Chemistry: Seperation Techniques and Diffusion, Dilution and Solution
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is diffusion?
The spreading out of particles from where they're at a high concentration to where they are at a low concentration.
How is diffusion is gas like?
Gas particles will move freely and randomly until they are evenly distributed.
How is diffusion is Liquid like?
Diffusion in liquid is slow in stationary liquid.
What is dilution?
Dilution is when we continue to dilute a coloured solution (add water) and colour will begin to fade until we can no longer see it at all.
What is a solute?
the substance that dissolved in a solvent
What is a solvent?
the liquid that a solute dissolves in
What is a solution?
the mixture formed when a solute dissolves in a solvent.
What is a saturated solution?
a solution which contains as much dissolved solid as possible at a particular temperature
A heavier compound...
Will move slowly
How can mixtures be separated and some examples?
Physically, through a temperature change or dissolving a part of the mixture in a solvent.
What can simple distillation be used for?
For separating a solvent/components from a solution.
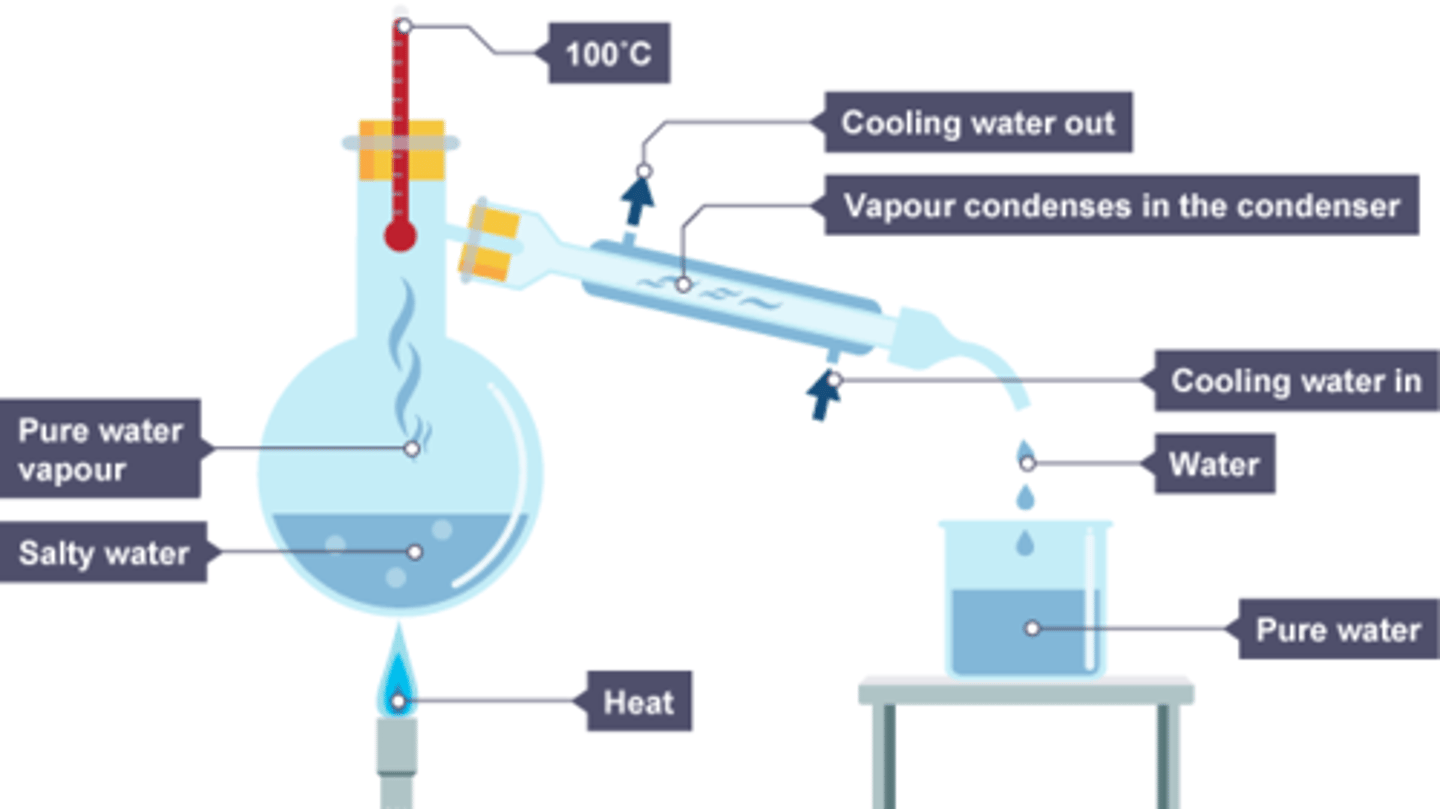
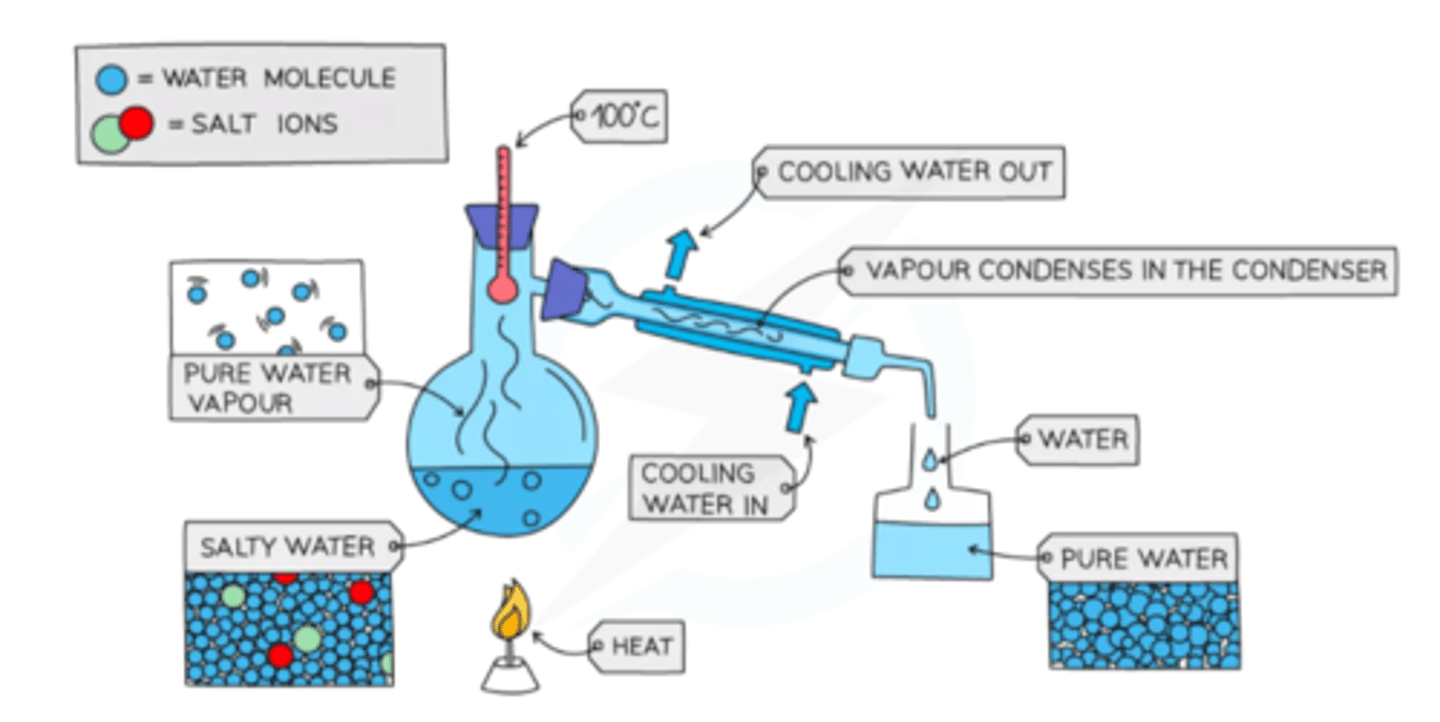
How does simple distillation work?
When the solution is heated, the water evaporates. It is then cooled and condensed into a separate container. The solvent will be left in the container. This works for separating something like salt water because salt has a higher boiling point.
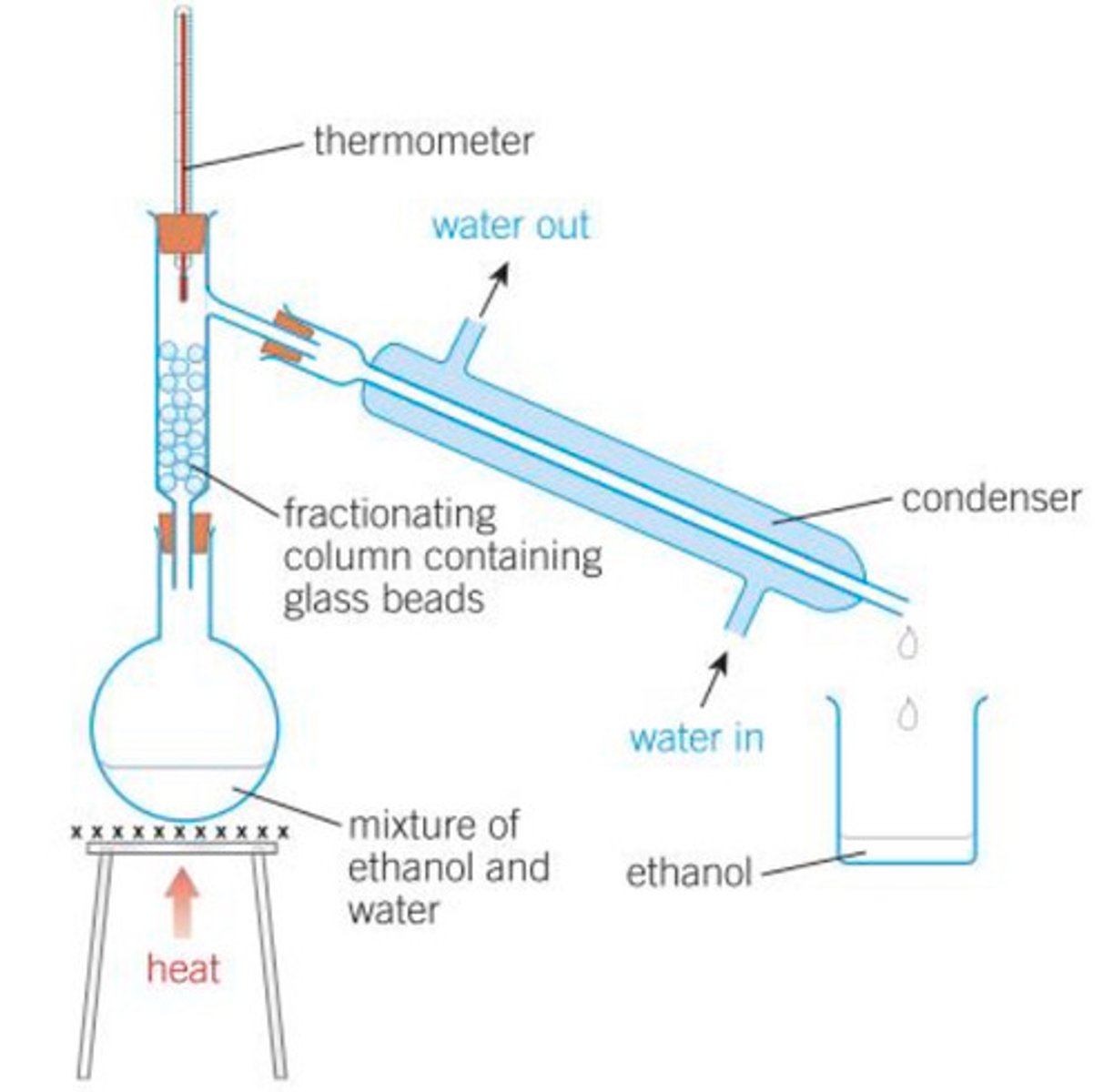
What can fractional distillation be used for?
For separating liquids that are miscible (if you mix them, you will forma single liquid layer).
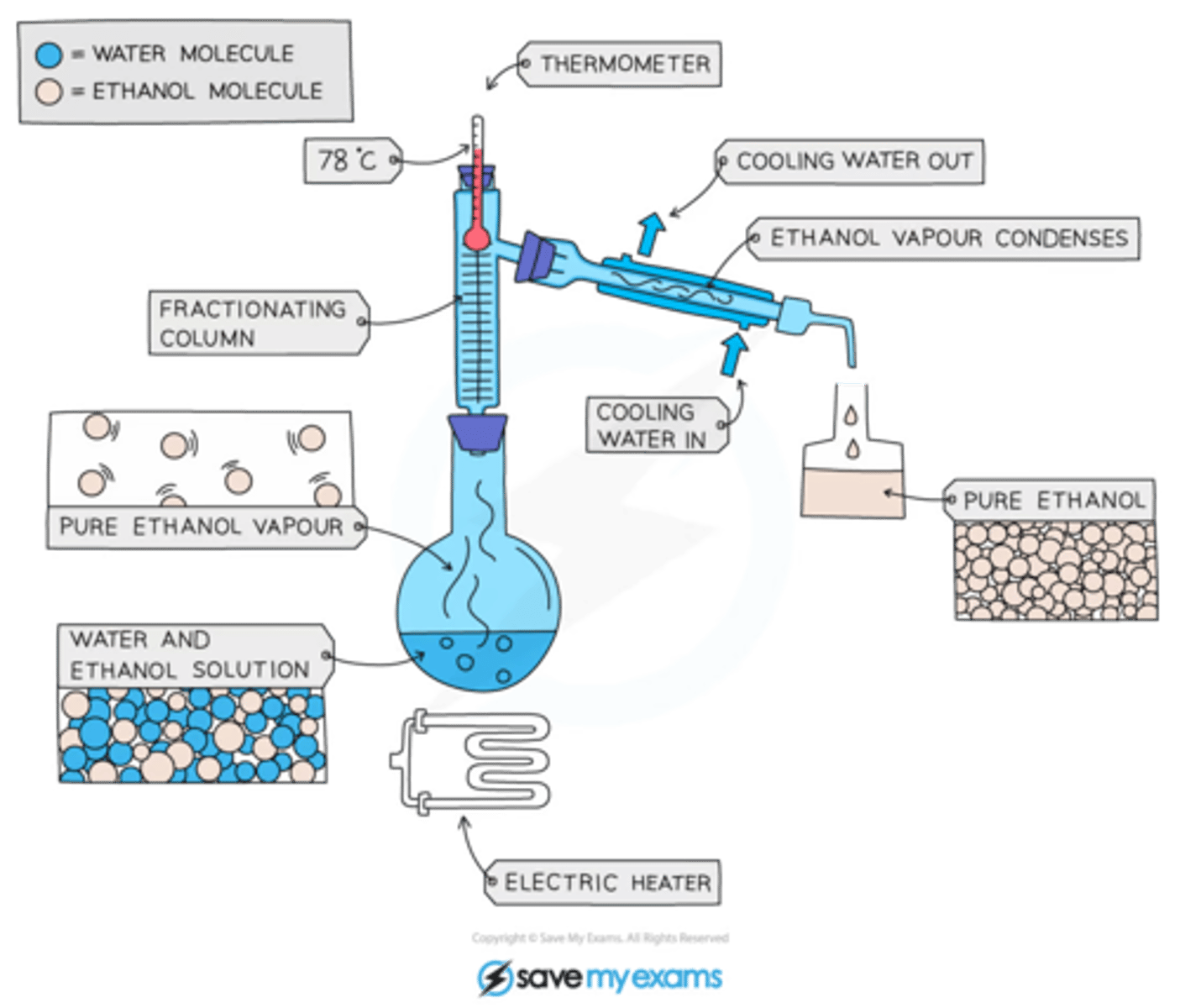
How does Fractional distillation work?
You separate the liquids using their boiling points. The two liquids have different boiling points meaning when the solution is heated the lower boiling point liquid, it will evaporate. The vapour is then cooled and condensed in a separate container.
What can filtration be used for?
For separating a solid from a liquid.
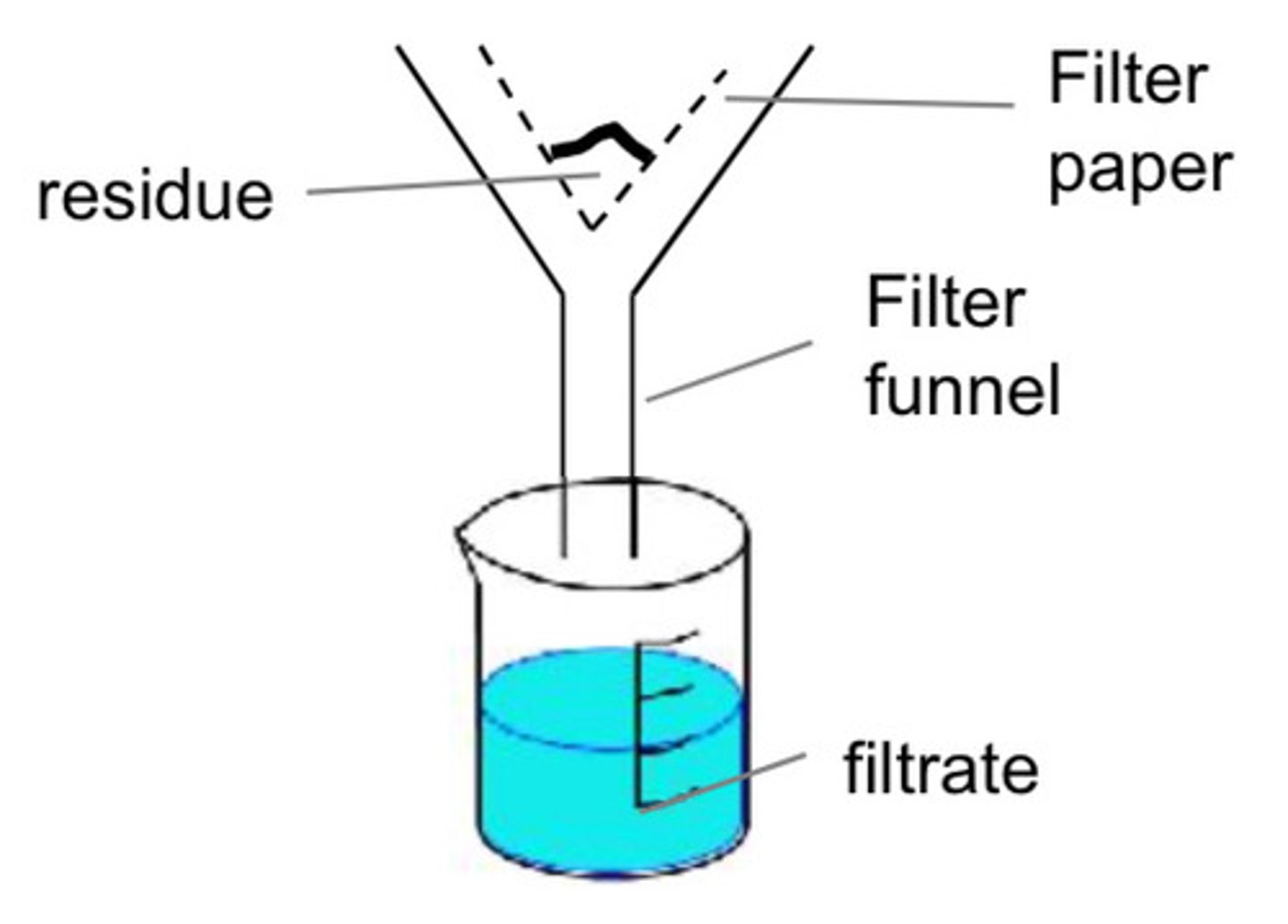
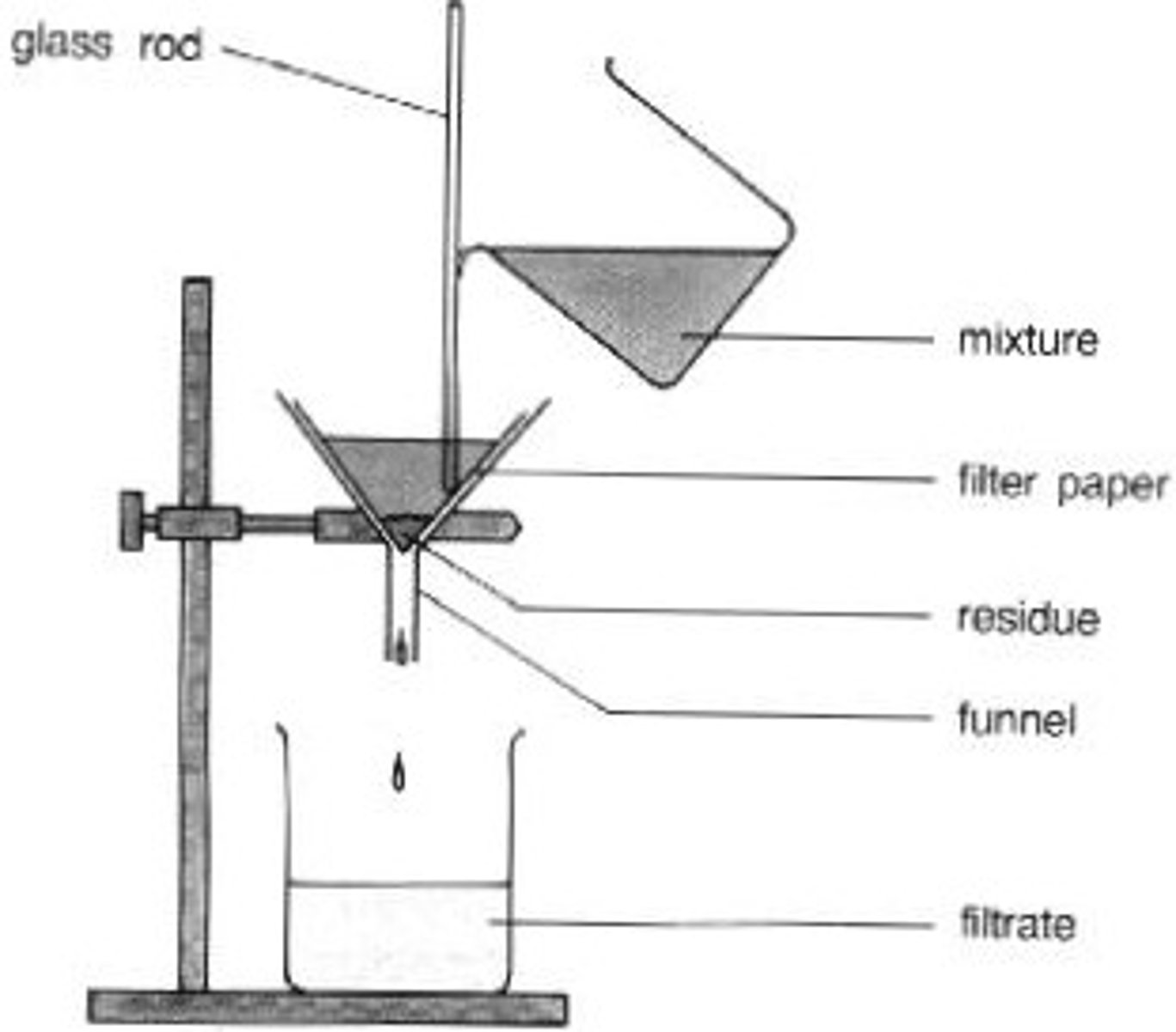
How does filtration work?
liquid passes through filter paper and insoluble solid get caught by the filter paper. The substance in filter paper is the residue and the liquid that moves through is the filtrate.
What can crystallisation/evaporation be used for?
For separating a solute from a solution. Forms pure crystals.
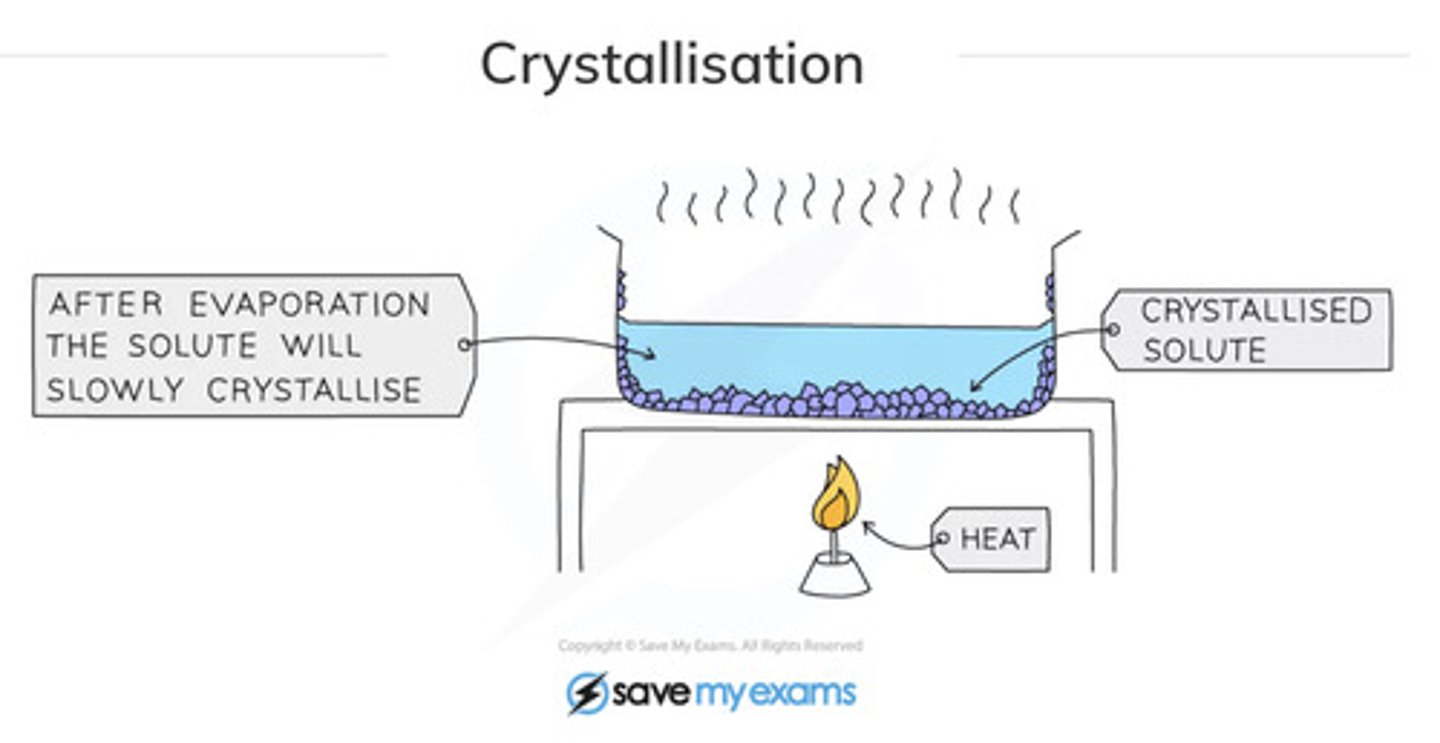
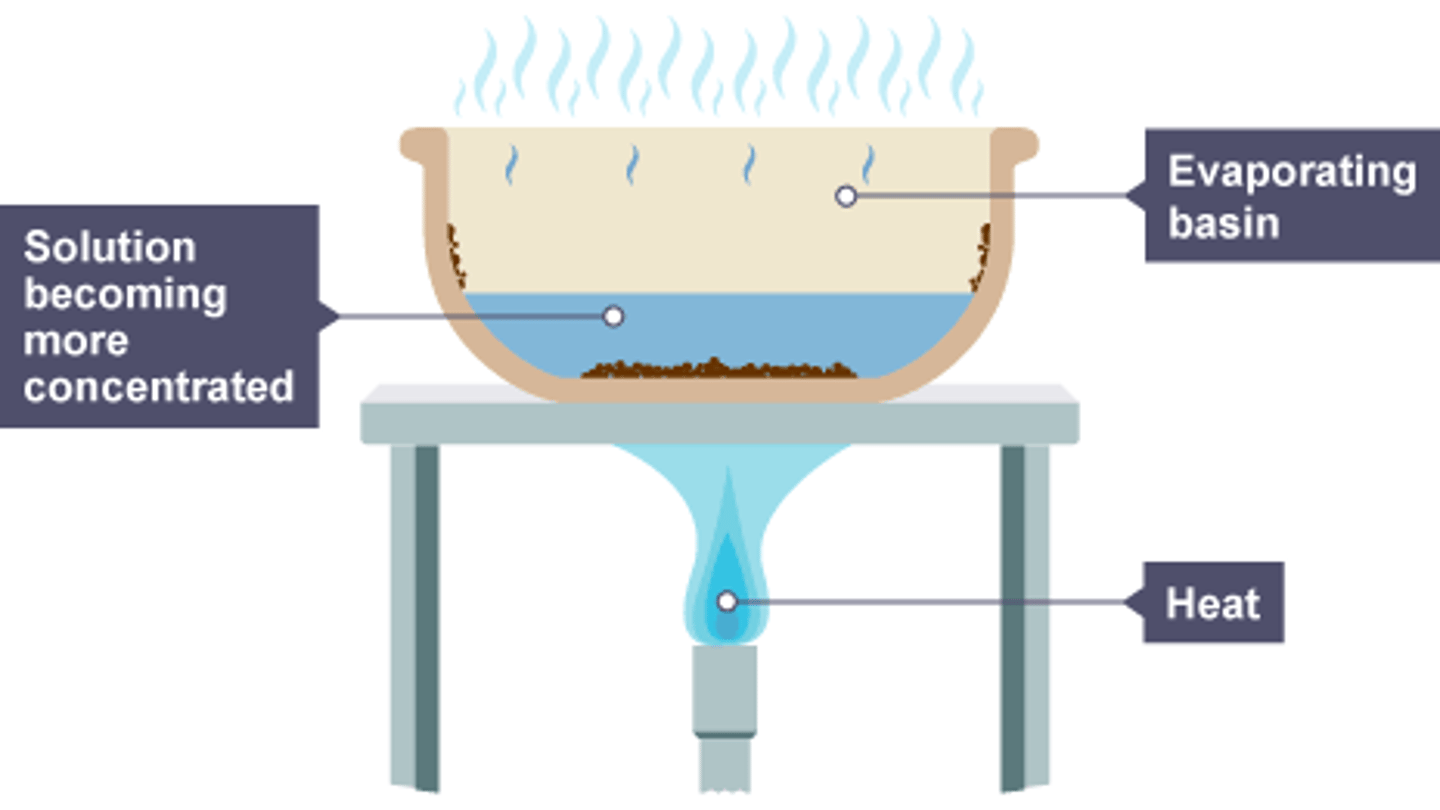
How does crystallisation/evaporation work?
Heat solution in an evaporating basin to boil off water until it is almost saturated. Turn off heat and allow crystals to form as more water evaporates and the solution cools. You can now separate them by filtration.
What can separating funnel be used for?
for liquids that do not mix (immiscible)
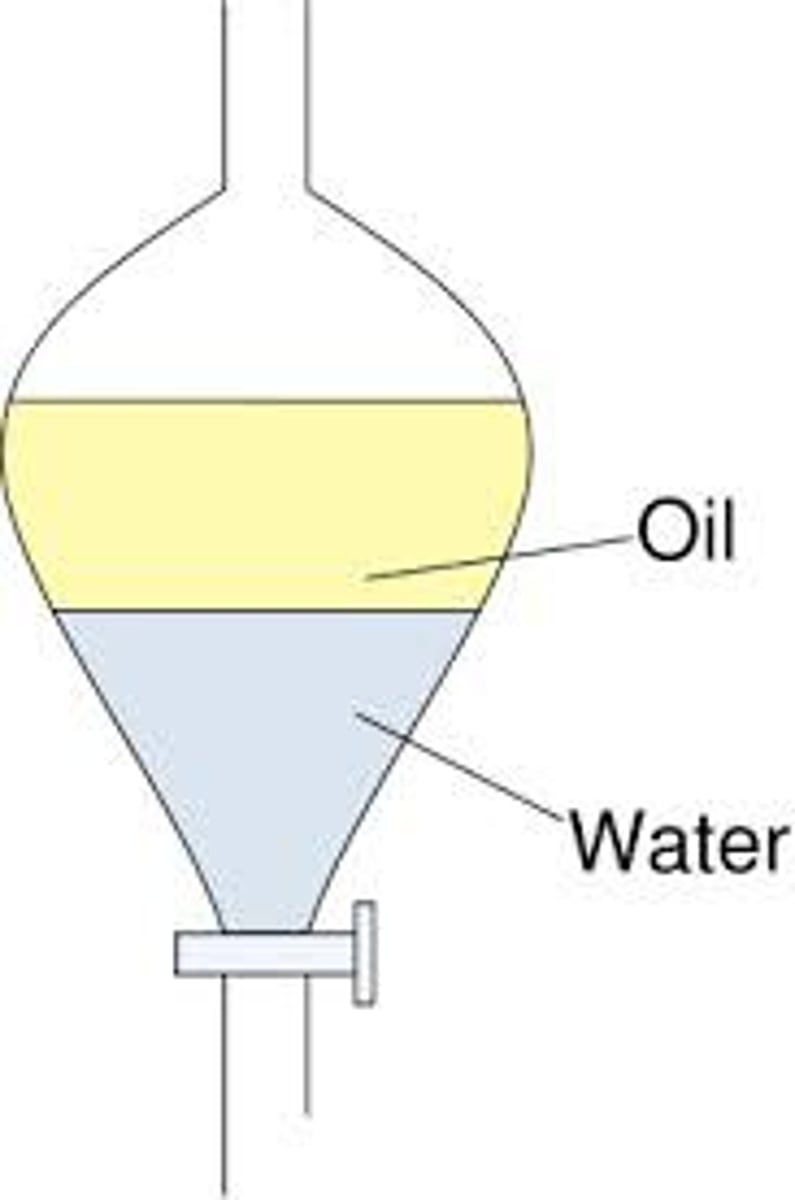
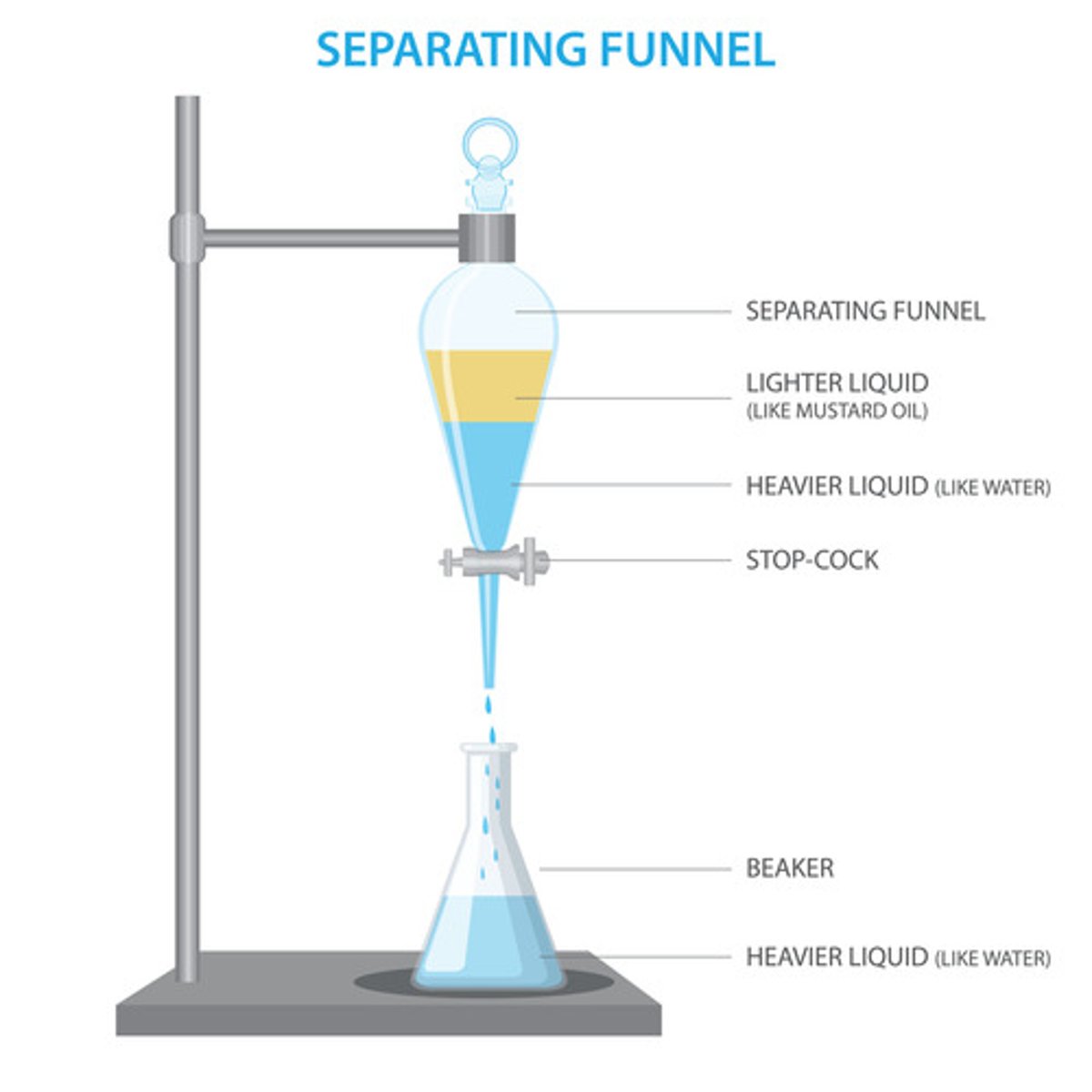
How does separating funnel work?
The mixture is placed inside the separating funnel and left to settle. The less dense liquid will form a layer above the more dense layer below. The stopcock can be used to remove the more dense bottom layer.
What can paper chromatography be used for?
For separating a variety of mixtures. You use it to separate coloured inks or food colourings.
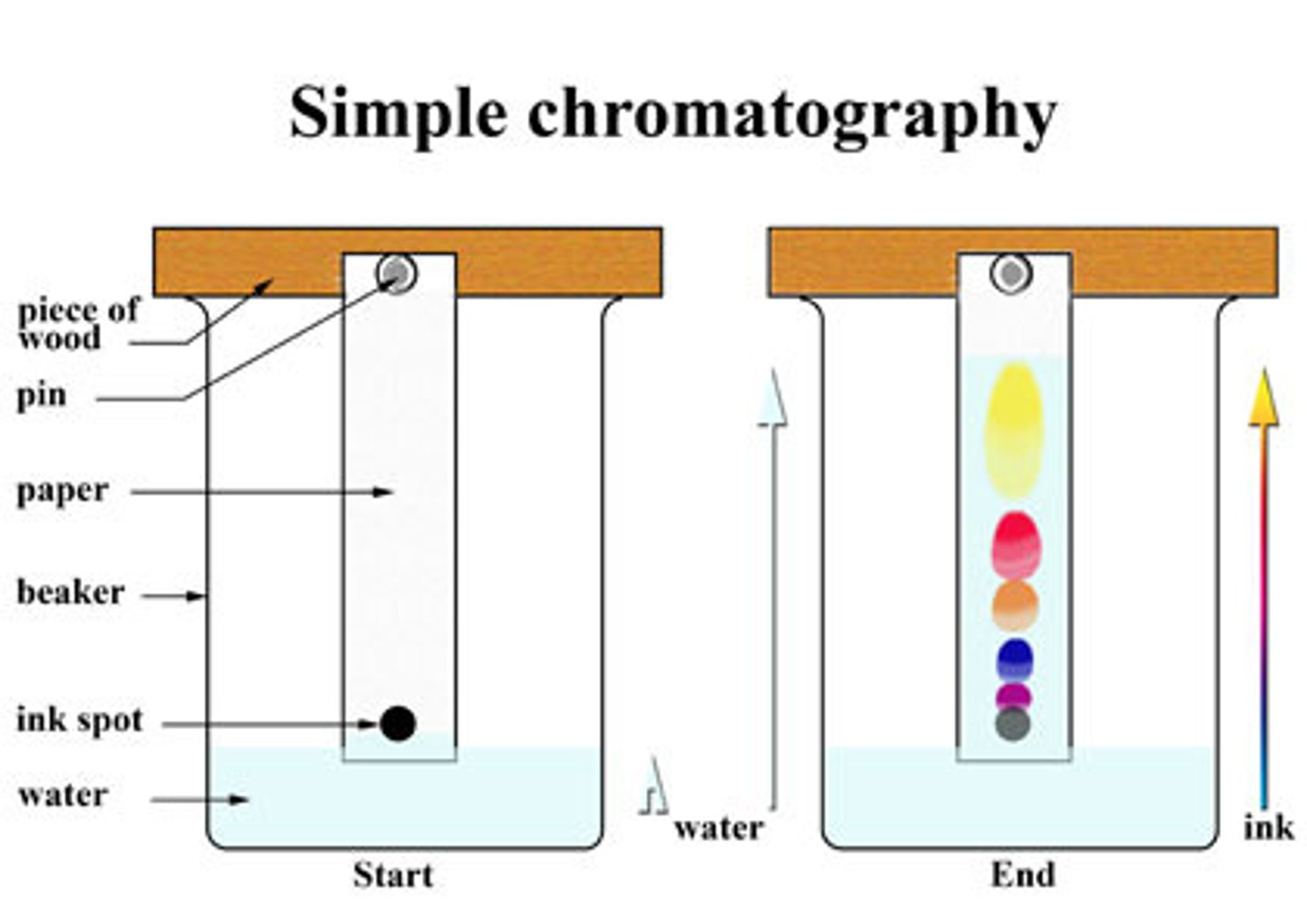
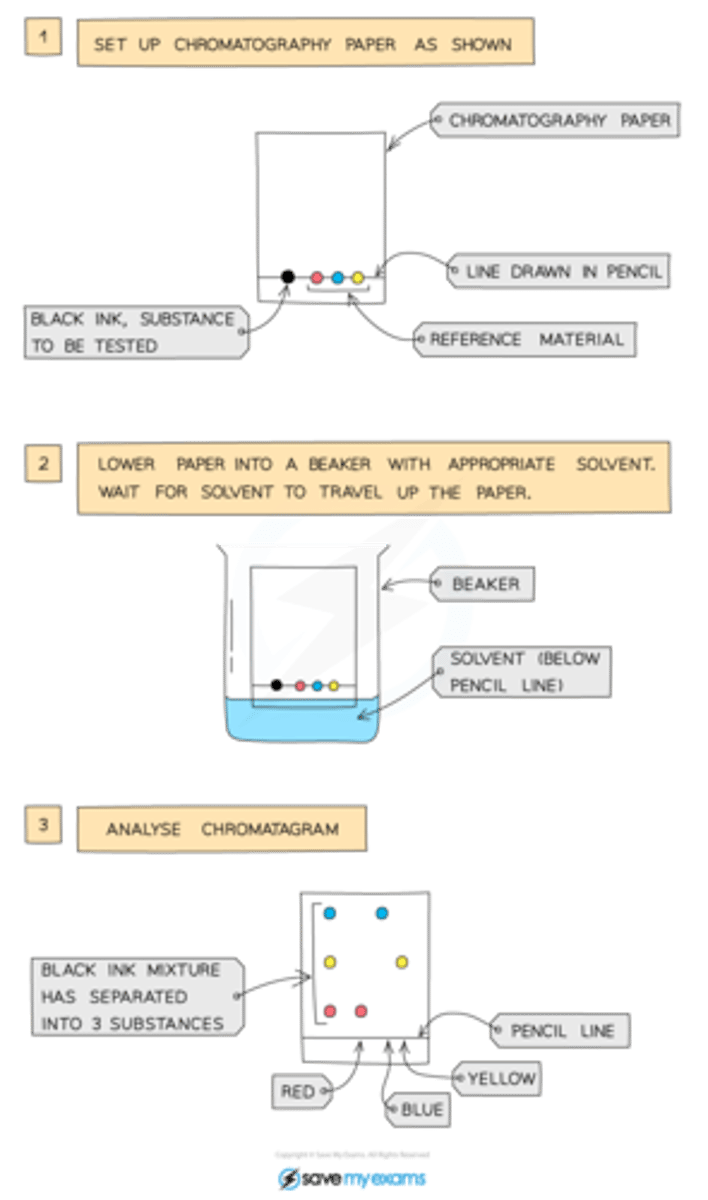
How does paper chromatography work?
First, set up the paper with your substance on the drawn in paper line at the bottom of the page. Then lower the beaker (below the pencil line) with the paper in the appropriate solvent and wait for the solvent to travel up that paper. Analyze chromatogram.
How do you calculate the Retardation Factor (Rf)?
Distance moved by a spot (from the pencil line) / distance moved by the solvent front (from the pencil line)