Human Anatomy Unit 7 - Respiratory System
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Nose
Filters and moistens air
Pharynx
Directs air to respiratory tract
Eustachian tubes connect from pharynx to ear to stabilize pressure
Larynx
“Voicebox”
Contains vocal cords
Epiglottis covers larynx when swallowing
Epiglottis
Made of elastic cartilage
Allows air to enter lungs
Prevents food/liquid from entering the lungs while eating
Trachea
Cleans, warms, and moistens incoming air
Stiff cartilage rings surrounds trachea to keep it open
Last cartilage ring is sensitive
Triggers cough reflex if anything but air enters
Bronchi
Right & left branches
Connects trachea with lungs
Branch into bronchioles
Lungs
Bronchioles end in alveoli
Alveoli
Site of gas exchange
Pleural Fluid
Enables lungs to move easily during respiration
Natural lubricant
Pleural Effusion
Excess amount of fluid in pleural cavity
Limits ability for lungs to expand during inhalation
Can be seen in symptoms if you have…
Heart failure
Pneumonia
Lung Cancer
Pleural Effusion Treatment
Thoracentesis
Process to remove excess fluid
Surfactant
Produced by alveoli
Made of lipids and proteins
Breaks apart cohesiveness of water —> surface tension decreases
Less energy is required to expand lungs
Respiratory System Image
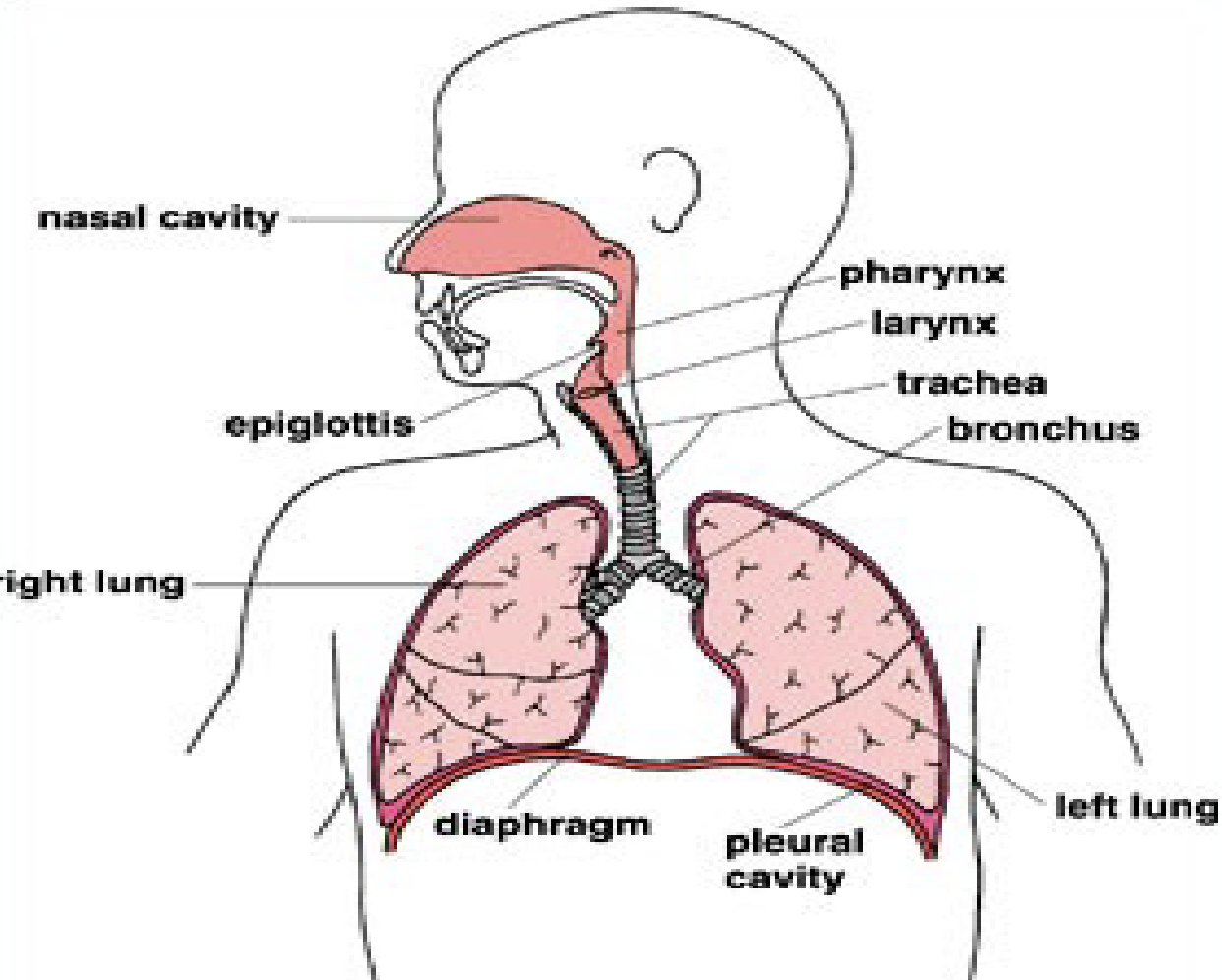
Breathing is controlled by the…
Respiratory center in the medulla oblongata
Located in brain stem
Inhalation/Exhalation Image
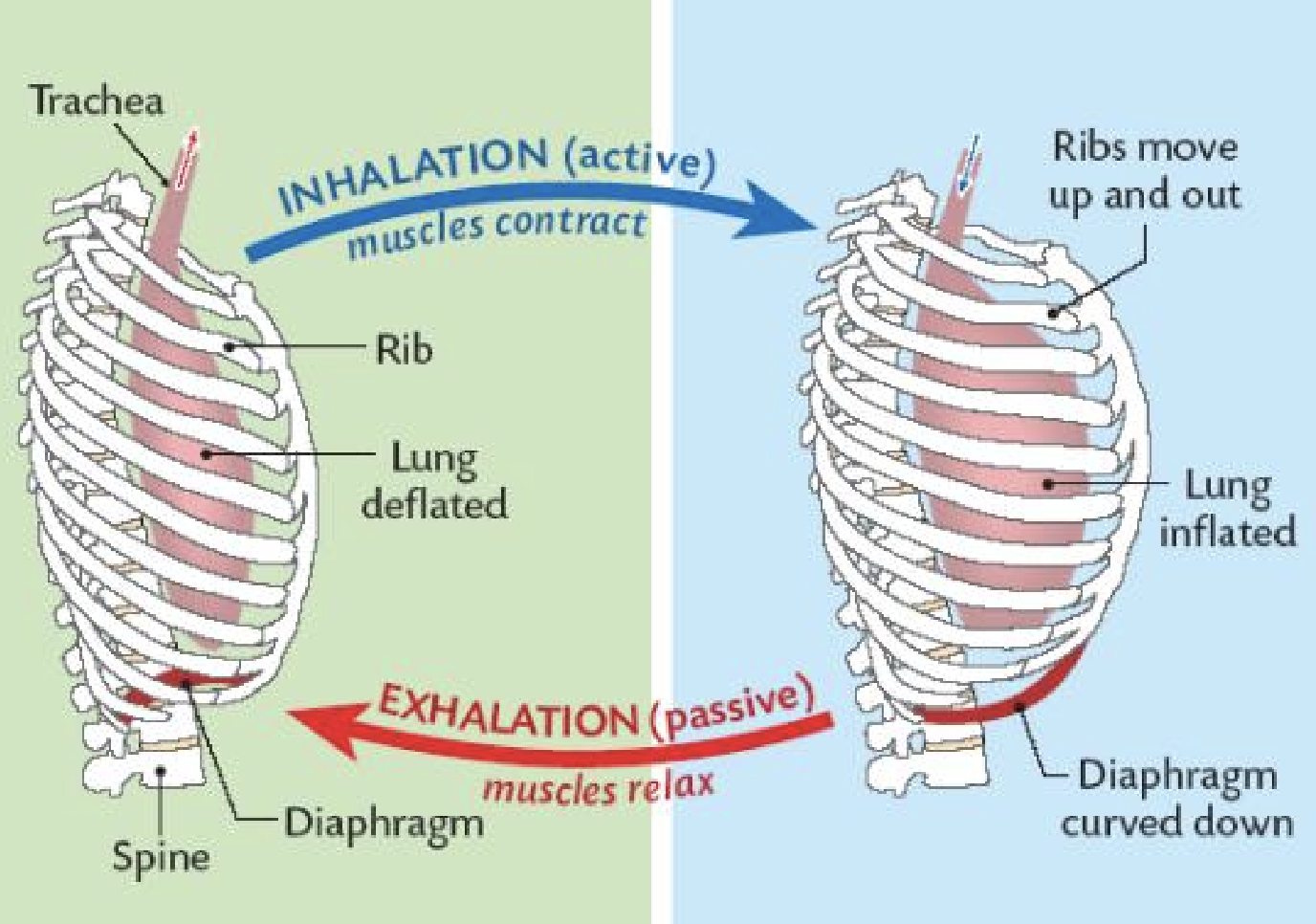
Inhalation: Step 1
Nerve impulses
Diaphragm contracts and moves farther down in the abdominal cavity
Inhalation: Step 2
Increased size of chest cavity —> decreases pressure within lungs
Air moves from HIGH to LOW pressure —> air flows into lungs
Inhalation: Step 3
External intercostal muscles raise ribs and expand thoracic cavity
Exhalation: Step 1
NO nerve impulse
Diaphragm relaxes and moves farther up in the abdominal cavity
Exhalation: Step 2
Decreased size of chest cavity —> increases pressure within lungs
Air rushes out of lungs
Exhalation: Step 3
Internal intercostal muscles decrease thoracic cavity and lower ribs
“Mouth Breathers”
Urinate more at night, become more dehydrated
Sinuses produce x6 the amount of nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide: simulates pituitary gland, tells kidney to store water, prevents urination during the night
Cystic Fibrosis
Recessive, autosomal genetic disorder
Build up of thick mucus in the lungs
Makes breathing difficult
Frequent infections
Build up in pancreas and digestive system
Average life expectancy - 37.41 years
CF Causes
Mutation in CFTR gene
Changes how salt moves in & out of cells lining the lungs & other organs
Results in thick, sticky mucus building up in respiratory, digestive, & reproductive tracts
CF Image
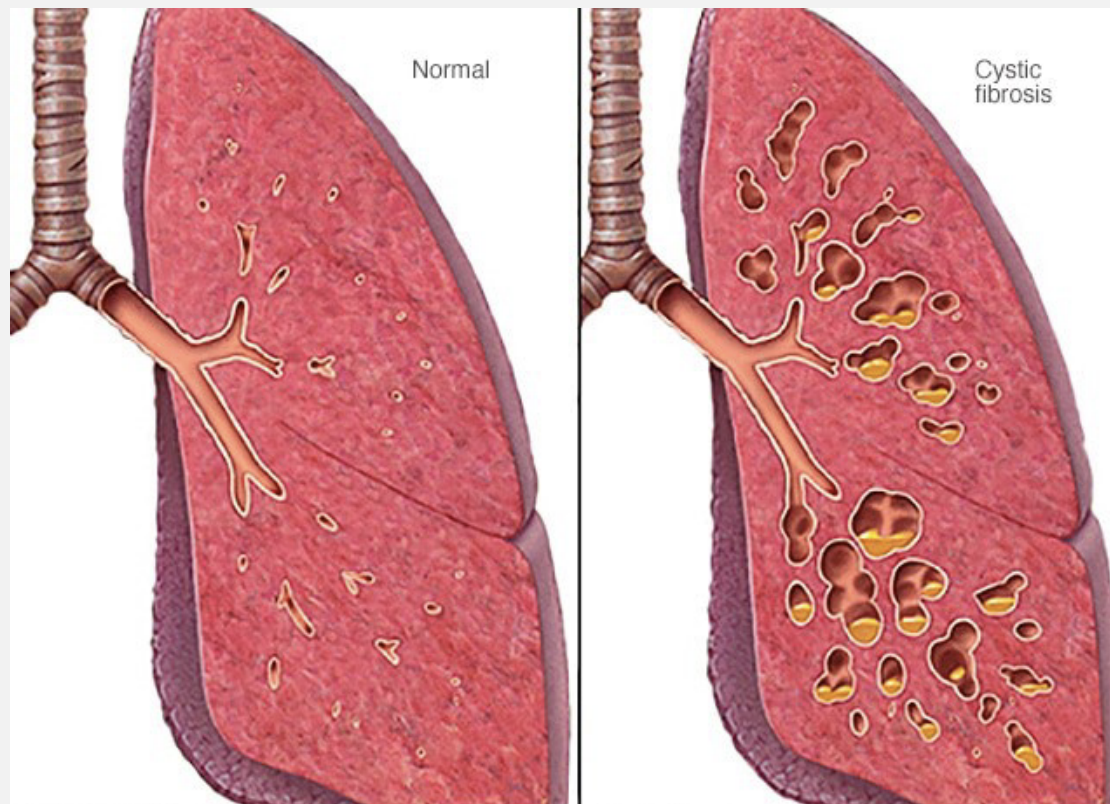
CF Treatments
Medication: CFTR Modulator
Gene Therapy
Using GE Stem Cells
CFTR Modulator
Targets the CFTR protein that is caused by a mutation in the CFTR gene
Does not correct the mutation in the gene
Targets the errors that occur after transcription
(Making the protein & forming the protein’s the proper shape)
Gene Therapy
Goal
To deliver correct CFTR gene to patients with CF
Challenges
Delivery is difficult because vectors that normally deliver the “working copy” are blocked by thick mucus
Respiratory tract cells divide/replace quickly so the application of the new gene needs to be repeated
Using GE Stem Cells
2½ hours of aerosols each morning + 1½ hours each night
To maintain lung function and prevent infection
Proven to be safe
CF Current Research
Infusing genetically modified stem cells (CFTR gene mutation corrected)
Stem cells can replace the affected cells with healthy ones
GE stem cells carry new genetic codes —> correcting the mutation of thick mucus
Hopes to reduce inflammation, improve length & quality of life for CF patients
Small cell lung cancer
Less common (15%)
Spreads more quickly and aggressively
Non-small cell lung cancer
More common (85%)
Spreads slower, not as aggressive
Tuberculosis
Caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Asthma
A disease that affects your lungs with wheezing and breathlessness
Pneumonia
Inflammation and fluid in your lungs caused by a bacterial, viral, or fungal infection
Emphysema
A condition in which the air sacs of the lungs are damaged and enlarged
Bronchitus
Inflammation of the tubes that carry air to and from the lungs
Asbestosis
A chronic lung disease caused by inhaling asbestos fibers
Sinusitis
An inflammation of the tissues in your sinuses
Pulmonary Edema
A condition caused by too much fluid in the lungs
Swine Influenza
A respiratory disease of pigs caused by type A influenza viruses