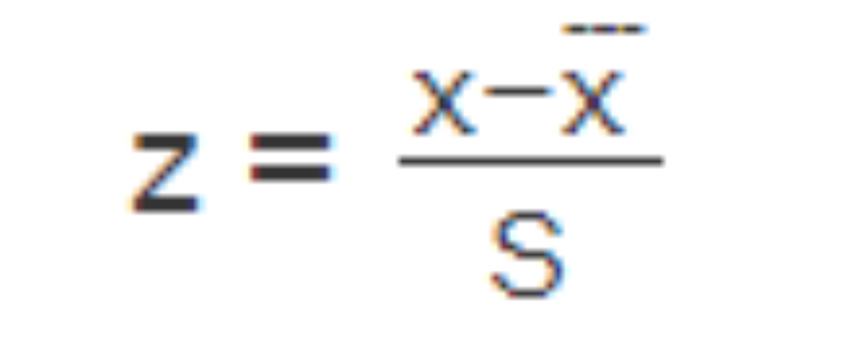MMW
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
symmetry
bilateral symmetry two sides are mirror like.
Radical Symmetry
identical parts are arranged around the fixed point.
Fractals symmetry
mini version are same as the whole object.
Fibonacci sequence
an infinite number sequence in which each number (term) is the sum of the two preceding numbers.
Fibonacci sequence
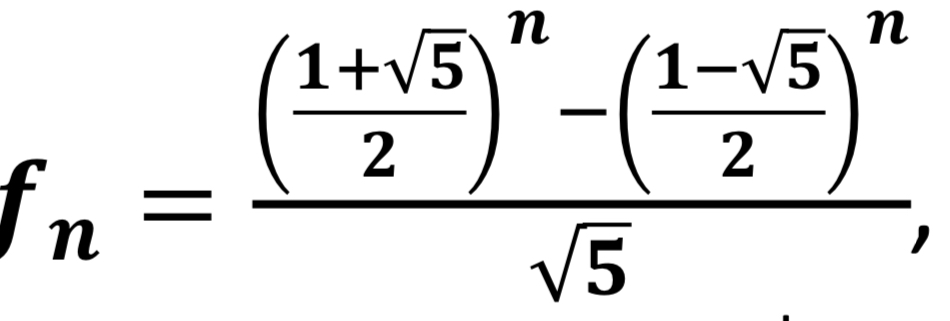
Golden ratio
another mathematical theory that connects well with nature.
Precise
use of symbols
concise
words are turn into symbols
powerful
able to express complex thoughts with relative ease.
mathematical expression
without a comparison symbols or equal sign
mathematical sentence
statement that includes a comparison symbol
sets
The groups are called sets for as long as the objects in the group share a characteristic
and are thus, well defined
Finite set
a set whose elements are limited or countable
Infinite set
a set whose elements are unlimited or uncountable
Unit set
a set with only one element.
Empty set
a set with no elements.
Joint sets
two or more sets with at least one common element.
Disjoint sets
two or more sets with no common elements.
Universal set “U”
a set that refers to the totality of all elements.
Cardinal sets
refers to the number of elements or members in the set.
Equivalent sets
two or more sets with the same cardinal number.
Equal
sets two or more sets with the same elements, regardless of the order.
Subsets
a set where all its elements are also elements of another larger set.
Power sets “P(S)”
refers to the set of all subsets of a given set.
Inductive reasoning
Drawing a general conclusion from a repeated observation or limited sets of observations of specific examples.
Inductive reasoning
Specific to General
Deductive reasoning
Drawing general to specific examples or simply from general case to specific case.
Deductive reasoning
General to specific
Conjecture
A conclusion or generalization drawn by using inductive reasoning.
Counterexample
A specific example that shows a conjecture is false.
Argument
Are the reason or reasons offered for or against something
Premises
Minor or major propositions or assertions that serve as the bases for an argument.
Syllogism
An argument composed of two statements or premises followed by a conclusion.
Conclusion
The last step in a reasoning process.
Polya’s Strategy
Named after George Polya (1887-1985). It is a four-step problem solving strategy that are deceptively simple.
Polya’s first step
Understand the problem
Polya’s second step
Devise a plan
Polya’s third step
Carry out the plan
Polya’s fourth step
Review the solution
Statistics
branch of mathematics that deals with collecting, organizing, presenting, analyzing, and interpreting data to help make decisions or draw conclusions.
Data
statistics is always a result of experiment, observation, investigation and other means and often appears as a numerical figure and then evaluated to make it into useful knowledge.
Descriptive statistics
summarizing values to describe its group characteristics.
Variable
a numerical characteristic or attribute associated with the population being studied.
Inferential statistics
interpretation of the results of the information gathered by the statistician.
Discrete variable
type of variable that can take only specific, separate values
Continuous variable
type of variable that can take any value within a given range.
Nominal
Tags or Labels
Ordinal
Order or ranking
Interval
No absolute 0
Ratio
With absolute 0
Population
defined as groups of people, animals
Sample
Section or part of a population
Mean
Average
Mean
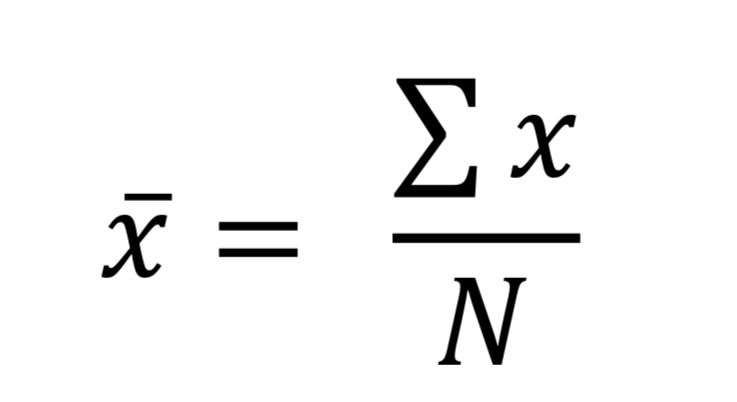
Median
Middle data
Mode
Most frequent data
Measures of dispersion
describe how spread out or scattered the values in a data set are.
Range
simplest measure of variation to find.
Range

Mean Absolute Deviation
Is the average of how much the data values differ from the mean.
MAD
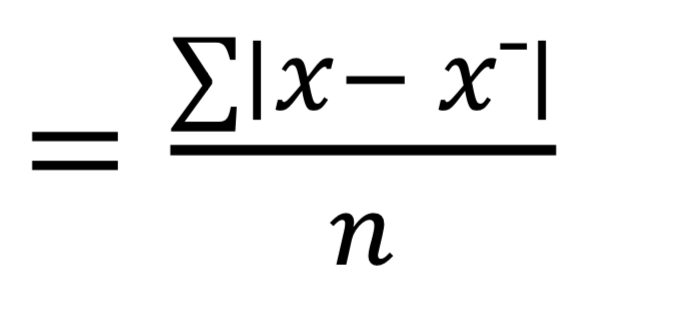
Variance
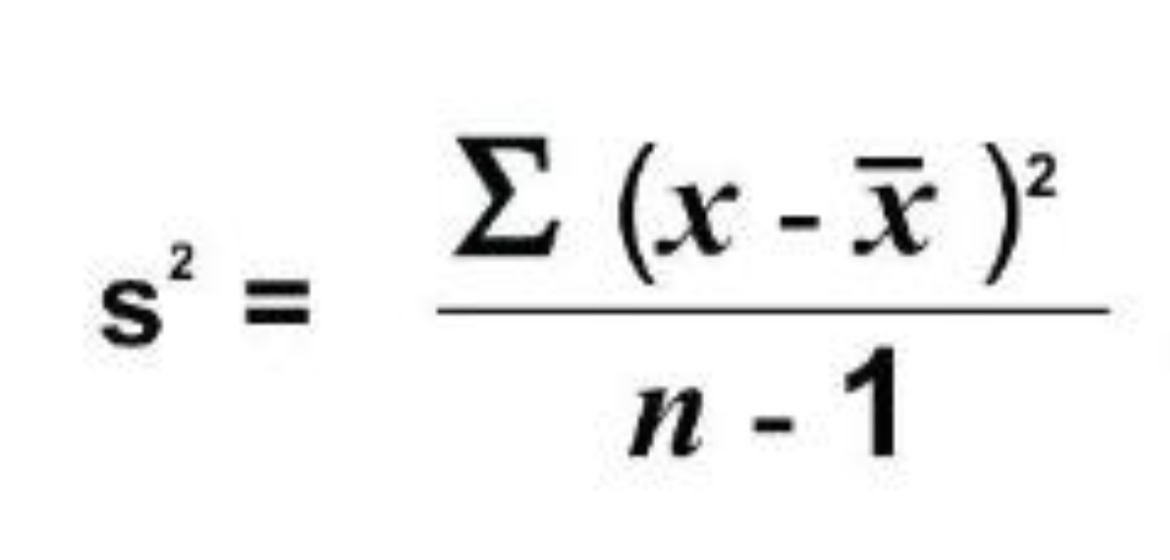
Standard Deviation
Coefficient Variation
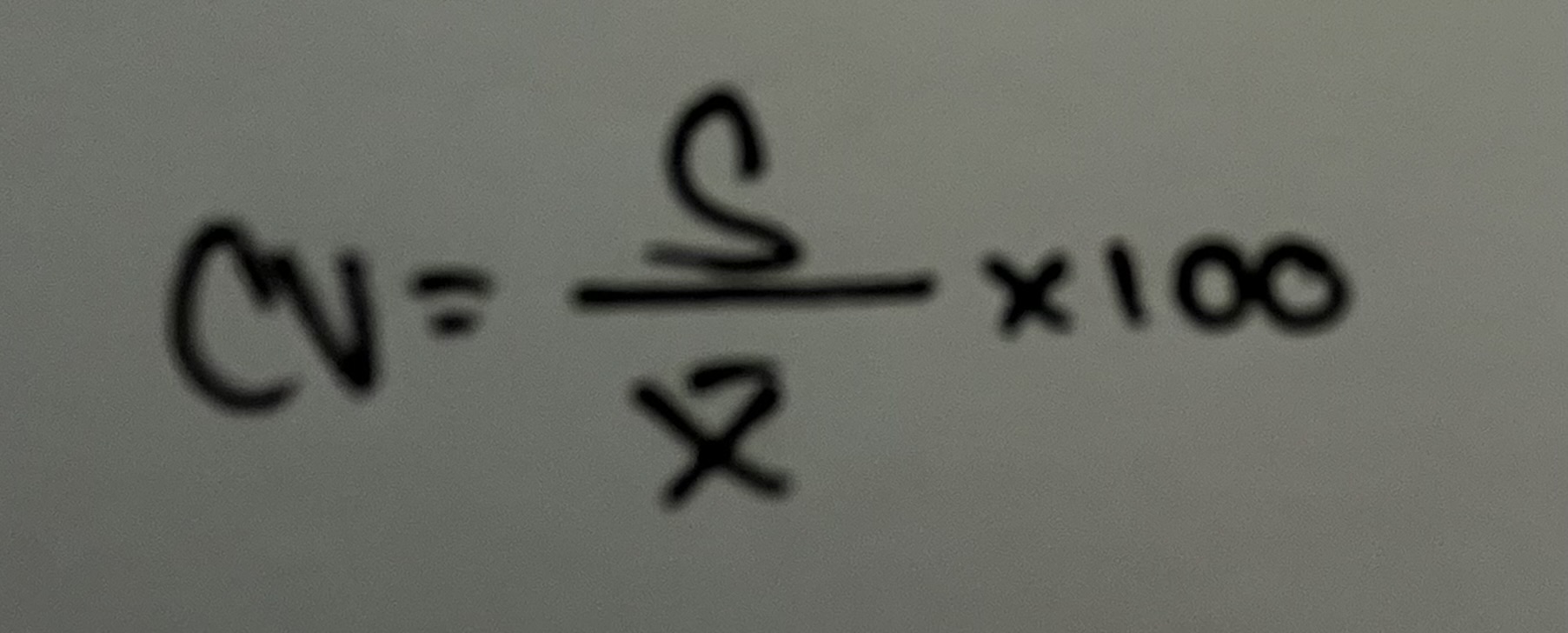
Normal Distribution
a bell-shaped and symmetric probability distribution
Standard Normal Distribution
A z-score value is needed to convert a normal distribution into a standard normal distribution.
Z-score