Government and The Macroeconomy
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Government: Local Role
Fund Local services (eg Garbage collection)
Government: National Role
Achieve macroeconomic goals (Eg Economic Growth)
Government: International Role
Trading of goods and services
Macroeconomic aims of the Government
Economic Growth, Low Unemployment, Low Inflation, Balance of Payments Stability, Redistribution of Income
Fiscal Policy
Use of Taxation and government spending to inluence aggregate demand
Budget
Financial planning of revenues and expenditures of the government
Reasons for taxation
Finance public expenditure
Discourage certain activities, eg taxes on cigarettes
Discourage import of goods, tariffs are import taxes and can be levied as a % of the value of imports or a set tax on each item
Redistribute income from the rich to the poor
Achieve other macroeconomic objectives
Expansionary Fiscal Policy
Reducing taxes and increasing gov spending to boost demand - employment and output rise - may be used to reduce recession
Contractionary Fiscal Policy
Increasing taxes and reducing gov spending to reduce demand - may be used to reduce price inflation
Monetary Policy
Use of interest rates, direct control of money supply and exchange rate to influence aggregate demand
Expansionary Monetary Policy
Cutting interest rates - may be used during a recession, to increase employment
Contractionary Monetary Policy
Increasing interest rates - May be used to reduce price inflation
Supply-Side Policies
Aim to increase economic growth by raising productive potential of the economy
Economic Growth
The annual increase in the level of the national output ie the country’s GDP
Recession
Significant decline in economic activity spread across the economy for 6 or more consecutive months
A recession would cause the economy to produce at a point that is within the PPC (insufficient)
Unemployment rate formula
Number of Unemployed People / Labour Force
Cyclical Unemployment
Occurs during recession due to falling consumer demand & incomes - Firms reduce their output and lay off workers
Structural Unemployment
Caused by changes in industrial structure of an economy - entire industries close due to a permanent fall in demand for their goods/services
Frictional Unemployment
Transitional unemployment - when people move between jobs
Seasonal Unemployment
Consumer demand for goods/services change with seasons e.g. no job for a ski instructor when there is no snow
Inflation
General & sustained increase in the level of prices of goods/services in an economy over a period of time
Deflation
General decrease in the level of prices of goods/services in an economy over a given period of time - occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0%
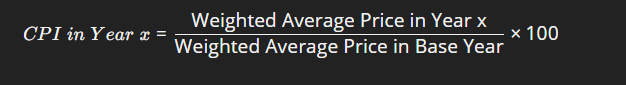
Calculating Consumer price index
Base year - First year with which the prices of subsequent years are compared
Inflation rate - Percentage change in annual CPI
Causes of Inflation
Demand-Pull Inflation, Cost-Push Inflation
Causes of Deflation
Fall in the money supply
Decline in confidence
Lower production costs
Technological advances
Increase in unemployment
Increase in the real value of debt