Perfect competition
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What are the four features of a perfectly competitive market?
Many small buyers and sellers
No barriers to entry or exit
Homogeneous products
Perfect information
Elastic demand is when PED is between:
negative 1 and negative infinity
If demand is elastic, what will our demand curve look like?
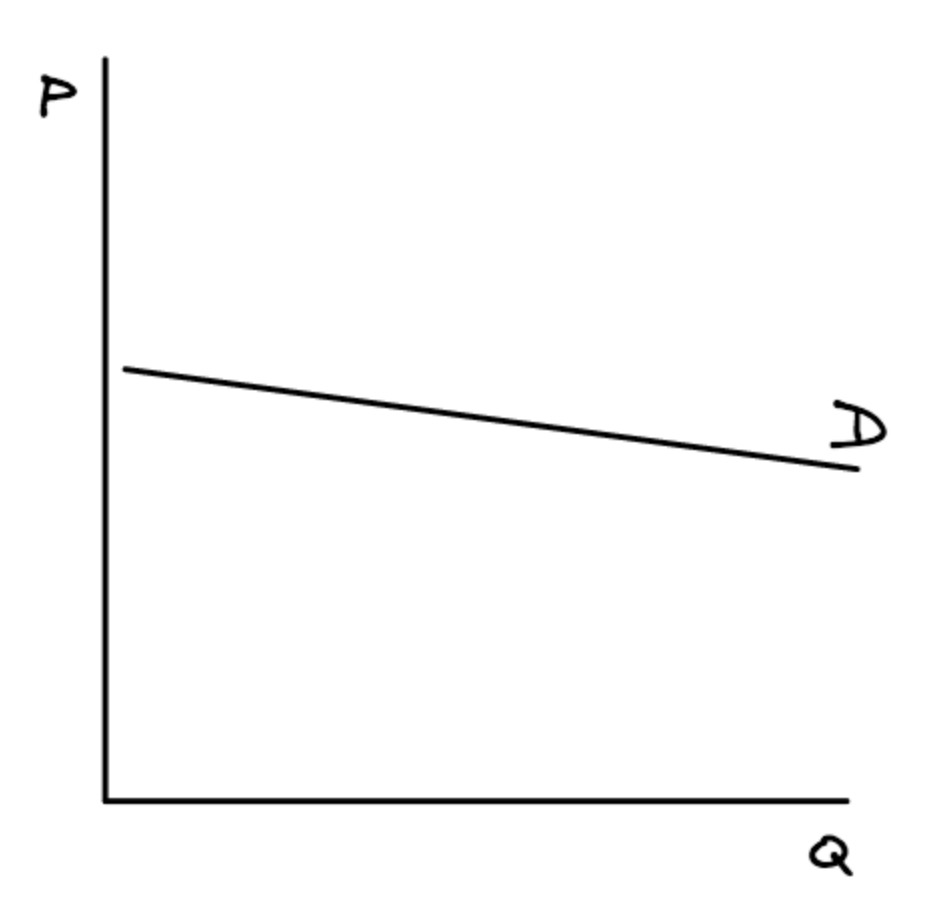
As PED gets closer to negative infinity, demand becomes:
more elastic
As demand becomes more elastic, consumers will:
respond more to changes in price.
When PED = negative infinity, demand is:
perfectly elastic
Mandy’s demand is perfectly elastic, so if Mandy puts her price up, even just a little bit to £3.10...her demand will:
Perfectly elastic demand means consumers are ultra-mega-super-responsive to price changes! If Many puts her price up even just a bit, her consumers will stop buying from her completely because they’re so sensitive to price changes. They’ll immediately switch to another seller in the market.
What is a perfectly competitive firm’s AR and MR curves?
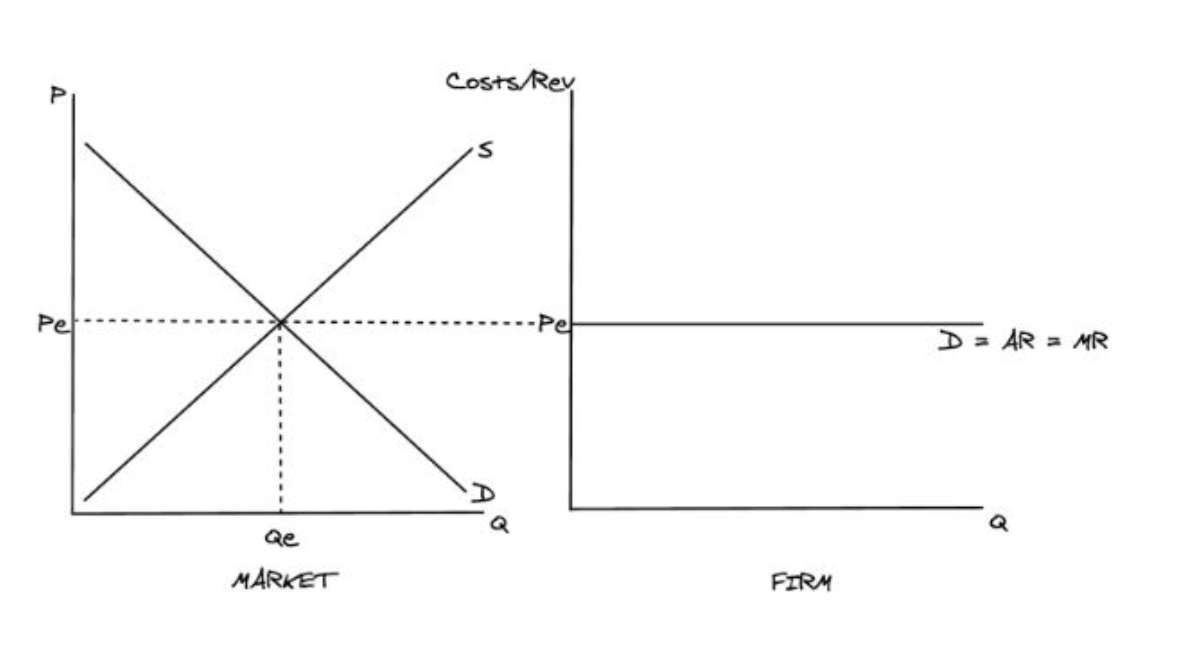
What is a perfectly competitive diagram?
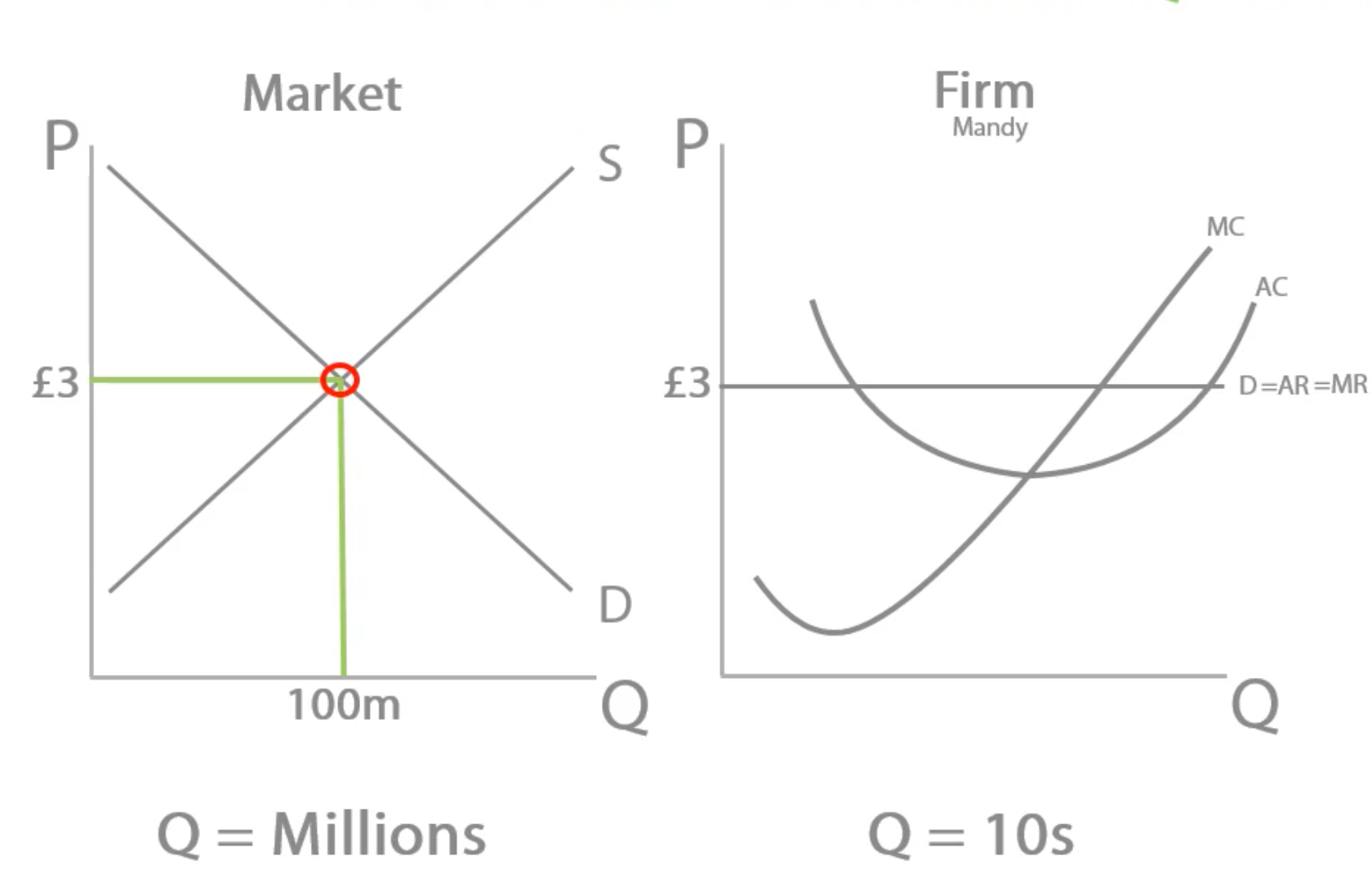
Explain how a perfectly competitive market moves to its long run equilibrium. (4 marks)
In the long run, perfect information means potential sellers outside the market will see the opportunity to make supernormal profit by entering the market.
There are no barriers to entry, so new firms will enter the market, increasing supply and decreasing price until AR touches the bottom of the firm’s AC and all the supernormal profit is gone.
New firms will no longer enter the market because they can no longer make supernormal profit, so we have reached the long run equilibrium.
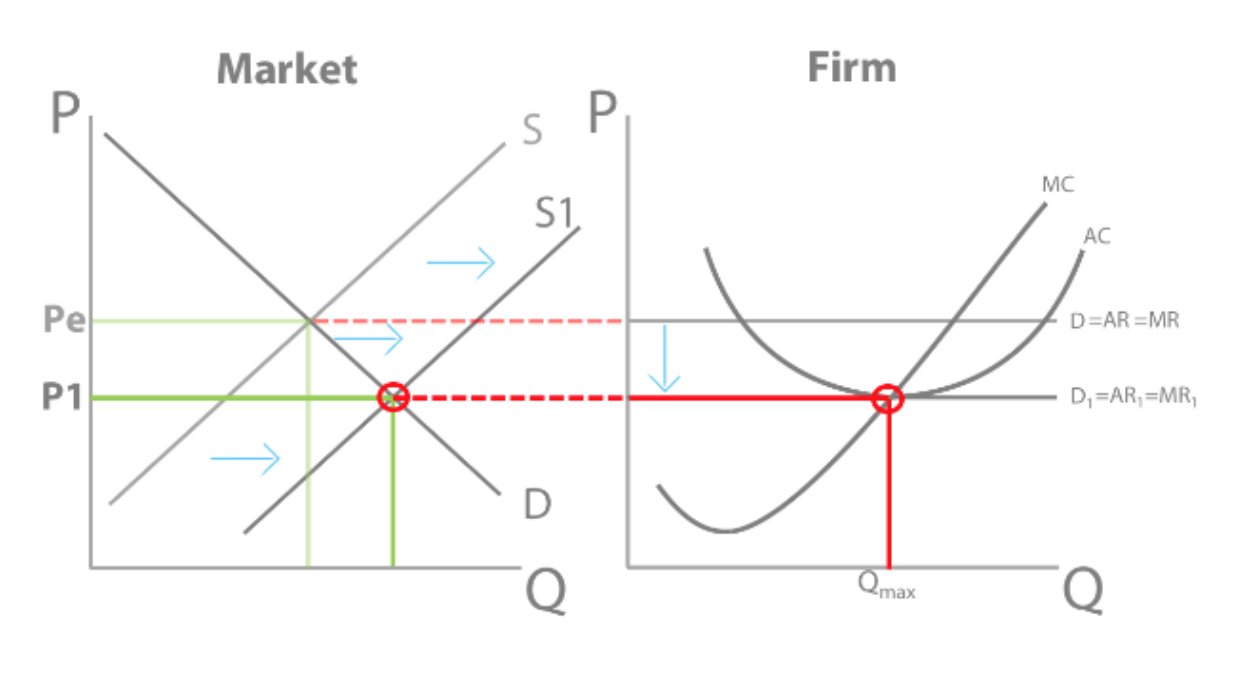
Sketch a diagram showing what will happen between the short run and long run, if a firm is making supernormal profit in the short run:
Firms are incentivised by supernormal profit to enter the market. There are no barriers to entry so they can easily enter the market. This increases supply from S to S1. This decreases price from Pe to P1, so price = lowest point along AC and all supernormal profit has been competed away. Only normal profit can be made in the long run.
Explain how a perfectly competitive market, where firms are making a short run loss, moves to its long run equilibrium. (4 marks)
If firms are making a short run loss, they will leave the market and this is easy to do because there is no barriers to exit.
As firms leave the market, supply decrease and prices will increase back up, until normal profit can be made.
At this point, firms will be covering their opportunity cost - so they’ll no reason to leave the market anymore. Which means we’ve reached our long run equilibrium - where firms are making normal profit.