Electromagnetic induction
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is induced when a conductor or a coil moves through a magnetic field or when the magnetic field changes through it?
A voltage
What factors affect the size of the induced voltage of the conductor or coil when it moves through a magnetic field or a magnetic field changes through it?
The speed at which the conductor or coil is moved through the magnetic field
The speed at which the magnet is moved through the coil
The strength of the magnetic field used
The number of loops of coil
The size of the loops of coil
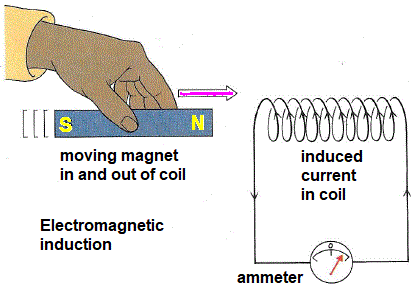
Describe the generation of electricity by the rotation of a magnet within a coil of wire and the coil of wire within a magnetic field.
The rotation of the magnet inside a coil of wire or by rotating a coil of wire inside a magnetic field induces a potential difference (voltage) between the ends of the coil, causing the current to flow, generating electricity.
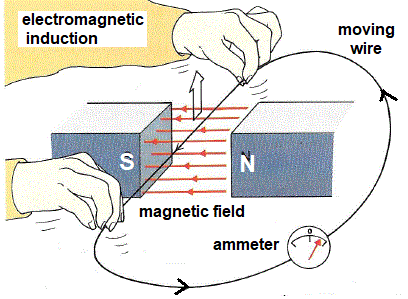
What factors affect the size of the induced voltage when rotating a magnet within a coil of wire and the coil of wire within a magnetic field?
Strength of magnetic field
Size of coil
Number of loops of coil
Speed of magnet
Speed of rotation of coil of wire
What is the purpose of a transformer?
It is used to increase or decrease the voltage of of an alternating current by having different numbers of turns on the input and output sides.
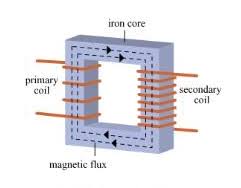
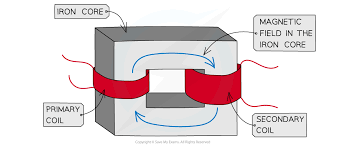
How does a transformer work?
When supplied with an alternating current, the primary coil will generate an alternating magnetic field
Which then induces an alternating magnetic field in the iron core
Which then induces an alternating voltage in the secondary coil
And if the circuit is complete, will lead to an alternating current
Describe the structure of a transformer.
Iron core (magnetic field)
a.c. input
a.c. output
primary coil
secondary coil
What is a step-up transformer?
It increases the voltage and decreases the current
Explain the use of a step-up transformer in the large scale generation and transmission of electrical energy.
It could be used as electricity leaves a power station and enters the national grid
Why is it important to use a step-up transformer before electricity is transmitted from a power station to the national grid?
It is important to have a high voltage and low current in order to minimise energy loss during transmission as a high current would heat the wires, causing energy loss via heat
What is a step-down transformer?
It decreases the voltage and increases the current
Explain the use of a step-down transformer in the large scale generation and transmission of electrical energy.
It could be used before electricity enters a home, to ensure the voltage is low enough
State the equation linking the relationship between input (primary), output (secondary) voltage and turns (primary, secondary)
input (primary) voltage / output (secondary) voltage = primary turns / secondary turns
State the equation linking input and output power for 100% efficiency
input power = output power
VpIp = VsIs
V = voltage
I = current
p = primary
s = secondary