Lecture 9: Normal Hemostasis
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
At baseline, __ should occur.
hemostasis
What is hemostasis?
sequence of processes that maintain blood in a fluid, clot-free state in normal vessels with the ability to rapidly form a blood clot at site of vascular injury
At baseline, what 2 things should not happen?
thrombosis = formation of clot in an intact vessel
hemorrhage when there is an inability to form a blood clot at a site of injury
What helps to maintain hemostasis?
endothelial & smooth muscle cells
platelets
coagulation factors
The endothelium maintains __ and regulates the __. Thus, it maintains the balance between the __.
blood flow; blood coagulation system; anti- and prothrombotic events
How does the endothelium maintain balance between the anti- and prothrombotic events?
various surface molecules normally inhibit the activation of platelets and the coagulation cascade, but injury exposes molecules that promote activation of platelets and the coagulation cascade
In antithrombic properties of the endothelium, the endothelium serves as a __ between platelets and highly thrombogenic extracellular matrix. This is an example of an __ effect.
barrier; antiplatelet
In antithrombic properties of the endothelium, products of __ & __ hamper platelet adhesion and aggregation and are potent __.
PGI2 (prostacyclin); NO; vasodilators
In antithrombotic properties of the endothelium, __ is elaborated, which degrades __ and inhibits platelet __.
adenosine phosphatase; adenosine diphosphate (ADP); activation
What are the 3 antiplatelet effects of antithrombotic properties in the endothelium?
barrier between platelets and highly thrombogenic ECM
produces PGI2 & NO
elaborates adenosine phosphatase
In antithrombotic properties of the endothelium, factors on the epithelial surface, like __ (3) produce __ effects. These factors act __ to inhibit __.
heparin-like molecules (cofactor for antithrombin III inhibits factors II, IX, X, XI)
thrombomodulin (binds to thrombin to help it activate protein C and S)
tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) (inhibits factor VII)
anticoagulant; indirectly; coagulation
In antithrombotic properties of the endothelium, synthesis of __, which activates __ to break down __, is an example of a __ effect.
tissue-type plasminogen activation (tPA); plasminogen to plasmin; fibrin; fibrinolytic
In prothrombotic properties of the endothelium, production of __ is an example of a platelet activator.
von Willebrand factor (vWF)
__ are proteins expressed by cells to interact with platelet glycoprotein Ib (GPIb) to help anchor platelets to the site of injury.
von Willebrand factor (vWF)
In prothrombic properties of the endothelium, production of __, which activates coagulation and down regulates thrombomodulin, is an example of a __ activator.
tissue factor; coagulation factor
What do tissue factors activate/down regulate?
activates coagulation, down regulates thrombomodulin
In prothrombic properties of the endothelium, secretion of __ limit __ much more than it favors __. This is an example of __ effects.
plasminogen activator inhibitors (PAIs); fibrinolysis; thrombosis; antifibrinolytic
How do we stop bleeding or make a clot?
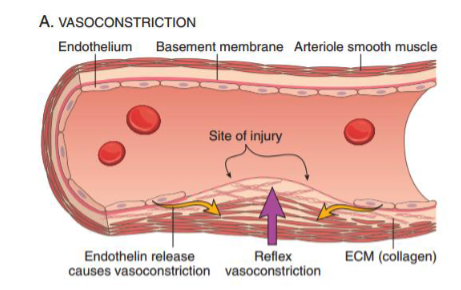
stop bleeding: vasoconstriction to decrease blood flow
make clot: primary or secondary hemostasis
What is primary hemostasis?
activation and aggregation of platelets —> platelet plug
What is secondary hemostasis?
activation of coagulation factors —> mature fibrin clot
In response to an injury site, reflex vasoconstriction is mediated by:
endothelin release
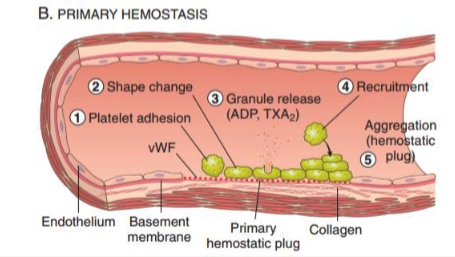
What are the steps in primary hemostasis?
platelet adhesion
shape change
granule release (ADP, TXA2): recruit more platelets
recruitment
aggregation = hemostatic plug
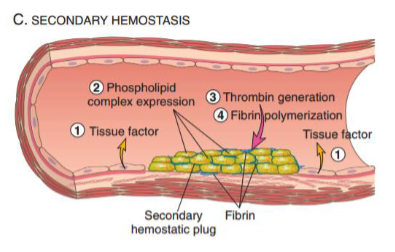
What are the steps in secondary hemostasis?
tissue factor
phospholipid complex expression (on platelets)
thrombin generation
fibrinpolymerization
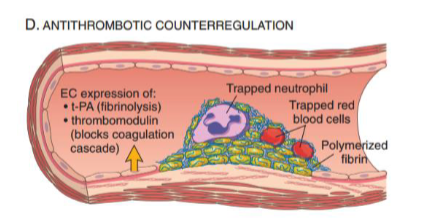
What occurs in antithrombotic counterregulation?
expression of t-PA (—> fibrinolysis) and thrombomodulin (blocks coagulation cascade) will counter excess clotting
__ are anucleuated disc-shaped cell fragments released from the bone marrow by megakaryocytes.
platelets
__ are a critical component of hemostasis and clot formation.
platelets
Platelets accumulate at the site of endothelial injury by: (3)
adhering
activating
aggregating
Platelets interact with endothelial cells to: (2)
facilitate clot formation
prevent clot formation
Platelets adhere to __ within the ECM via interactions with: (2)
exposed collagen; vWF & platelet surface receptors (glycoproteins)
Platelets can undergo __ shape change.
irreversible
Platelets activate by secretion of their __
granules
alpha granules: fibrinogen, factors V and VIII, platelet factor 4
gamma granules: ADP, Ca2+, serotonin, epinephrine
Platelets synthesize __ when they are activated.
thromboxane A2 (TXA2)
Platelets aggregate to transform __ into __
temporary hemostatic plug —> more definitive thrombus
__ and __ are stimulators of platelet aggregation.
ADP; TXA2 (stimulate formation of primary hemostatic plug)
__ induces conformational change of GPIIb-IIIa receptors, allowing for binding of __, which connects multiple platelets together to form __.
ADP; fibrinogen; larger aggregates
Primary hemostatic plugs are converted into a larger definitive secondary plug via: (3)
ADP
TXA2
thrombin
__ deposition stabilizes and anchors aggregated platelets
fibrin
Activation of platelets results in: (2)
secretion of granules (ADP) and synthesis of TXA2
Platelets have surface expression of __.
phospholipid complexes
facilitates platelet aggregation and thrombus formation
Injured or activated endothelial cells expose __, which triggers the extrinsic coagulation cascade.
tissue factor
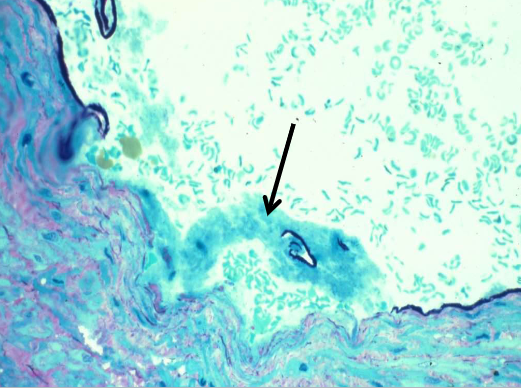
What does this image show?
activated platelets aggregating
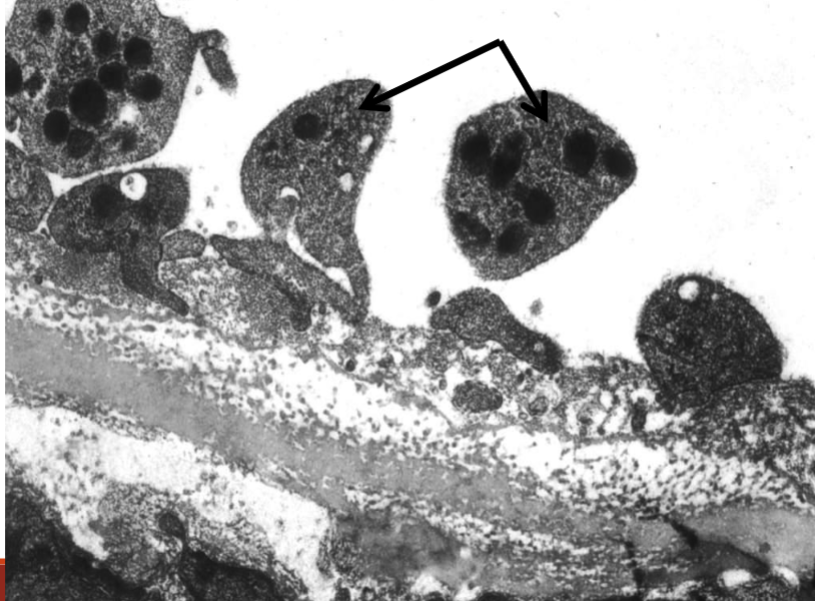
What does this image show?
activated platelets aggregating
__ are a series of enzymatic conversions from inactive proenzymes into their active state. Each reaction results from the formation of enzyme-proenzyme-cofactor complex assembled at the __ complex held together by Ca2+.
coagulation factors; phospholipid
Coagulation factors’ prothrombotic goal is to:
activate thrombin and form fibrin to be cross linked
What are the 2 coagulation cascade pathways in the laboratory? How are they measured?
intrinsic pathway- measured by aPTT
extrinsic pathway- measured by PT/INR
The two coagulation cascade pathways converge on a common pathway because they both activate __. Thus, cascade can be separated into __ (3) pathways.
factor X; intrinsic, extrinsic, common
Most factors are made in the __. The exceptions are factors __ & __.
liver; VIII (made by endothelial cells); IV (Ca2+)
Factors __ (4) are also vitamin K dependent.
II, VII, IX, X
In fibrinolysis, __ activates plasminogen to plasmin.
tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)
__ cleaves fibrinogen and fibrin into fibrinogen/fibrin degradation products (FDPs). This removes the __ that is no longer necessary when the endothelial damage is fully __ by new endothelial cells restoring the integrity of the blood vessel.
plasmin; mature clot; repaired
Things that help you form a clot or prevents a clot from breaking down are: (5)
coagulation factors
platelets
vWF
PF4
plasminogen activator inhibitor
Things that prevent you from forming or helps break down clots are:
AT-III (antithrombin III)
thrombomodulin
protein C/S
tPA
plasmin
What are basic lab tests to screen for coagulopathy? (5)
complete blood count (CBC)
activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)
prothrombin time (PT/INR)
vWF antigen/activity
platelet aggregometry testing
Describe the coagulation cascade.
sequence of proenzymes converted to activated enzymes —> formation of thrombin —> converts fibrinogen to fibrin
activation of factors require calcium and phospholipid membranes
Natural anticoagulants include: (4)
antithrombin III
proteins S and C
thrombomodulin
tissue factor pathway inhibitor
What does the fibrinolytic cascade involve?
tPA —> converts plasminogen to plasmin —> breaks down fibrin to fibrin split products
__ occurs when there is an imbalance of prothrombotic vs antithrombotic mechanisms.
coagulopathy
Coagulopathy may be due to a __ or __ defect.
quantitative; qualitative
In coagulopathy, taking a good __ is paramount.
clinical history