SHS: Lab Nine
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Explain the use of speech intelligibility tests as means to evaluate communication systems for listeners
They evaluate the effect on intelligibility of the noise in the transmission system to evaluate the effect of restricted frequency bandwidth on speech intelligibility.
Explain the use of speech intelligibility tests as means to evaluate hearing loss
They evaluate the effect of hearing loss on the ability to perceive speech to evaluate the effect of listener experience on speech intelligibility.
Explain the use of speech intelligibility tests as means to evaluate speaker proficiency
They evaluate the intelligibility of individuals with motor speech disorders to provide a longitudinal index of improvement of speech intelligibility to intervention.
List the ways to measure speech intelligibility
Word identification tests (% intelligibility)
Scaling tests
Phonetic Transcription Test
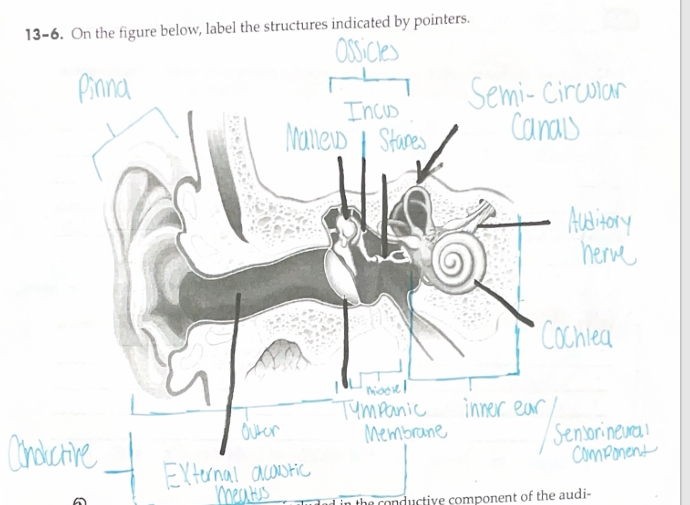
Which anatomical structures are included in the conductive component of the auditory mechanism
Pinna, external auditory/acoustic meatus, tympanic membrane, Malleus, Incus, and Stapes
Which anatomical structures are included in the sensorineural component of the auditory mechanism
Semi-circular canals, cochlea, and vestibulocochlear nerve
Explain impedance mismatching
The measure of how much a medium resists the flow of sound energy through it; Mismatch occurs through different mediums such as the inner and middle using air to move sound energy, but then gets to the inner ear and then impedes or mismatches with fluid in the inner ear.
How is impedance mismatching overcome
It is overcome by area difference; sound pressure at the footplate of the stapes is around 20 -25 dB greater than sound pressure at the tympanic membrane (The Big tympanic membrane area to the stapes window area)
State the functions of the peripheral vestibular system
Head position and space
Balance/steadiness
Diagram of pathway through the cochlea
Sensory organ → Hair cells → Nerve fibers → Sensory cells → Vestibular cochlear nerve → Brainstem
The membranes that separate the three cochlear ducts
Reissner’s and Basilar membrane
The organ of Corti
The end organ of hearing
Sits on top of the basilar membrane
Contains hair cells and other supporting structures
Moves from shortest to longest (Hair cells)
What are stereocilia?
Hair cells with the role of sensorial function
Connected their “tips” and move as a unit “Tip-linked”
Stereocilia bend toward the longest hair cell, which ion channels open, leading to hair cell depolarization and triggering an action potential in the connected nerve
What is the tonotopic organization of the basilar membrane
The highest frequency Sensitivity (20,000 Hz) is at the base (front), and the lowest frequency sensitivity (20 Hz) is at the apex (The end). Piccolo → Tuba (Base → Apex)