BIo 1AL- lab 5 (photosynthesis and vibrio colony restreak)
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
chloroplast vs thylakoid membranes
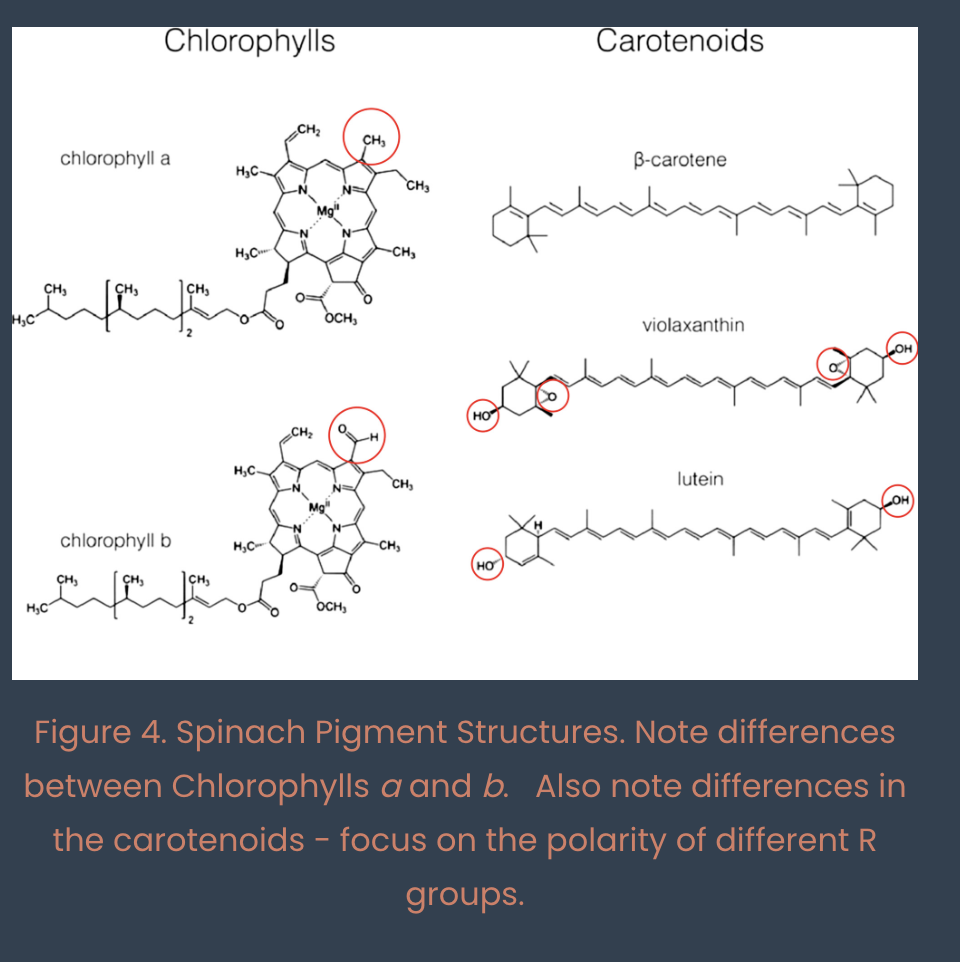
pigments (chlorophyll a, b, and carotenoids) located in thylakoid membranes
flowchart list of photosynthesis inc. reactants and products
light rxns in thylakoid membrane:
hill rxn: H20 + NADP++ ADP + Pi —> ½ O2 + 2(NADT + H+) + ATP
PSII, Pq, Cyt, Pc, PSI, Fd, NADP+ reductase
describe the series of chemical rxns in chloroplasts that lead from absorption of light to transfer of E- from water to NADP and production of both O2 and ATP
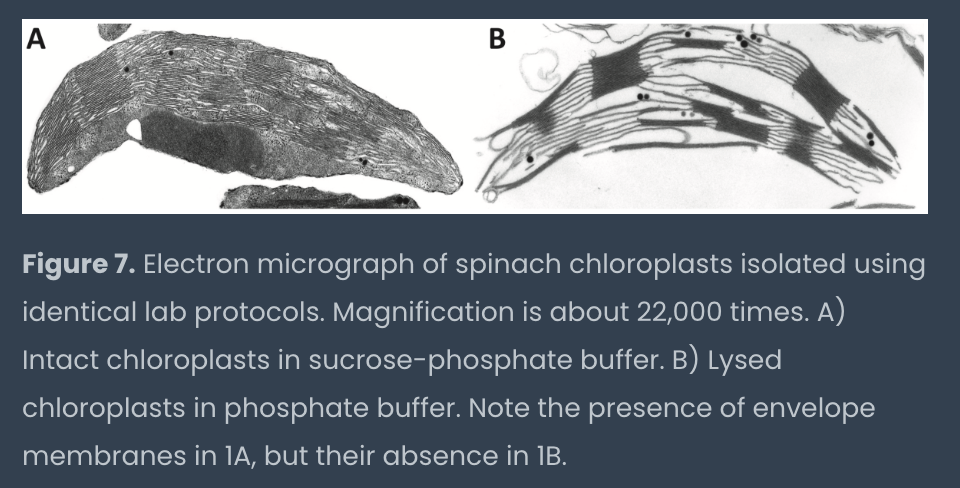
explain each step of the chloroplast isolation procedure: use of blender on spinach leaves, filtration with cheese cloth, pelleting chloroplasts, use of suc-phos, and phos buffers, and generating standardized concentrations of chloroplasts
blend spinach w sucrose-phos buffer (chloroplasts stay intact due to sucrose osmoticum)
pour off supernatant to leave pellet of chloroplast
tube A: add acetone to extract pigments
supernatant II includes pigments and used for paper chromatography
tube E: resuspend pellet with cold suc-phos buffer
add E to tube L (phos only buffer) and spec for absorbance
calculate and create standardized chloroplast soln (0.1 mg Chl/mL
explain the role of controls when testing drugs
provide a baseline for comparison to ensure that any observed effects are truly caused by drug being tested
understand how paper chromatography works to permit isolation of pigments, and identify chlorophylls a and b, carotenoids, and carotene on your chromatogram
pigments partition betwen hydrophilic paper and hydrophobic developing solvent
polar pigments migrate a SHORTER distance
hydrophobic pigments migrate a FARTHER distance
bottom to top (polar to nonpolar) : Chl b, Chl a, carotenoids, carotene
calculate an Rf value
RF = migration distance of substance/ migration distance of solvent(solvent front)
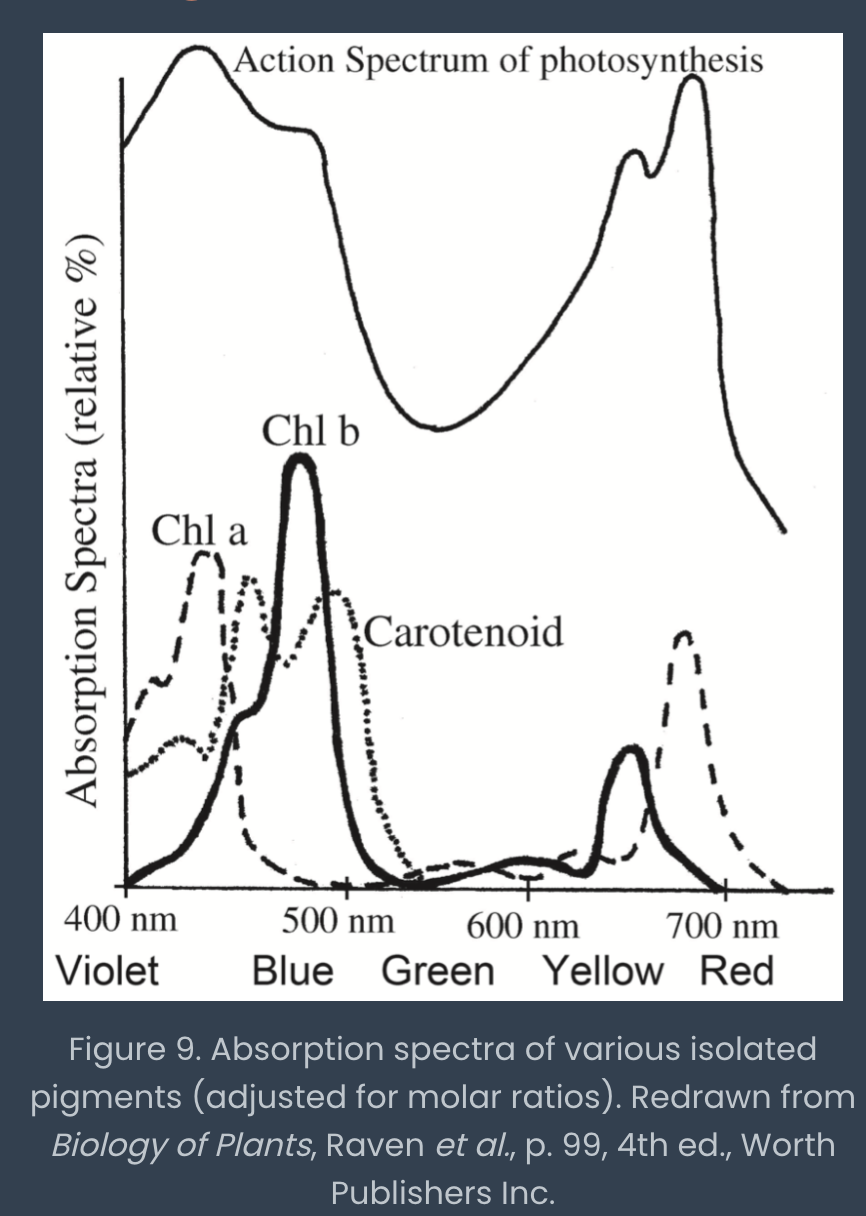
absorption/action spectrum of a mixture of pigments
graph of the amount of light absorbed by a given substance at various wavelengths
DCPIP vs DCMU vs methylamine
DCPIP- artificial e- acceptor (end of ETC), used to assess rate of photosynthesis bc it loses blue color as it recieves e-
correlates to the rate of e- transfer from H20 to PSII, the ETP, PSI, and the reductase
DCMU- uncharged hydrophobic, inhibits photosynthesis by blocking e- flow from PSII to Pq
methylamine- uncharged weak base, enters lumen to bind to H+ in thylakoid
adding it should speed rates of ETC (loss of blue color)
how to make a standardized chloroplast soln
0.0533 x absorbance “L” x 36 = mgChl/mL in “E”
CxVx = XyVy to calculate Vx mL to add to make standardized soln
Cx- “E”
Cy- 0.1 mgChl/mL
Vy- 5mL buffer + Vx mL
add 5 mL cold suc-phos buffer and add Vx mL of tube E
effect of phosphate buffer
lack of sucrose lyses chloroplasts allowing us to add a loss of color e- acceptor (DCPIP)