Genetics and DNA definitions need to know
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Gene
a section of the DNA code for a particular trait or protein
Allele
are variations of a gene
Genotype
the genetic information carried by an individual
Phenotype
the observable characteristics of an individual
Dominant Allele
alleles that are expressed in heterozygous individuals
Recessive Allele
alleles that are hidden in heterozygous individuals
Homozygous
individuals that carry the same alleles in their chromosomes
Heterozygous
individuals that carry different alleles in their chromosomes
Karyotype
an arrangement of photographed chromosomes into homologous pairs
Meiosis
cell division by which sex cells, with half the number of chromosomes are produced
Mitosis
Mitosis is the process of cell division where one parent cell becomes two identical daughter cells
why does mitosis occur
to replace or repair cells during growth
DNA Function
is to store biological/genetic information
Gene
a gene is a section of DNA that codes for a protein which determines a trait.
Storage of DNA
is coiled onto itself and around histone proteins to form a chromatin in the nucleus
Histone Proteins
a protein found in the nucleus of a cell with DNA wrapped around it to form a chromatin
Chromatin
a thread-like mass of DNA in the nucleus of a cell that is not dividing
Chromosome
a rod-like structure containing super-coiled DNA
Chromatid (Sister)
one of a pair of duplicated chromosome joined at a centromode
Centromere
a section of a chromosome that joins 2 chromatids
How does coiling DNA around proteins help?
-Save space
-Prevent DNA from tangling
-Controlling access to DNA
XX Chromosome
male
XY Chromosome
female
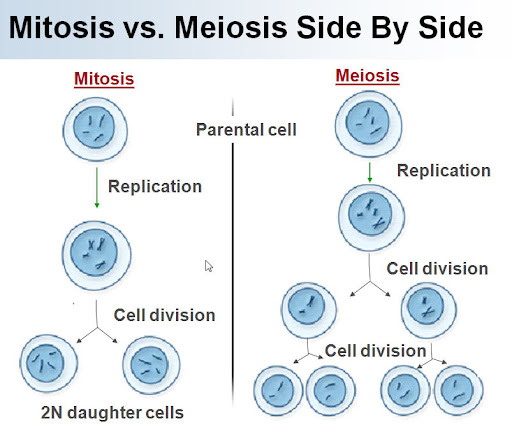
Mitosis and Meiosis side by side
Mitosis= Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
Meiosis= Interphase |, Prophase |, Metaphase |, Anaphase |, Telophase |, Prophase ||, Metaphase ||, Anaphase ||, Telophase ||
Nucelotides are?
Cytosine
Guanine
Thymine
Adenine
Backbone of the DNA structure is made up of?
phosphate and sugar
Mitosis Def
is the process of making new cells
Meiosis Def
Cell division, by which sex cells, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced
Interphase def
Prepare for cell division
Prophase def
Prepare chromosome separation
Metaphase def
Ensure equal division
Anaphase def
Distribute genetic material
Telophase def
Form new nucle
Cytokinesis def
Complete cell division
Key steps for DNA Replication
Enzymes (helicase) unzips the DNA double helix creating a replication fork
Free nucleotides are attracted to exposed bases of each strand of DNA
Sugar and phosphate bond together to form the backbone of the new strand by DNA Polymerase.
2 identical strands of DNA
.
.
What is the DNA molecule made out of?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorous and nitrogen
Where is DNA found?
it is found in the mitochondria cell and the nucleus
What is the location of Mitosis?
in sex cells, sperm and egg cells
Purpose of mitosis?
to produce two identical daughter cell for the growth and development
Location of meiosis?
in the germ cells of the reproductive organs (testes of males and the ovaries of females)
Purpose of meiosis?
to produce gametes with a haploid number of chromosomes
Result of meiosis?
production of four haploid cells (gametes)
Nucleotide
phosphate, sugar and nitrogenous base
Semi-conservative
DNA replication where each new DNA molecule consists of one original leading strand and one lagging strand