APES Unit 1
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Symbiosis
The interaction between two different organisms living in close physical proximity
Resource Partitioning
A process where species divide a niche to avoid competition for resources, allowing them to coexist in the same environment.
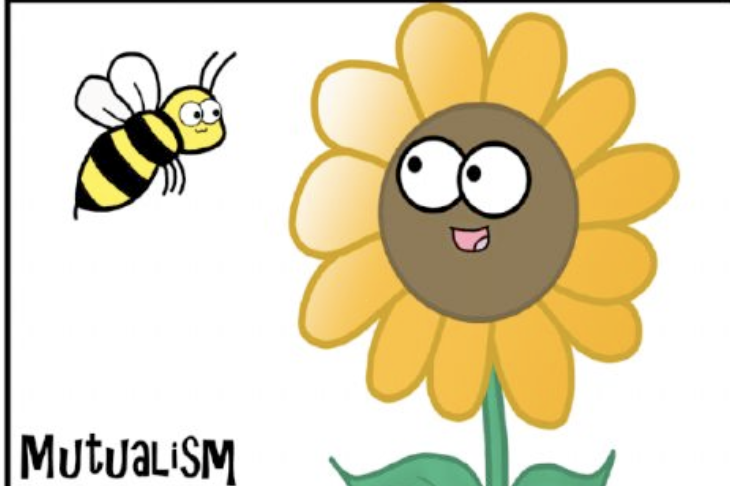
Mutualism
Both organisms benefit

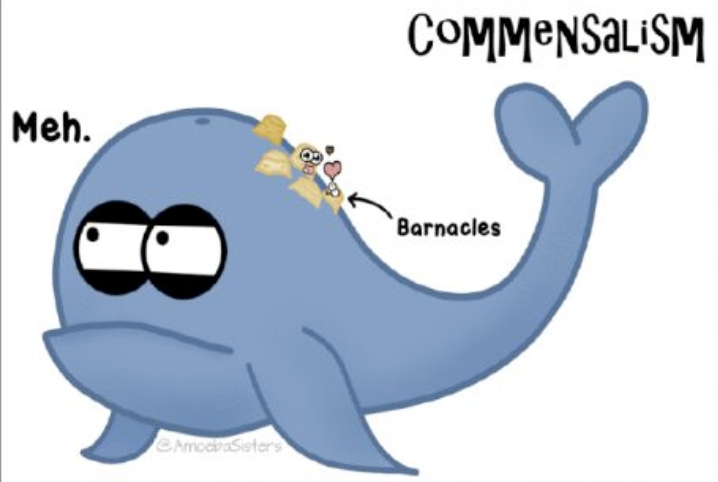
Commenslaism
One organisms benefit the other is unaffected
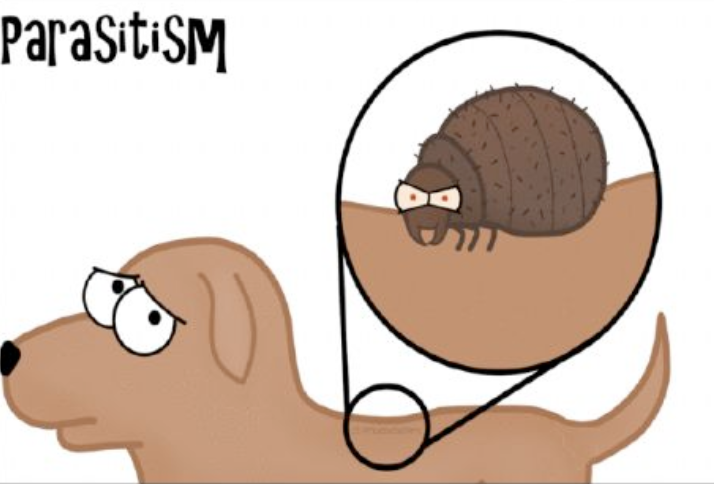
Parasitism
One organisms benefits the other is harmed
How are terrestrial biomes determined
Tempature and Rainfall
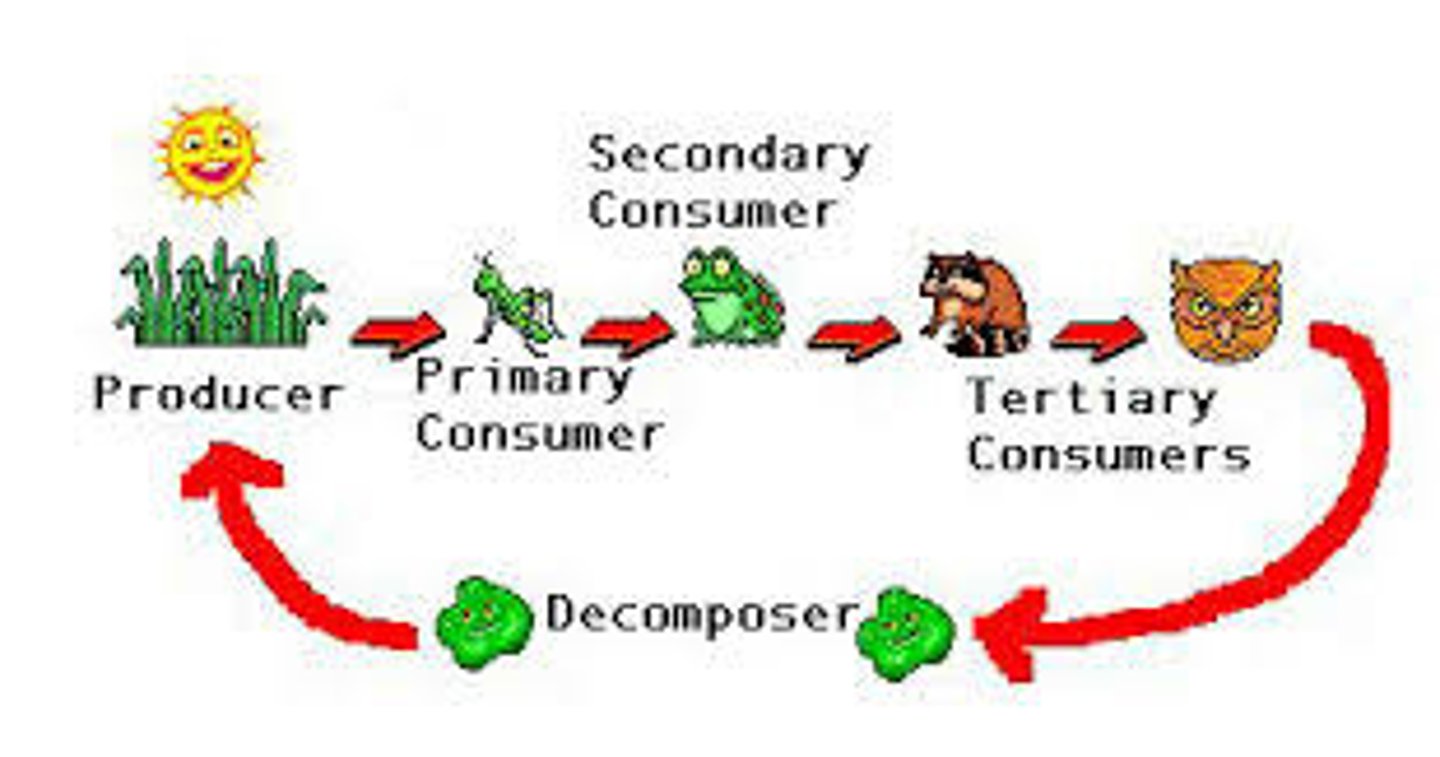
10% Rule
Only about 10% of the energy from one trophic level is transferred to the next level, the rest is lost as heat.
Net Primary Productivity
The rate at which plants in an ecosystem produce net useful chemical energy.
Gross Primary Productivity
The total amount of energy produced by photosynthesis in a given area minus energy used for respiration.
NPP Formula
GPP - R = NPP
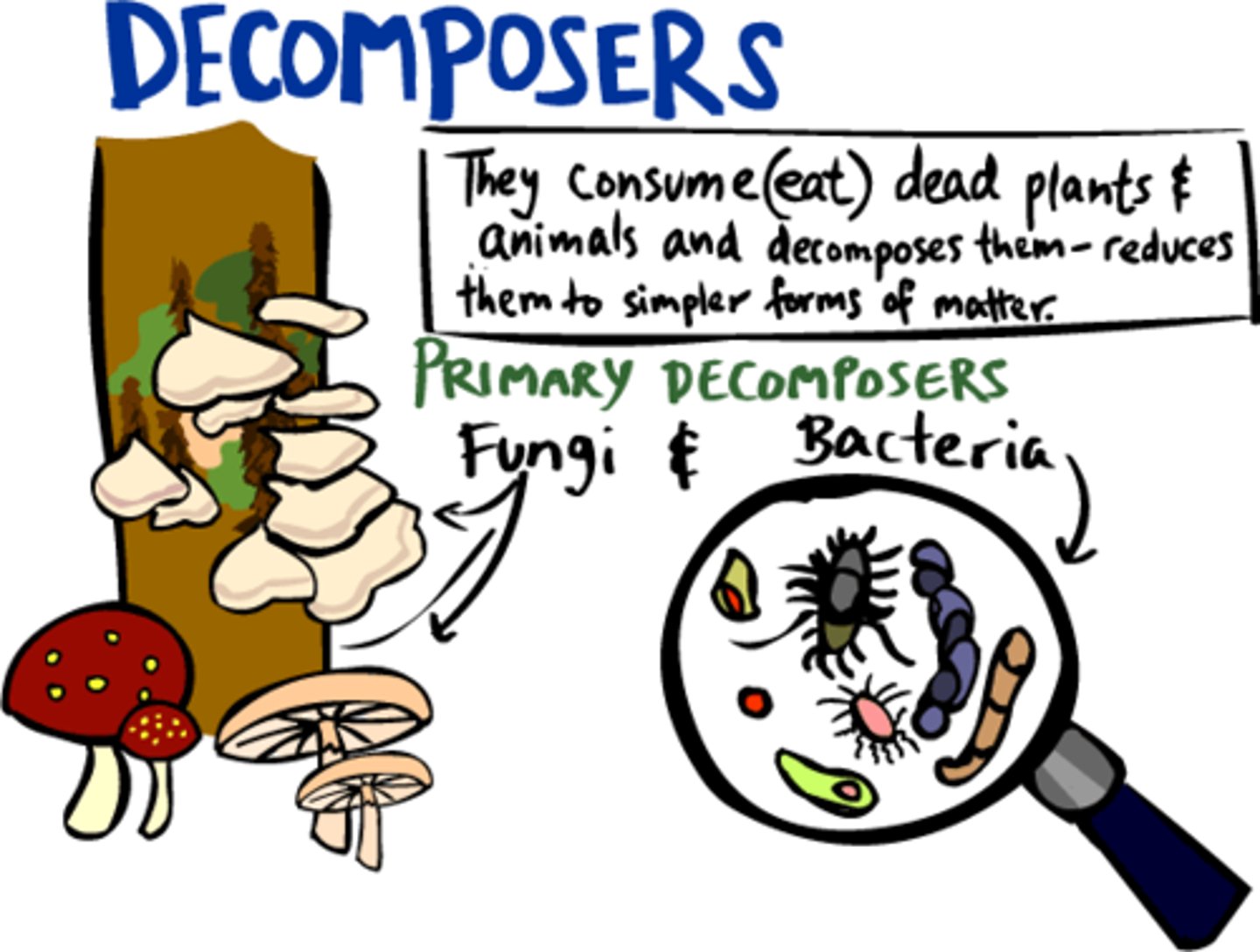
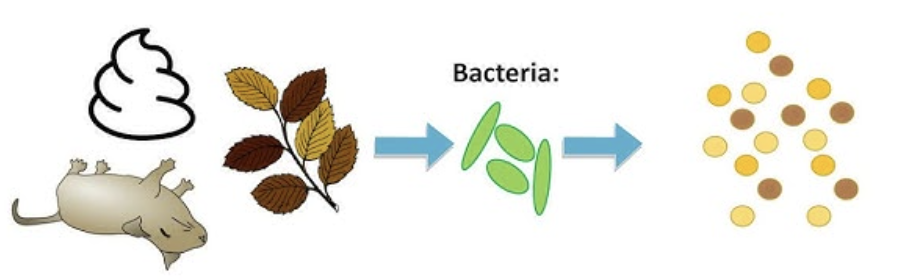
Decomposition
The breakdown of dead matter and wastes by decomposers; stored carbon from animal remains is released back into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide
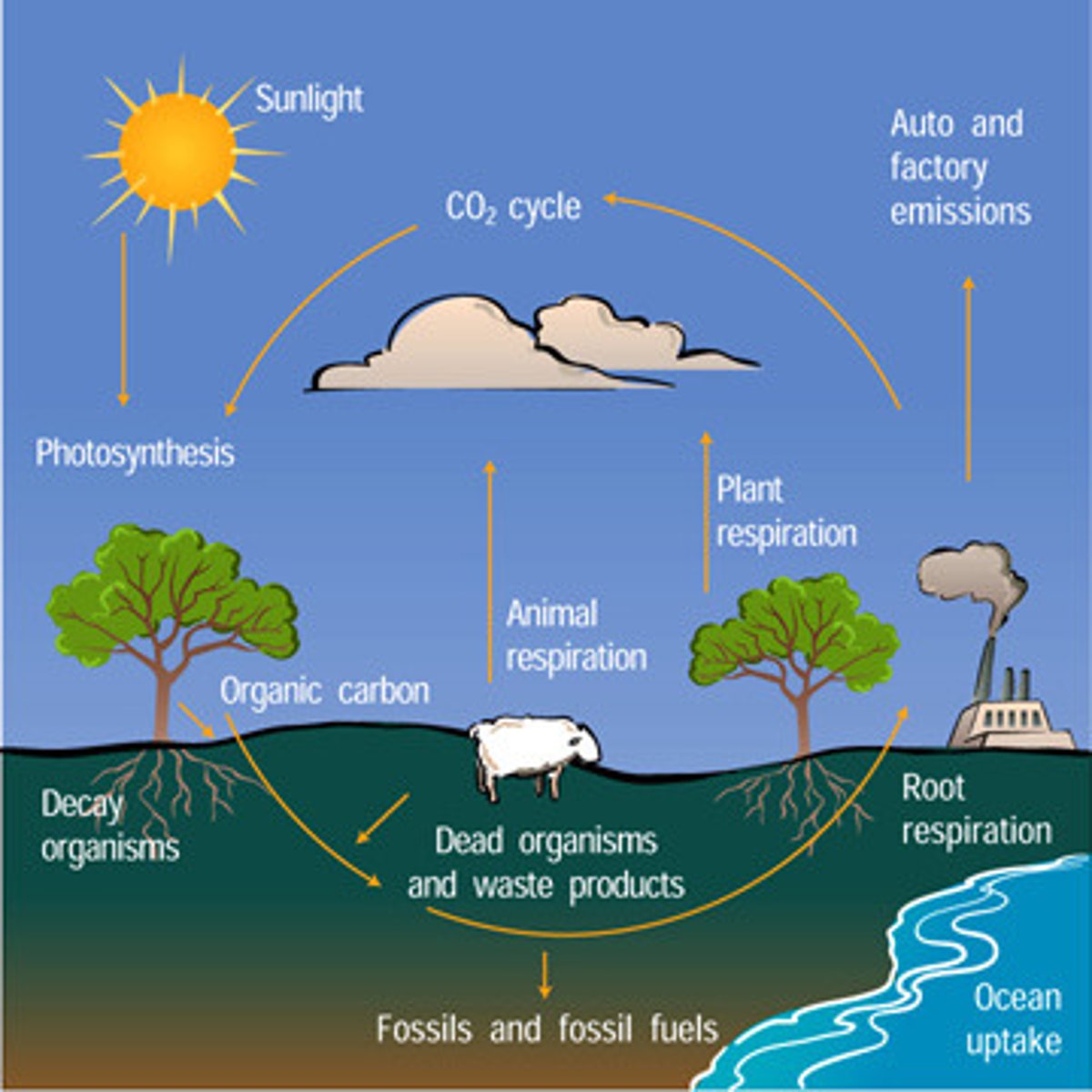
Carbon Dioxide
The form of carbon released into the atmosphere
Autotroph
(auto=self, troph=feeding); An organism that can create its own food; producers in an ecosystem
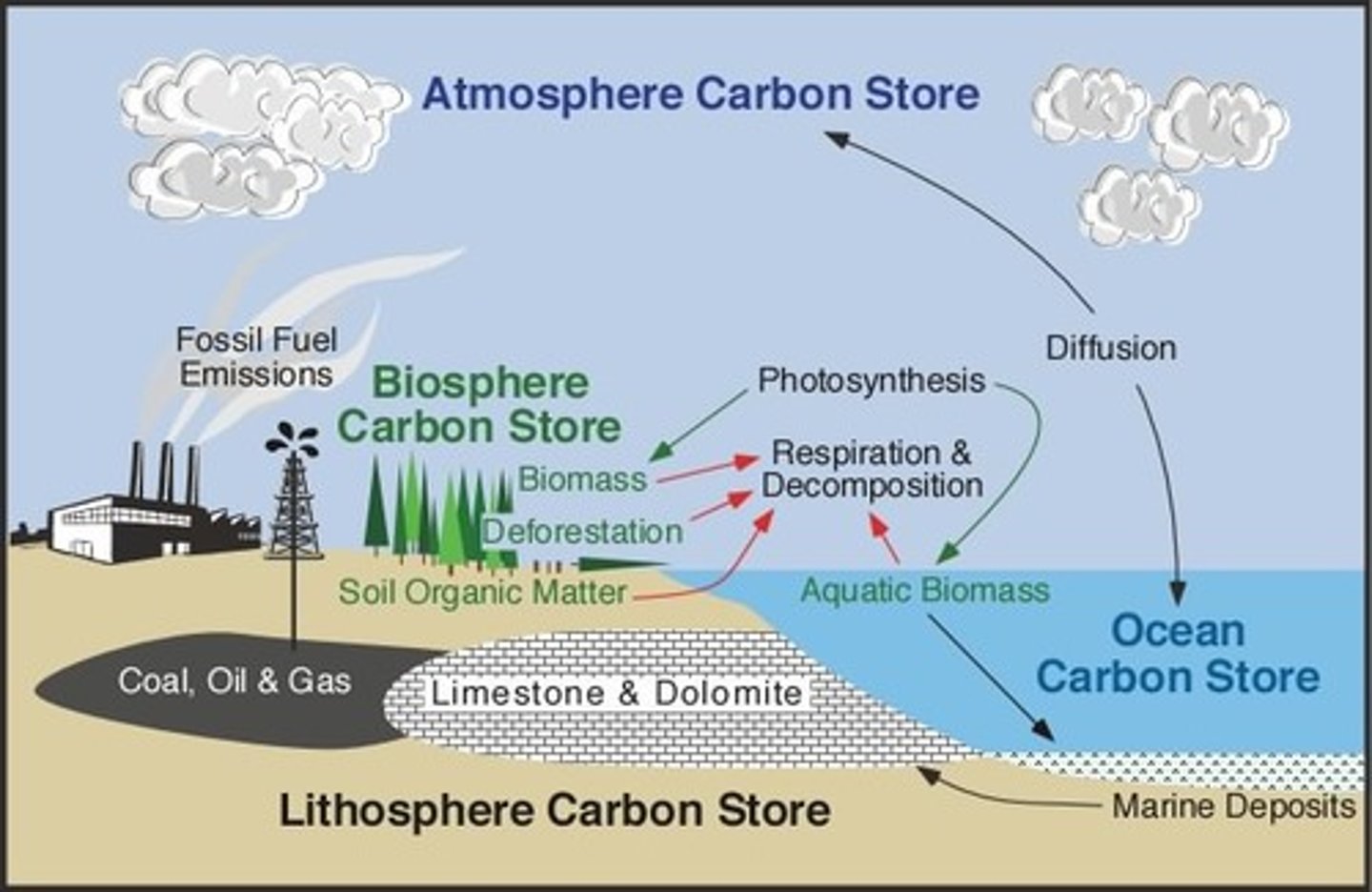
Carbon sink
A body or process that removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and stores it
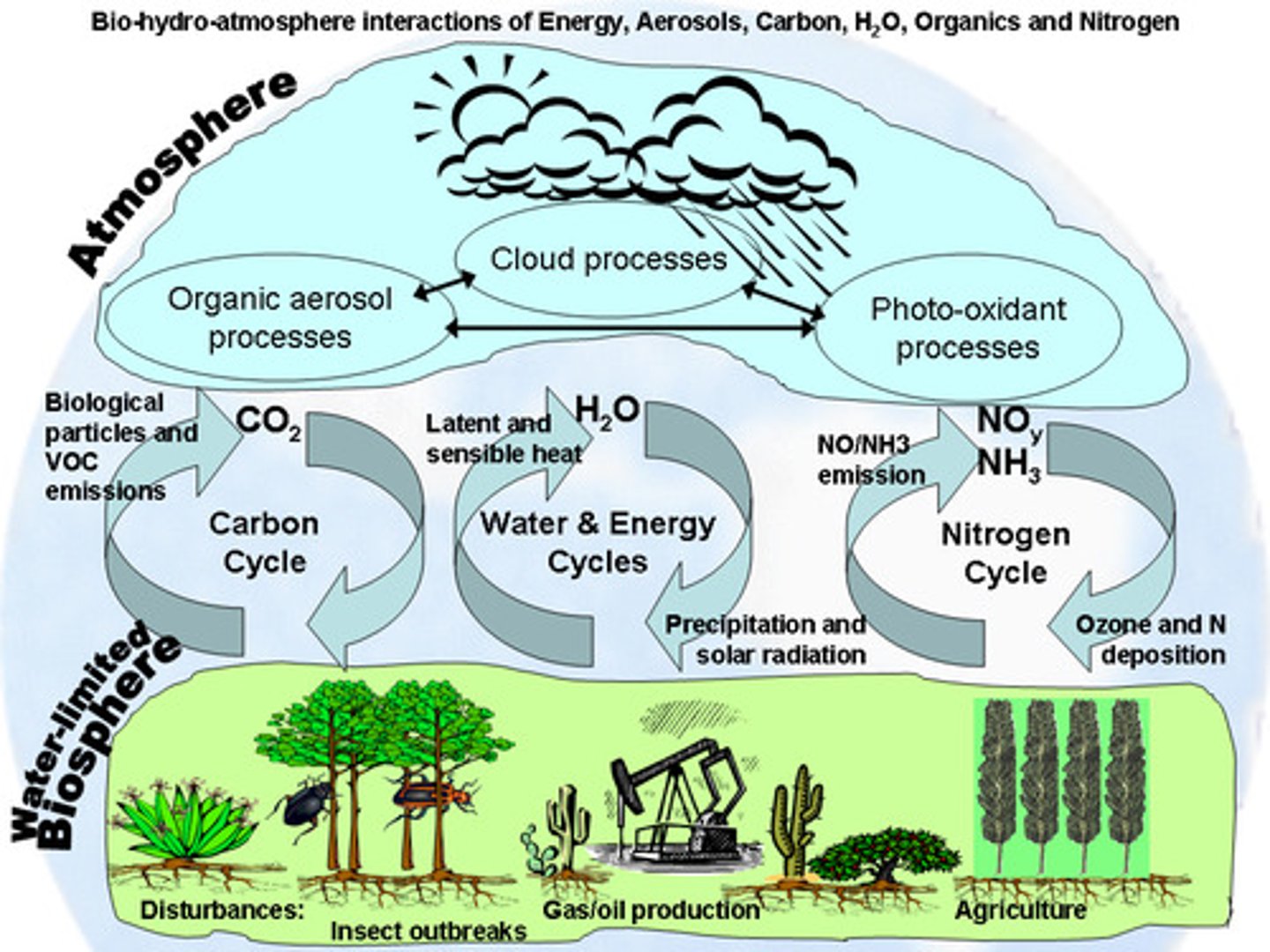
Biosphere
Part of Earth in which life exists (including land, water, and air or atmosphere)
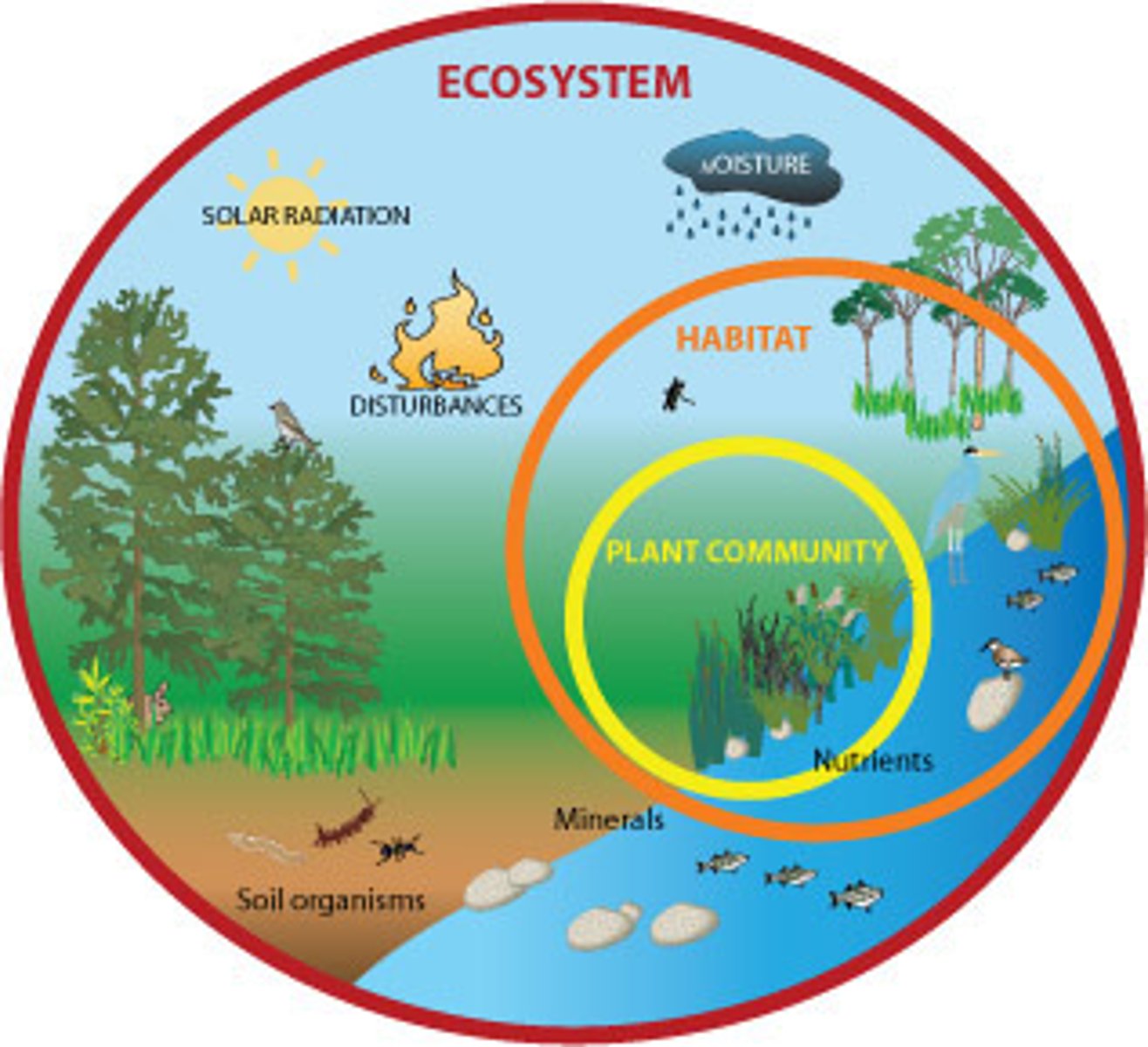
Ecosystem
A system formed by the interaction of a community of organisms with their physical environment
What way can nitrogen become "fixed"?
nitrogen fixing bacteria or lightning
Denitrifying
What type of bacteria release nitrogen into our atmosphere
How is nitrogen used on crops?
Fertilizer
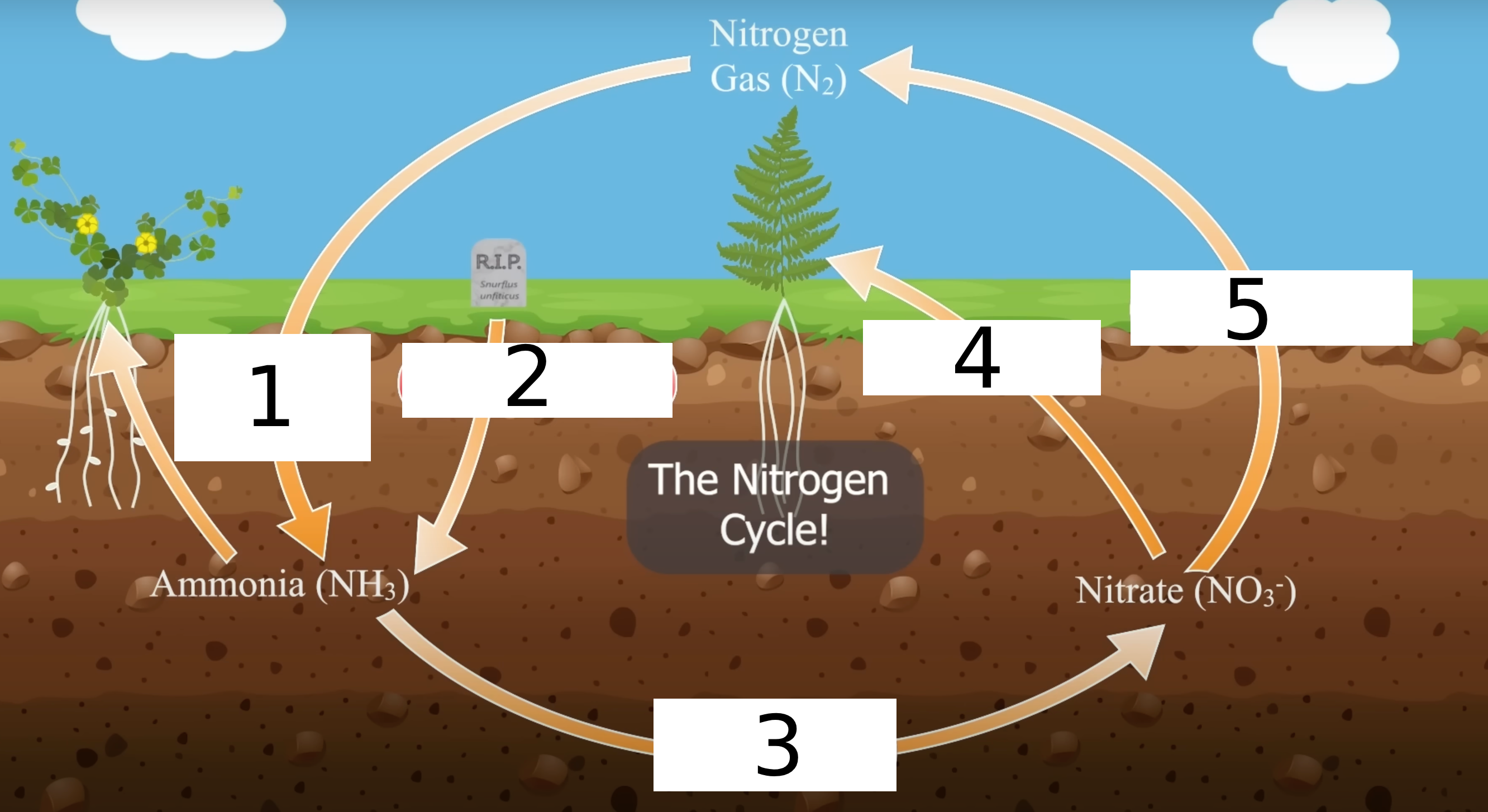
What are the 5 processes of the nitrogen cycle?
Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrification
Assimilation
Ammonification
Denitrification
Nitrogen Fixation
Ammonification
Nitrification
Assimilation
Denitrification
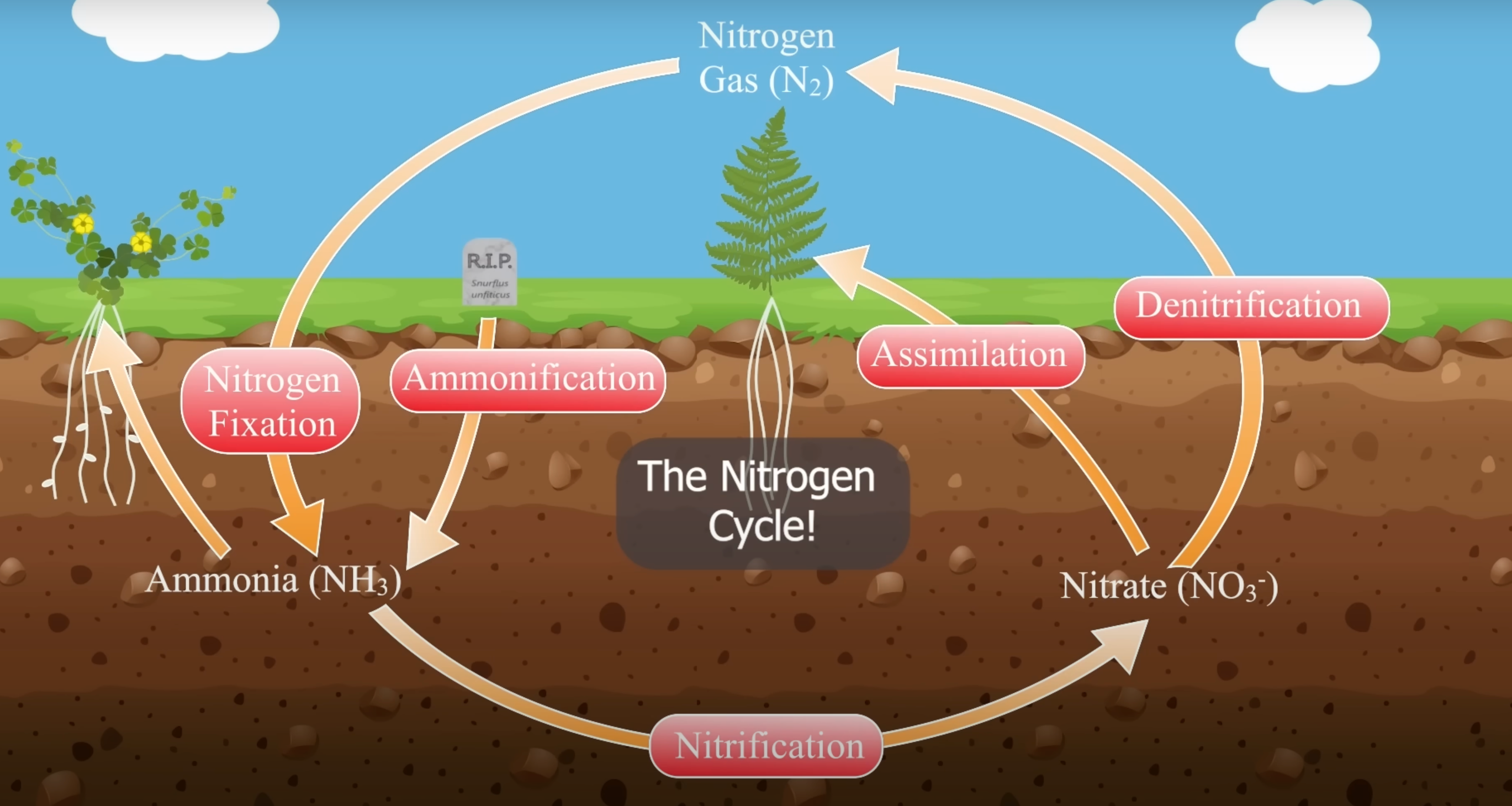
Nitrogen Fixation
Atmospheric nitrogen is converted into a form usable by living organisms. Facilitated by nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
Ammonification
The process by which organic nitrogen is converted into ammonia by decomposer organisms, making it available for uptake by plants.
Nitrification
The biological process in which ammonia is oxidized to nitrites and then to nitrates, making nitrogen available to plants.
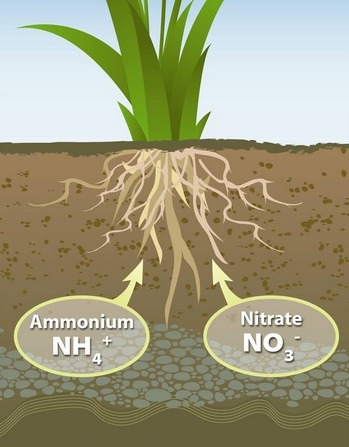
Assimilation
The process by which plants and animals take up nitrogen from the soil, converting it into organic molecules. This is essential for the formation of proteins and nucleic acids.
Denitrification
The process by which nitrates and nitrites are reduced to gaseous nitrogen and released back into the atmosphere, completing the nitrogen cycle.