Chem 115 Final (Exams 1-3 and New Material)
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
number of moles
grams / molar mass
molarity (M)
number of moles / volume (L)
limiting reagent
least number of moles AFTER dividing by lead coefficients
dilution
M1V1 = M2V2
% error
((experimental - actual) / actual) * 100
cation (+)
less electrons
anion (-)
more electrons
law of conservation of mass
total mass doesn’t change during a reaction
what does an acid produce?
H+
what does a base produce?
OH-
positive delta H
endothermic (heat gained)
negative delta H
exothermic (heat released)
delta H reaction
H product - H reaction
calculating delta H
-(heat released) / number of moles
H
E + PV
work on system
volume of gas decreases, w = +
work by system
volume of gas increases, w = -
calculating work
-P * deltaV
heat capacity
q = C * deltaT
specific heat capacity
q = m*c*deltaT
heat released
q = -
heat gained
q = +
calculating change in energy
delta E = q + w
alpha decay
change in both atomic mass and number (top right corner on band of stability)
beta decay (negitron)
change in atomic number (+ 1) (top left above band of stability)
beta (positron)
change in atomic number (-1) (under band of stability)
electron capture
change in atomic number (-1) (under band of stability)
gamma
no change in atomic number or atomic mass
isotope model “A”
represents the atomic mass
isotope model “Z”
represents the atomic number (number of protons)
isotope model “X”
represents symbol of element
isotope model “A-Z”
number of neutrons
nucleon
number of protons and neutrons
fusion
small mass to big mass
fission
big mass to small mass
light shining on metal
when light shines at metal at specific wavelength an electron is ejected
shells in first row
1
shells in second row
2
shells in third row
3
IE on periodic table
increases to top right corner
electron affinity
increases to top right corner
electronegativitiy
increases to top right corner
atomic radius
increases to bottom left corner
non metal characteristics on periodic table
increases diagonally to top right corner
metal characteristics on periodic table
increases diagonally to bottom left corner
dimagnetic
electrons are only paired in orbitals, they are not attracted by magnetic field
paramagnetic
one or more orbits with unpaired electrons, weakly attracted by magnetic field
n (principle)
size given by row on periodic table
lower = smaller orbit and energy
l (angular)
shape given by s p d and f
s orbitals
far left section on periodic table
2 electrons
l = 0
p orbitals
far right side of periodic table
6 electrons
l = 1
d orbitals
center section of periodic table
10 electrons
l = 2
f orbitals
separate section on periodic table
14 electrons
l = 3
ml (magnetic)
orientation in space or orbitals
corresponds to l
l = 1 : ml = (-1,0,1)
ms (spin)
two directions possible (arrow up or arrow down)
sub level filling order
diagonal starting with s1 → s2 → 2p → 3s
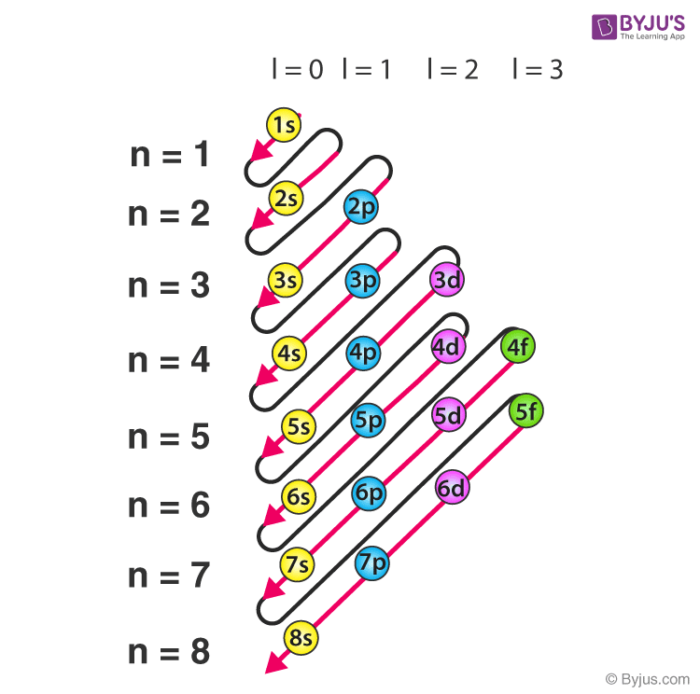
final electron level shows…
row section ^ number in section
characteristics of a metal
form cations
basic
reductive → electrons gained
high melting point
good conductor
nonmetal characteristics
form anions
acidic
oxidation → electrons lost
low melting point
bad conductors
bond strength
increases up columns
ionic bond characteristics
different electronegativities
between metal and nonmetal
nonpolar
covalent bond characteristics
similar electronegativies
between 2 non metals
polar
bent shape
2 lone pairs and 2 bonds
valance electrons on periodic table
increases left to right skipping center section
lattice energy
given steps work backwards, then total each delta H (MIND THE LEAD COEFFICIENTS)
enthalpy
Hf = Hreactant - Hproduct
lattice energy increases with
small radius
lattice energy decreases with
large radius
stable electron configuration
full or half filled sections
noble gases on periodic table
far right column
isoelectronic
same charge as a noble gas
isoelectronic series
in order from atom increasing charge, to noble gas, to atom decreasing charge
outer electrons
furthest out shell with the highest n number
valance electrons
last set of electrons in diagonal structure
low bond dissociation
low electronegativity
high bond dissociation
high electronegativity
polarity
difference in electronegativity
covalent bonding
2 non metals
similar electronegativity
e- shared
ionic bonding
metal and nonmetal
different electronegativity
e- fully taken by more electronegative
metallic bonding
2 metals
conductive
electron group arrangements
linear
trigonal planar
tetrahedral
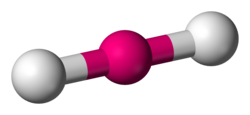
name this structure and its angles
linear
180
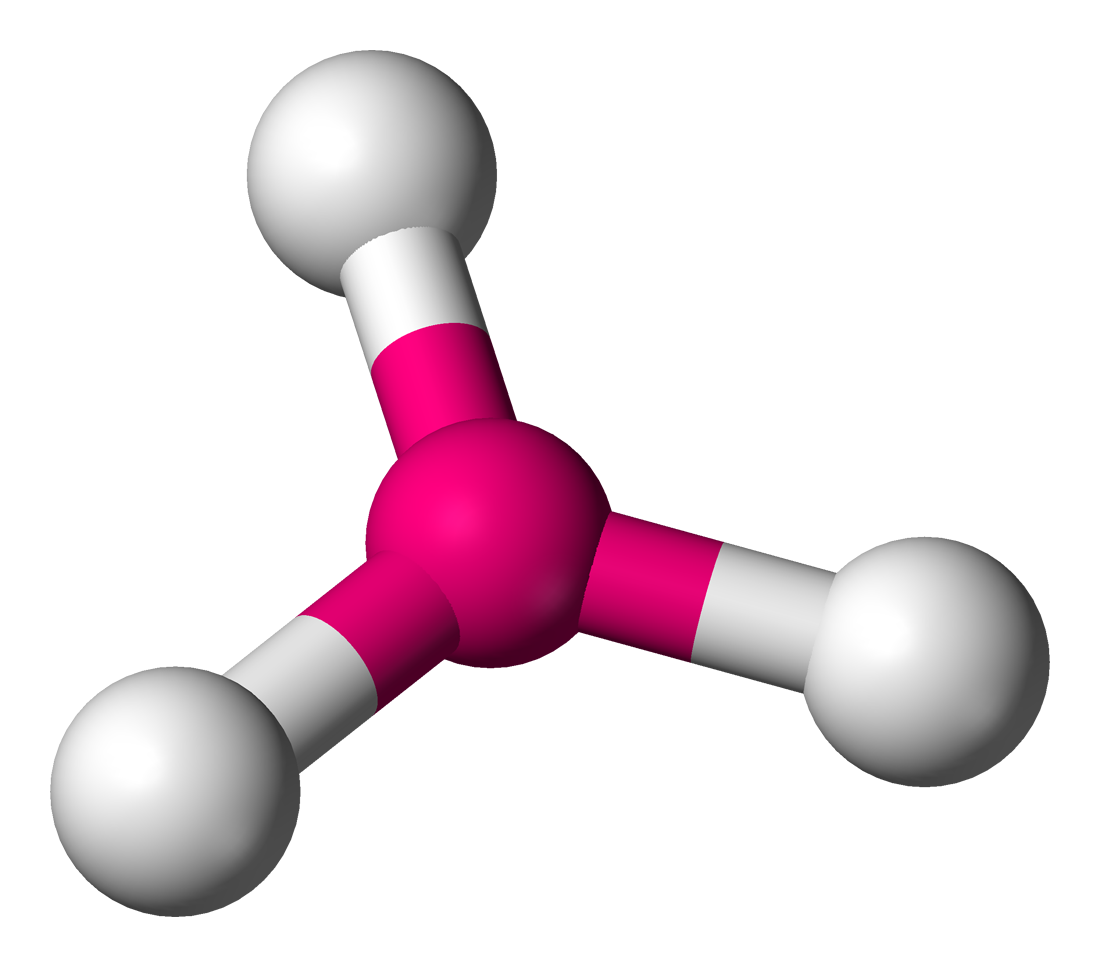
name this structure and its angles
trigonal planar
120
name this structure and its angles
bent
< 120
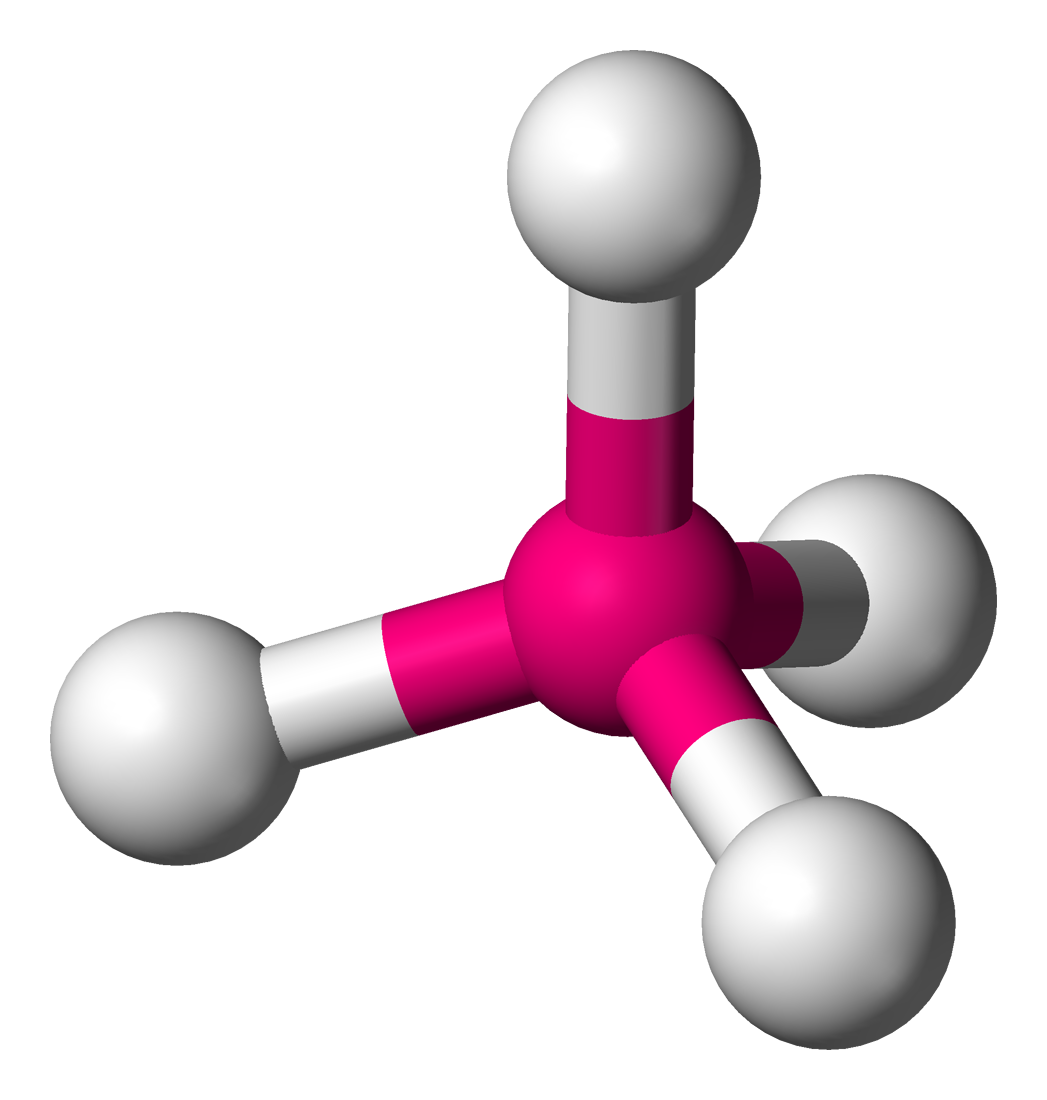
name this structure and its angles
tetrahedral
109.5
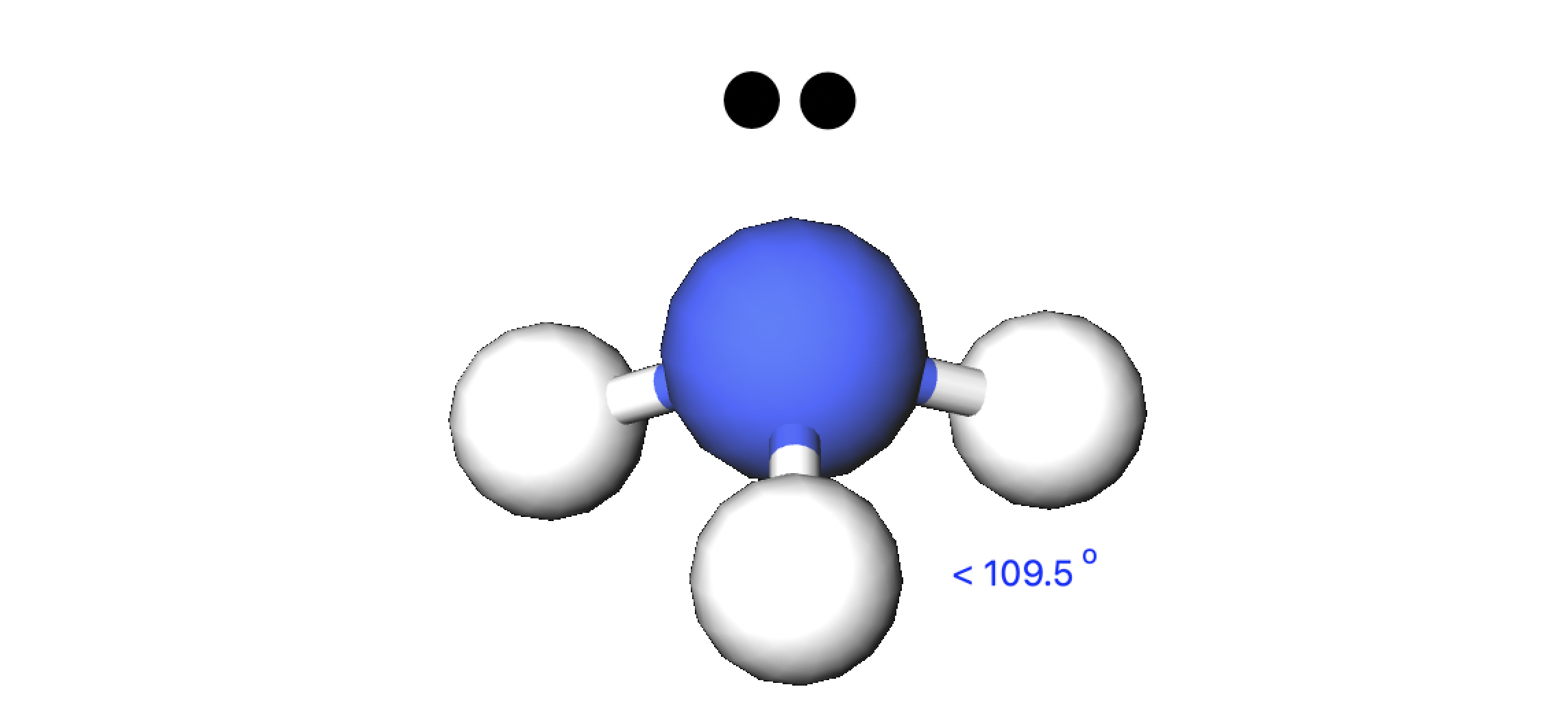
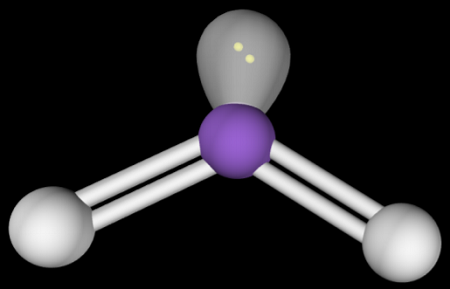
name this structure and its angles
trigonal pyramidal
<109.5

name this structure and its angles
bent
< 109.5
formal charge formula
valency - (#sticks around atom + #dots around atom)
when can elements overfill their octet?
when they’re past phosphorus
single bonds
1 sigma
weak
free rotation
double bonds
1 sigma 1 pi
no free rotation
triple bonds
1 sigma 2 pi
no free rotation
strong
prefix for 1
meth-
prefix for 2
eth-
prefix for 3
prop-
prefix for 4
but-
prefix for 5
pent-
prefix for 6
hex-
prefix for 7
hept-
prefix for 8
oct-