1/2) Intro and Porosity
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
what does evaporation rate depend on?
availability of water
heat/energy (easier to evaporate if it’s moving more)
strength of surface to air vapour gradient
turbulent air to bring in more dry air
what are groundwater inputs and outputs?
inputs: recharge, from rain or river, lateral, or upward flow in
GW recharge: downward mass flux entering an aquifer (at water table)
outputs: discharge, evapotranspiration (shallow aquifers), interaquifer flow out, pumping
GW discharge: the mass flux leaving an aquifer at the surface
details on water ages
younger water at the surface
slightly younger water in the fractures of bedrock, and macropores where roots have allowed movement of younger water down
discharge out of system is a mixture of these ages
what is porosity
porous media’s ability to store water
doesn’t control ability to transmit water
what is REV
representative elementary volume
what volume do we need to get representative sample of the things we are looking for
property values change depending on scale of measurement
if sample is homogeneous, can use large representative volume
using a too small REV results in too much variation, same with too big, so pick in between
what are geological controls on porosity?
grain-size distribution
grain shape
grain arrangement and packing
geochemical reactions
material type
how does grain size affect porosity?
grain size can be different but does not alone dictate porosity
same shape and packing = same porosity
differences arise with distribution
poorly sorted = lower porosity because small grains fill larger gaps = well graded (lots of grain sizes)
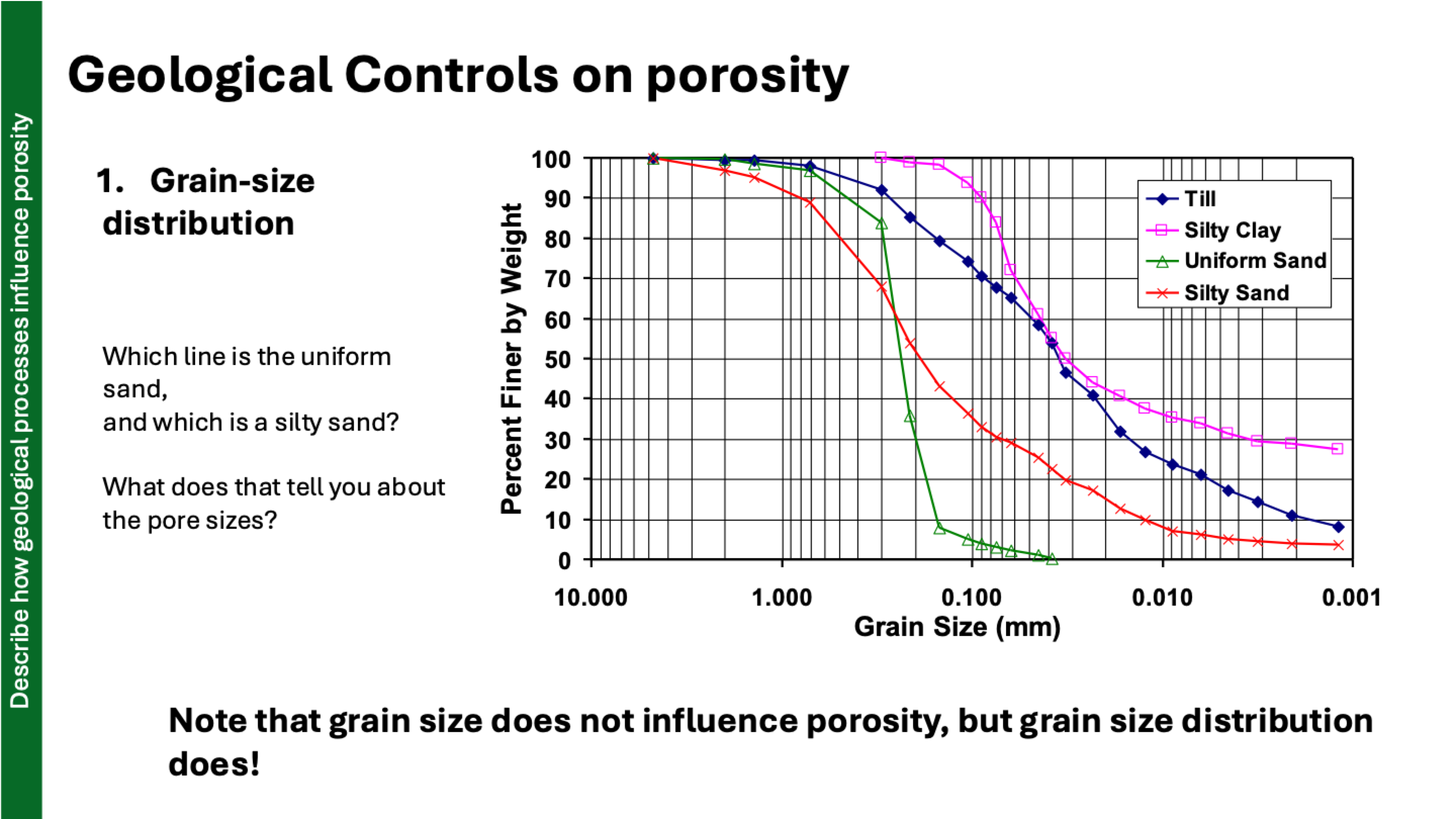
explain why each line is this way
uniform sand has bigger pore sizes = green line
silty sand, higher silt content = wider distribution = lower porosity
steeper line = more uniform grain size = higher porosity
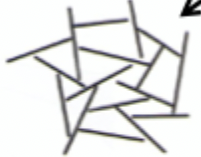
how does grain shape influence porosity?
fine grains have higher porosity due to disk shaped grains creating “house of cards” arrangement
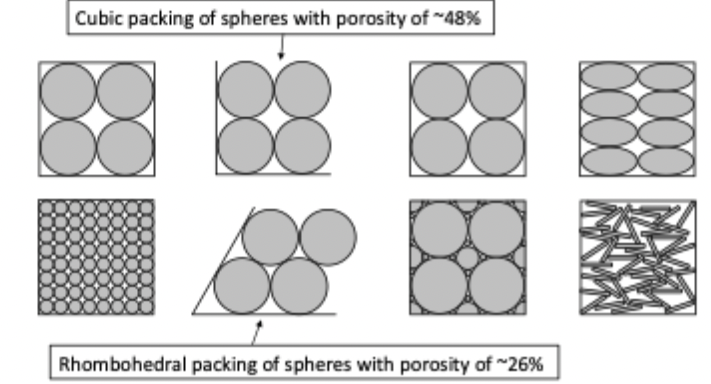
how does arrangement of grains/packing influence porosity?
cubic packing has porosity =0.48, rhombohedral packing = 0.26
how do geochemical reactions influence porosity?
mineral dissolution = increase
secondary mineral precipitation = decrease (lithification, cementation)
depends on chemical makeup of fluid running through sediment
how does material type influence porosity
unconsolidated sediments have higher porosity than rock
exceptions are sandstone and vesicular basalt
definition of void ratio
e = Vv / Vs
void volume / solid volume
definition of porosity
ne = Vv / VT
void volume / volume porous media (total volume)
details on measuring porosity
directly measuring void volume is difficult
can take known volume and saturate it, record mass, then dry and record mass again to infer VV. (fully saturating sample is difficult
definition of particle density
mass of solids / volume of solids
ps = Ms / Vs
weighted average density of mineral grains making up a soil (mass per unit volume of soil solids
definition of dry bulk density
mass of solids (dry) / volume porous medium (total volume)
Pbd = Ms / VT
dry density of the soil, usually considered constant over time, but increases with depth due to compaction by weight of overlying soils
definition of wet bulk density
mass of solids + fluid / volume porous medium (total volume)
Pbw = (Ms + Mf) / VT
equation for porosity
as porosity decreases ___
ø = 1 - (pb/ps)
1 - bulk density / particle density
as porosity decreases, bulk density increases
difference between primary and secondary porosity
primary: caused during deposition of unconsolidated material or original formation of rock (magma cooling), intrinsic porosity
voids between individual grains
very little in igneous and metamorphic
more storage
secondary: additional porosity caused by fracturing or dissolution
more connectivity
porosity of fractured rock is quite low
reasonable porosities for various sediments
sand: 0.20-0.5
silt: 0.35-0.5
clay: 0.25-0.7
total (n) vs effective porosity (ne)
some pores are dead end or isolated, this means the ability to transmit water is decreased
disconnected pores won’t contribute to flow or storage of groundwater
effective porosity is always less than or equal to total porosity. sand and gravel its close or equal
clays have high total but low effective porosity: lots of saturated void space, very small pores
vesicular basalts, many of the vesicles are not connected
definition for volumetric water content
volume of water / total volume
mass wet - mass dry / density*total volume
theta = Vw / VT
theta = Mwet - Mdry / pw*VT
definition of water saturation
volume of water / void volume
volumetric water content / porosity
Sw = Vw / VT = Vw / (Vair + Vw) = theta / n