Chapter 20: Cancer Genetics and Genomics
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Cancer
abnormal growth that invades and spreads
What is the relationship between genes and cancer?
Genetic changes can lead to cancer if they alter the way your cells grow and spread
3 cellular pathways affected by cancer-causing gene mutations
1. Cell fate: differentiation
2. Cell survival: oxygen availability & preventing apoptosis
3. Genome maintenance: ability to survive in presence of reactive oxygens species
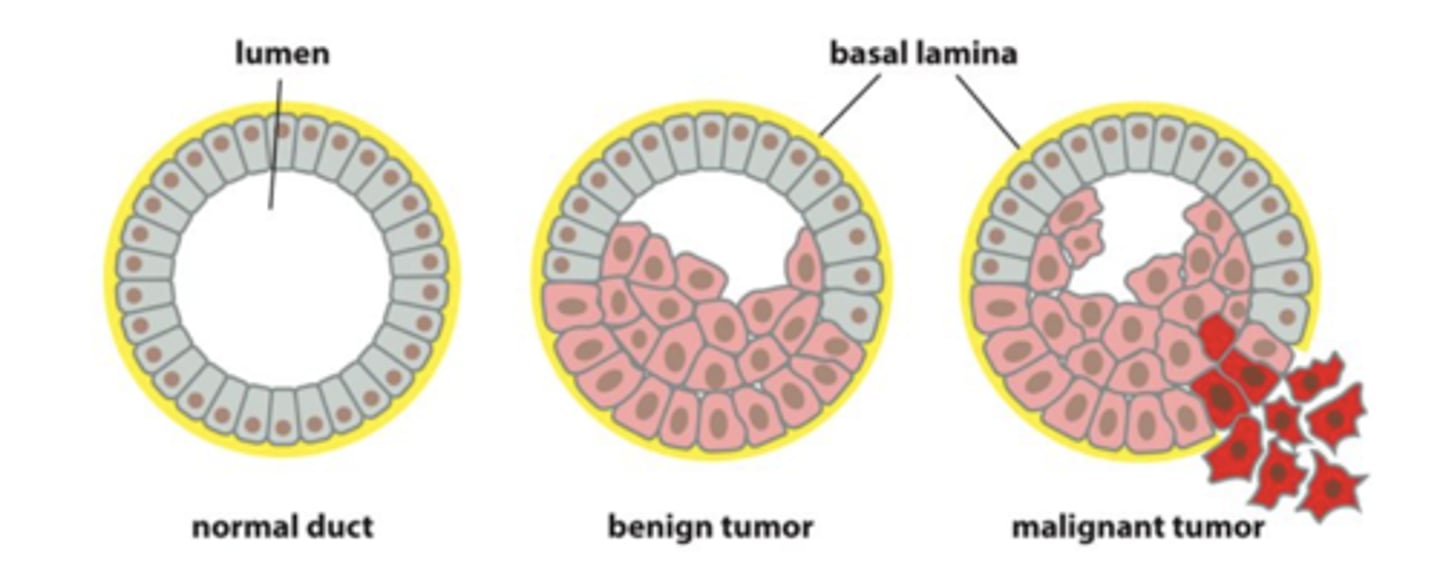
Distinguish between a benign and a malignant tumor.
Benign: does not spread or invade surrounding tissue
Malignant or cancerous: invade other tissues
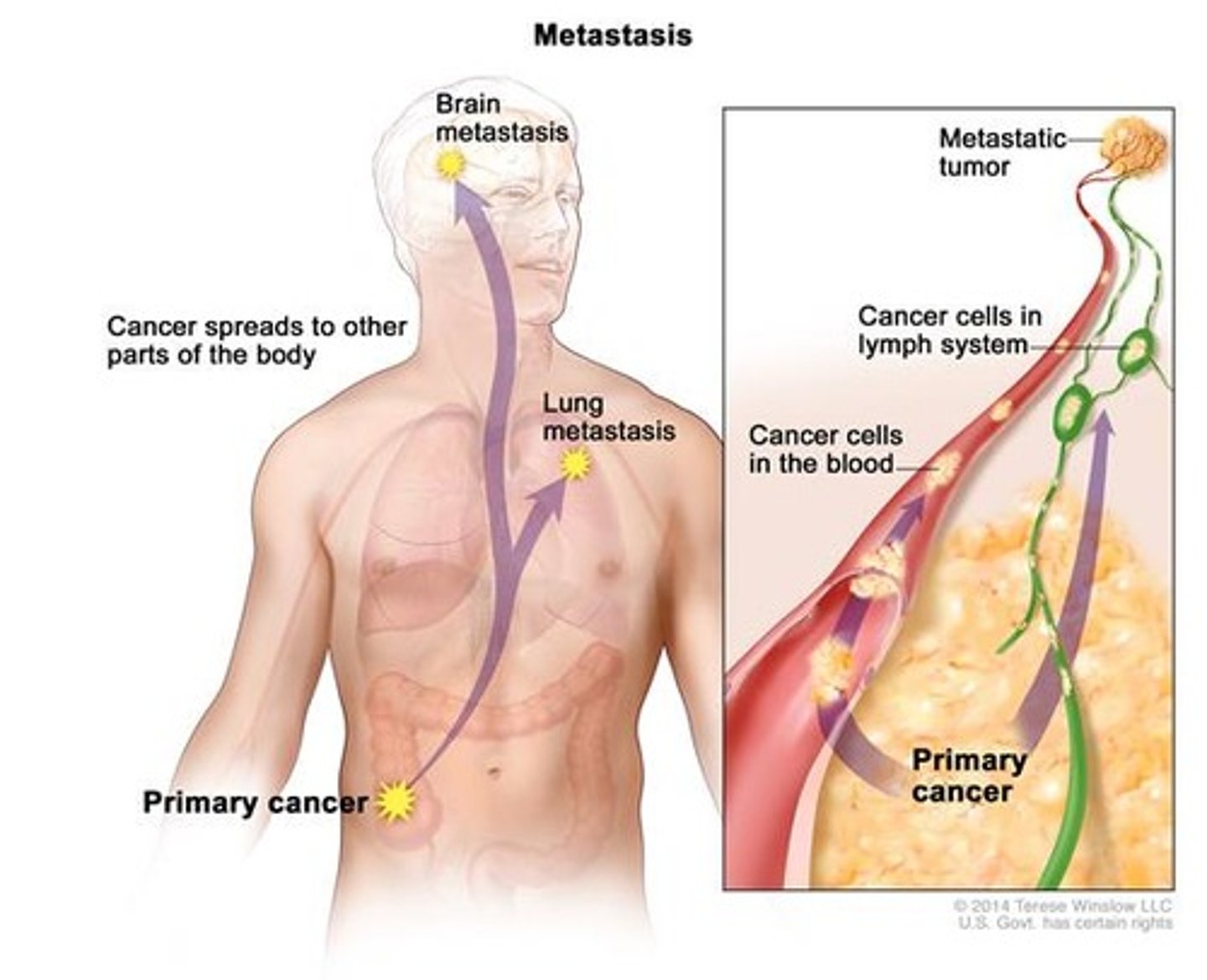
Why is metastasis dangerous?
When tumor detaches and spread to far regions of the body via blood or lymph which makes cancer difficult to detect and treat
Define carcinogens
substances that cause cancer
What are the 3 categories of cancer critical genes
1. Oncogenes (100+)
2. Tumor suppressor genes (30+)
3. DNA repair genes
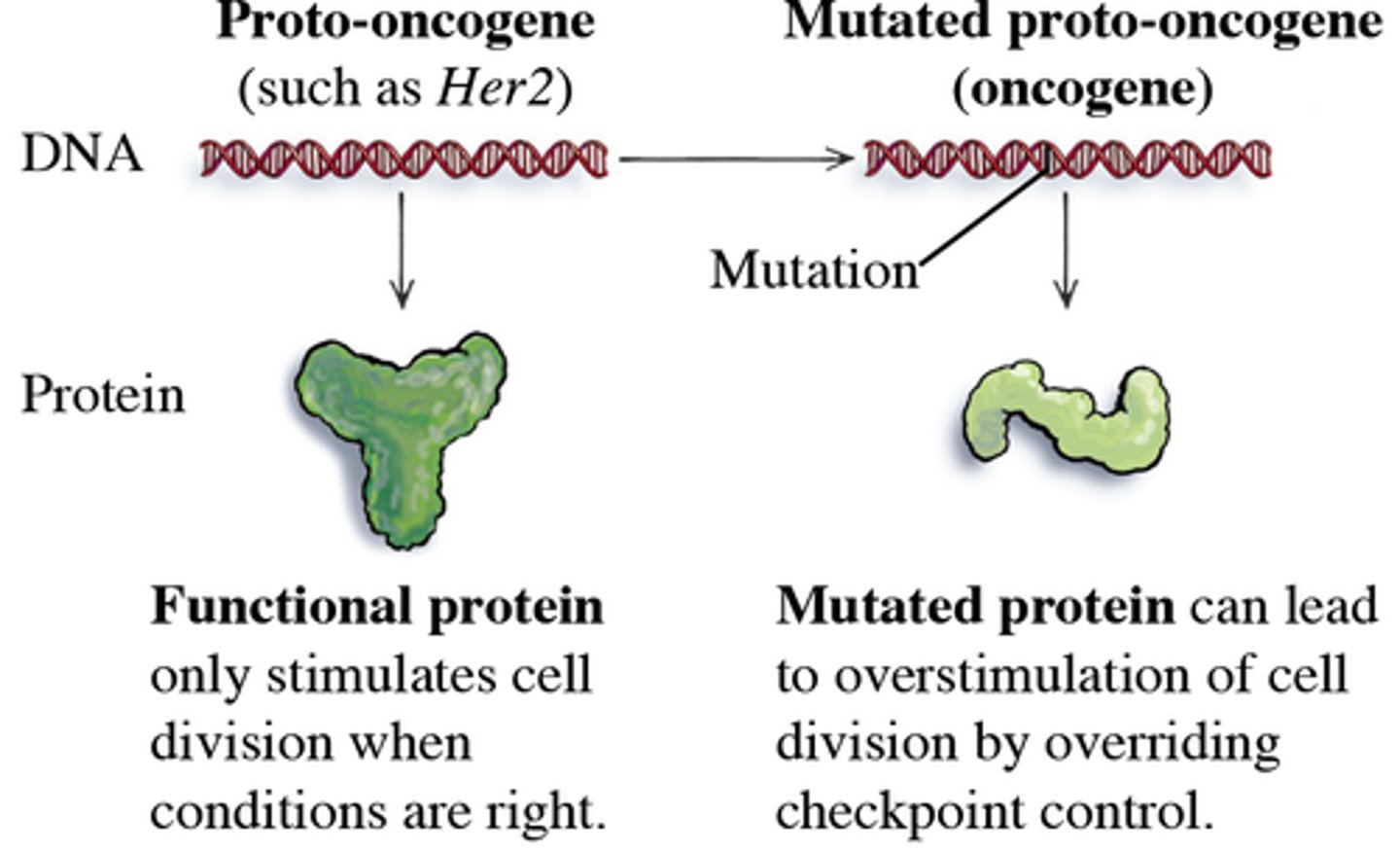
What are oncogenes?
-Mutated versions of proto-oncogenes (normal genes that control normal growth)
-Cause cancer if inappropriately activated
-Dominant gain-of-function (only one dominant mutation is needed to cause a cell to become cancerous)
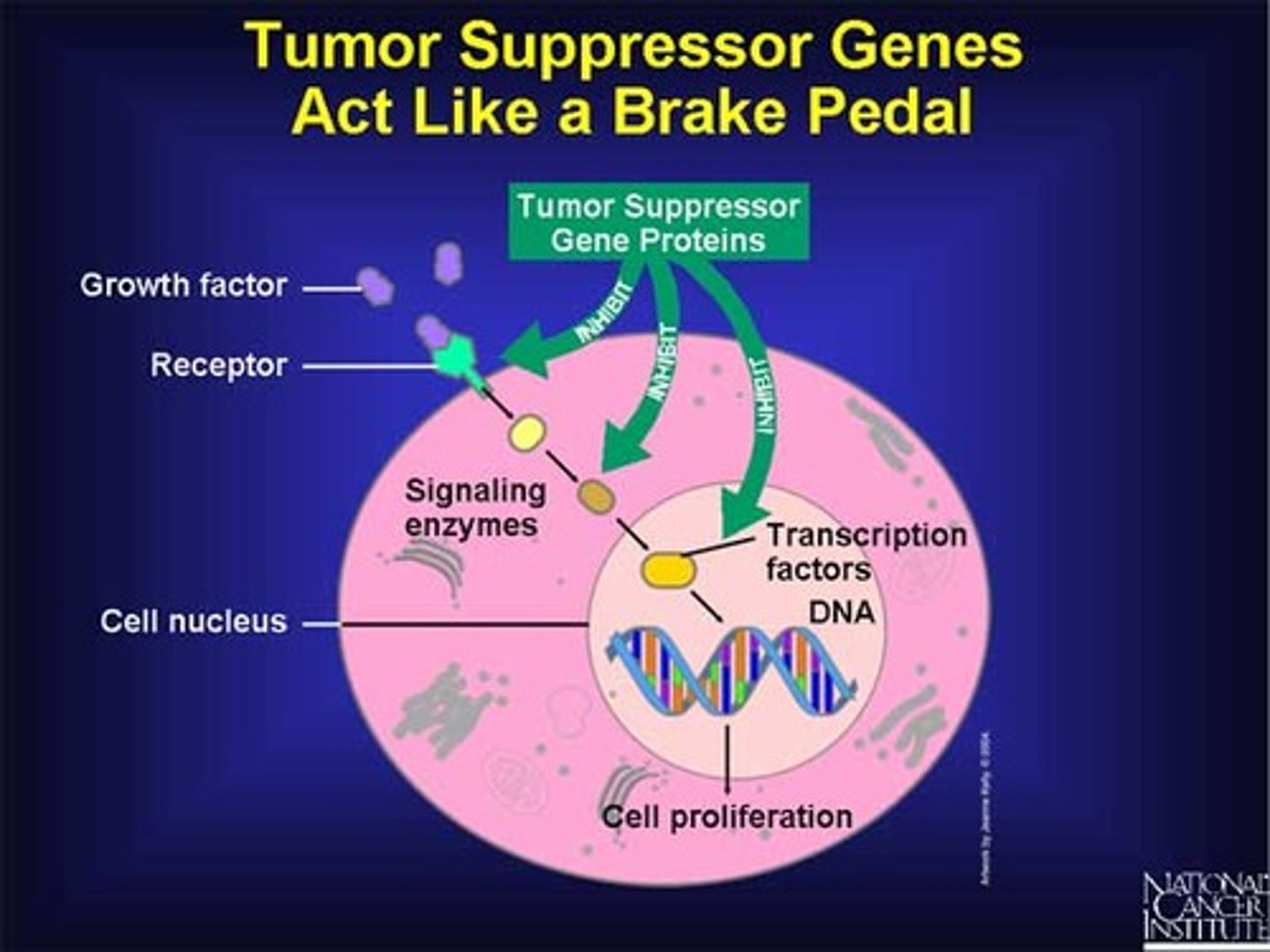
What are tumor suppressor genes?
-Control cell cycle checkpoints & apoptosis
-Cause cancer when deleted or inactivated
-Recessive loss-of-function mutations (knock out 2 copies of TSG for cancer to result)
What are DNA repair genes?
-Allow other mutations to persist
-Inherited in a single-gene function > cause diverse and widespread tumors
What happens when there is a mutation in the gene that controls the cell cycle
There will be inappropriate mitosis and failure to pause and repair DNA will cause mutations to persist
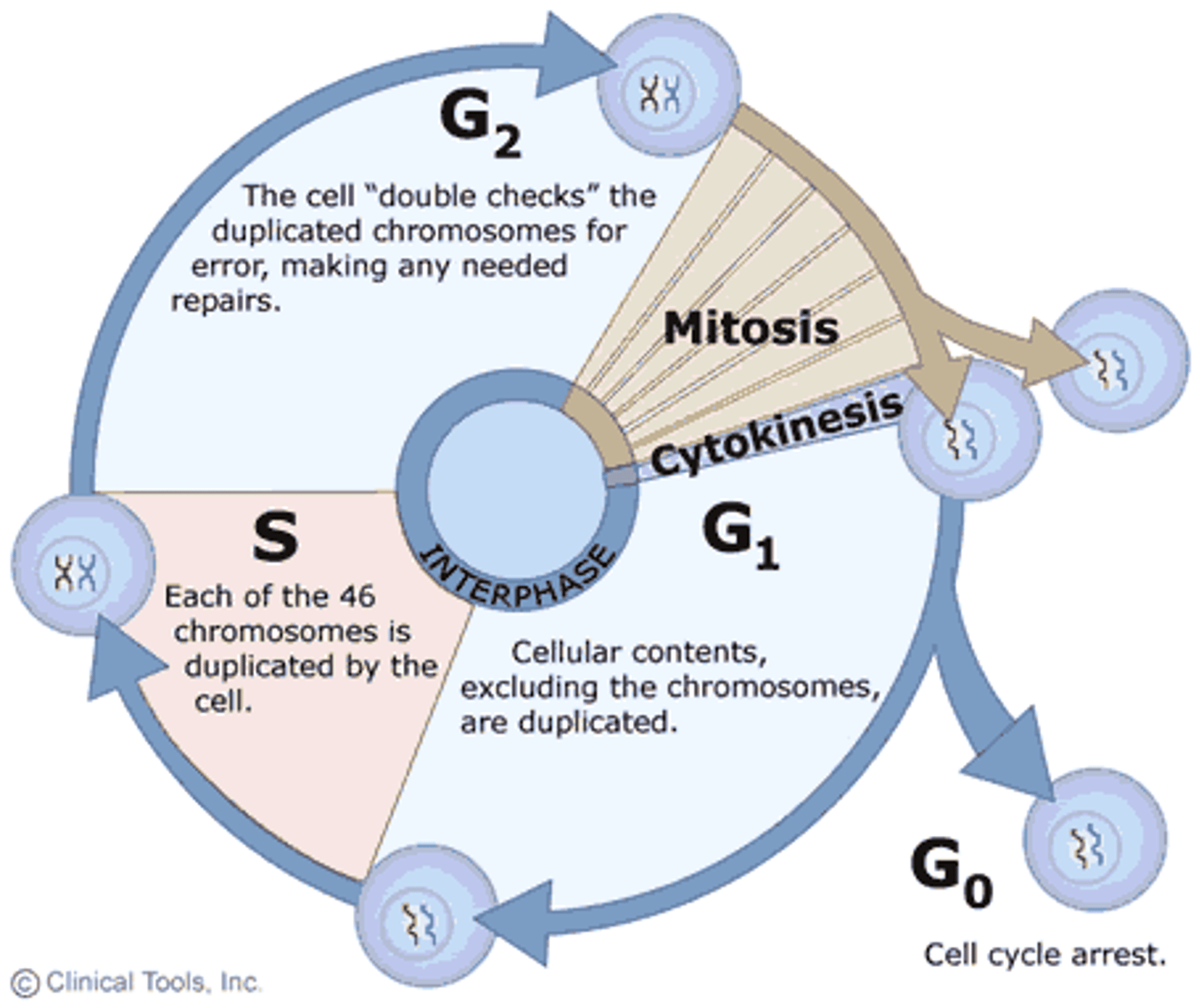
Explain how the loss of control of telomere length may contribute to cancer
Telomerase keeps telomeres long in gametes and stem cells > if telomerase is left on, telomerase extend and there is no brake on rapid cell division
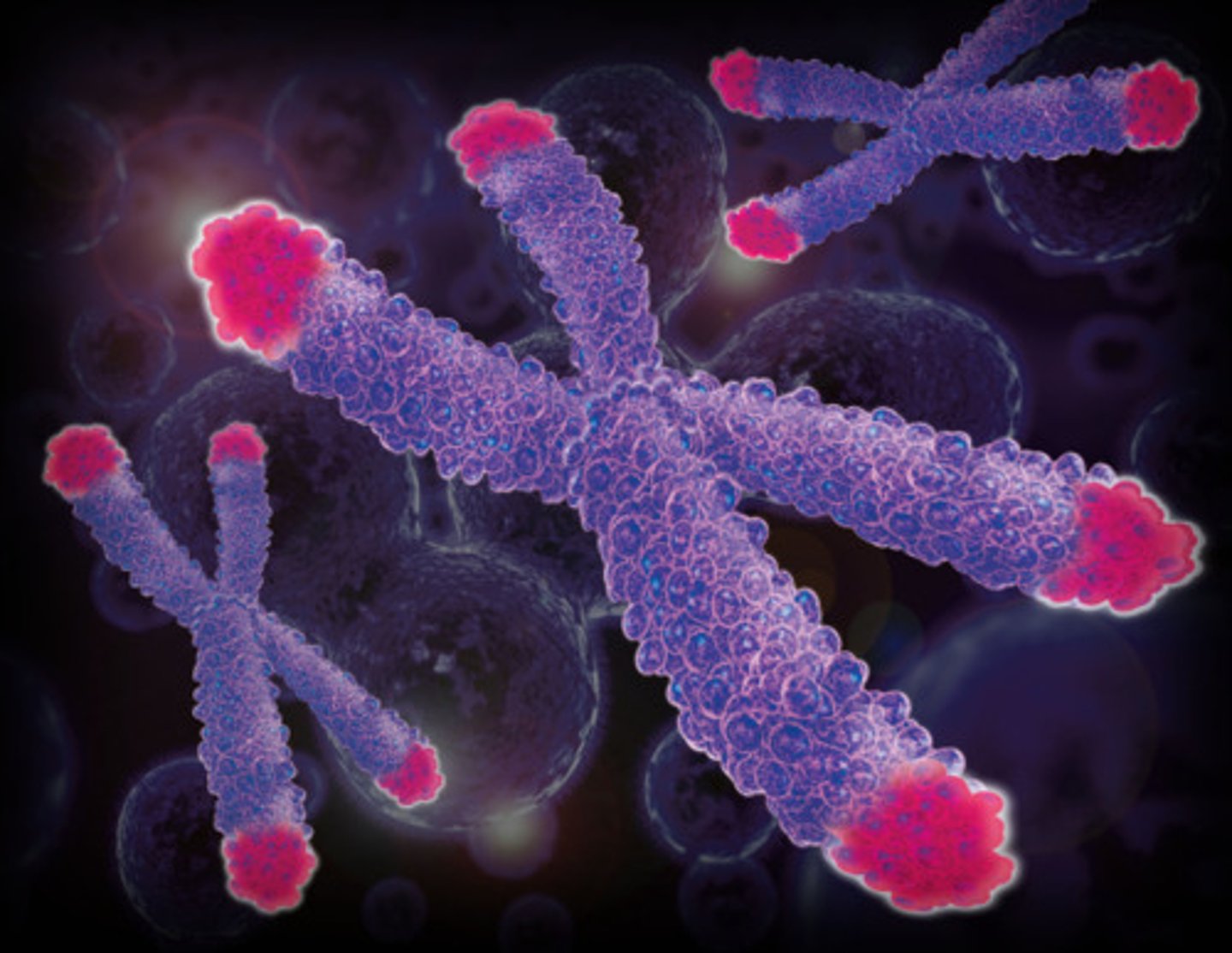
Describe two abnormalities of chromosomes in cancer cells.
Aneuploidy is when there is a missing or extra chromosome
Translocation can increase expression of a gene
What is the difference between Inherited (germline) and Sporadic (somatic) mutations
Germline mutations when gametes (10% of cases) are affected
-passed on to offspring (mutation present in all cells of the individual)
-cancer develops when 2nd somatic mutation occurs
Somatic mutations occur sporadically in non-sex cells (90% of cases)
List the characteristics of cancer cells
-Contain heritable mutations (passed to daughter cells)
-Dedifferentiated (less specialized than normal cell types)
-Unusual cell growth (no contact inhibition)
-Invasive (squeeze into any space)
-Metastatic (able to move to new locations)
-Induce angiogenesis (formation of new capillaries)
-Secrete hormones that encourage their own growth
-Aneuploid (missing or extra chromosomes)
Explain how cancers form from shifting the balance of cell types in a tissue
Cancers result from the loss of balance at the tissue level that favors cells that can divide continually or frequently
Mutation shifts balance to create more stem and progenitor cells > tumor formation
List and the 3 strikes of cancer
1. Breakthrough
2. Expansion
3. Invasion
Describe the strike of cancer: Breakthrough
1st driver mutation in a gatekeeper (oncogene on or tumor suppressor gene off) enables a normal cell to divide faster clones accumulate
Describe the strike of cancer: Expansion
2nd driver mutation boosts division rate cancer cells divide more frequently & survive in harsh environments
Describe the strike of cancer: Invasion
further mutations in multiple pathways cancer grows and spreads
How do environmental factors contribute to cancer
by mutating or altering the expression of genes that control the cell, apoptosis, and DNA repair
True or false: Both environmental and genetic factors contribute to cancer risk
True
Is melanoma only caused by environmental factors (sun exposure)? Explain why or why not
No, melanoma can also be caused by the variant of melanocortin-1 receptor (MC1R) gene