Qi: Oral Anticancer Agents in Hematology – 2
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
List the BCR-ABL inhibitos
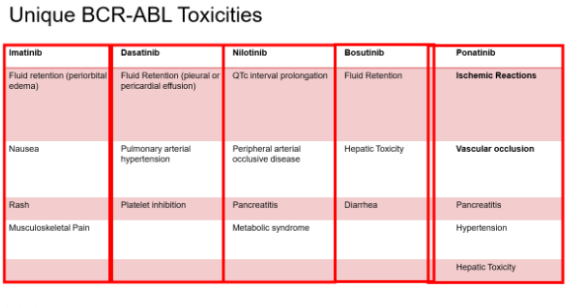
What are the typical adverse effects of the drugs that target BCR-ABL?
Bone marrow suppression: Neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia
Rash
Which BCR-ABL drugs should be taken on an empty stomach?
Nilotinib
Which BCR-ABL-targeting drugs should not be taken with H2RA or PPI drugs?
Dasatinib, Nilotinib, Bosutinib
Which BCR-ABL-targeting drugs have some form of interaction with CYP enzymes?
All
Which of the JAK inhibitors will likely need dose reduction for impaired renal function?
Ruxolitinib for CrCl < 60 ml/min
Which of the JAK inhibitors requires monitoring for and possible supplementation with vitamin B1?
Fedratinib- associated with Wernicke's encephalopathy, a serious neurological condition caused by thiamine deficiency.
What is the hematologic malignancy for which FLT3 receptor inhibitors are most commonly used, and why would we use this class of drugs?
FLT3 receptor inhibitors are most commonly used for acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Because FLT3 mutations (especially ITD, which has a poor prognosis) drive uncontrolled cell growth, proliferation, and survival in AML. FLT3 inhibitors block this abnormal signaling to slow disease progression and improve outcomes.
What is the common cardiac adverse effect of the FLT3 receptor inhibitors?
QTC prolongation
For which of the FLT3 inhibitors is antiemetic premedication required?
Midostaurin
For which of the FLT3 inhibitors is/are interactions from inducers or inhibitors of CYP3A4 expected?
All
What is the hematologic malignancy for which IDH inhibitors are most commonly used, and why would we use this class of drugs?
IDH inhibitors are most commonly used to treat acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with IDH1 or IDH2 mutations.
Mutant IDH enzymes block cells from maturing into normal blood cells, causing a buildup of leukemic blasts. IDH inhibitors restore normal cell differentiation by reducing the harmful metabolite R-2-hydroxyglutarate, helping control the leukemia.
What is the common cardiac adverse effect of the IDH receptor inhibitors?
QTc Prolongation
What are the common adverse SYMPTOMS of IDH inhibitors?
Differentiation syndrome,Nausea, diarrhea, elveated bilirubin
For which of the IDH inhibitors is/are interactions from inducers or inhibitors of CYP3A4 expected?
Mostly ivoasdienib and olutasidenib, but enasidenib as well (multiple enzymes not just 3A4)
What are the characteristics of Differentiation Syndrome, and what is the treatment response?
Occurs due to rapid proliferation and differentiation of myeloid cells
Dysnpea, Peripheral edema with rapid weight gain, pulm infiltrated, pleural effusion, renal impairment, fever
Hold therapy pending improvement
Start Dexamethsone until symptom resolution
For what type of leukemia is tretinoin used, and with what other drug is it combined?
Tretinoin is used for acute promyelocytic leukemia (APML) and is combined with arsenic trioxide
What is the primary contraindication for tretinoin that includes an ETASU?
Pregnancy
How is the response vs prevention of Differentiation Syndrome different between the IDH inhibitors and tretinoin?
In tretinoin, onset is hours to months after the initial dose
In IDH inhibitors, the onset is 10 days to 5 months
In Tretinoin (ATRA): Prevention: prednisone 05mg/kg PO daily