basal ganglia & cerebellum 🏃♀️ dr candelaria
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Pyramidal system; corticospinal, corticobulbar
Motor system circuit thats for Primary control of voluntary movement at precentral cortex,
through:
▪ X (Pyramidal tract)
▪ Y Pathways
Extrapyramidal system
Motor system circuit involving the Basal Ganglia (nuclei)
→ Cerebellum
→ Other integration centers:
▪ Thalamic nuclei
▪ Reticular formation
▪ Vestibular Nuclei
Basal ganglia
plays an important role in the control of posture and voluntary movement
Motor area, lower motor neurons
BG does not have direct input / output within the spinal cord. It also has NO DIRECT CNX to the
X
Y
Pre-motor & association
BG has DIRECT cnx to wc areas?
Cerebellum, Basal Ganglia
In Supra segmental control, the output of:
X is excitatory to the cerebral cortex
Y is inhibitory to cerebral cortex
Gray
BG is made of white/gray matter.
Corpus striatum, amygdaloid nucleus, claustrum
Big 3 components of BG
Corpus striatum & Claustrum; striatum & lentiform nucleus; caudate nucleus & putamen; globus pallidus & putamen
The basal ganglia is made of X & Y.
Corpus striatum is made of X & Y.
Striatum is made of X & Y
Lentiform nucleus is made of X & Y.
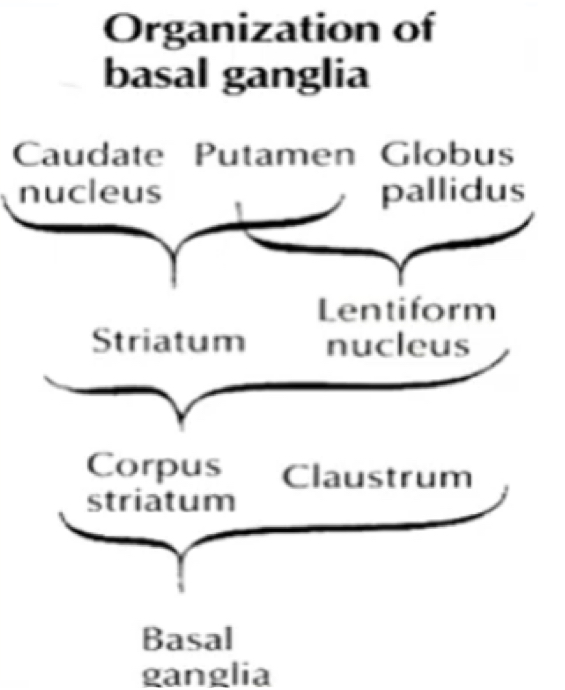
Corpus striatum
Lateral to the thalamus (see Figure 5)
Divided by the internal capsule into:
→ Caudate Nucleus (Tail)
→ Lenticular (Lentiform) Nucleus
Caudate nucleus
C-shaped mass of gray matter (all BG is gray)
Largest nucleus
Lies dorsolateral to the thalamus
Inferior horn, Anterior horn, Body LV
Caudate n. is related to lateral ventricles:
Roof of X horn
Lateral wall of X horn
Floor of X
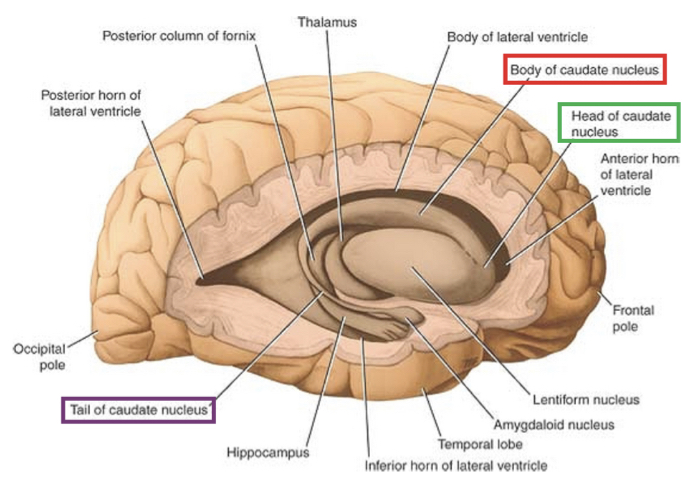
Lentiform nucleus
Collectively is a wedge-shaped mass of gray matter
Related laterally to the external capsule
Amygdaloid nucleus
In temporal lobe near uncus
● Part of limbic system
→ Can influence the body’s response to environmental changes
→ Can affect blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate when afraid (AM so afraiddd)
Claustrum
Thin sheet of gray matter
● Separated from the lateral surface of the lentiform nucleus
(putamen + globus pallidus) by the external capsule
Substantia nigra, parkinsonism
Lies in upper (rostral) midbrain between the cerebral
peduncle and tegmentum
● Appears brownish black due to neuromelanin
● Disorder: ?
Subthalamic nucleus, ballism
● Shape of a biconvex lens between the thalamus and tegmentum
● Function: integration of smooth movements of different parts of the body
● Disorder: ?
Eyy we x~ (nct is full of subs)
Progress
The BG:
monitors X of movement
Participates in sequencing & autonomic execution of learned motor plans
Does not initiate movement, bc that happens in the Pyramidal Tract.
Contralateral, Involuntary, No
The BG exhibits:
effects IPSI/CONTRA lateral to the lesion?
Strength of ms persists but there is emergence of X movement when there is a lesion
Thus there is (yes/no) Atrophy
Glutamate, GABA
Excitatory neurotransmitter
INHIBITORY NEUROTRANSMITTER
Indirect, thalamus, glutamate, excited, more, ; GABA, increase
PRINCIPLES:
Control of BG to motor cortex is DIRECT/INDIRECT via the ? (치와와)
Since the BG is INHIBITORY:
An excited thalamus = release X, excited/inhibited motor cortex? = more/less movement? Because what leash has loosened?
But if the BG which are alr inhibitory is excited = release X, inc/dec inhibition?