UCF Biomedical Sciences Exit Exam Study Guide
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
eukaryotic cells
- nucleus
- membrane bound organelles
- Larger, complex, mostly multicellular
- DNA is linear in chromosomes
- DNA tightly wrapped around histone proteins (chromatin)
- mRNA is edited
- replicate through mitosis and meiosis
- free and bound ribosomes
- 80S ribosomes
prokaryotic cells
- smaller, less complex
- no membrane bound organelles
- no nucleus
- DNA is circular, not packaged as chromosomes
- no histones
- mRNA usually unedited
- replicate through binary fission
- free ribosomes
- 70S ribosomes
Eubacteria
- Domain of unicellular prokaryotes whose cell walls are made up of peptidoglycan
- thrive in normal conditions
- lipid bilayer as cell membrane
Archaea
- Domain of unicellular prokaryotes that have cell walls that do not contain peptidoglycan (pseudo)
- thrive in extreme conditions
- lipid monolayer in cell membrane
endospore
a dormant, tough, and non-reproductive structure produced by certain bacteria (gram pos) typically due to lack of nutrients/periods of stress
capsules
protect a bacterial cell from ingestion and destruction by white blood cells (prevent phagocytosis)
flagella
long, whip-like filament that helps in cell motility. Many bacteria are flagellated, and sperm are flagellated.
gram positive
- thick peptidoglycan layer
- no outer membrane
- contain teichoic acids
- stain purple/blue
gram negative
- thinner layer of peptidoglycan
- has outer membrane
- contains lipopolysaccharides
- stain pinkish/red
microorganism growth phases
1. lag phase = population remains constant, metabolically active, cells grow in size
2. log phase = cell population size increases logarithmically as cells begin to reproduce
3. stationary phase = population size is constant, though some cells are dying and others are dividing
4. death = total lack of nutrients and reproduction stops; death rate exceeds division rate
generation time
the time it takes for a population to double in number
ex: if E. coli's generation time is 20 minutes and you start with a colony of 3 cells, after an hour there will be 243 cells
binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction in single-celled organisms by which one cell divides into two cells of the same size
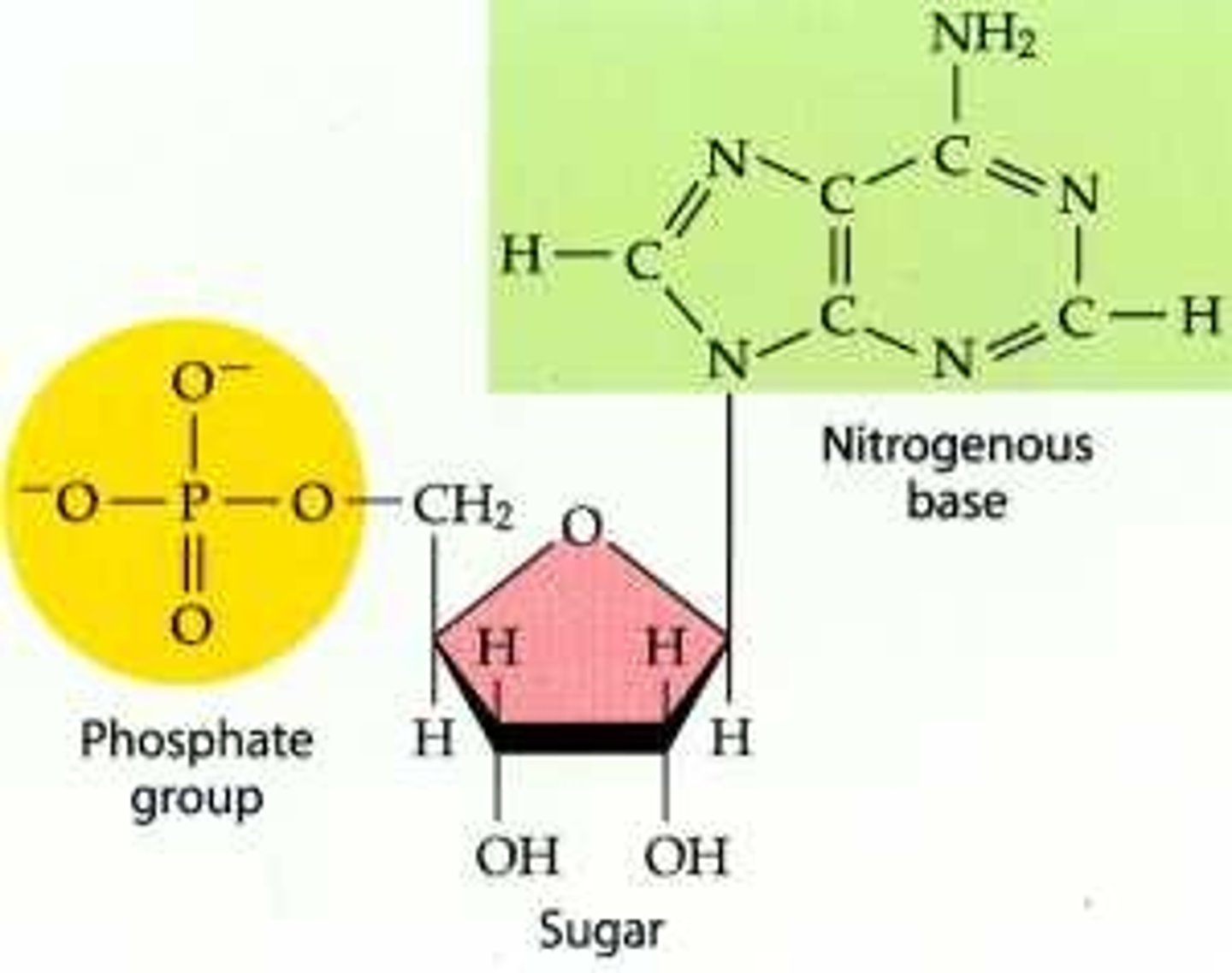
nucleic acids
macromolecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus
DNA and RNA
sugars are linked by phosphodiester bonds while bases are linked by hydrogen bonds
make up genetic information in cells, function in protein production (DNA --> RNA --> protein)
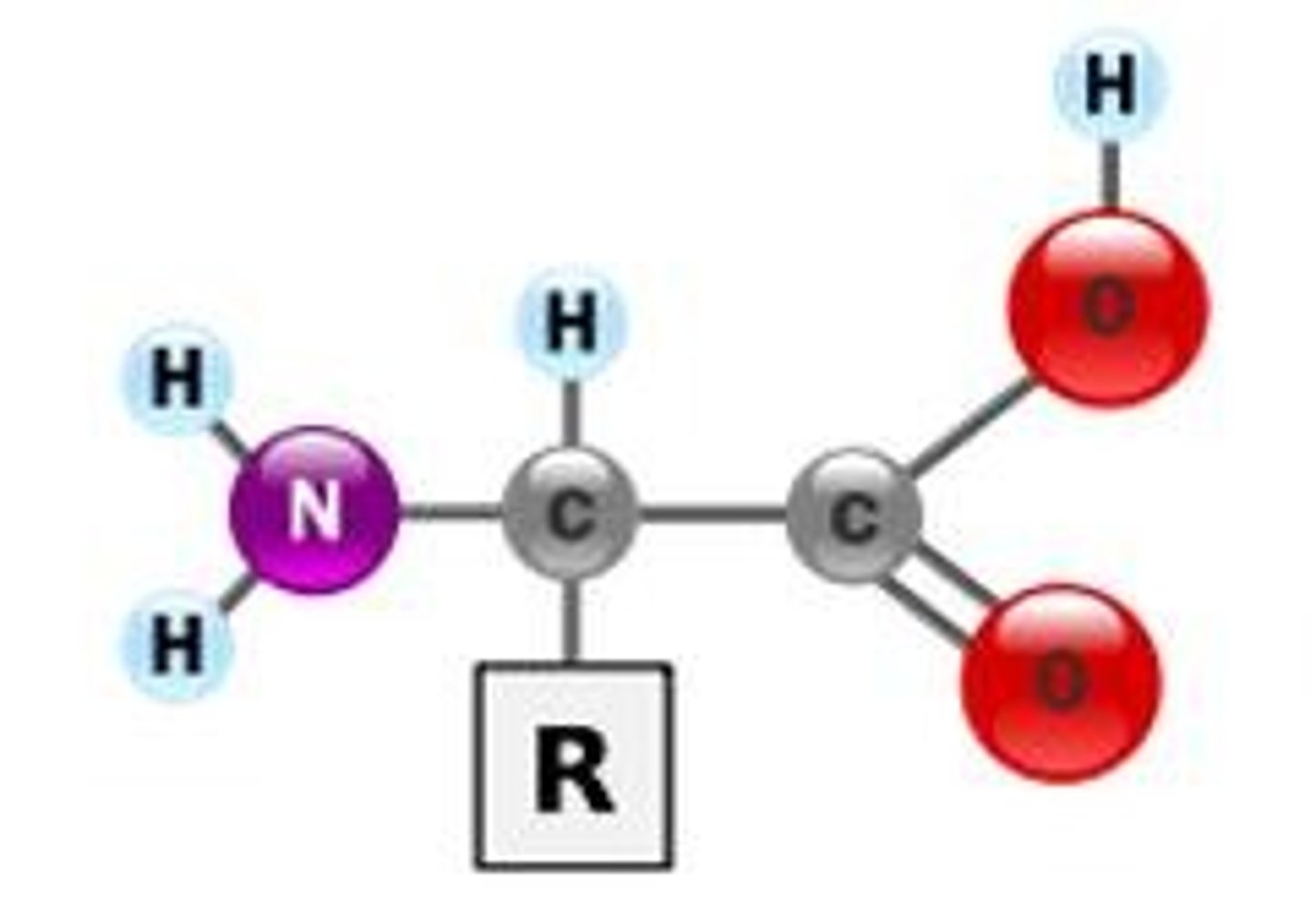
proteins
chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds
disulfide bridges and hydrophobic interactions also exist
functional metabolic molecules in cells; also play structural roles
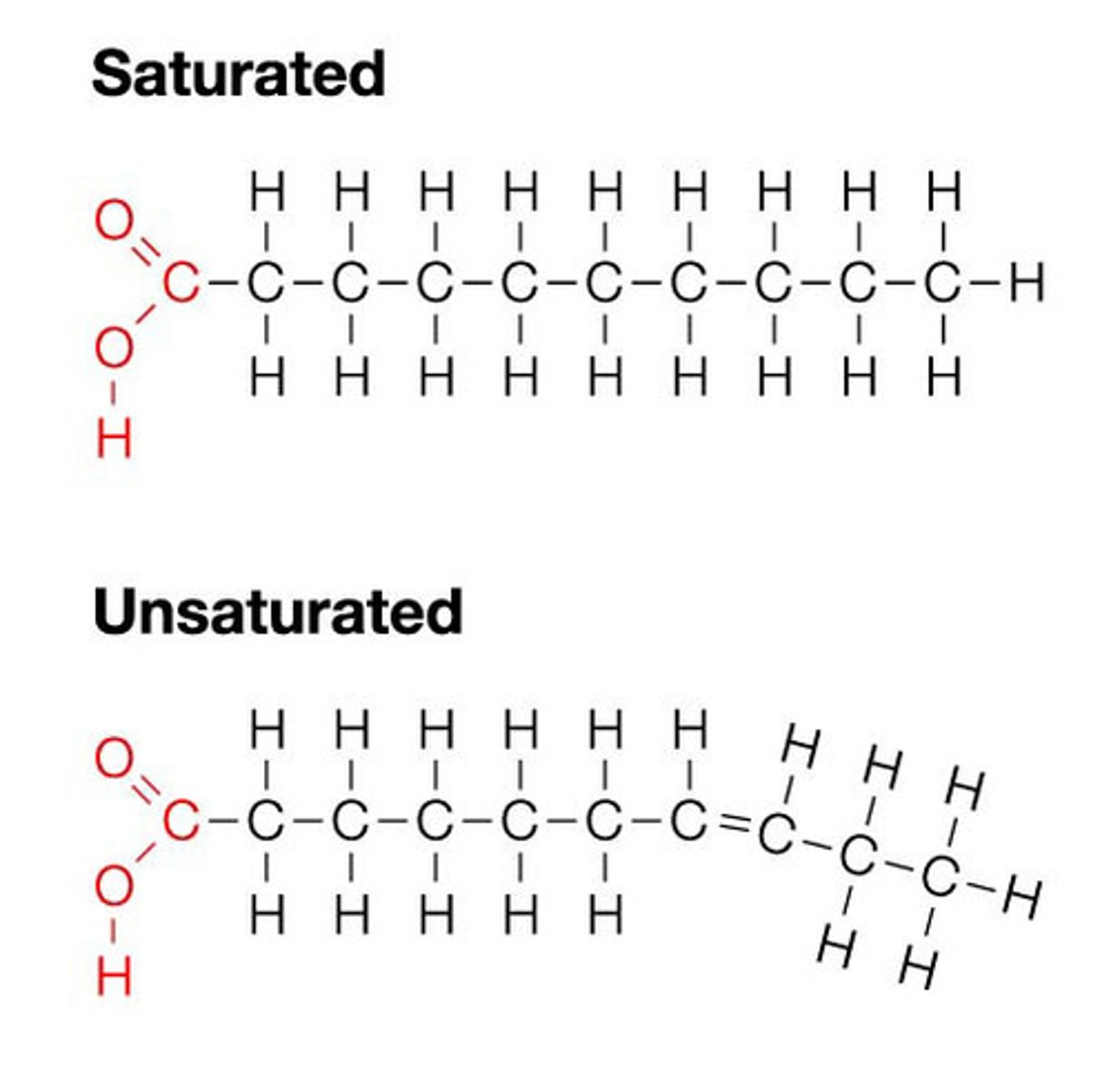
lipids
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; micromolecule = fatty acid
bound by non-polar covalent bonds = hydrophobic molecules
primarily make up cell membrane but also function as signaling molecules and can be used for energy
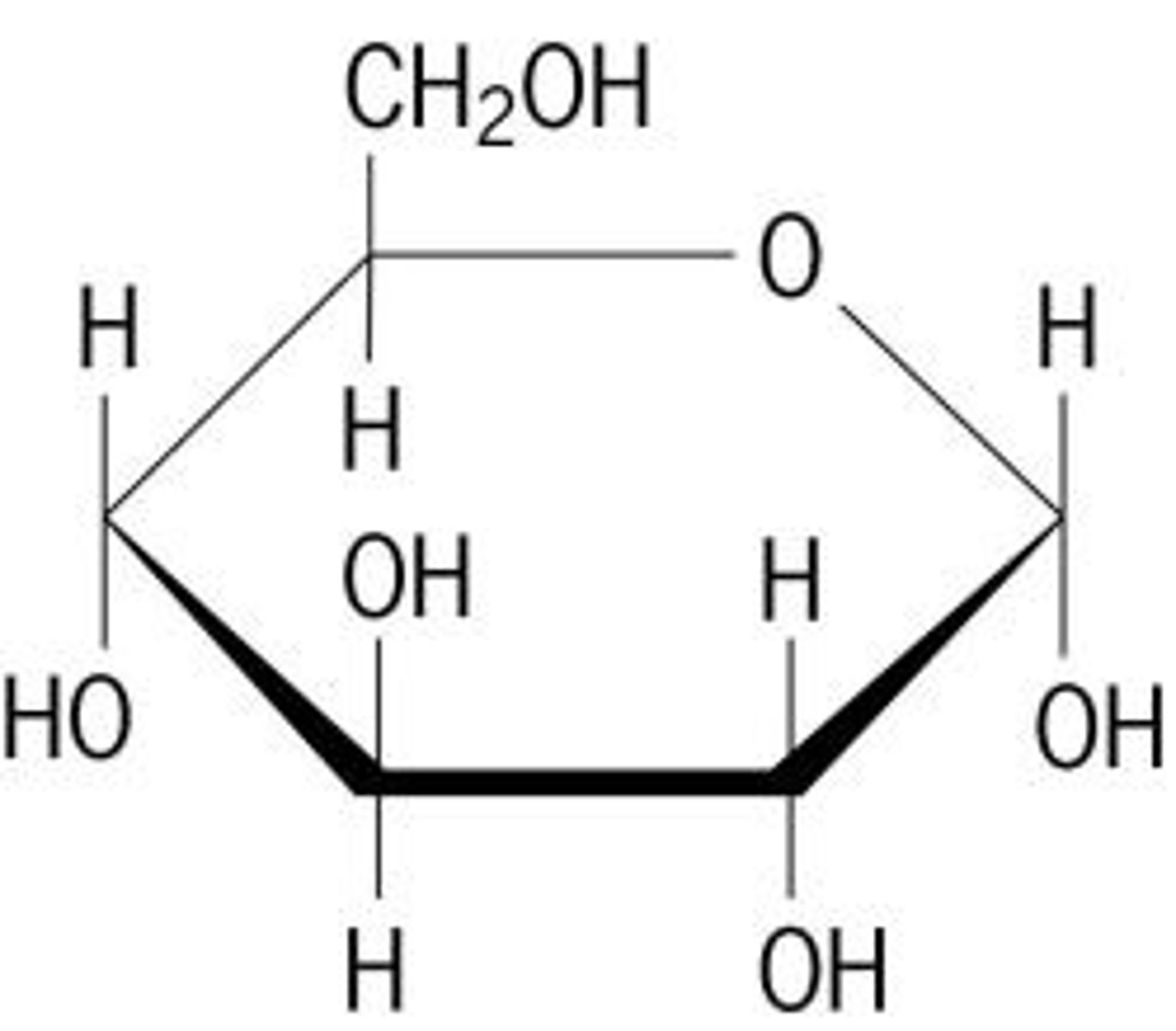
carbohydrates
molecules made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
mono- di- and polysaccharides
monosaccharides are linked together through a type of covalent bond called a glycosidic bond
main energy source for cells = glucose and other sugars are broken down into ATP and other energy molecules
cell wall characteristics
- helps determine the shape of a bacterium
- provides strong structural support to keep the cell from bursting or collapsing due to osmotic pressure
- primarily made up of different carbohydrate molecules such as cellulose fibers
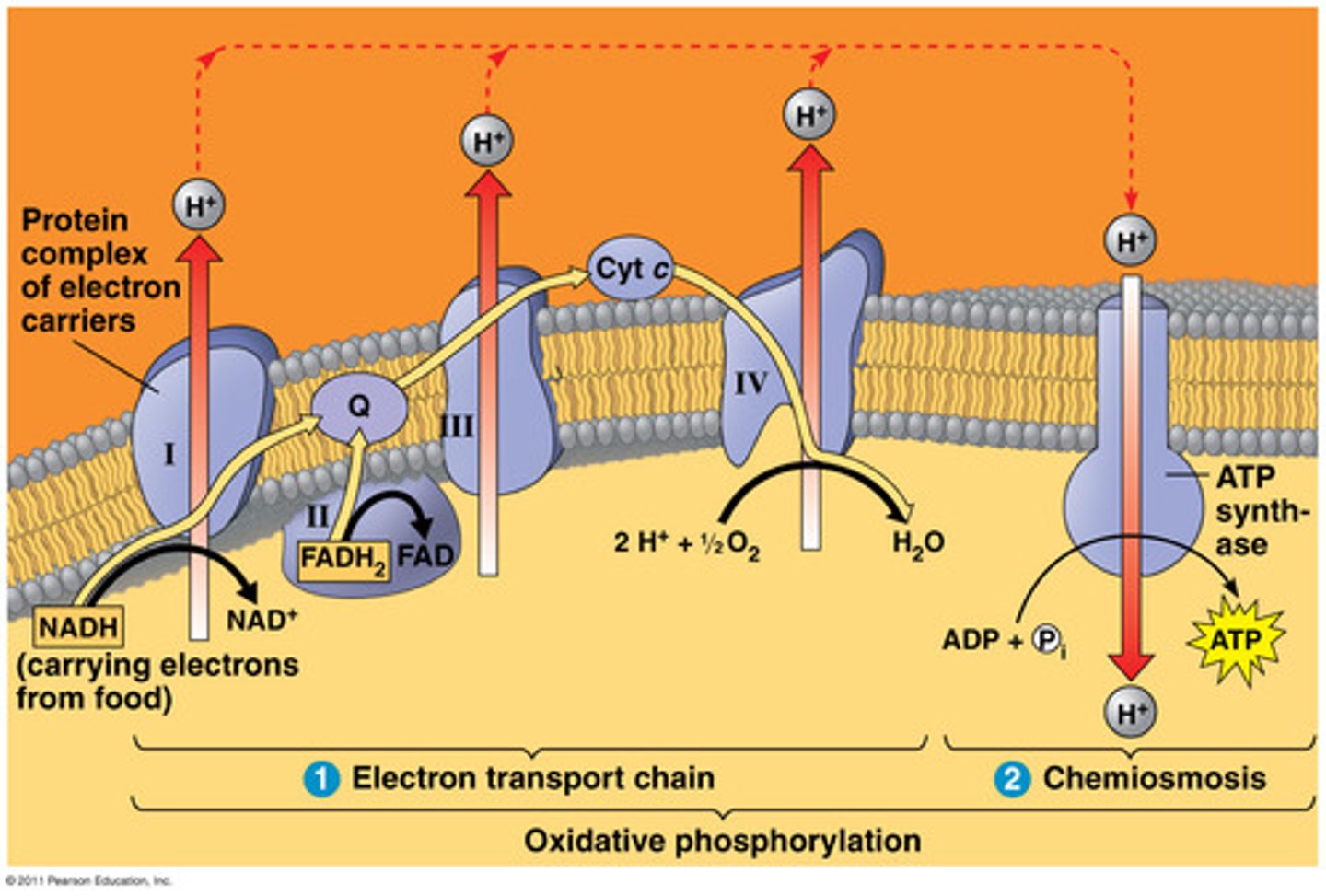
oxidative phosphorylation
the production of ATP using energy derived from the redox reactions of an electron transport chain; the third major stage of cellular respiration.
occurs in plant and animal cells as part of ETC in Kreb's cycle
takes place on inner cytoplasmic membrane in prokaryotes
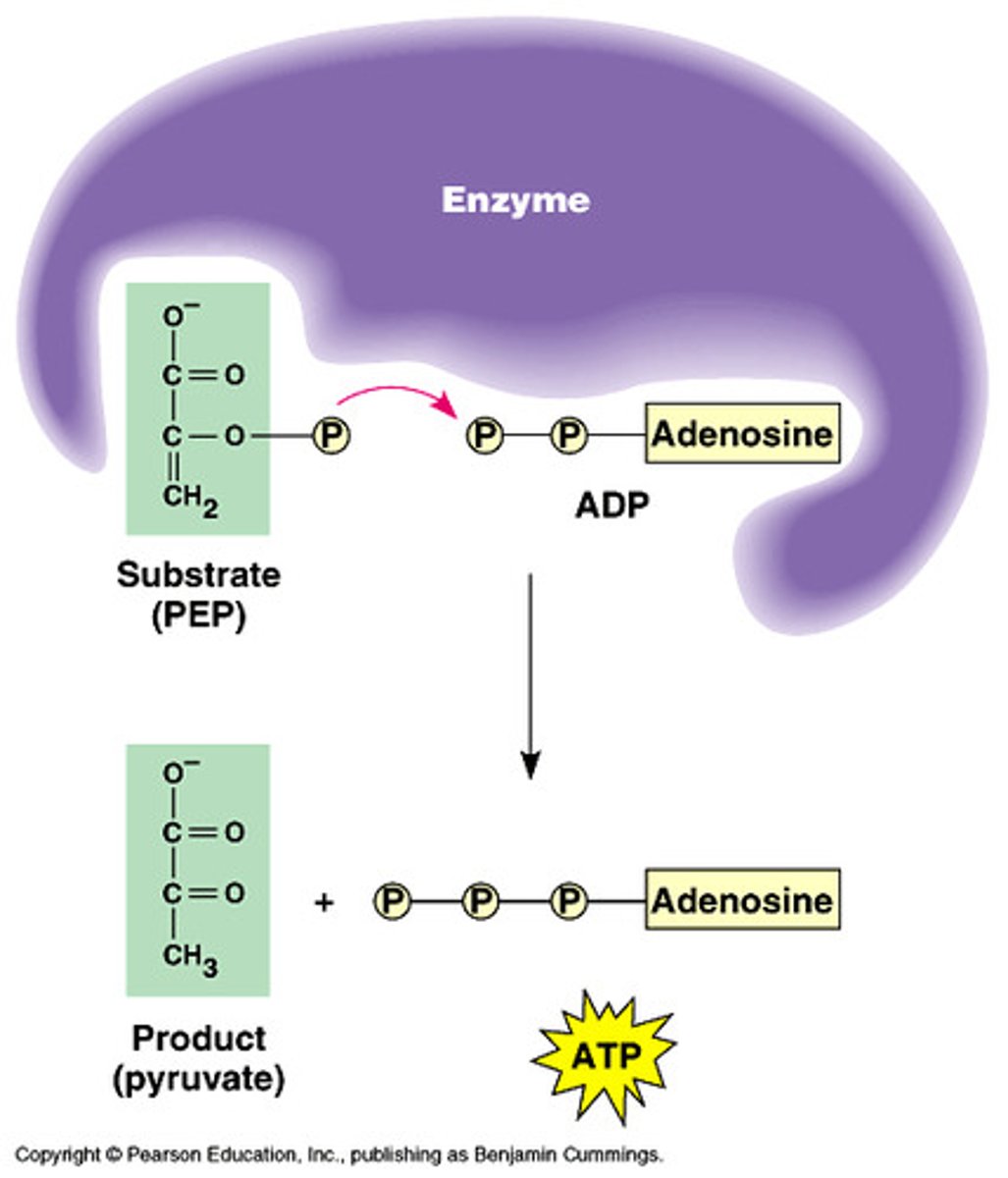
substrate-level phosphorylation
the enzyme-catalyzed formation of ATP by direct transfer of a phosphate group to ADP from an intermediate substrate in catabolism
occurs in cytoplasm of cells during glycolysis and in the mitochondria as part of the Kreb's cycle
less efficient source of ATP compared to oxidative phosphorylation, but can function aerobically or anearobically
fermentation
a catabolic process that makes a limited amount of ATP from glucose without an electron transport chain and that produces a characteristic end product, such as ethyl alcohol or lactic acid
process by which cells release energy in the absence of oxygen
final electron acceptor = pyruvate? just definitely not oxygen as this is anaerobic
glycolysis
the breakdown of glucose by enzymes, releasing energy and pyruvic acid
electron acceptor = NAD+
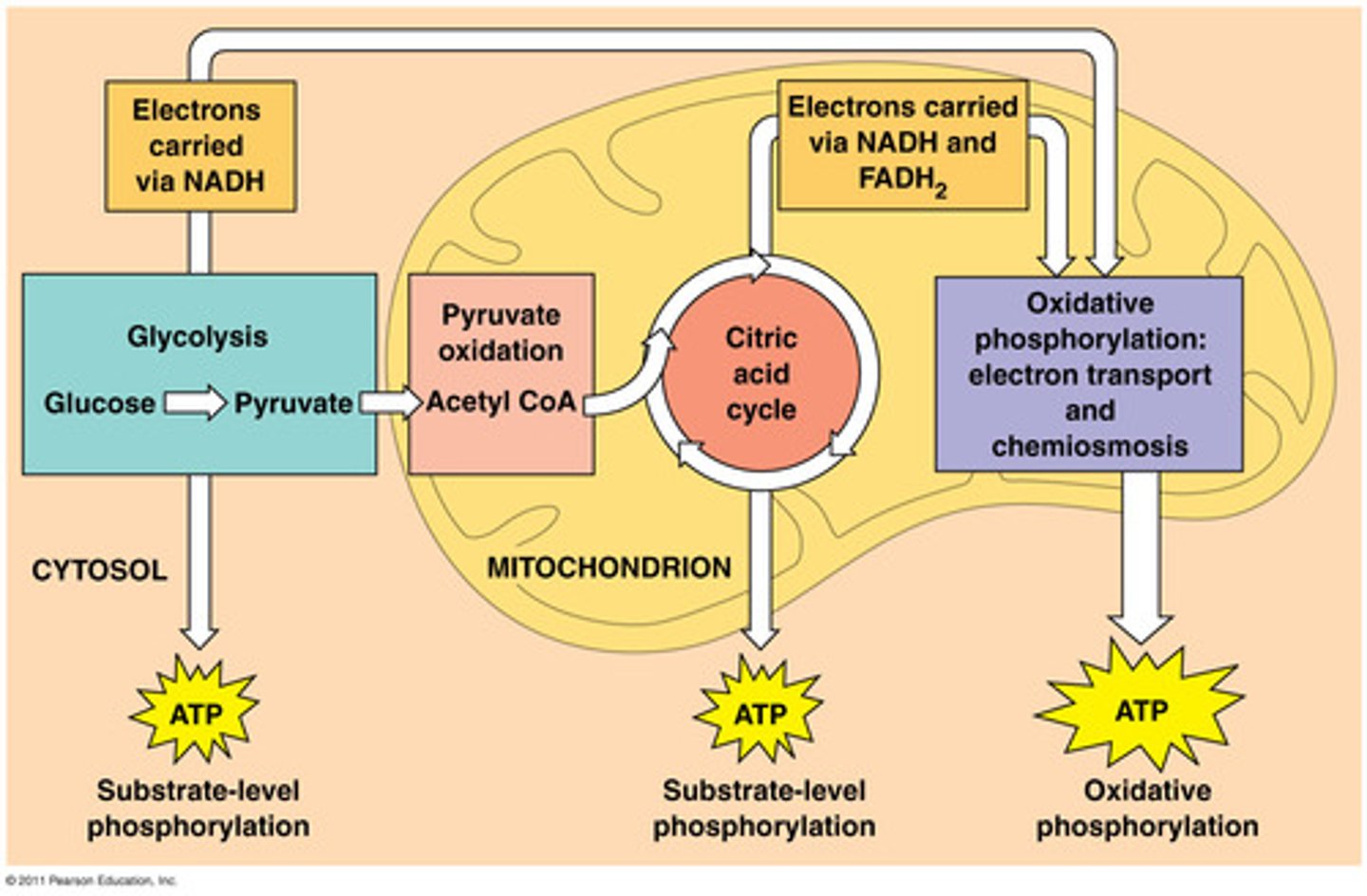
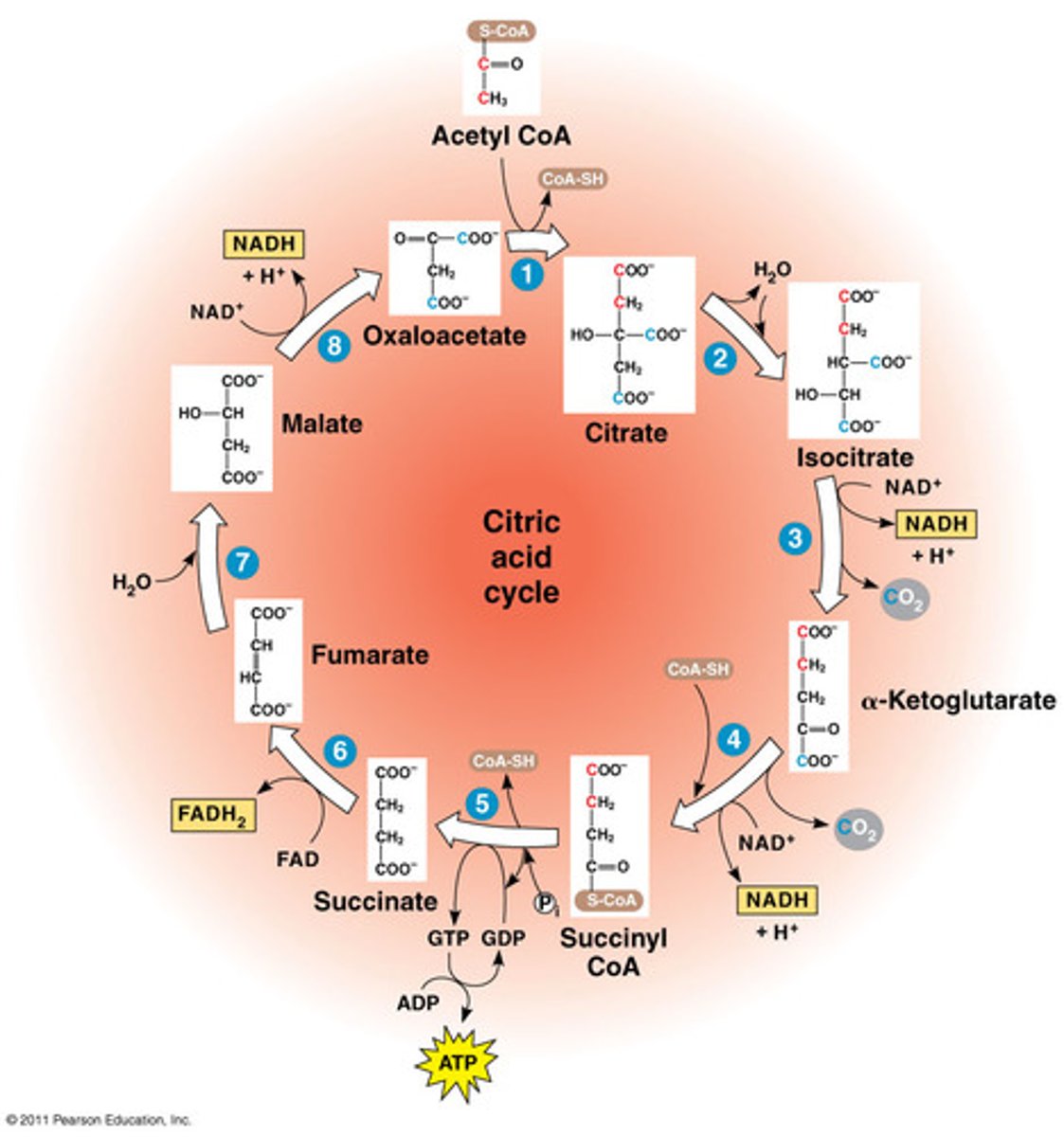
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
-Pyruvic acid combines with coenzyme A to form Acetyl-CoA which enters Krebs cycle
-in matrix of mitochondria
- each turn of Krebs cycle produces 1 molecule of ATP, 1 molecule of FADH2, and 3 molecules of NADH
-byproduct CO2 is exhaled
oxidized: citrate
reduced: NAD+ and FAD+
final electron acceptor = oxygen
NADH produced in this process pass their electrons along the ETC on the inner membrane of the mitochondria = oxidative phosphorylation
exotoxin
a toxin released by a living bacterial cell into its surroundings
heat labile
endotoxin
a toxin that is present inside a bacterial cell and is released when the cell dies and cell wall disintegrates
heat stable
contain LPS = typically gram - cells
virulence
the degree of toxicity or the injury-producing potential of a microorganism
defined by a microorganism's invasiveness and toxigenicity
invasiveness
ability of a bacterial pathogen to rapidly spread through tissue
toxigenicity
ability of a microorganism to produce a toxin
host resistance
the host's ability to limit pathogen burden and includes such diverse defenses as physical barriers (e.g. skin), behavioral modifications or a rapid immune response
humoral immune response
the branch of adaptive immunity that involves the activation of B cells and that leads to the production of antibodies, which defend against bacteria and viruses
cellular immune response
certain lymphoid cells recognize material as foreign and initiate a chain of responses that permit them to destroy intracellular (think activation of phagocytic cells, NK cells, cytotoxic T cells)
innate immunity
- fixed response that is general and inherited
- based on recognition of foreign material (PAMPs and PRRs) and recruitment of effector cells
- results in inflammation and degradation of foreign material
- involves activation of complement system to tag pathogen for destruction (opsonization)
- complement is considered humoral immunity
active humoral immunity
occurs when B cells encounter antigens and produce specific antibodies against them
characterized by production of memory cells
can be natural or artificial if through vaccination
passive humoral immunity
occurs when ready-made antibodies are introduced into body (transfer from mom to baby through breastmilk)
no memory cells are made, so immunity only lasts a short time
self antigen
any molecule or chemical group of an organism which acts as an antigen in inducing antibody formation in another organism but to which the healthy immune system of the parent organism is tolerant
particularly important for RBCs (your blood type is determined by what antibodies are on your cells and what antigens you have)
autoimmune disease occurs if body reacts against self antigens
recall concept of positive selection and tolerance in immuno --> immune cells are self tolerant if they do not bind tightly to your own cells and therefore are positively selected
immunoglobulin
an antibody
contains a variable region made up of the light chain and heavy chain that binds antigen
also contains a constant region made up of the heavy chain
if constant region is bound to membrane = membrane bound Ig = BCR
if secreted = antibody
antibodies can neutralize pathogens, tag them for destruction by phagocytosis (opsonization) by activating the complement system, and also kill them by activating MAC
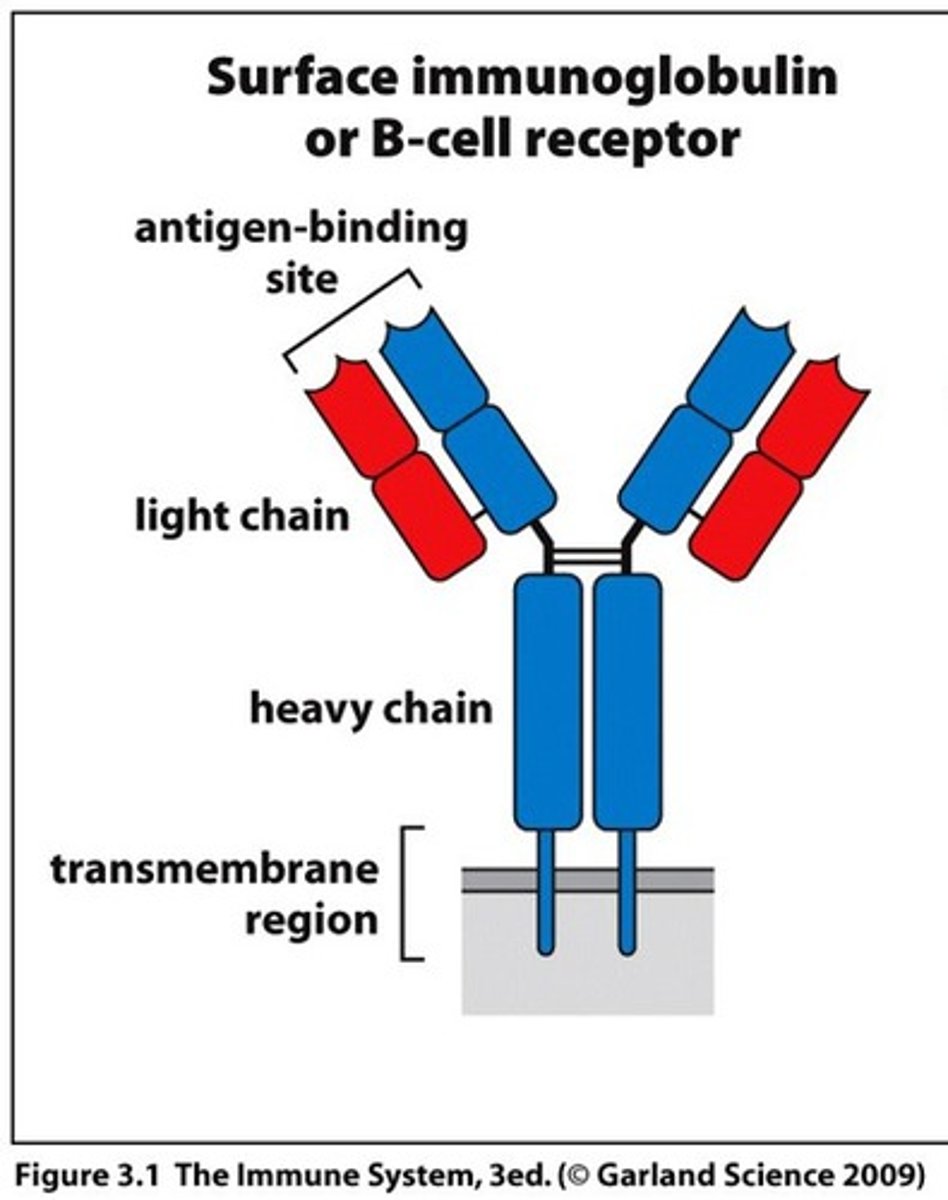
T cell receptors
T lymphocyte receptors that recognize and bind antigen presented by MHC receptors
MHC
Major Histocompatability complex, a set of proteins found on the plasma membranes of cells that help display antigen to T cells.
MHC I is found on all cells and displays bits of proteins from within the cell; this allows T cells to monitor cell contents and if abnormal peptides are displayed on the surface, the cell is destroyed by killer T cells.
MHC II is found only on macrophages and B cells, and follicular dendritic cells. This class of MHC allows these cells (known as antigen presenting cells) to display bits of "eaten" (phagocytozed or internalized) proteins on their surface, allowing the activation of helper Ts --> thus further activating immune response.
cytokines
hormone-like chemicals facilitating communication between brain and immune system
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes
A=T
C-=G lol
two antiparallel strands bound by hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases
backbone is alternating sugars and phosphates
transcribed by RNA pol to form RNA
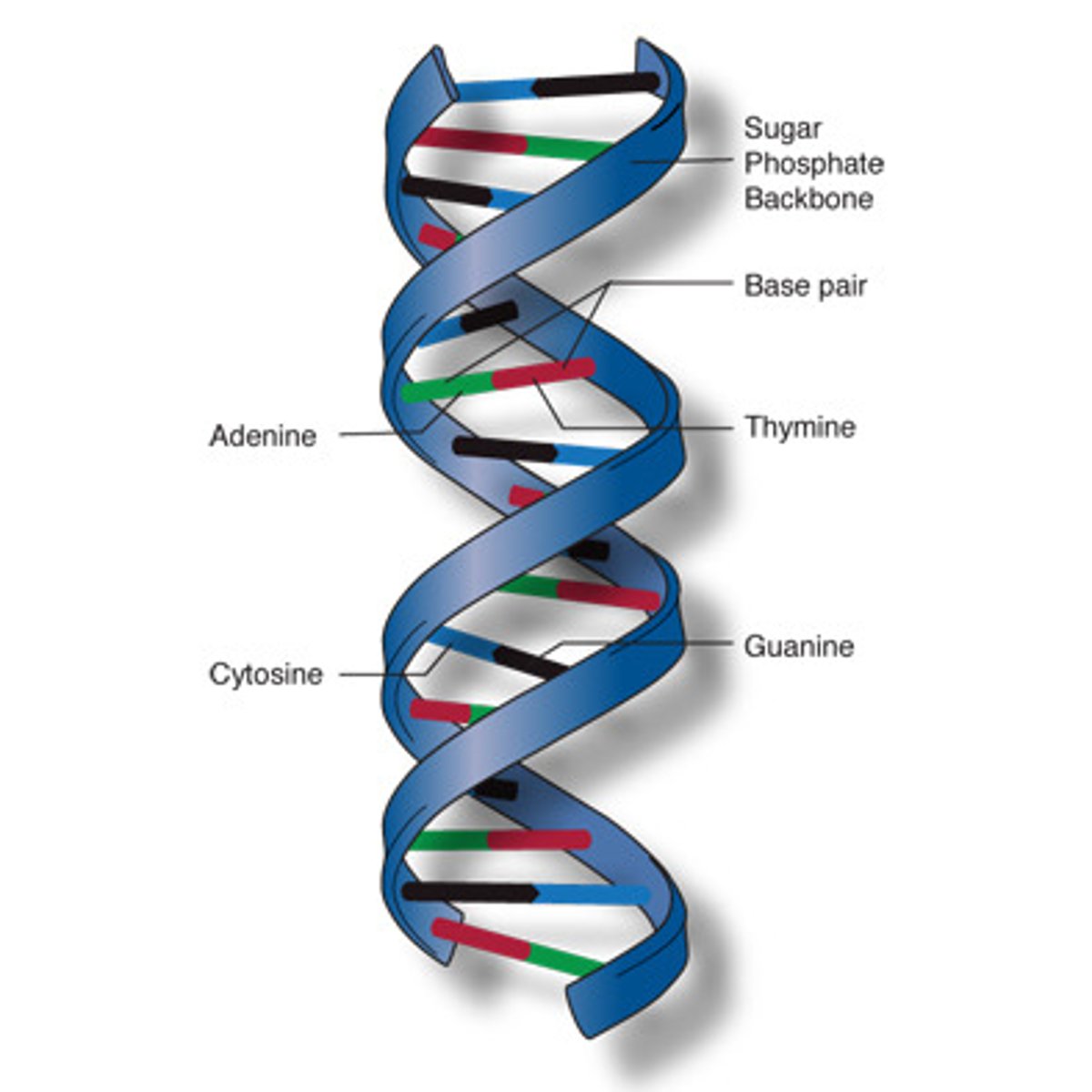
DNA vs RNA
deoxyribose sugar vs. ribose sugar, thymine vs. uracil , double strand vs. single strand
DNA transcribed to form RNA, RNA translated to form polypeptide
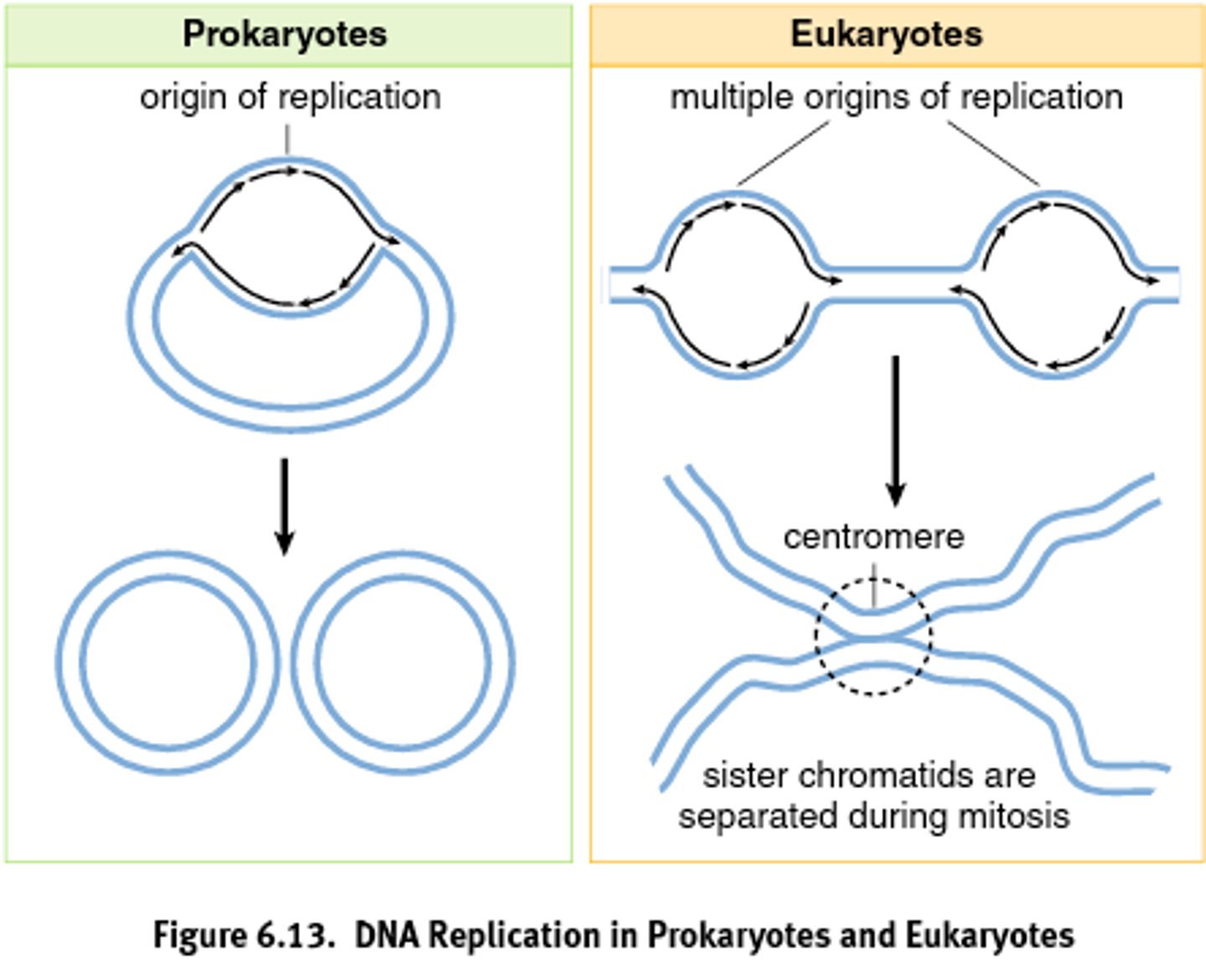
DNA replication prokaryotes vs eukaryotes
Eukaryotic DNA unwinds in multiple areas as DNA is replicated. Occurs in the nucleus
In prokaryotes, the circular DNA strand is opened at one origin of replication. Occurs in the cytoplasm
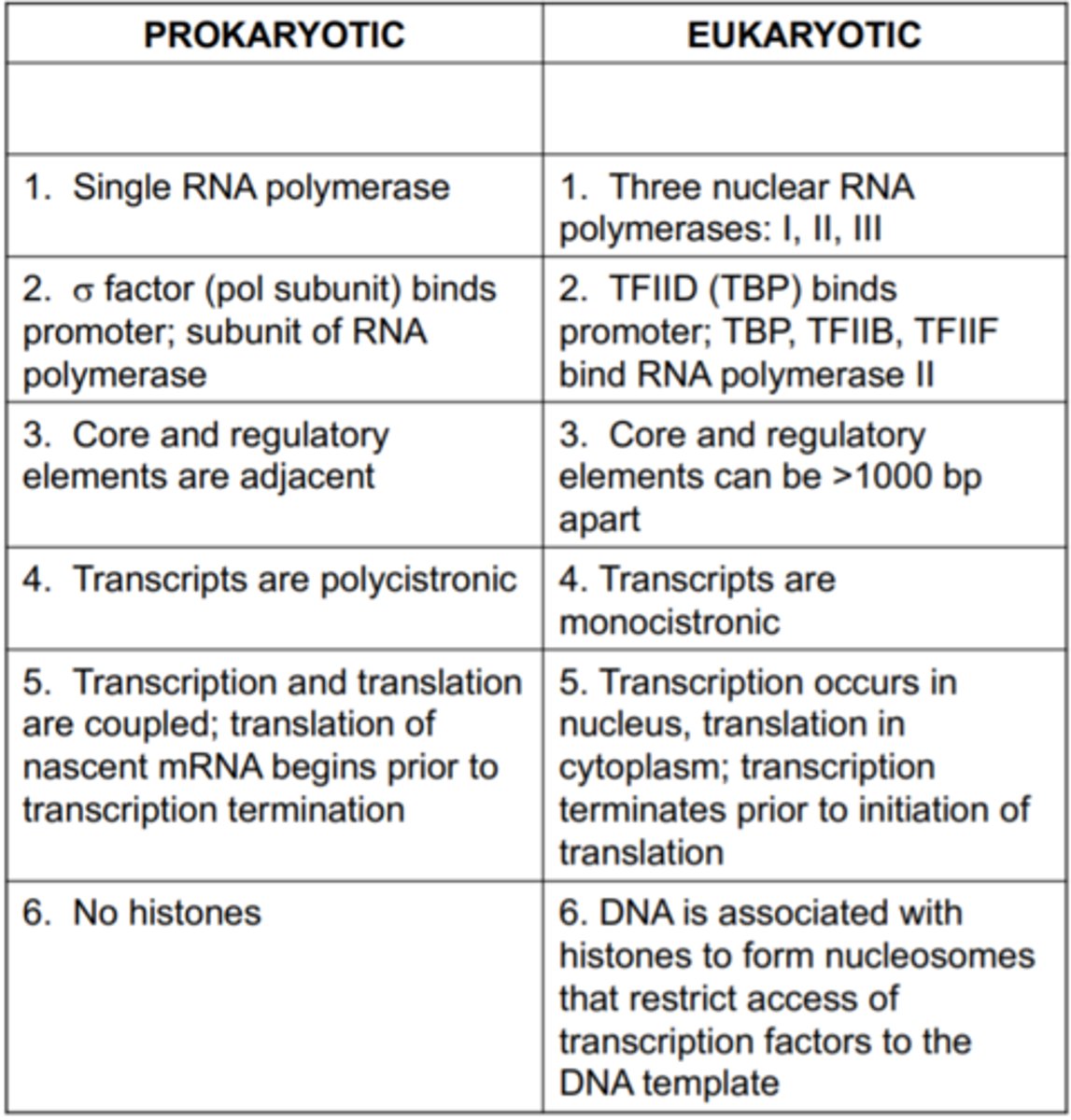
transcription prokaryotes vs eukaryotes
Prokaryotes- in cytoplasm
DNA is more accessible to RNA poly, RNA poly can interact directly with genes
mRNA is not modified; transcription and translation occur simultaneously in cytoplasm
Eukaryotes- in cell's nucleus
DNA is wrapped histone proteins to form nucleosomes..packed to form chromatin
proteins mediate activity between RNA polymerase and DNA
mRNA is modified, RNA splicing and 5' cap, poly AAA tail; transcription occurs in nucleus, translation later in cytoplasm
Prokaryotic regulation of gene expression
Because lack of nucleus transcription and translation occur almost simultaneously in cytoplasm and regulation occurs at a transcriptional level.
default = ON = needs to be inhibited
Eukaryotic regulation of gene expression
Regulated during transcription and RNA processing which take place in nucleus and during protein translation in cytoplasm.
default = OFF = needs to be activated
lytic cycle
a viral reproductive cycle in which copies of a virus are made within a host cell, which then bursts open, releasing new viruses
lysogenic cycle
a viral reproductive cycle in which the viral DNA is added to the host cell's DNA and is copied along with the host cell's DNA
lytic cycle steps
1. Virus attaches to host cell and inserts genetic material into cell
2. Viral genetic material takes over host cell
3. Host cell makes viral parts and assembles them to make viruses.
4. Host cell burst and releases viruses and the cycle continues with other cells.
lysogenic cycle steps
1. Virus attaches to host cell and inserts genetic material into cell.
2. Genetic material is copied into the host cell's own chromosome.
3. Every time the cell divides the viral genes divide too
4. A trigger from the environment could causes the viral genes to begin a different cycle
antibiotics
Drugs that block the growth and reproduction of bacteria
may act by inhibiting transcription or translation
antibiotic resistance
the evolution of populations of pathogenic bacteria that antibiotics are unable to kill
bacterial transformation
ability of bacteria to alter their genetic makeup by uptaking foreign DNA from another bacterial cell and incorporating it into their own
bacterial transduction
DNA transferred from one bacterium to other via virus
bacterial conjugation
the direct transfer of genetic material (DNA) from one bacterial cell to another
horizontal gene transfer (HGT)
transfer of genes between unrelated species