Current-Voltage Characteristics
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is a simple electrical circuit require?
a conductor through which current can flow
a source of potential difference
What is electric current?
The rate of flow of electric charge
What are the units of current?
Amperes(A) or Amps(A)
What is one amp equal to?
1 amp is equivalent to a charge of 1 coulomb flowing in 1 second, or 1 A = 1 C s−1
What is the equation for current
Current = amount of charge flowing(C)/time intervals
When can current flow?
Current flows when a circuit is formed
This is when a conductor, such as a wire, connects two oppositely charged terminals of a source, such as a cell
What is conventional current and how does it flow?
Conventional current is defined as the flow of positive charge
This is from the positive terminal of a cell to the negative terminal
How do electrons really flow?
Electrons are negatively charged so they flow from the negative terminal of a cell to the positive terminal
This is the opposite of the direction of electron flow
How is current measured?
Ammeter
How is an ammeter connected?
In series with the component measured
What is potential difference in terms of work?
The electrical work done per unit charge flowing between two points
What are the units for potential difference?
Volts(V)
What is 1V equivalent to?
1 volt is equivalent to the transfer of 1 joule of electrical energy by 1 coulomb of charge, or 1 V = 1 J C−1
What is the equation for potential difference?
Potential difference = work done/Charge flow
V = W/Q
What does a simple cell create?
A simple cell creates a potential difference through the separation of charge
How does a simple cell work?
One end (terminal) of the cell has an excess of positive charge and the other an excess of negative charge
Negatively charged electrons are repelled by the negative terminal and attracted to the positive terminal
Therefore, when a wire is connected between the two terminals, the potential difference causes the flow of electrons (current)
How is potential difference measured?
Voltmeter
How are Voltmeters measured?
Voltmeters must be set up in parallel with the component being measured
What is resistance?
The opposition of a component to the flow of electric current through it
What is the resistance of a conductor?
the ratio of the potential difference V across to the current I in it
What is the equation of resistance?
R = V/I
Where:
R = resistance of a conductor (Ω)
V = potential difference across the conductor (V)
I = current in the conductor (A)
What are the units of resistance?
ohms (Ω)
What is 1 ohm equivalent to?
A resistance of 1 Ω is equivalent to a potential difference across a component of 1 V which produces a current of 1 A through it
What does the resistance of a component affect?
The current in a circuit
What happens when reistance increases across a given component?
The lower current can flow
What happens when reistance decreases across a given component?
the higher the current that can flow
What is an example of a good conductor and why is it a good conductor?
Copper as it has low electrical resistance
What does Ohm’s law state?
For a conductor at a constant temperature, the current through it is proportional to the potential difference across it
What does a constant temperature imply?
Constant temperature implies constant resistance
What is the equation for Ohm’s Law?
Potential difference = Current x resistance
V = IR
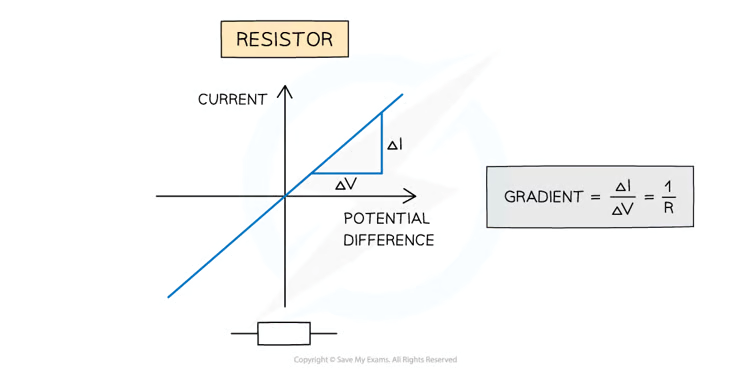
What is the IV graph for a resistor?
Graph
What is the IV graph of semiconductor diode?
Graphs

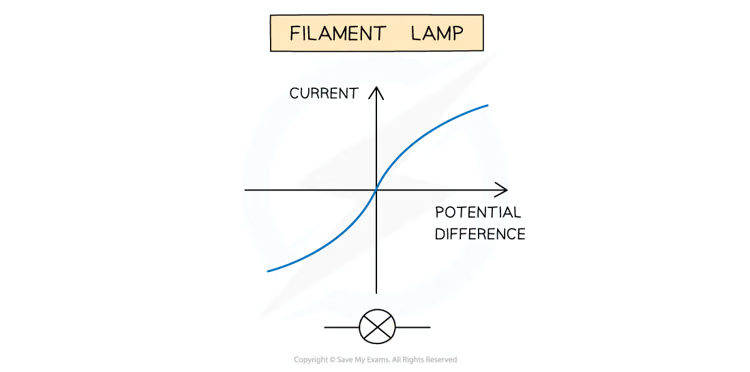
What is the IV graph of filament lamp?
Graph
What is the relationship between current and potential differenec in a Ohmic conductor?
The current is directly proportional to the potential difference
This is demonstrated by the straight-line graph through the origin
What is a diode?
A component that allows current to flow in one direction
How does the graph of a semiconductor diode look like?
When the current is in the direction of the arrowhead symbol, this is forward bias. This is shown by the sharp increase in potential difference and current on the right side of the graph
What happens when a diode is switched around?
When the diode is switched around, it does not conduct and is called reverse bias. This is shown by a zero reading of current or potential difference on the left side of the graph
What doe sthe IV graph of a filament show?
The I–V graph for a filament lamp shows the current increasing at a proportionally slower rate than the potential difference
What are reasons for trends in the IV graph of a filament graph?
As the current increases, the temperature of the filament in the lamp increases
Since the filament is a metal, the higher temperature causes an increase in resistance
Resistance opposes the current, causing the current to increase at a slower rate
What happens as current increases in a filament lamp?
As the current increases, the temperature of the filament in the lamp increases
Since the filament is a metal, the higher temperature causes an increase in resistance
Resistance opposes the current, causing the current to increase at a slower rate