Week 3: Electrolytes Na+ and H2O (Dr. Zhang)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
total body water is distributed primarily into two compartments which are
ICF osmolality is primarily determined by the concentration of potassium and its accompanying anions (mostly organic and inorganic phosphates).
Sodium and its accompanying anions (chloride and bicarbonate) comprise more than 90% of the total osmolality of the ECF;
most cell membranes are freely permeable to water, thus the osmolalaties of ICF and ECF are equal
true
(e.g., 0.9% sodium chloride [NaCl] solution) to the ECF will result in no change in intracellular volume because there will be no change in the effective ECF osmolality is what
isotonic
e.g., 3% NaCl) to the ECF will result in a decrease in ICF (cell) volume is what
hypertonic solution
e.g., 0.45% NaCl) to the ECF will result in an increase in cell volume is what
hypotonic solution
The ECF concentration of effective osmoles determines its tonicity, which directly affects the distribution of water between the extra- and intracellular compartments.
true
Plasma osmolality is primarily determined by the sodium concentration, but serum glucose and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) may contribute
true
what is commonly known as antidiuretic hormone (ADH), is synthesized in the hypothalamus and released from the posterior pituitary as a result of both osmotic and nonosmotic regulators.
arginine vasopressin
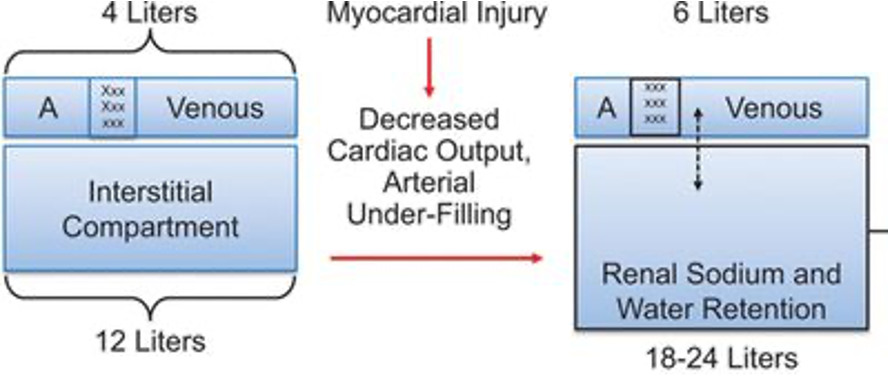
how do the following change in heart failure patient
1)Extracellular Fluid volume
2)Interstitial fluid volume
3)Arterial volume
what is the level for hypenatremia
higher than 145mEq/L
what is the level for hyponatremia
lower than 135 mEq/L
1a. Hypovolemic hypernatremia, decreased ECF volume
1b. Euvolemic (isovolemic) hypernatremia, normal ECF volume
1c. Hypervolemic Hypernatremia, increased ECF volume
hypernatremia
2a. Hypertonic hyponatremia
2b. Hypotonic hyponatremia
2b1. Hypovolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia, decreased ECF volume
2b2. Euvolemic (isovolemic) hypotonic hyponatremia, normal ECF volume
2b3. Hypervolemic Hypotonic Hyponatremia, increased ECF volume
hyponatremia
is always associated with hypertonicity and cellular dehydration, resulting from a deficit of water relative to ECF sodium content.
hypernatremia
most often results from water loss by either renal or extrarenalmechanisms. Less commonly, hypernatremia can result from administration of hypertonic fluids or excess sodium ingestion.
hypernatremia
what develops when the net result of these effects is the loss of more sodium than water.
hyponatremia
a.blocks sodium reabsorption in the distal tubules in renal cortex , increases sodium and water removal from the body.
b.decreases in effective arterial volume stimulates ADH release,
c.ADH increases free water reabsorption in the collecting duct,
d.increases water intake because of stimulation of thirst
thiazide diuretics
what causes more severe hyponatremia than loop diuretics
thiazides diuretics
The most common causes of SIADH include tumors such as small cell lung or pancreatic cancer, CNS disorders (e.g., head trauma, stroke, meningitis, pituitary surgery), and pulmonary disease (e.g., tuberculosis, pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome).
true
what is associated with ECF volume expansion occurs in conditions in which the kidney’s sodium and water excretion are impaired.
hyponatremia
Patients with cirrhosis, HF, or nephrotic syndrome have an expanded ECF volume and edema, but a decreased effective arterial blood volume (EABV).
true