PPHS 511- Week 3
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
what is white saviorism
concept that privilege want to save under privileged groups, stemming from this belief of supriority
what is the white savior industrial complex
big emotional experience that validates privilege
explain the concept of social determinants of health
non-medical conditions in which people are born, grow, work, live, and age, profoundly influencing health outcomes and health equity
—> CAUSED BY STRUCTURAL DRIVERS ( political, social, cultural..) shape our health outcome and access

explain the coin model
privilege←system of inequality—> oppression
—> stresses the systemic routes of the issues
ex: system of inequality: sexism, racism…
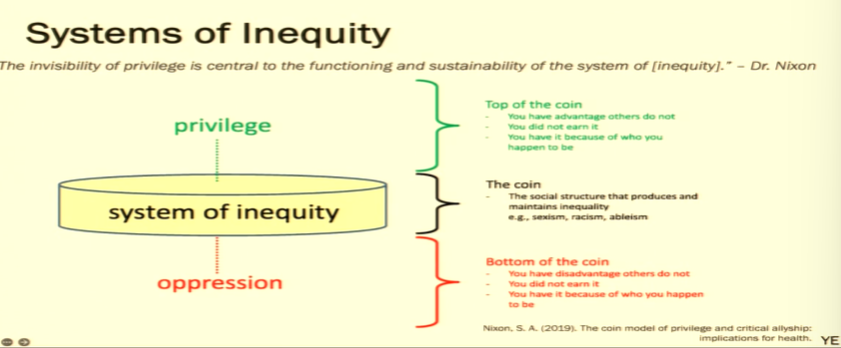
how is coined model applied to global health
GH focuses on how to get oppresses to the privileged side of the coin
—> WRONG, need to focus on dismantling the systems of inequality
—> the privilege need to understand the systems that have allowed them to be there
what is intersectionality and coin theory
multiple identities can shape your lived experiences ( the sides of the coin)
—> can have oppression AND privilege
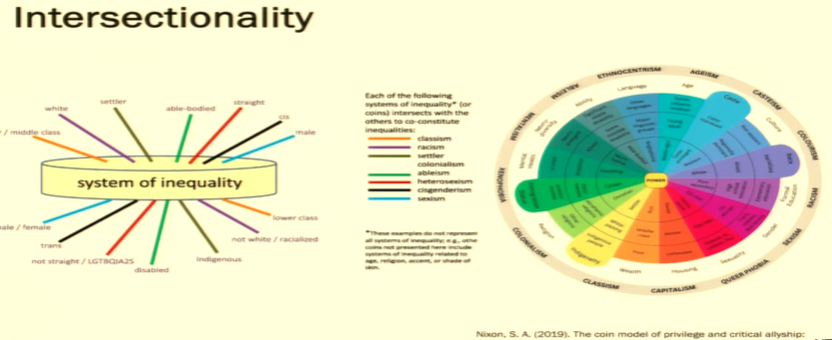
How should you take into consideration intersectionality
recognize diversity in age, gender, sexuality…
need to understand how these different factors affect your health access
what is biological embedding
stressful experiences ( discriminattion..) alters your nerodevelopment and biology
—> concept of “weathering” is intergenertional and leads to disparate health outcomes
ex: black women lived experiences affect health outcomes
how does gin and tonic relate to Global Health
british soldiers took quinone to treat malaria and afdded gin ( quinone found in tonic)
give example of how global health rooted in colonialism
malaria! driving force for tropical medicine
docs trying to find cures to protect soldiers abroad
new goal of global health
achieving advancing and achieve health equity
what is the foreign gaze
the way researchers, particularly from low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), shape their work for external audiences—northern donors, editors, reviewers, and institutions.
—> Elitism of academia
what are different ways we adress decolonization and reconliation in canada
symbolic: land acknowledgment
impactful: sharing power with indigenous peoples
what are the origins of epidemiology
transatlantic slave trade—> the ships created the perfect environment to study spread of diseases
stats eugenics and racism?
founded on eugenics and racism
Galton founder of stats
Pearson also
fisher
NOT OBJECTIVE WORK
what can we do to adress global health issues
strength based lens
—> when reading literature what lens are you using
—> join student organizations where you can talk about this
become an ally
move from saviourism to allyship
what is an ally
active consistent, and unlearn and reevaluate
advocacy and activisim
powerful tools to push for change
methods: polcy recommendation, public awareness campaigns
activisim
direct action to challenge injustcies and push for change
ex: protests, demonstrations, boycotts, strikes
—> need to recognize it is a privilege
the three C of critical allyship and solidaroty
collaborations
communication
connection
what is ableism
discrimination in favor of nondisabled people.
why is ableism a global issue
We live in an inaccessible society
ableism in health is a global structural injustice
disabled people face systemic exclusion
stigma
barriers to equitable care
where do the systemic issues around ableism stem from?
rooted in eugenics movement and forced sterilization of people with disabilities
what is the disaparities of disabilities in GN vs GS
GN have 90% access to proudcts vs 3% in LMICs
—> LMICs lack access to the technology
concept of perfect ability?
termination of down syndrome eradication: 100% on Iceland
—> lack of understanding that people can live full lives