Histopathology Lab - Lesson 3 Part 2: Sectioning and Microtomes
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Sectioning
A process where tissues are cut into uniformly thin slice or "sections" with the aid of a machine to facilitate the studies under the microscope
Microtome
A machine or instrument designed for the actual cutting of thin sections of tissues.
Block holder (Chuck)
Microtome part that holds the tissue block in place.
Knife carrier and knife
Microtome part that is used for cutting tissues.
Pawl, ratchet feed wheel and adjustment screw
Microtome part that lines up the tissue in proper position to the knife and adjust the proper thickness of the tissue.
Cutting edge
Microtome knife part that is the cutting facet, found on the tapered edge of the knife. Angle 150 for maximum penetration of tissue and less distortion.
Wedge
Microtome knife part that is a part between cutting edge and knife back.
Knife back
Microtome knife part that is a spring-loaded semicircular sheet of metal slipped on to the knife with one or more plane surfaces to hold the cutting edge at a constant, correct angle during honing and stropping.
Bevel angle
Microtome knife part that is the angle formed between the cutting edge, normally 27-32 degrees.
Wedge angle
Microtome knife part that is the angle formed by the sides of the wedge knife, normally about 5-14 degrees.
Clearance angle
Microtome knife part that is angle formed between cutting facet presenting to the block and the surface of the block, normally 5-15 degrees.
Plane-concave knife
Type of microtome knife which has a length of 25 mm.
Plane-concave knife
Type of microtome knife which one side of the knife is flast while the other is concave.
Plane-concave knife
Type of microtome knife which its less concave sides are recommended for cutting celloidin-embedded tissue blocks and more concave ones are used for cutting paraffin sections.
Plane-concave knife
Type of microtome knife which is used on base-sledge, rotary or rocking microtome.
Bioconcave knife
Type of microtome knife which is 120 mm in length.
Bioconcave knife
Type of microtome knife which both sides are concave.
Bioconcave knife
Type of microtome knife which are recommended for cutting paraffin-embedded sections.
Bioconcave knife
Type of microtome knife which is only used on rotary microtome.
Plane-wedge knife
Type of microtome knife which length is 100 mm.
Plane-wedge knife
Type of microtome knife which both sides are straight.
Plane-wedge knife
Type of microtome knife which is recommended for frozen tissue sections or cutting extremely hard and tough specimen embedded in paraffin blocks.
Plane-wedge knife
Type of microtome knife which is used on base-sledge type or freezing microtome.
Belgium yellow (Belgian hone)
Type of hone which is used for manual sharpening when cutting edges has been rendered blunt or nicked; gives the best result.
Arkansas
Type of hone which gives more polishing effect than Belgian yellow.
Fine carborundum
Type of hone which is much coarser than the first two types and is used only for badly nicked knives followed by either one of the first two sharpeners.
Plate-glass hone
Type of hone which is 1.8x3x1 inches; Abrasive powder is used in conjunction with this, for grinding and removing nicks. Diamanthine is used for final polishing.
Machine hone
Type of hone which consists of glass disc or wheel driven by an electric motor. The knife is pressed against the flat side of a rotating glass wheel. The abrasive suspension is made by a mixture of alumina and 200ml water allowing to stand before use. The wheel and the trough are then cleaned with soap and water for final polishing.
Clove Oil
Liquid paraffin
Mineral Oil
Soapy water
Xylene
Enumerate the common lubricants used for honing. (Alphabetical, seperate by Enter, if otherwise, check yourself if got it right)
Heel to toe
Direction for Honing
Stropping
Removal of the "burr" or irregularities formed during honing and final polishing of the knife edge.
True
(True or False [Might not work in Multiple Choice]) Strop should be of the best quality of shell-horse leather/paddle strap.
Toe to heel
Direction for Stropping
False
(True or False [Might not work in Multiple Choice]) It should be oiled on the back using mineral oil and NEVER vegetable/castor oil.
Sliding
Type of Microtome which is used for cutting celloidin-embedded sections and invented by Adams in 1789
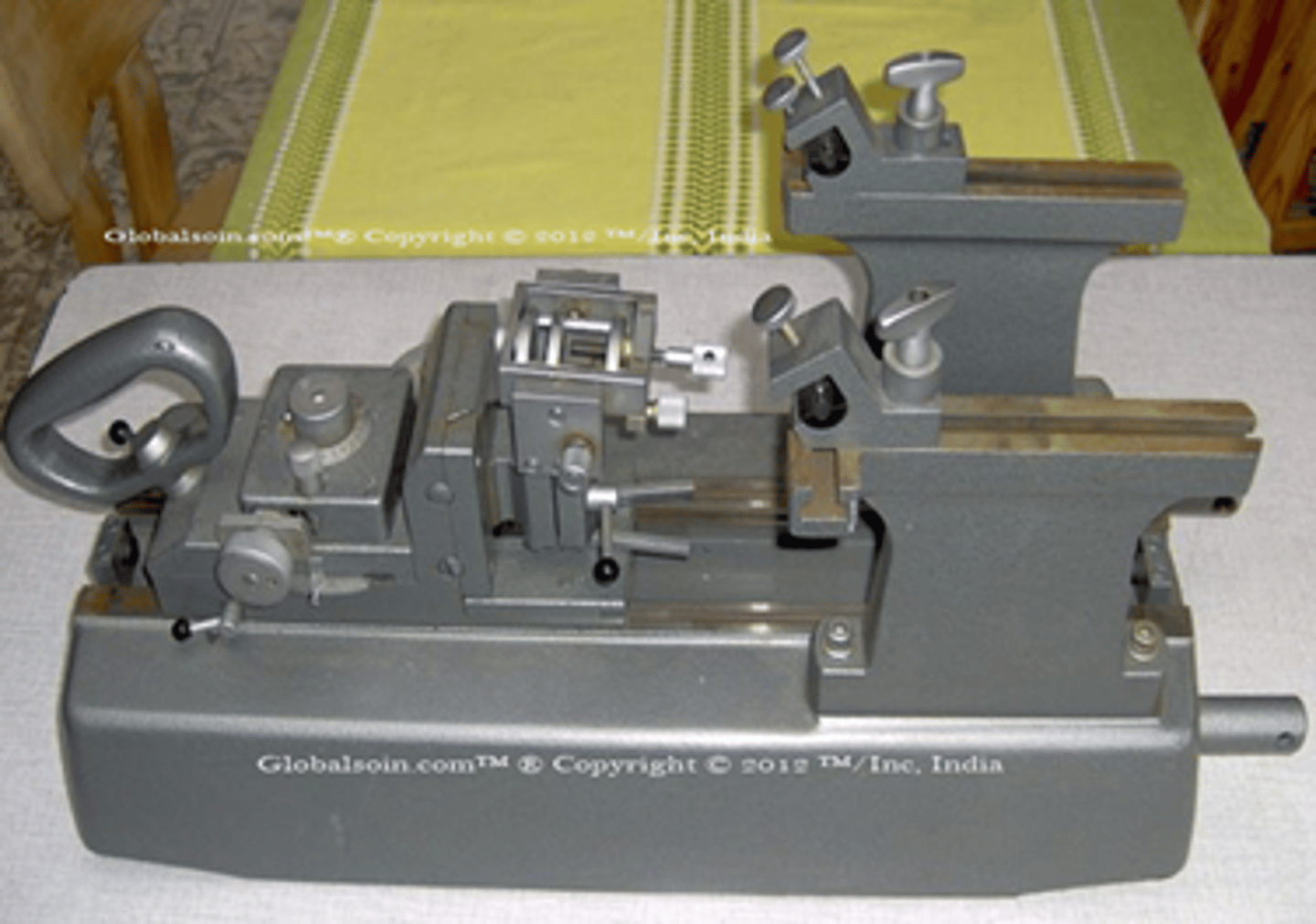
Base-sledge
Type of sliding microtome which the chuck or block holder is moved backwards and forwards under the knife.
Base-sledge
Identify this sliding microtome.
Sliding
Type of sliding microtome which the block remains stationary while the knife is moved backward and forward during the process of sectioning.
Sliding
Most dangerous type of sliding microtome due to movable knife
Sliding
Identify this type of sliding microtome.
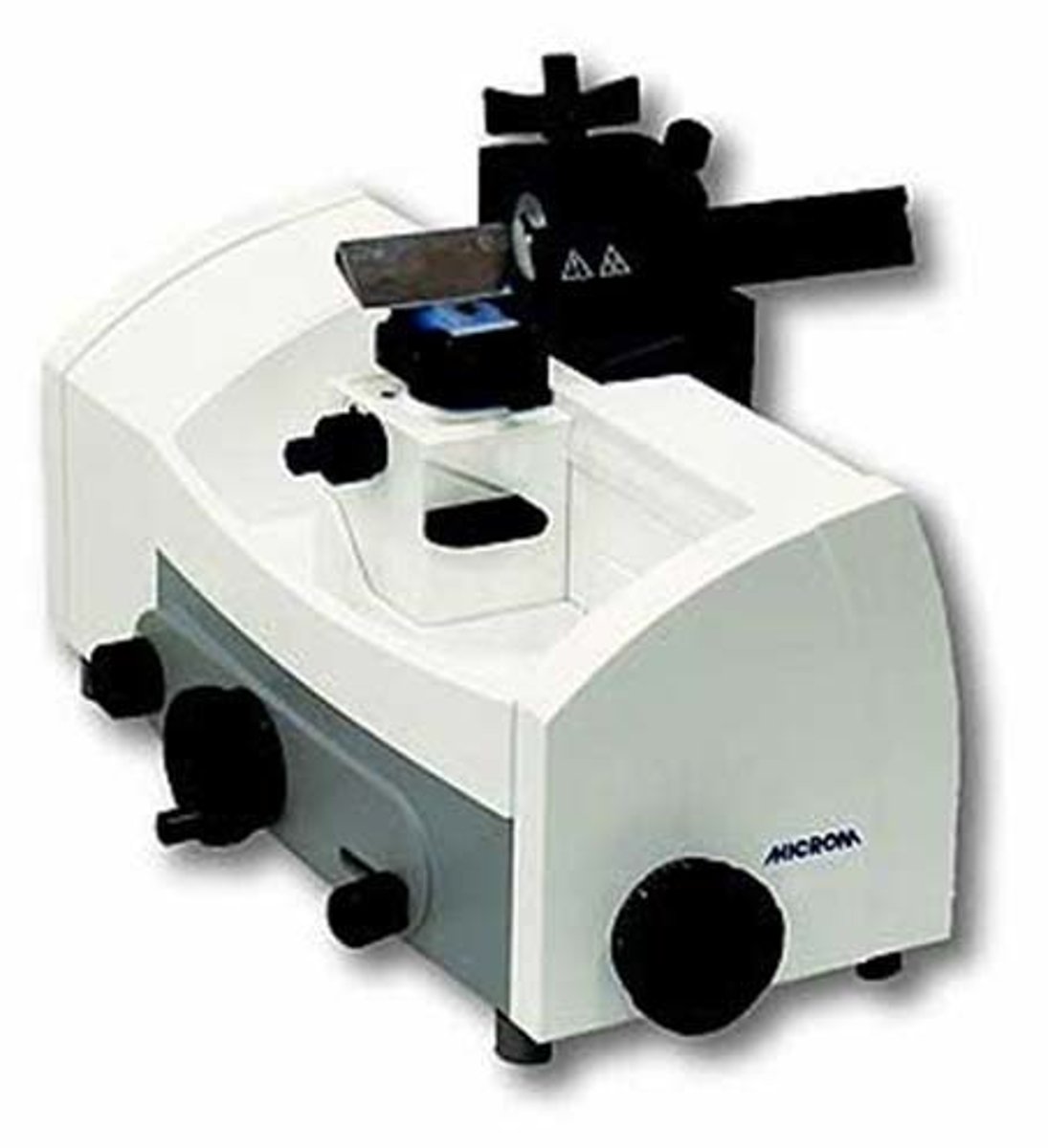

Rotary
Type of microtome which is used for cutting paraffin-embedded sections.
Rotary
Type of Microtome which is invented by Minot in 1885-1886.
Rotary
Type of Microtome which is the most common type used for both routine and research laboratories.
Rotary
Identify this microtome.
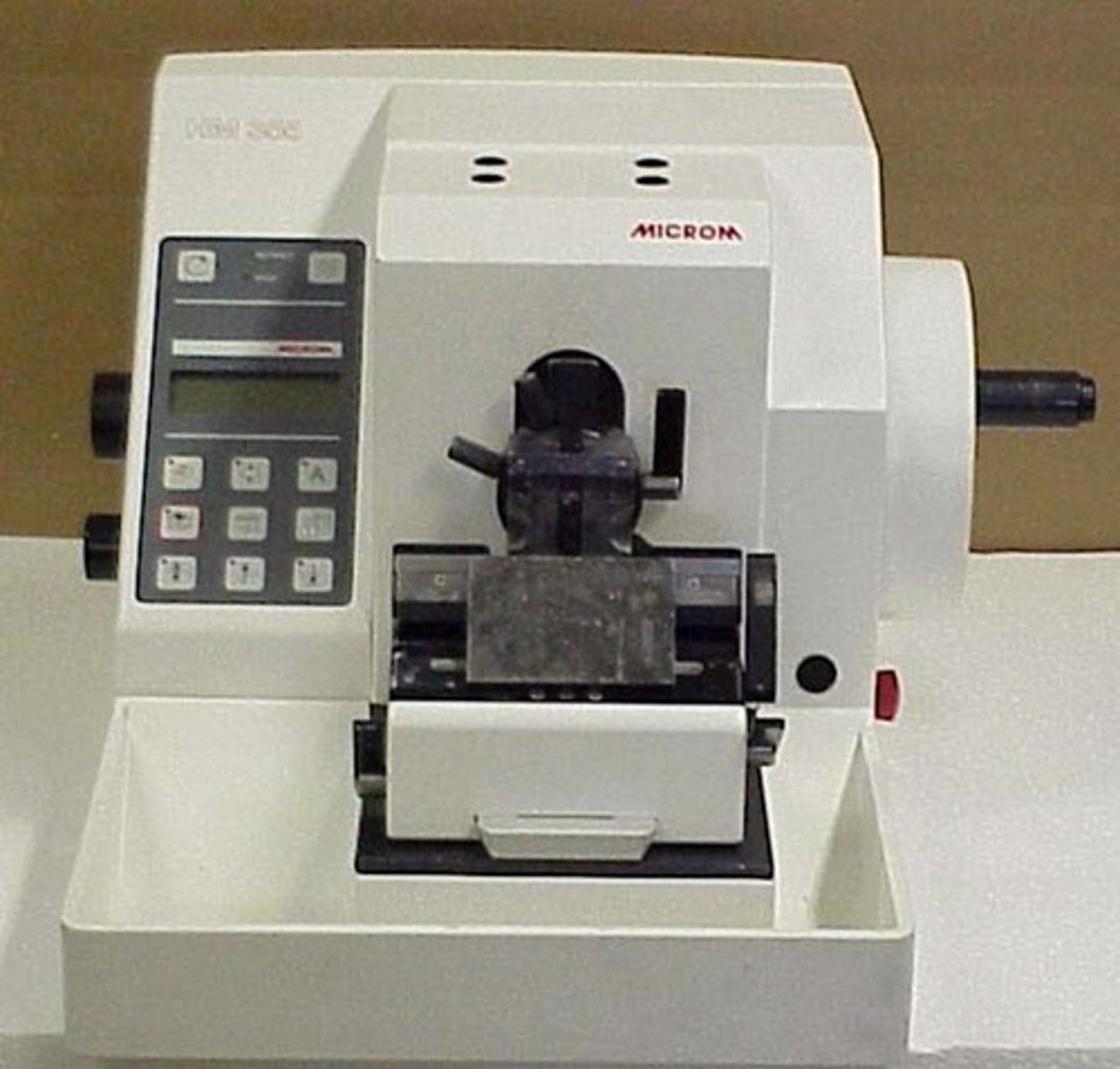

Freezing
Type of microtome used for cutting unembedded tissues that have been frozen with carbon dioxide and other refrigerants.
Freezing
Type of Microtome which is invented by Quechett in 1848
Freezing
Type of Microtome which is used to cut undehydrated tissues in frozen state, especially:
-When rapid diagnosis is required
-When histological demonstration of fat is needed
-When certain neurological structures are to be studied
-When sensitive tissue constituents to be studied are damaged or destroyed by heat
Freezing
Identify this type of microtome.
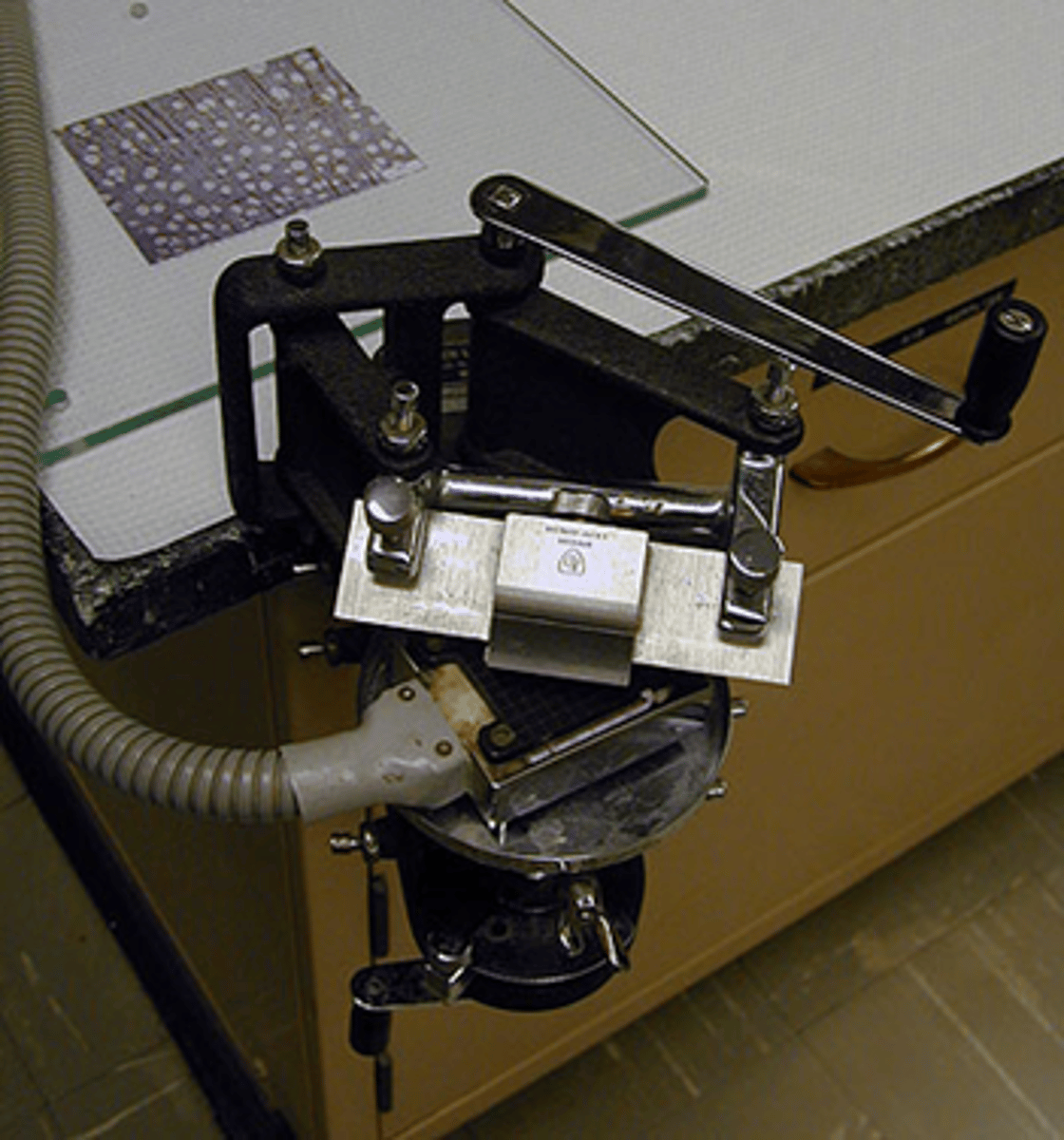
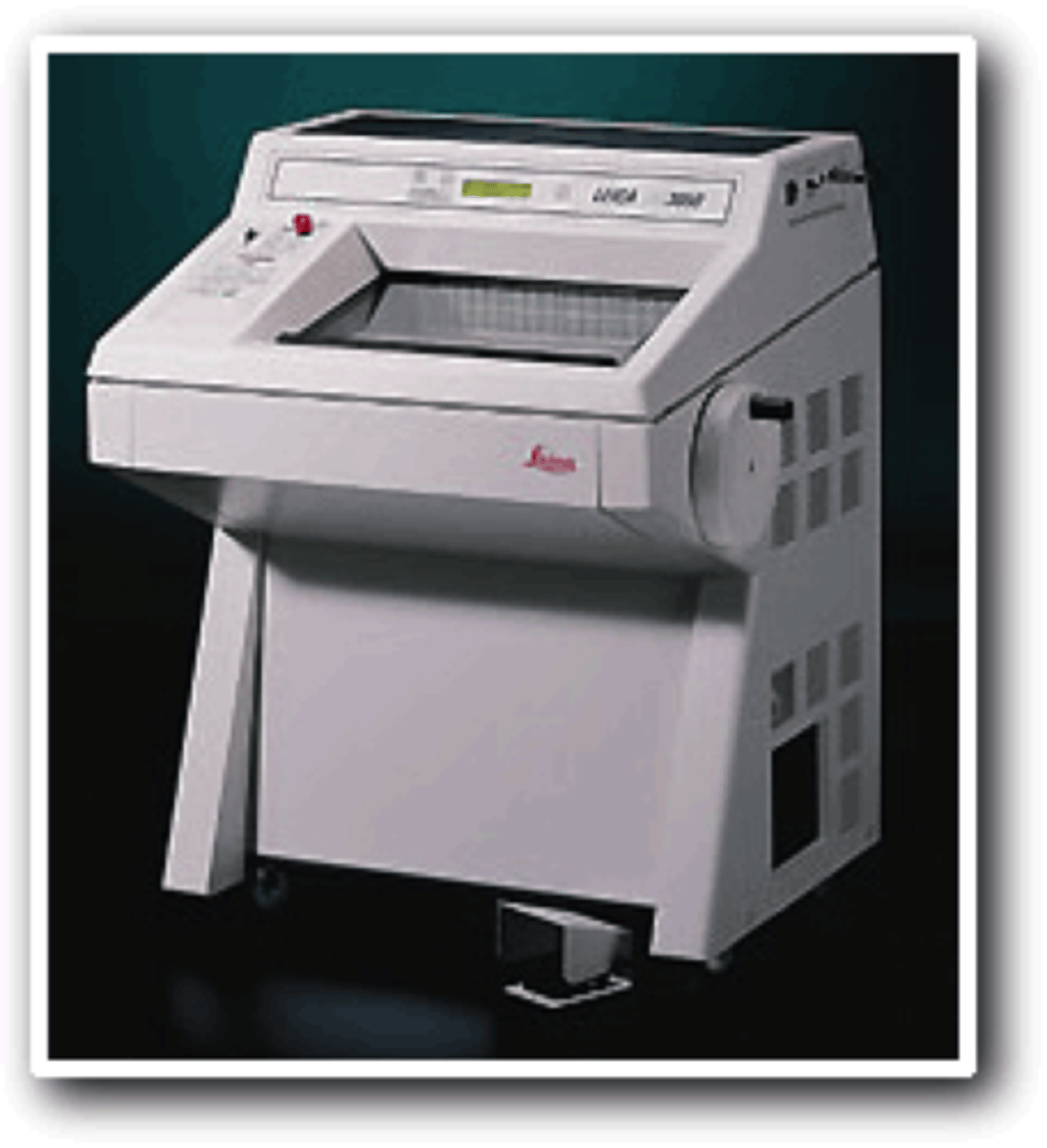
Cryostat/Cold Microtome
Type of freezing microtome used for rush frozen section; now commonly used, and forr refrigerated (-5 to -300C) ave.:-200C
Cryostat/Cold Microtome
Identify this microtome.

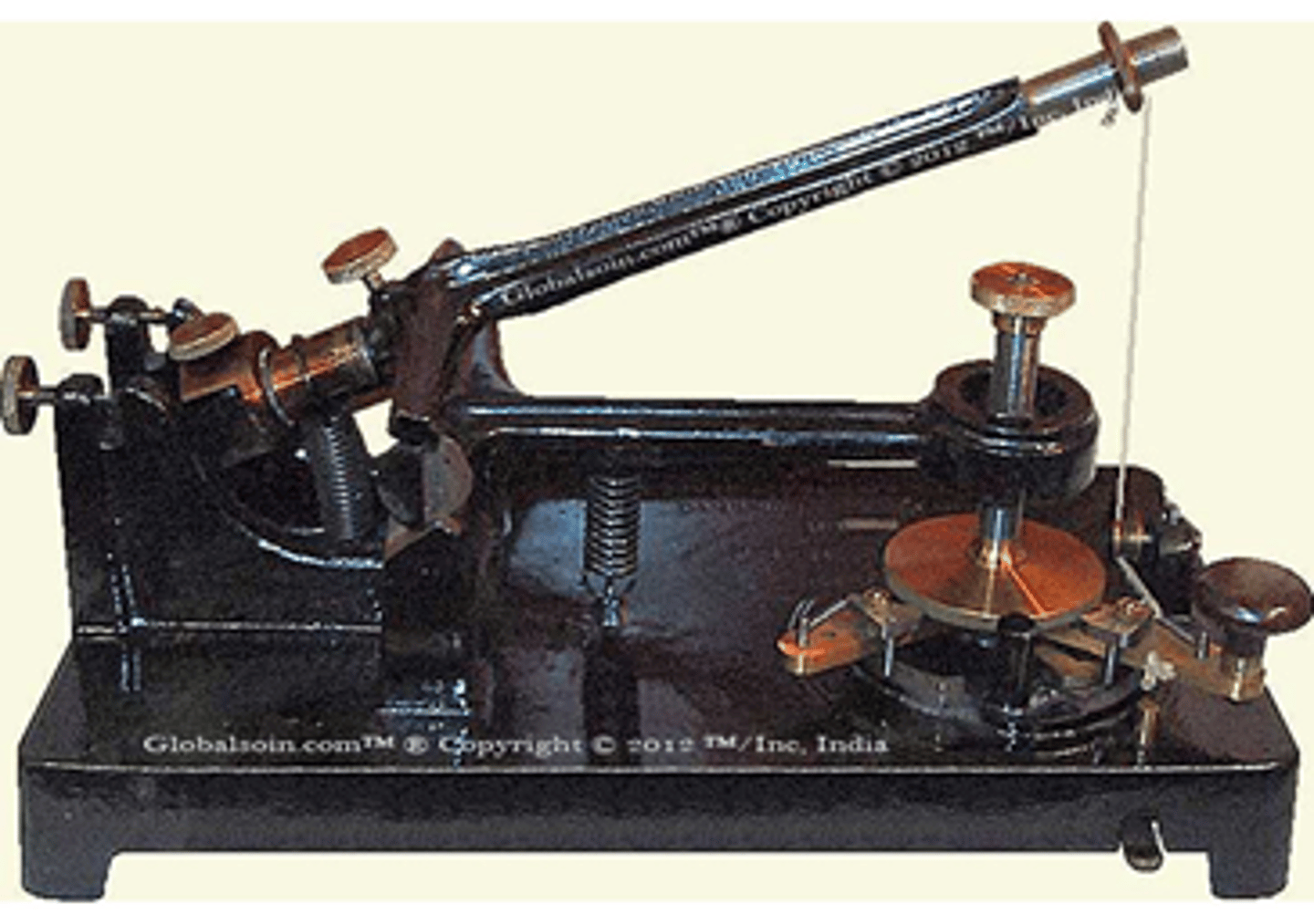
Rocking
Type of microtome for cutting serial sections of large blocks of paraffin-embedded tissues.
Rocking
Type of microtome which is invented by Trefall in 1881
Rocking
Type of microtome which its lower arm is resting on pivots and supporting column, and its upper arm carries the block holder on one end by a screw
Rocking
Identify this type of microtome

Ultra-thin Sectioning
Type of microtome for cutting sections for electron microscopy; 0.5 micron; fixed in Osmium tetroxide and embedded in plastic.
Ultra-thin Sectioning
Type of microtome which its knife consist of selected fragments of broken plate glass.