Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
solvent
the substance present in the greatest quantity
solute
are the substance(s) dissolved in the solvent
aqueous solution
solution in which water is the solvent
what do ionic compounds do when they dissolve in water
they ionize or form ions
ionic compounds dissolving in detail
each ion dissociates from the solid structure and disperses throughout the solution
anions are attracted to the partial positive end of water
cations are attracted to the partial negative end of water
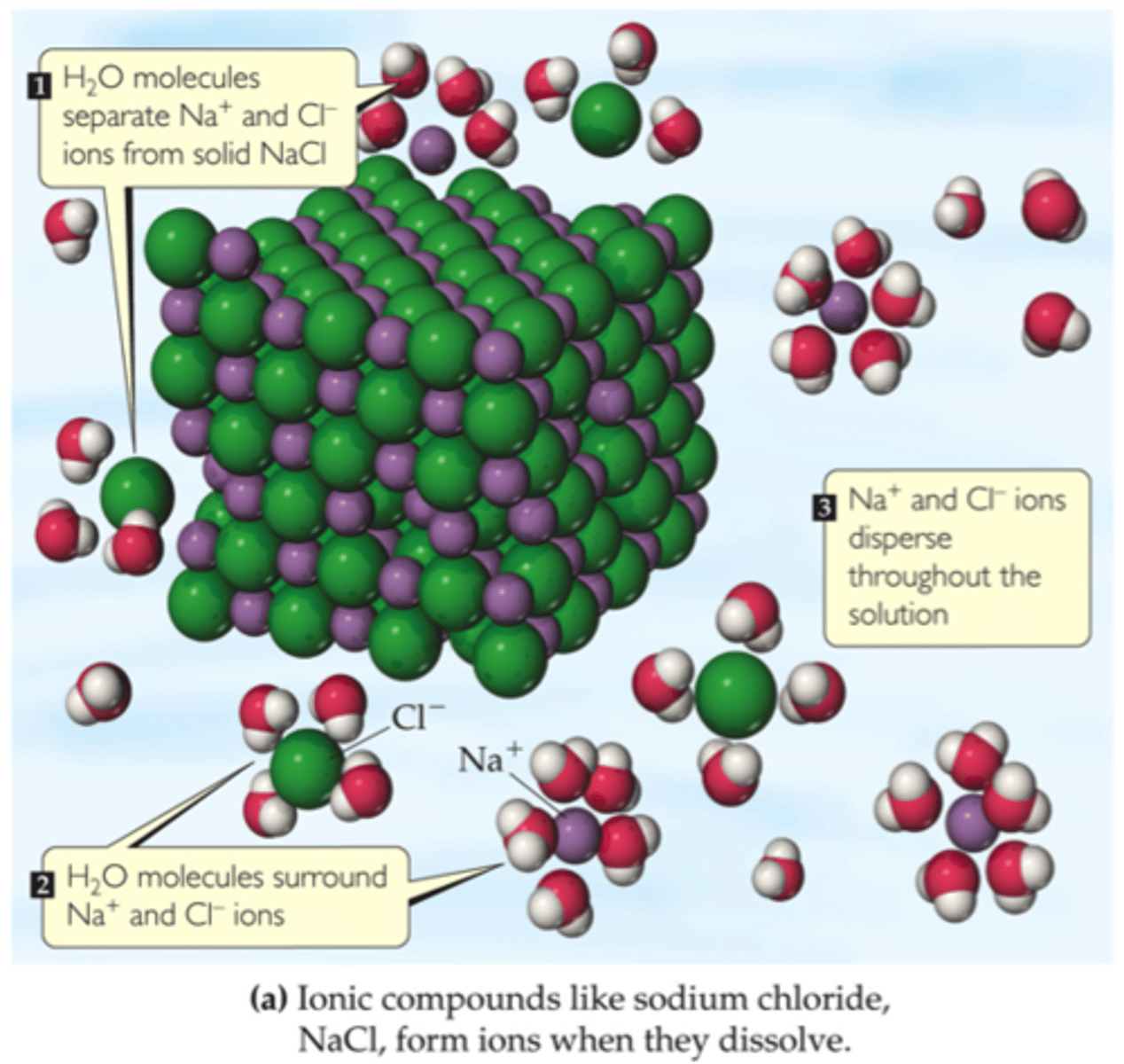
solvated
when ions are completely surrounded by solvent molecules to prevent them from recombining and to allow them to disperse uniformly throughout the solution
what happens to most molecular compounds when dissolved in water
the solution consists of intact molecules dispersed throughout
ex: some molecular compounds, such as acids, dissolve in water by ionizing
precipitation reactions
result in the formation of an insoluble product
follow the pattern of exchange reaction
what is the insoluble product called
precipitate
solubility
amount of substance that can be dissolved in a given quantity of solvent at the given temperature
how to write molecular equation for dummies
1. Use the chemicals formulas of the given reactants to determine which ions are present.
2. Write the chemical formulas of the products by combining the cation from one reactant with the anion from the other (following the basic form of an exchange reaction).
3. Check the water solubility of the products and give the states of the products.
4. Balance the equation.
important notes about molecular equations
1. This equation only contains compounds; not ions!
2. A precipitate must form for a reaction to occur!
how to write complete ionic equation for dummies
1. Start with a balanced molecular equation.
2. Show water soluble ionic compounds (strong electrolytes) as separate ions.
3. Distribute coefficients and physical states.
[ex. 2 KI(aq) becomes 2 K+(aq) + 2 I-(aq)]
4.Convert subscripts to coefficients EXCEPT those of polyatomic ions!
[ex. Pb(NO3)2 (aq) becomes Pb2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq)]
what does not separate into ions in complete ionic equations
the precipitate does not separate into ions (remains a compound)
how to write net ionic equation
1. Take complete ionic equation.
2. Remove spectator ions from both sides.
um, what are spectator ions
things that appear in identical forms on both sides of the equation and play no direct role in the reaction
important notes about net ionic equations
1. This equation only shows ions and compounds directly involved in the reaction (formation of a precipitate).
2. If every ion in a complete ionic equation is a spectator, no reaction occurs!!!!!!
ionic hydroxide compounds
dissociate into ions
ex: KOH (aq) → K⁺(aq) + OH⁻(aq)
bases that do not contain OH-
accept H⁺ ions
proton acceptors
ex. NH₃(aq) + H₂O(l) ↔ NH₄⁺(aq) + OH⁻ (aq)
substances that are insoluble in water cannot be
electrolytes