Zoo-Lab (Sem-1) - Exercise 9: Protozoa
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
protozoans
single-celled animals under Kingdom Protista; mostly microscopic
Paramecium; Amoeba; Euglena; Trypanosoma; Balantidium; Vorticella
examples of protozoans
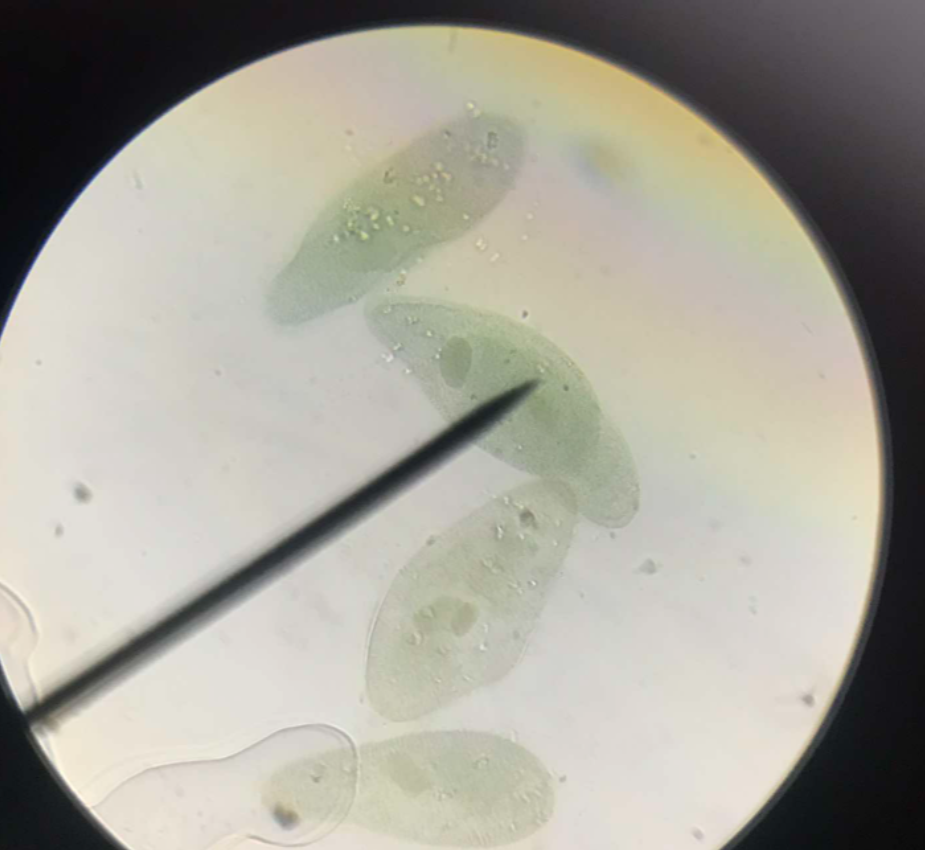
Paramecium sp.
slipper-shaped; swims with spiral or rotary movement; body is a mass of dense protoplasm
micronucleus
part of a Paramecium; a smaller isolated nuclear structure separated from the main nucleus
macronucleus
part of a Paramecium; the larger type of nucleus in ciliates
anterior
narrower and rounded end of a Paramecium
posterior
wider and pointed end of a Paramecium
cilia
hair-like projections; structures for locomotion
peristome
funnel-like bearing cilia lined in rows from anterior left to posterior right, slightly oblique
food vacuoles
sometimes contain solid particles; scattered inside the body of Paramecium; more numerous in the posterior portion than in the anterior end
contractile vacuoles
two clear vacuoles, one in the anterior end and another in the posterior end, appear and disappear at intervals
binary fission
asexual reproduction by a separation of the body into two new bodies; an organism duplicates its genetic material, or deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), and then divides into two parts (cytokinesis), with each new organism receiving one copy of DNA
early fission
elongation of the micronucleus and macronucleus
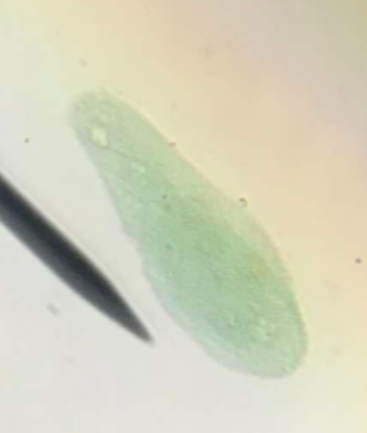
middle fission
deepening of constriction

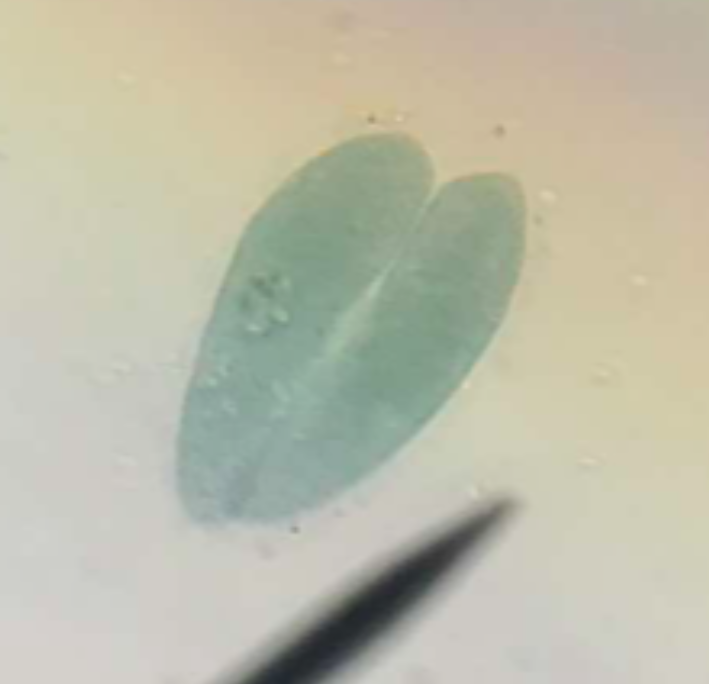
late fission
deepening of constriction result in the pinching off of the Paramecium into two daughter paramecia
conjugation
sexual reproduction; two paramecia joined at their oval grooves and swim around
trichocysts
membrane-bound extrusomes with a predatory or protective role