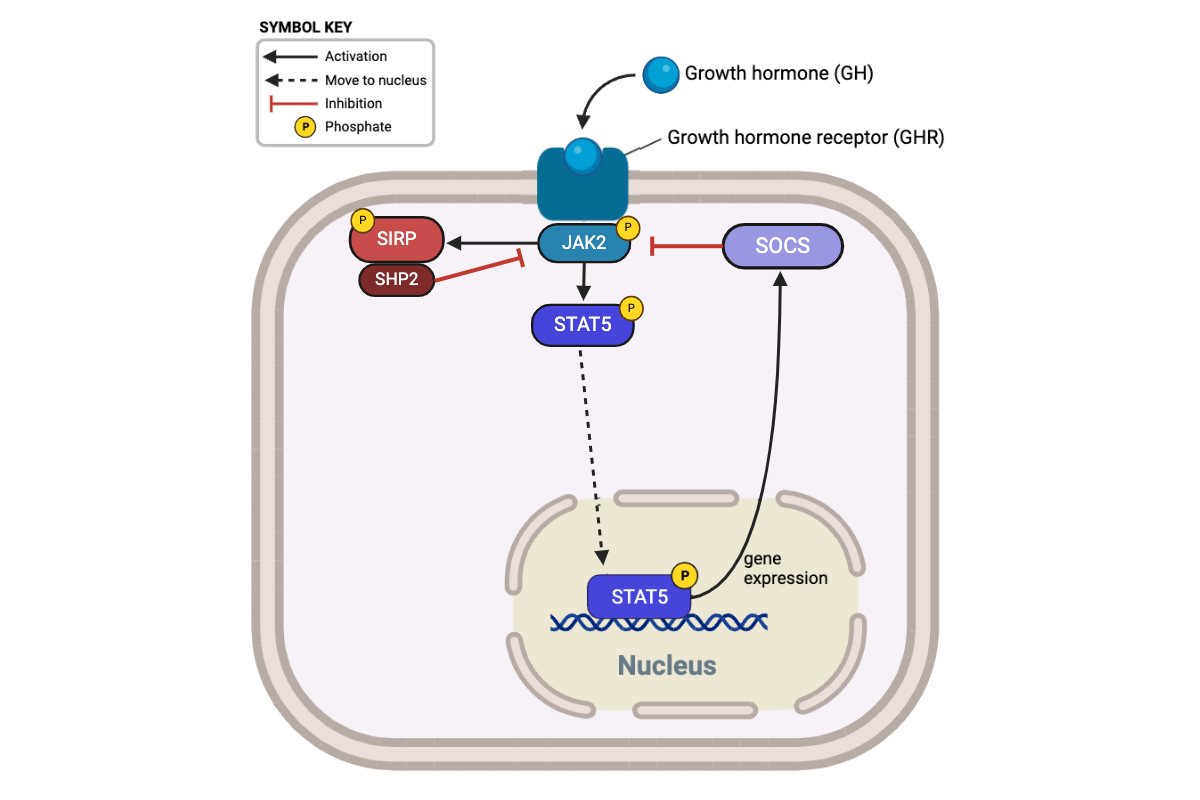
True or false? Inhibition of SHP2 would completely eliminate negative feedback in this signaling pathway.
False
Which relationship describes the effect of negative feedback on the phosphorylation of STAT5?
Relationship A
Which relationship would describe the rate of phosphorylation of STAT5 in the presence of a drug that inhibits the activity of SHP2?
a. Relationship A
b. Relationship B
c. Relationship C
a. Relationship A
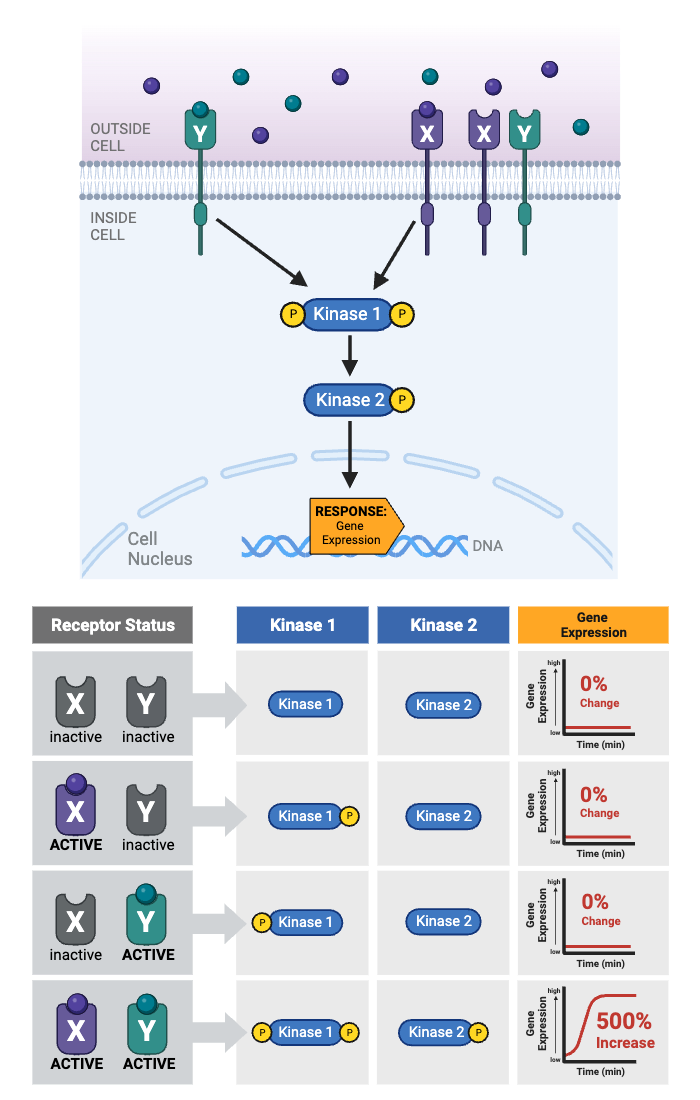
Which condition would alter gene expression?
a. Only Receptor X is activated.
b. Only Receptor Y is activated.
c. Either Receptor X or Receptor Y is activated.
d. Both Receptor X and Receptor Y are activated.
e. Neither Receptor X nor Receptor Y is activated.
d. Both Receptor X and Receptor Y are activated.
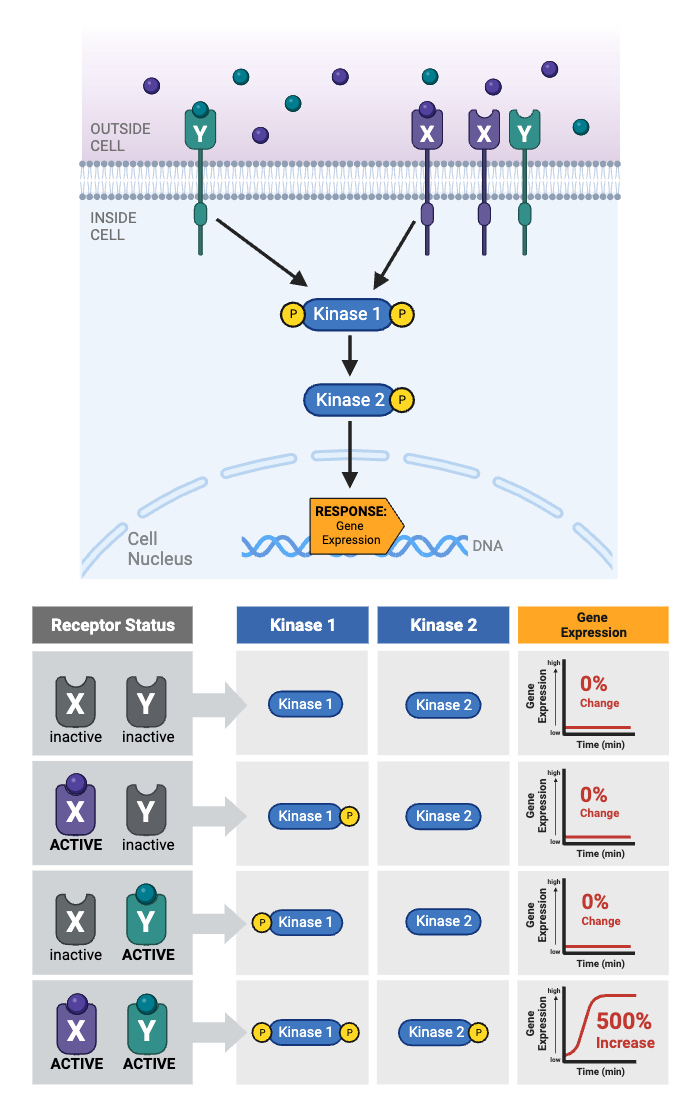
Which protein integrates the two signaling pathways?
a. Receptor X
b. Receptor Y
c. Kinase 1
d. Kinase 2
c. Kinase 1
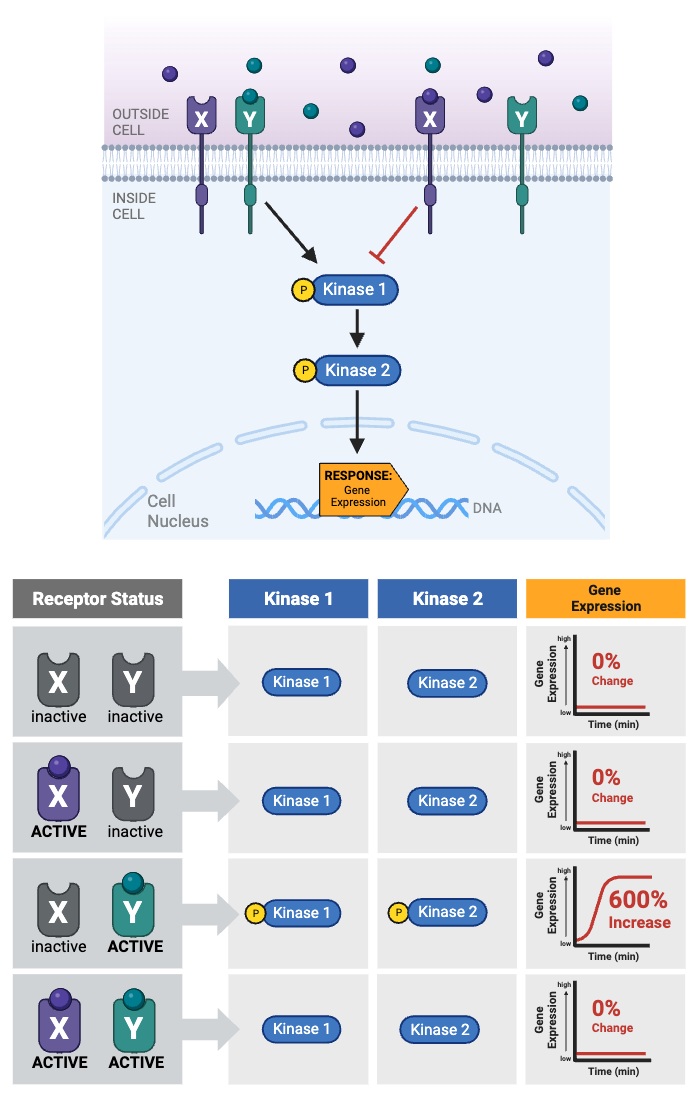
Which receptor(s) must be activated to cause a change in gene expression?
a. Only Receptor X is activated.
b. Only Receptor Y is activated.
c. Either Receptor X or Receptor Y is activated.
d. Both Receptor X and Receptor Y is activated.
e. Neither Receptor X nor Receptor is activated.
b. Only Receptor Y is activated.
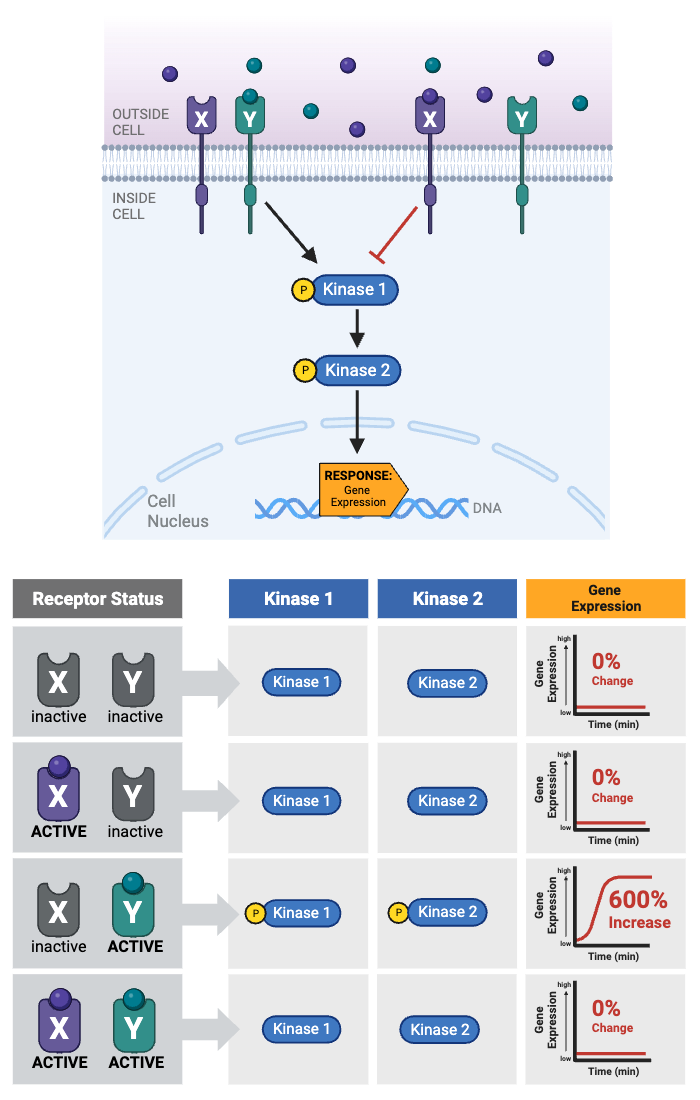
Which protein integrates the two signaling pathways?
a. Receptor X
b. Receptor Y
c. Kinase 1
d. Kinase 2
c. Kinase 1
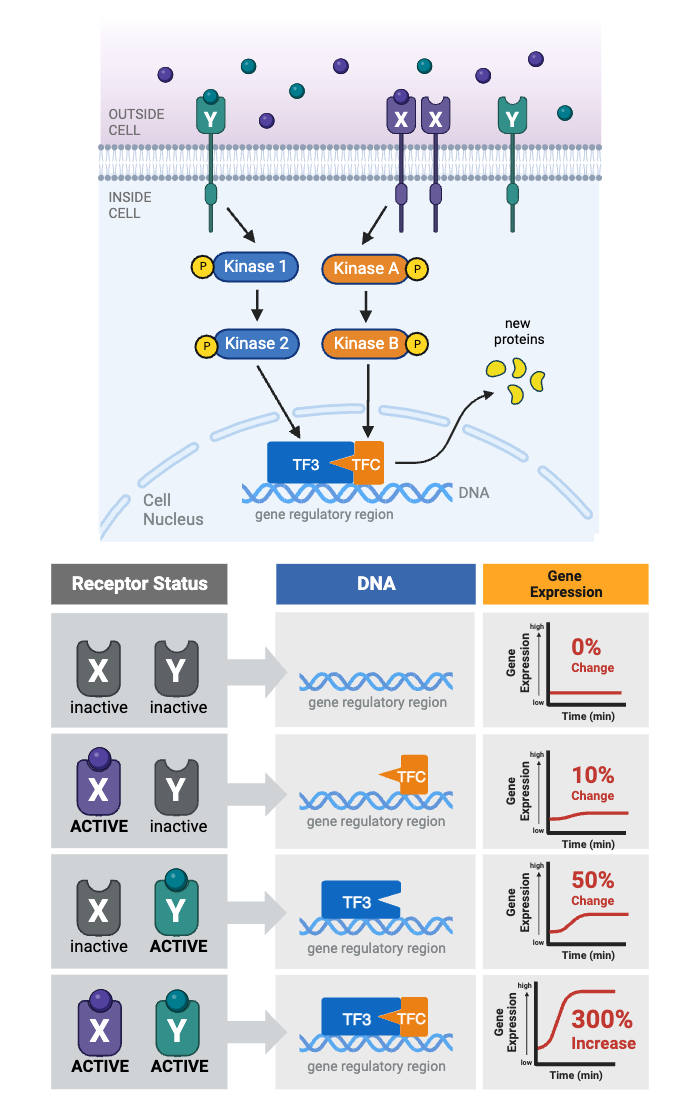
Which receptor(s) must be activated to cause a change in gene expression?
a. Only Receptor X is activated.
b. Only Receptor Y is activated.
c. Either Receptor X or Receptor Y is activated.
d. Both Receptor X and Receptor Y are activated.
e. Neither Receptor X nor Receptor Y is activated.
c. Either Receptor X or Receptor Y is activated.
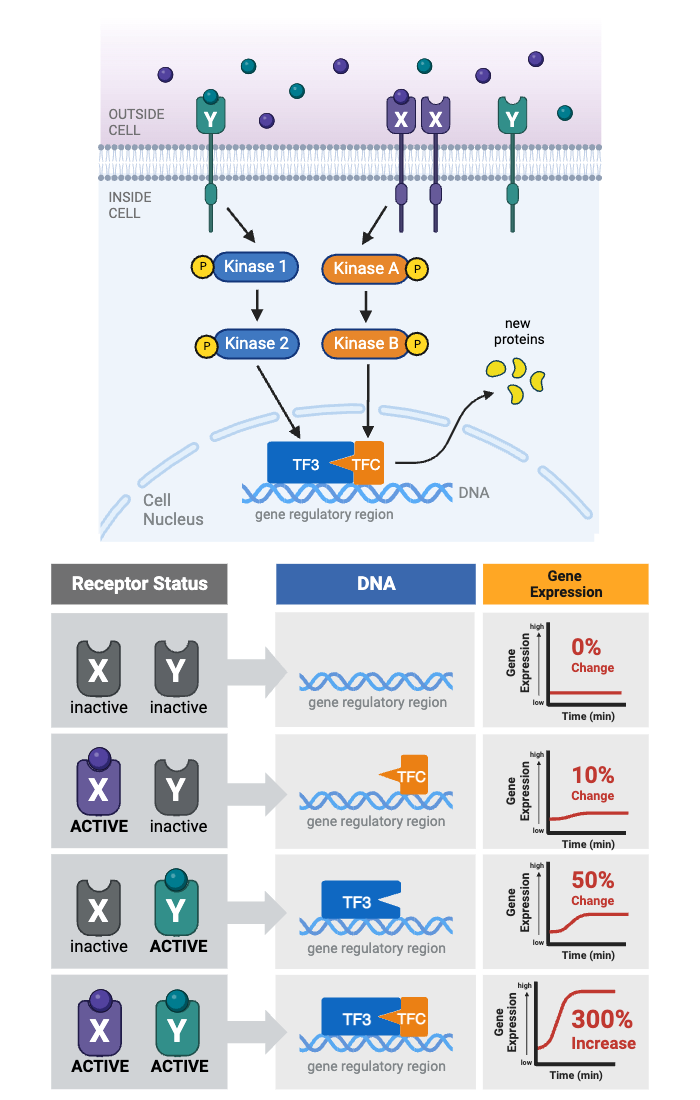
Which protein integrates the two signaling pathways?
a. Kinase 1
b. Kinase 2
c. Kinase A
d. Kinase B
e. TF3 and TFC
e. TF3 and TFC
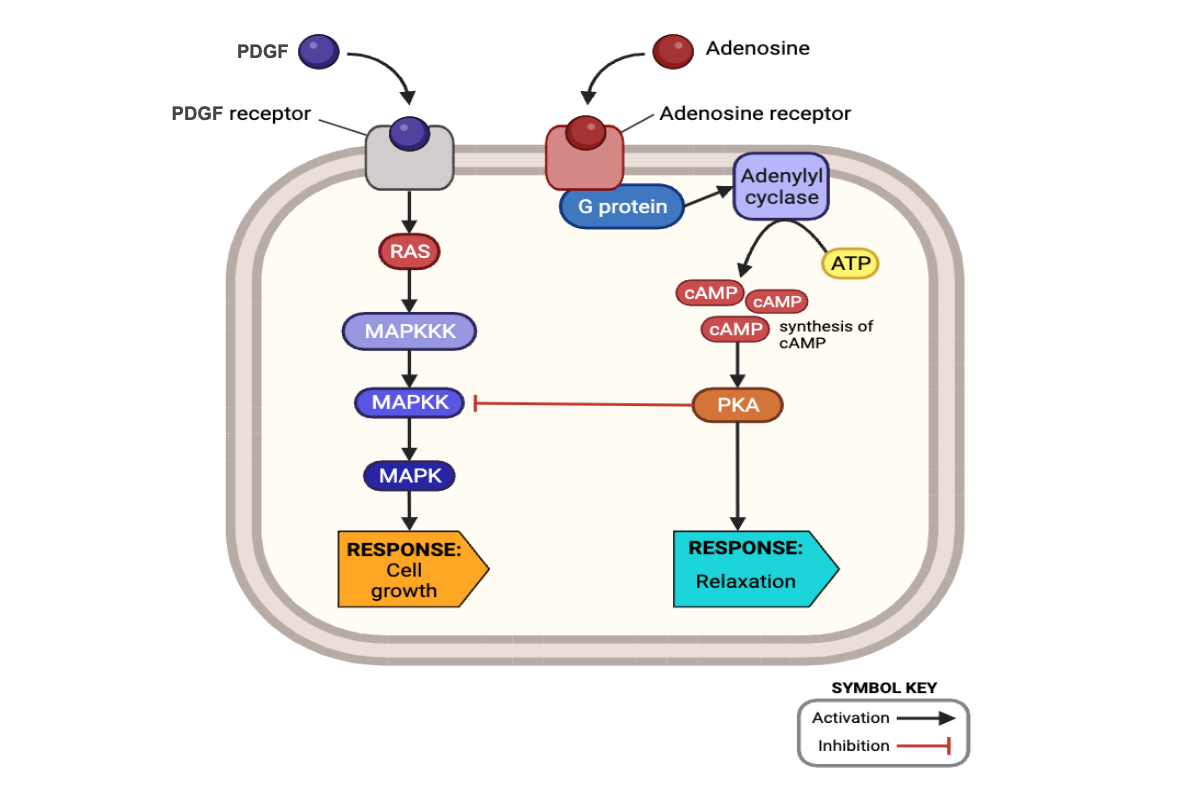
Which cellular responses should occur in the presence of PDGF and the absence of adenosine? Select all that apply.
a. activation of RAS
b. inhibition of RAS
c. activation of MAPKKK
d. inhibition of MAPKKK
e. activation of MAPKK
f. inhibition of MAPKK
g. activation of MAPK
h. inhibition of MAPK
i. increased cell growth
j. activation of G-protein
k. inhibition of G-protein
l. activation of adenylyl cyclase
m. inhibition of adenylyl cyclase
n. increased abundance of cAMP
o. decreased abundance of cAMP
p. activation of PKA
q. inhibition of PKA
r. relaxation of smooth muscle
a. activation of RAS
c. activation of MAPKKK
e. activation of MAPKK
g. activation of MAPK
i. increased cell growth
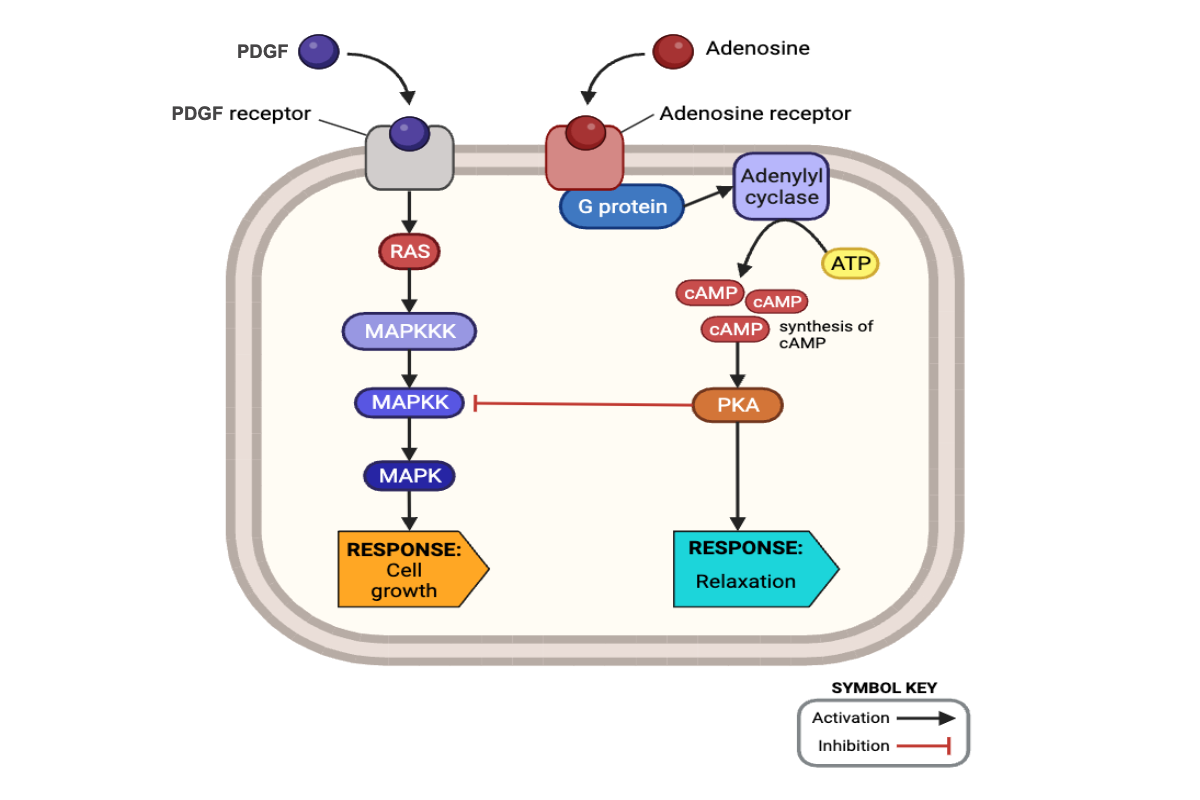
Which cellular responses should occur in the presence of adenosine and absence of PDGF? Select all that apply.
a. activation of RAS
b. inhibition of RAS
c. activation of MAPKKK
d. inhibition of MAPKKK
e. activation of MAPKK
f. inhibition of MAPKK
g. activation of MAPK
h. inhibition of MAPK
i. increased cell growth
j. activation of G-protein
k. inhibition of G-protein
l. activation of adenylyl cyclase
m. inhibition of adenylyl cyclase
n. increased abundance of cAMP
o. decreased abundance of cAMP
p. activation of PKA
q. inhibition of PKA
r. relaxation of smooth muscle
f. inhibition of MAPKK
j. activation of G-protein
l. activation of adenylyl cyclase
n. increased abundance of cAMP
p. activation of PKA
r. relaxation of smooth muscle
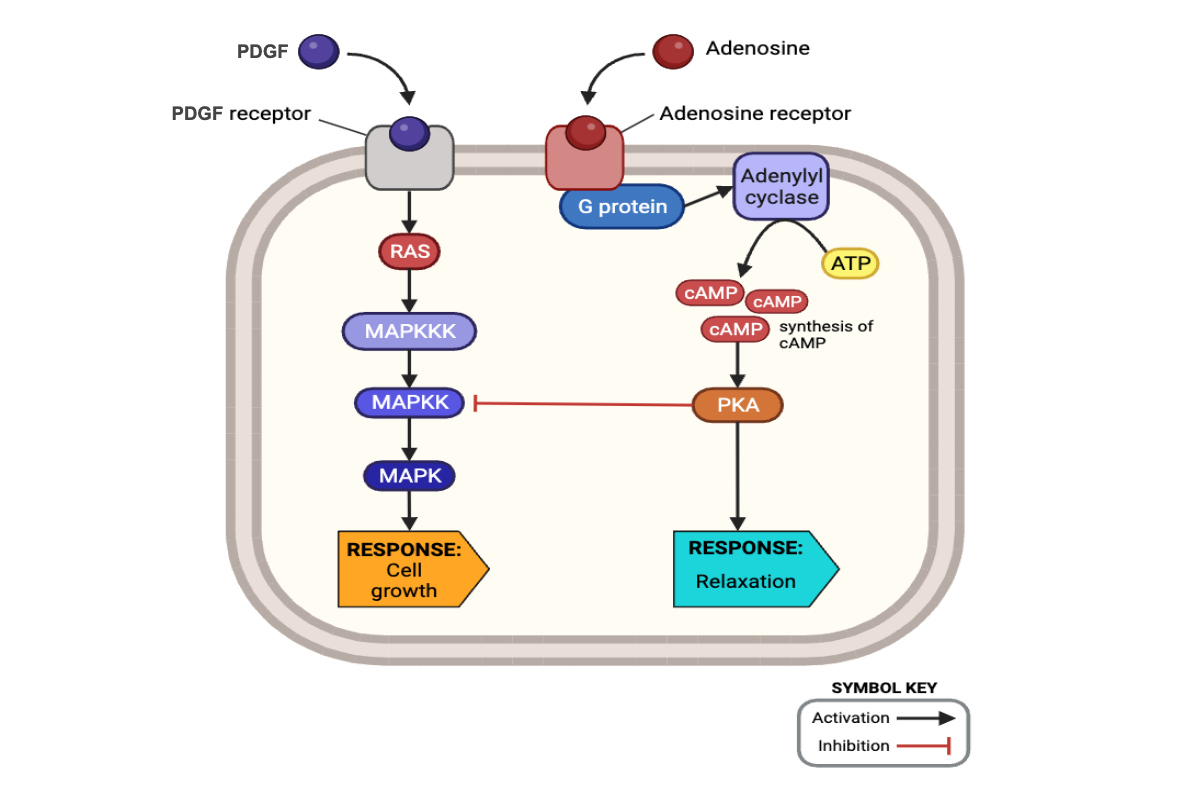
Compared to the previous two hours, which cellular responses likely occurred during the exposure to both PDGF and adenosine? Select all that apply.
a. increase in the activity of RAS
b. decrease in the activity of RAS
c. increase in the activity of MAPKKK
d. decrease in the activity of MAPKKK
e. increase in the activity of MAPKK
f. decrease in the activity of MAPKK
g. increase in the activity of MAPK
h. decrease in the activity of MAPK
i. increase in cell growth
j. increase in the activity of G-protein
k. decrease in the activity of G-protein
l. increase in the activity of adenylyl cyclase
m. decrease in the activity of adenylyl cyclase
n. increase in the abundance of cAMP
o. decrease in the abundance of cAMP
p. increase in the activity of PKA
q. decrease in the activity of PKA
r. relaxation of smooth muscle
f. decrease in the activity of MAPKK
h. decrease in the activity of MAPK
j. increase in the activity of G-protein
l. increase in the activity of adenylyl cyclase
n. increase in the abundance of cAMP
p. increase in the activity of PKA
r. relaxation of smooth muscle
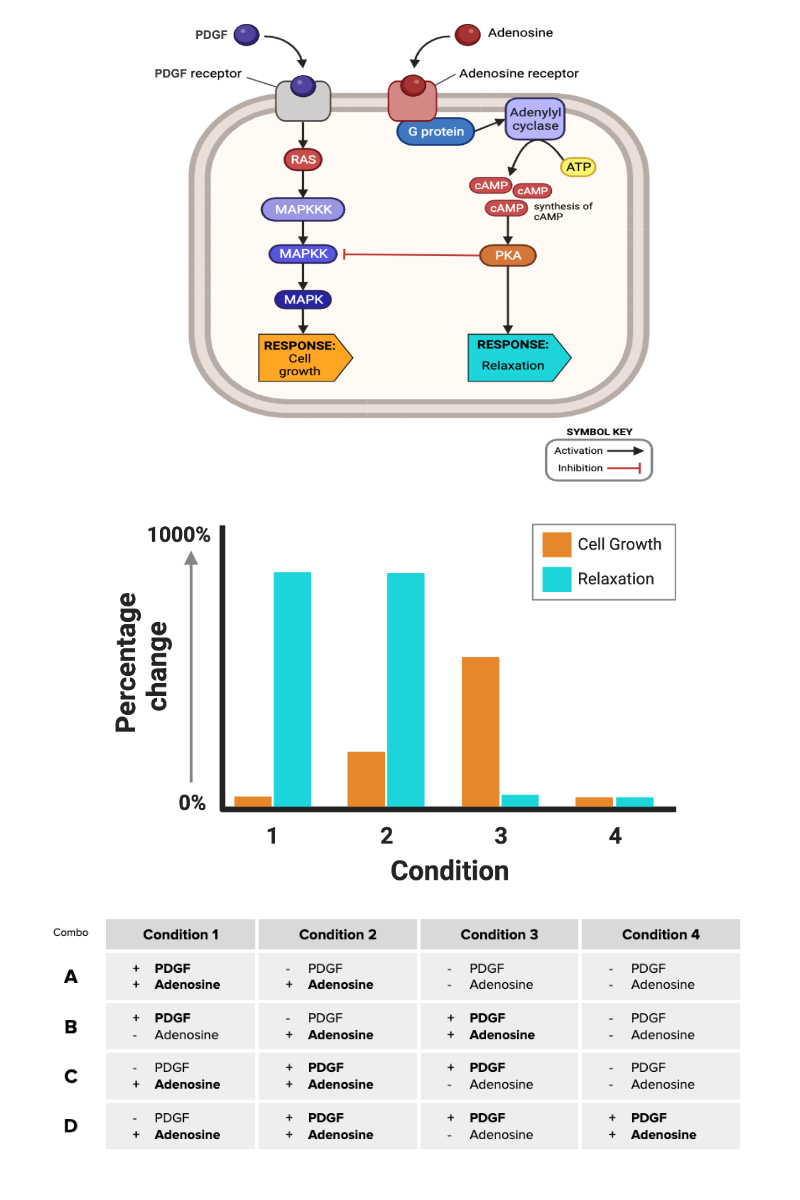
Which row of the table (A through D) contains the combination of signaling molecules needed to produce the cellular responses shown in the figure?
a. Row A
b. Row B
c. Row C
d. Row D
c. Row C
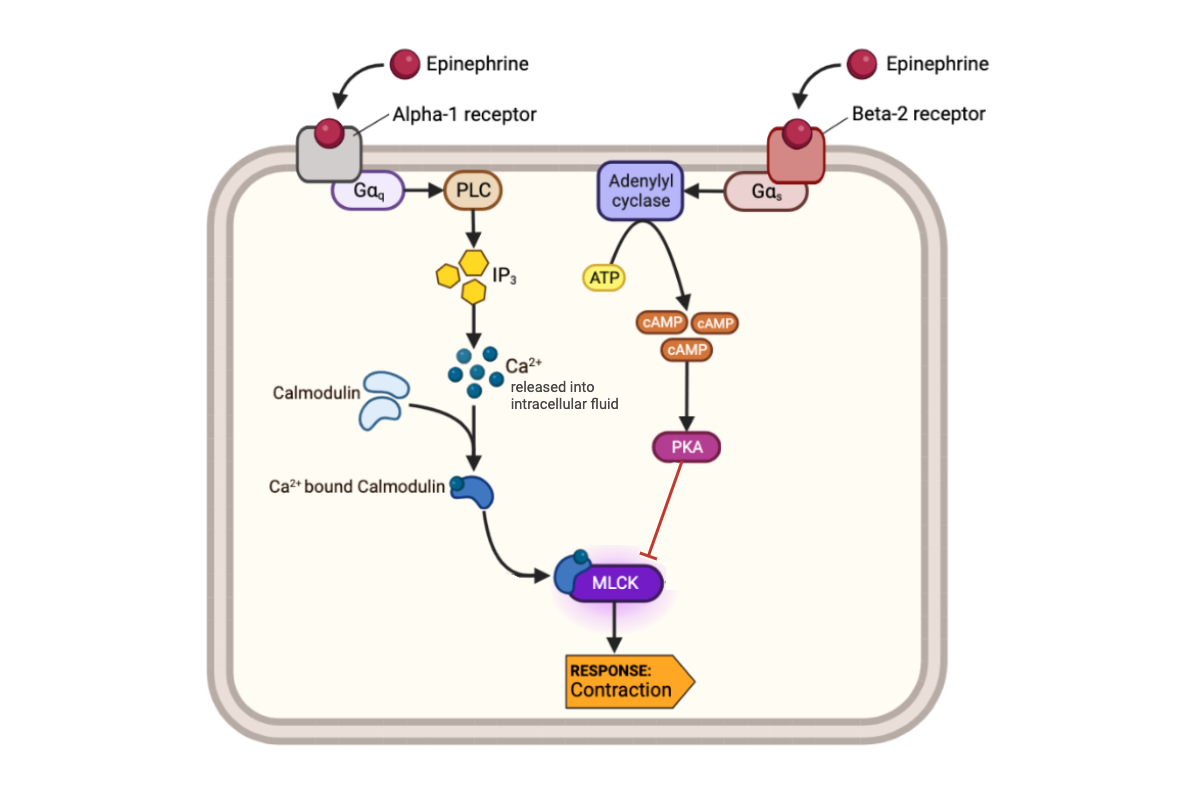
What happens to the concentration of calcium ions (Ca2+) in a cell when epinephrine binds to an alpha-1 receptor?
a. The concentration of Ca2+ increases.
b. The concentration of Ca2+ decreases.
c. The concentration of Ca2+ remains the same.
a. The concentration of Ca2+ increases.
What happens to the activity of MLCK-calmodulin complex when the concentration of Ca2+ increases?
a. The activity of MLCK-calmodulin complex increases.
b. The activity of MLCK-calmodulin complex decreases.
c. The activity of MLCK-calmodulin complex remains the same.
a. The activity of MLCK-calmodulin complex increases.
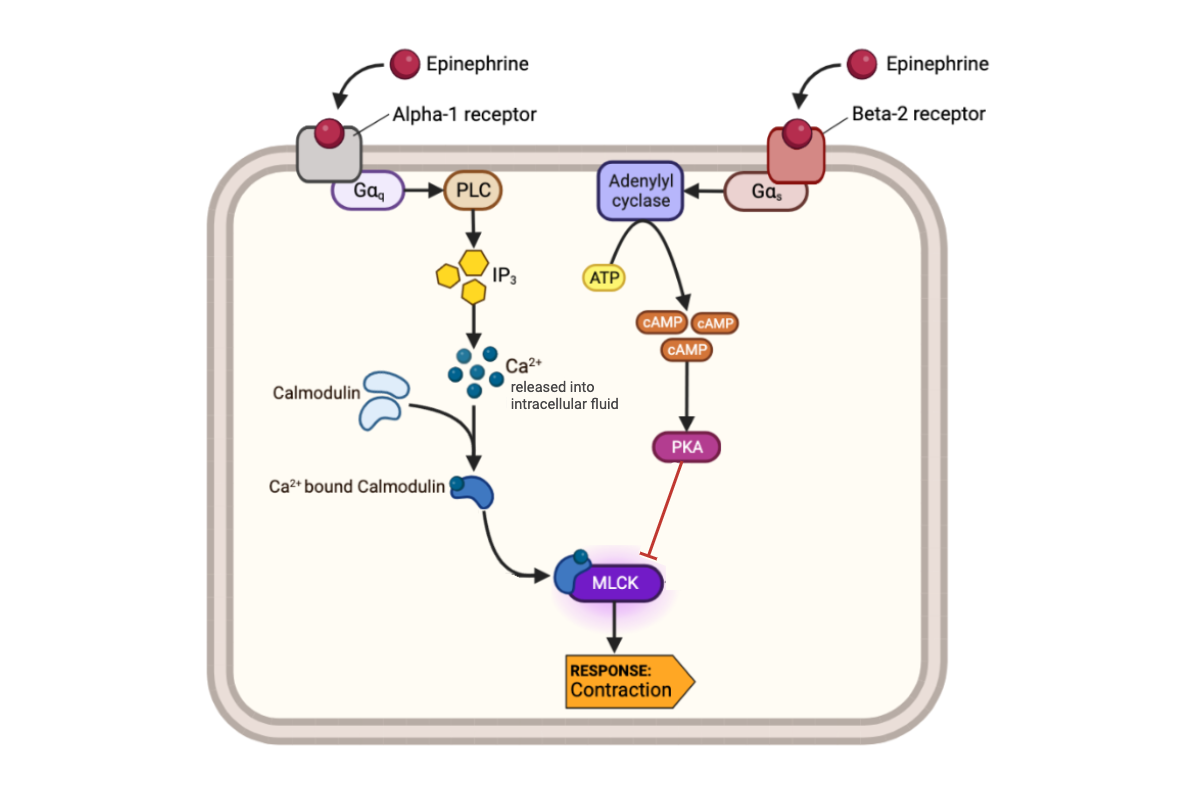
What happens to a muscle cell when the activity of MLCK-calmodulin complex increases?
a. The muscle cell contracts.
b. The muscle cell relaxes.
c. The muscle cell neither contracts nor relaxes.
a. The muscle cell contracts.
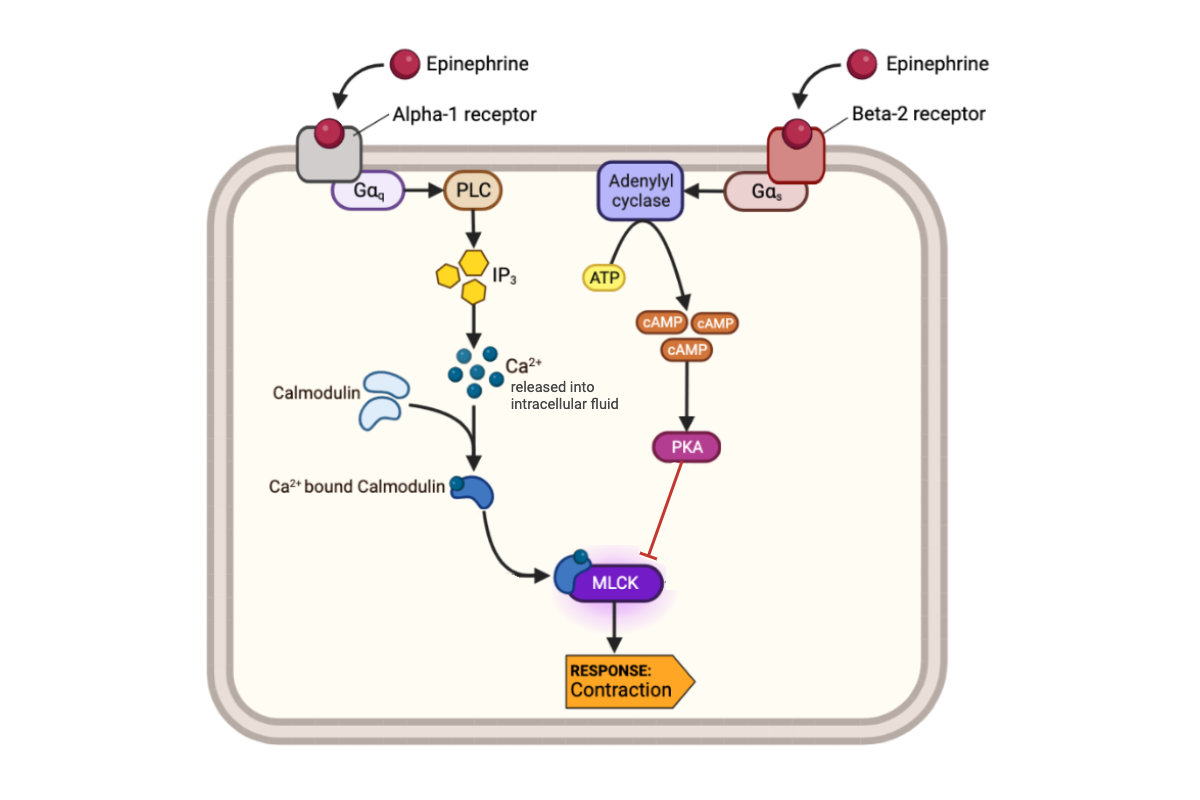
What happens to the concentration of cAMP in a cell when epinephrine binds to a beta-2 receptor?
a. The concentration of cAMP increases.
b. The concentration of cAMP decreases.
c. The concentration of cAMP remains the same.
a. The concentration of cAMP increases.
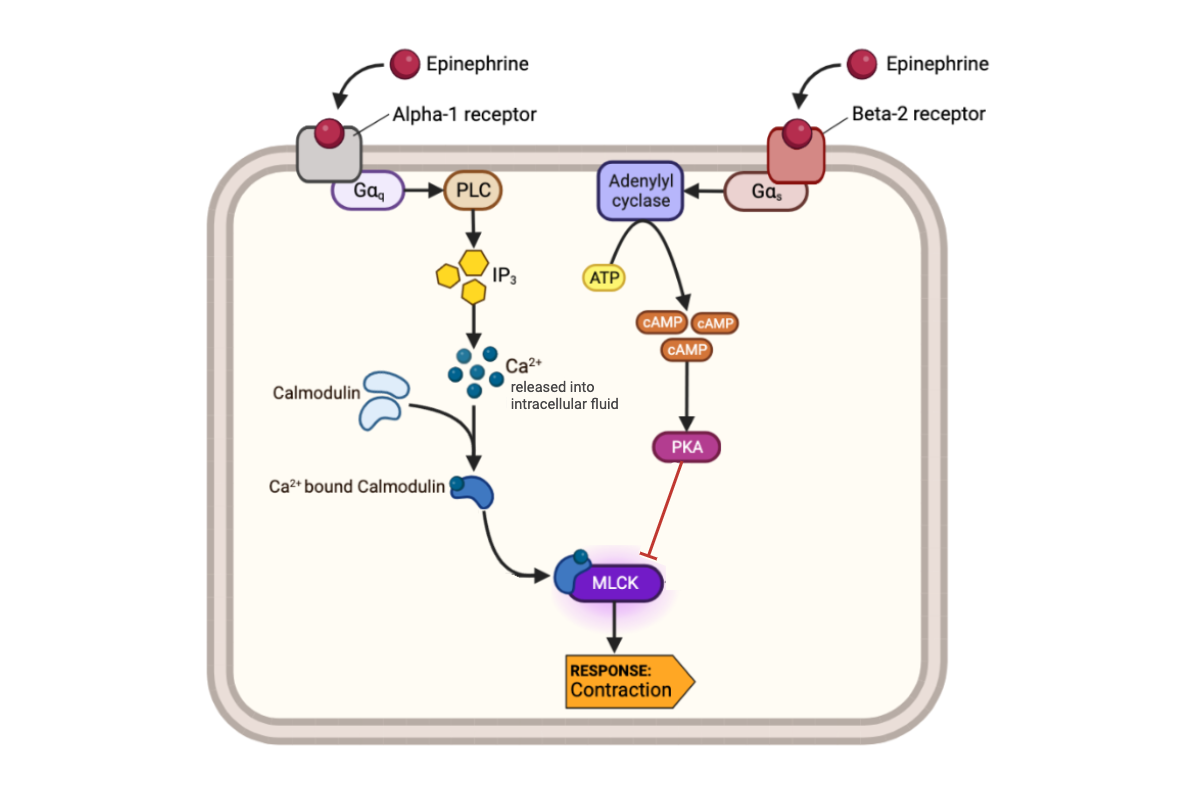
What happens to the activity of MLCK-calmodulin complex when the concentration of cAMP in a cell increases?
a. The activity of MLCK-calmodulin complex increases.
b. The activity of MLCK-calmodulin complex decreases.
c. The activity of MLCK-calmodulin complex remains the same.
b. The activity of MLCK-calmodulin complex decreases.
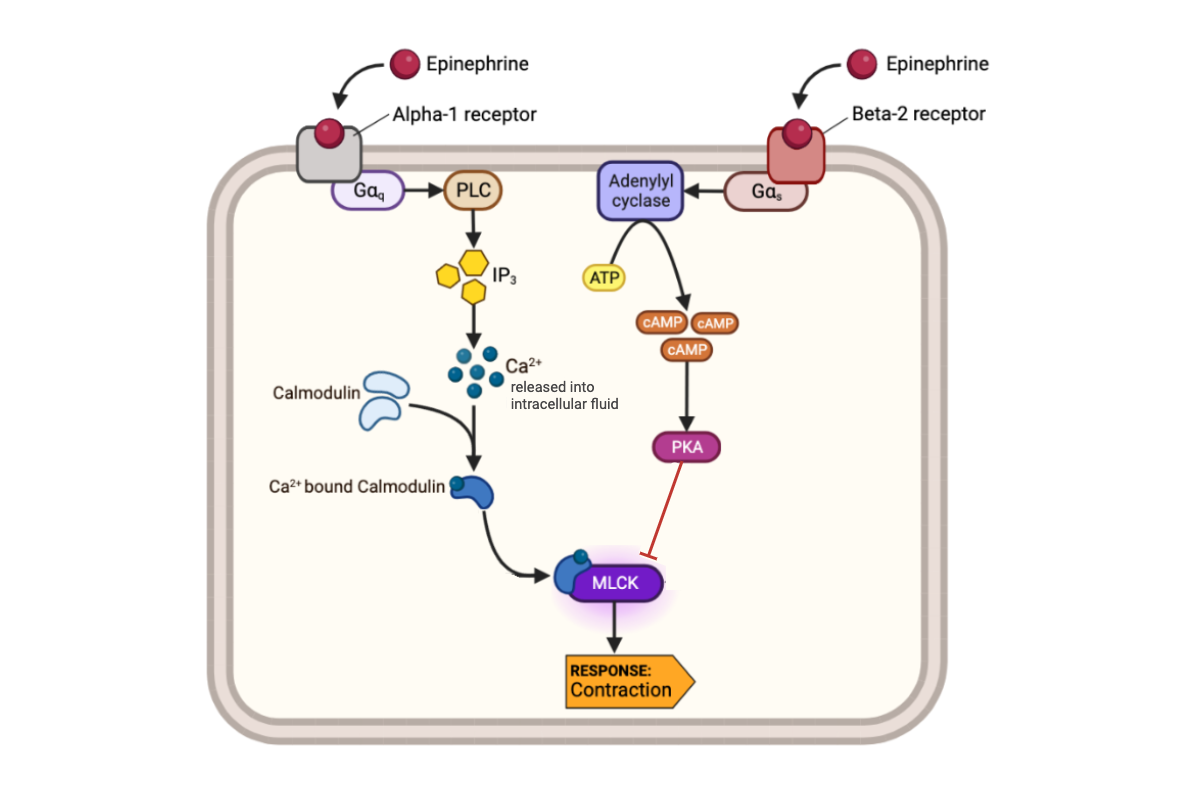
What happens to a muscle cell when the activity of MLCK-calmodulin complex decreases?
a. The muscle cell contracts.
b. The muscle cell relaxes.
c. The muscle cell neither contracts nor relaxes.
b. The muscle cell relaxes.
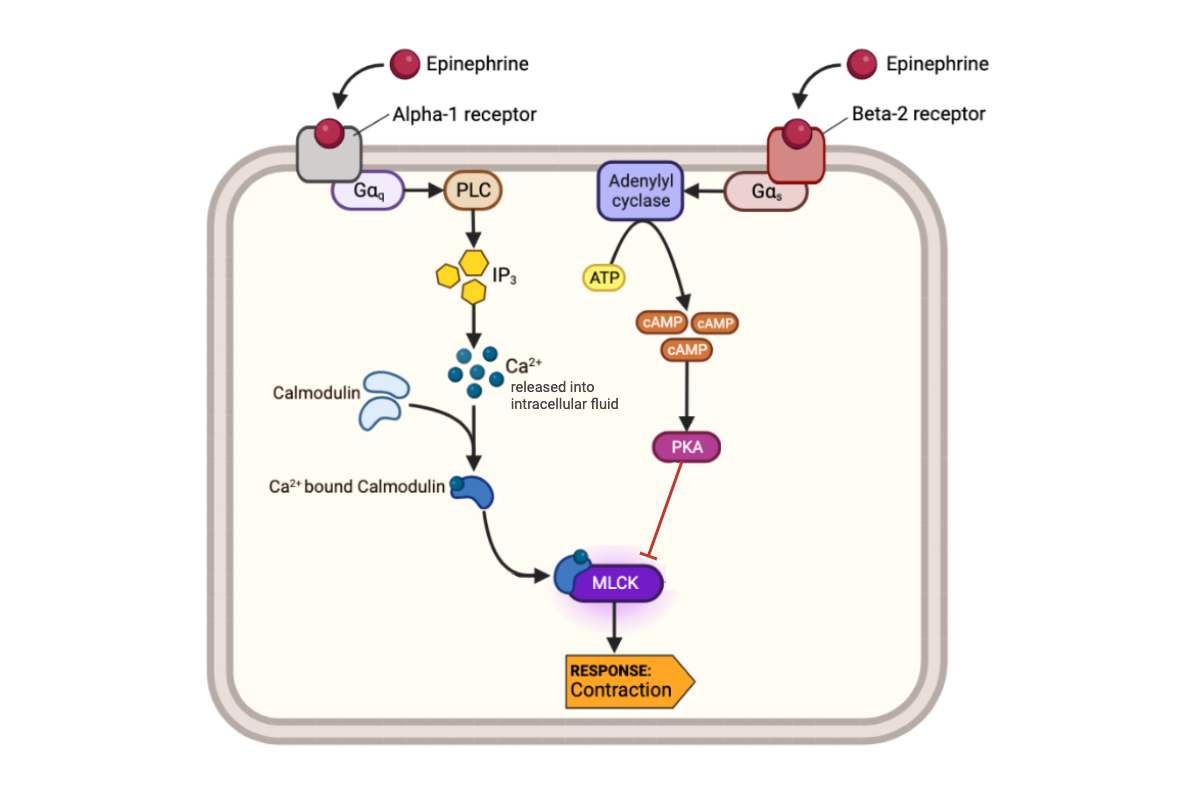
What happens to the concentration of calcium ions (Ca2+) when epinephrine binds to a beta-2 receptor?
a. The concentration of Ca2+ increases.
b. The concentration of Ca2+ decreases.
c. The concentration of Ca2+ remains the same.
c. The concentration of Ca2+ remains the same.
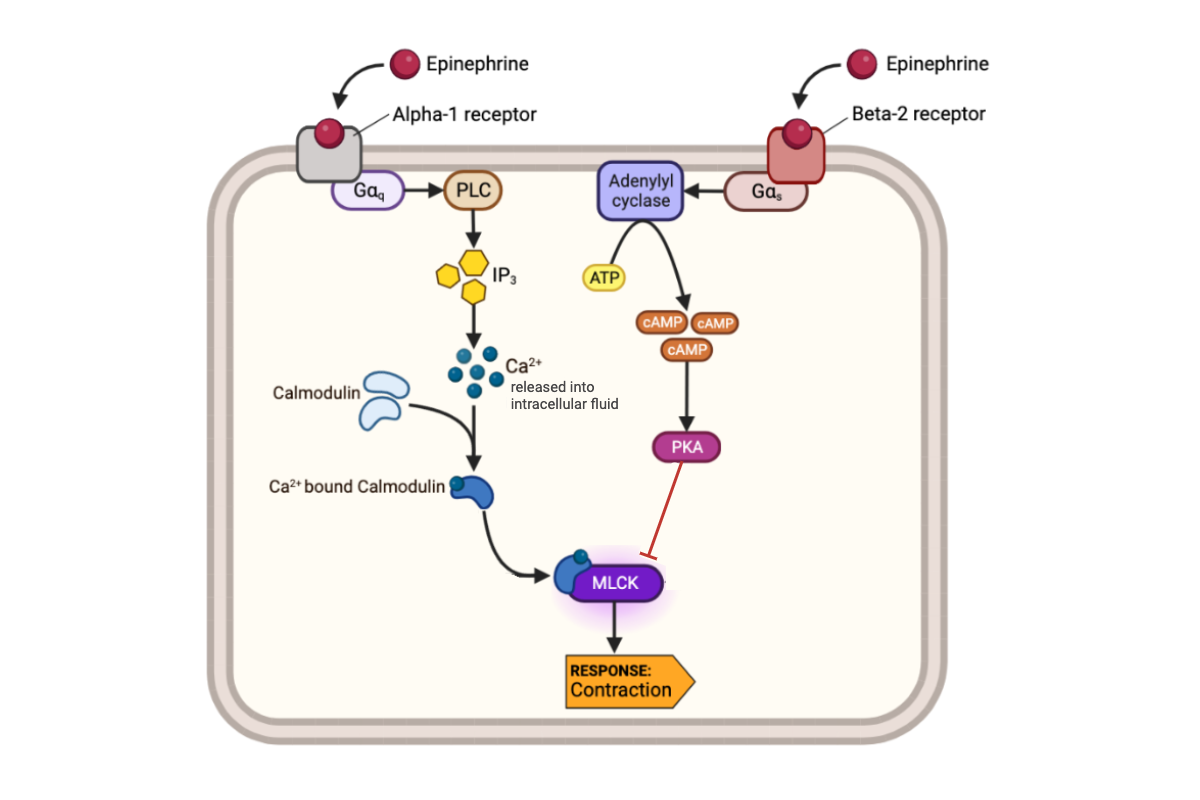
What happens to the concentration of cAMP in a cell when epinephrine binds to an alpha-1 receptor?
a. The concentration of cAMP increases.
b. The concentration of cAMP decreases.
c. The concentration of cAMP remains the same.
c. The concentration of cAMP remains the same.
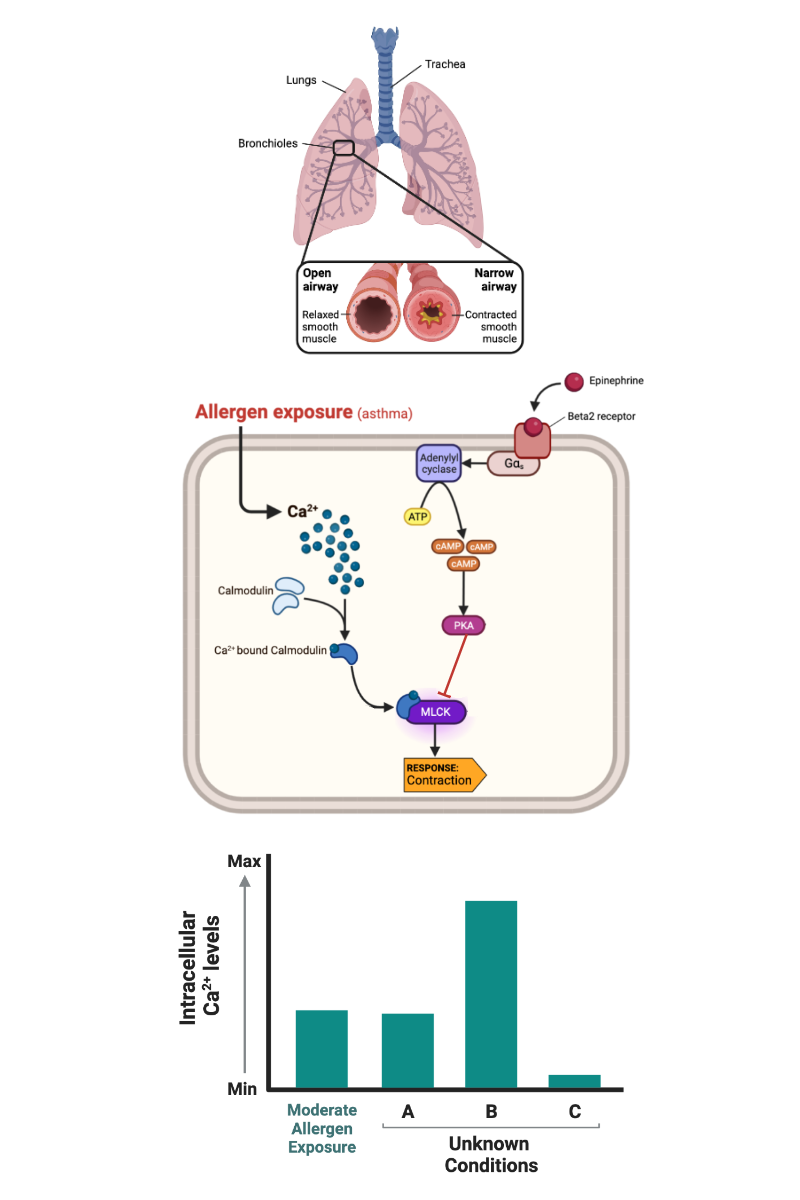
Which bar most likely represents the concentration of calcium ions (Ca2+) in a cell that has been exposed to a high concentration of allergen?
a. Bar A
b. Bar B
c. Bar C
b. Bar B
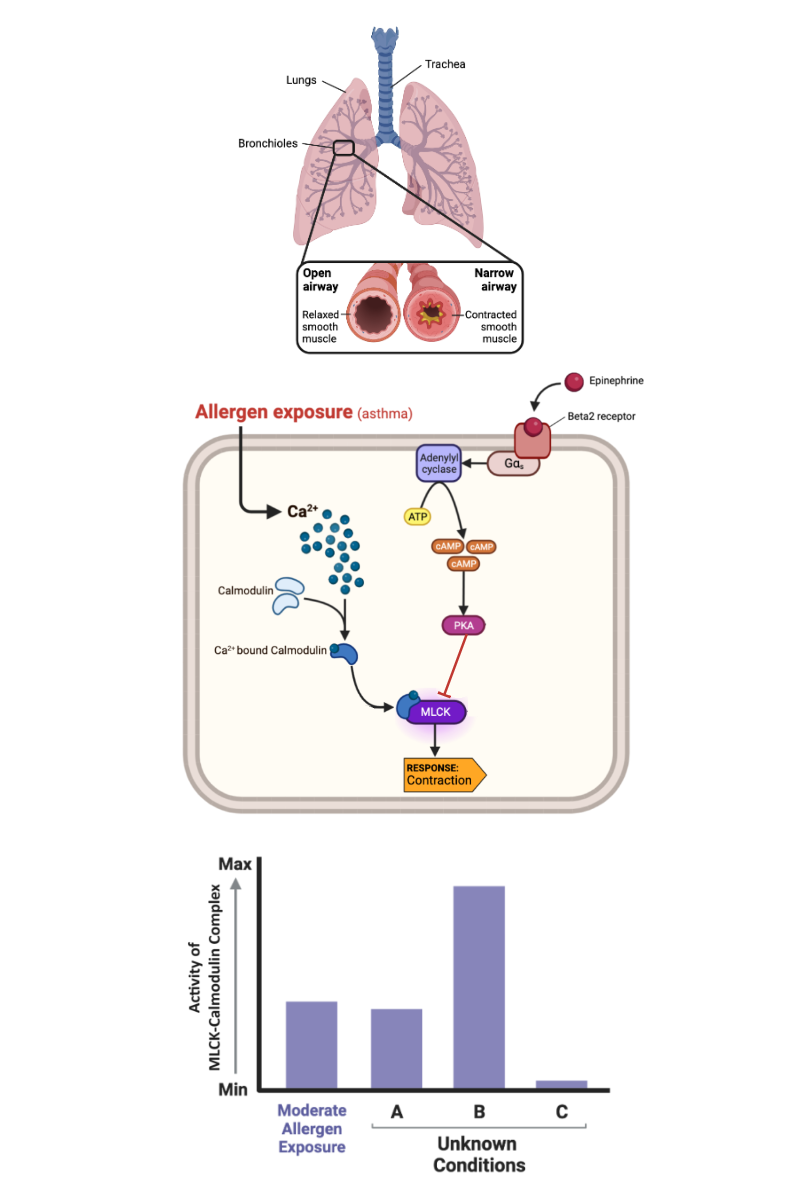
Which bar most likely represents the activity of MLCK-calmodulin complex in a cell that has not been exposed to any allergens within the last 48 hours?
a. Bar A
b. Bar B
c. Bar C
c. Bar C
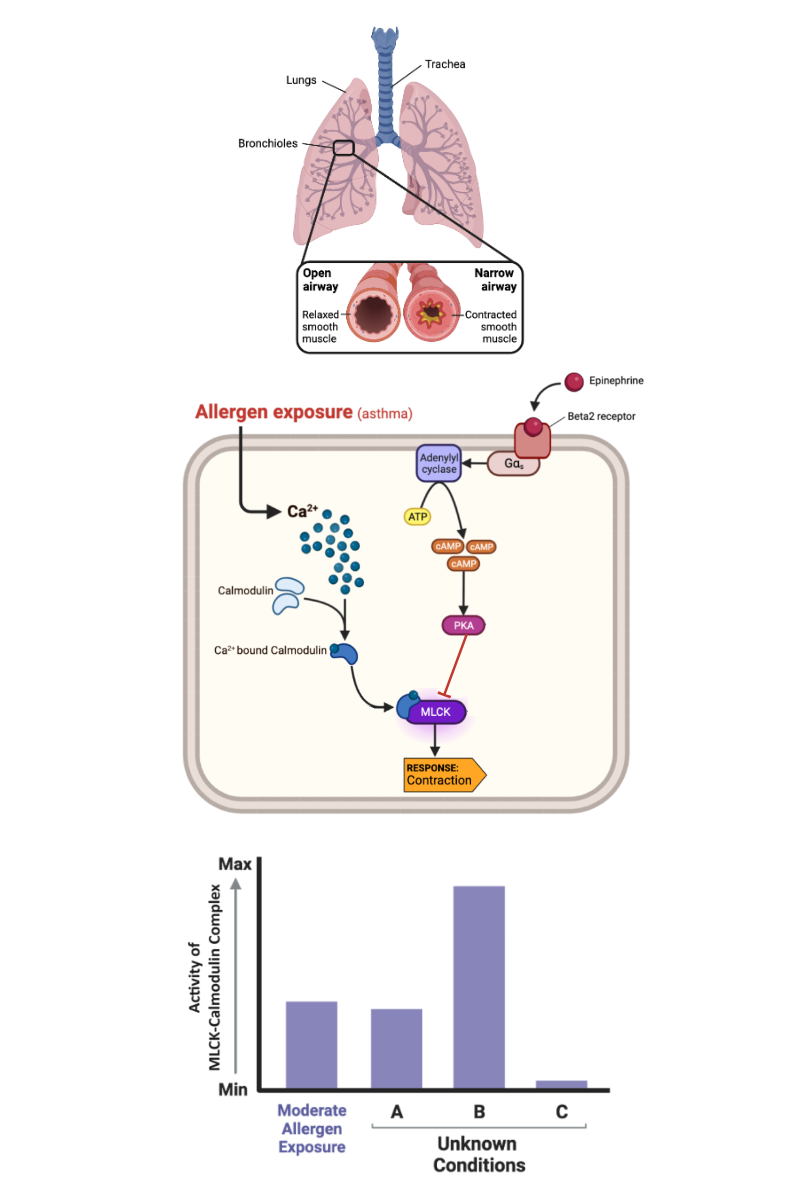
Which bar most likely represents the activity of MLCK-calmodulin complex soon after a person has been exposed to a large amount of allergen?
a. Bar A
b. Bar B
c. Bar C
b. Bar B
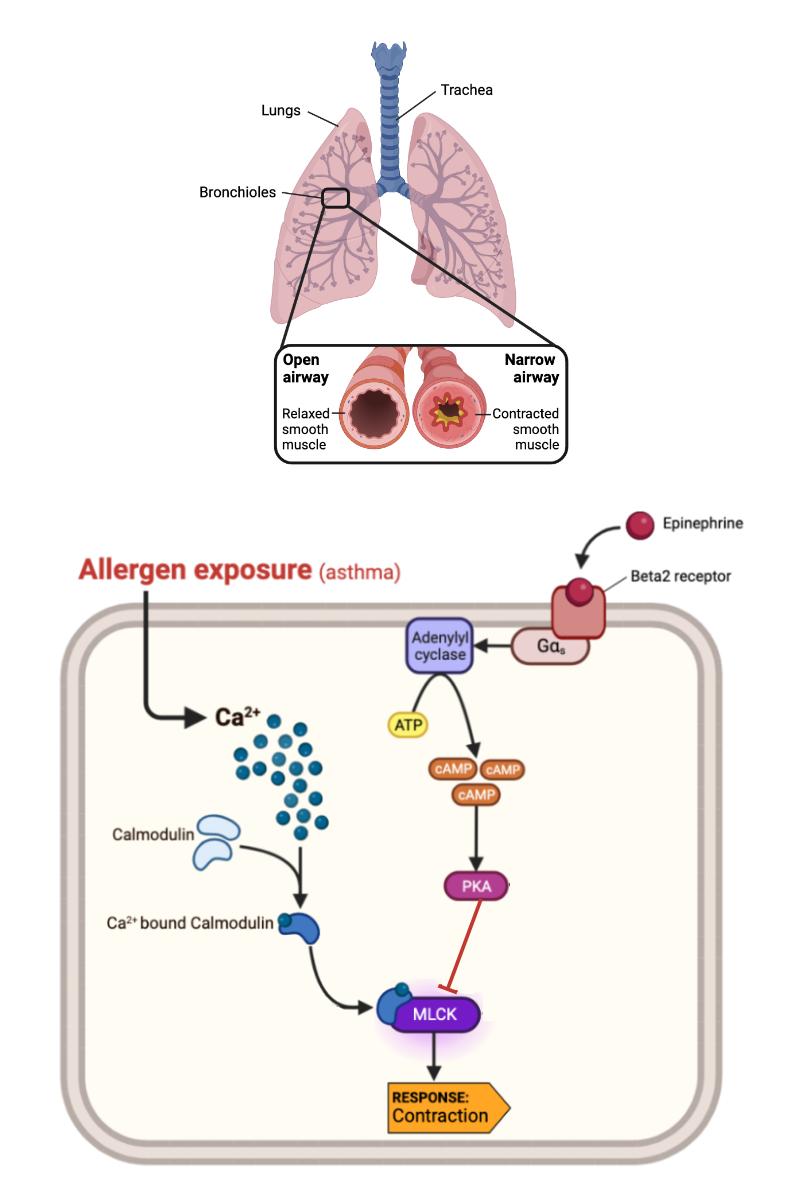
Complete the following sentence. As the concentration of allergen in a person's lung decreases, the concentration of calcium ions (Ca2+) in a smooth muscle cell should _______.
a. increase
b. decrease
c. no change
b. decrease
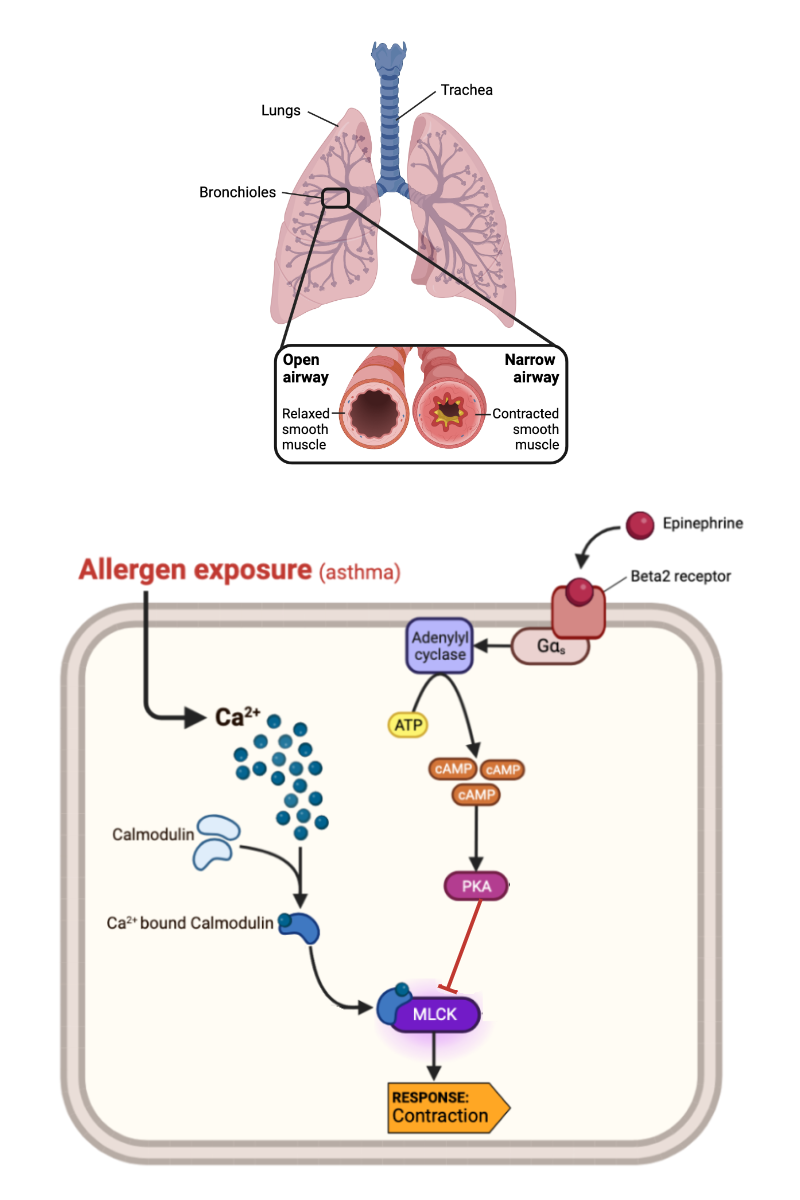
Complete the following sentence. As the concentration of allergen in a person's lung decreases, the activity of MLCK-calmodulin complex in a smooth muscle cell should _______.
a. increase
b. decrease
c. no change
b. decrease
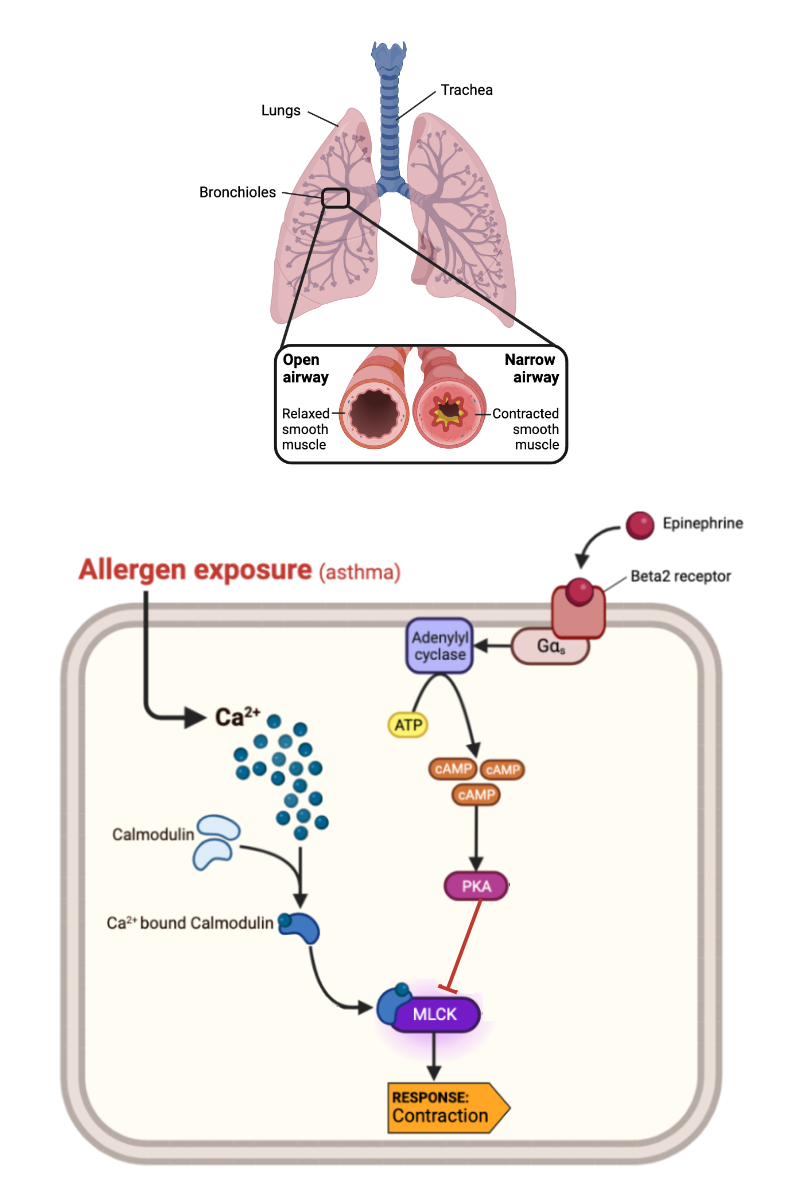
Complete the following sentence. As the concentration of allergen in a person's lung decreases, a smooth muscle cell should be _____ likely to contract.
a. more
b. less
c. equally
b. less