Human Reproduction: Grade 12 Life Sciences
1/209
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
210 Terms
haploid gametes
Gametes that contain half the number of chromosomes, specifically n = 23.
ovum
The female gamete, which is haploid (n).
sperm cell
The male gamete, which is haploid (n).
diploid
Cells that contain two sets of chromosomes, represented as 2n.
diploid zygote
A fertilized egg that contains two sets of chromosomes, represented as 2n.
meiosis
A type of cell division that produces haploid gametes from diploid cells.
mitosis
A type of cell division that produces identical diploid cells for growth and repair.
gamete
An egg or sperm cell with half the number of chromosomes.
gametogenesis
The process in which gametes are produced in the testes and ovaries through meiosis.
oogenesis
The process that occurs when egg cells are made in the ovary through meiosis.
spermatogenesis
The process that takes place when sperm cells are made in the testes through meiosis.
germinal epithelium
Cuboidal epithelium found on the surface of the testes and ovaries which gives rise to the cells that mature to form sperm cells and egg cells.
male reproductive system
Consists of the main male sex organ (testes), ducts and tubules (seminal vesicles, epididymis, vas deferens, urethra), accessory glands (prostate gland, Cowper's gland), and external genitalia (penis).
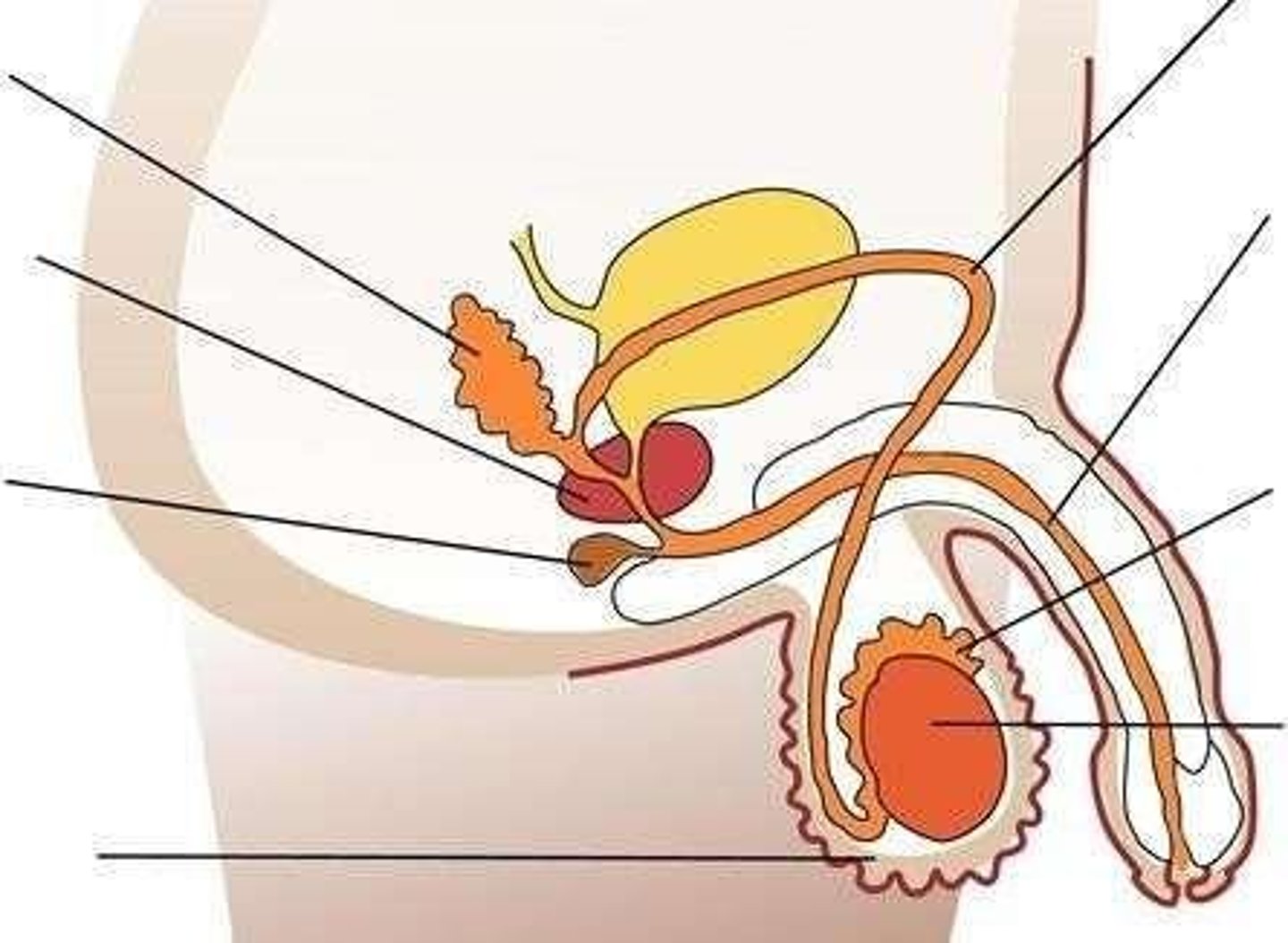
testes
The male reproductive organs that produce sperm and hormones.
scrotum
The pouch of skin that contains the testes.
seminal vesicles
Glands that produce seminal fluid to nourish and transport sperm.
epididymis
A duct where sperm mature and are stored.
vas deferens
The duct that transports sperm from the epididymis to the urethra.
urethra
The tube through which urine and semen are expelled from the body.
prostate gland
A gland that produces fluid that nourishes and protects sperm.
Cowper's gland
Glands that produce a pre-ejaculate fluid that lubricates the urethra.
puberty
The period during which adolescents reach sexual maturity and become capable of reproduction.
fertilisation
The process by which a sperm cell fuses with an egg cell to form a zygote.
implantation
The process by which a fertilized egg attaches to the lining of the uterus.
gestation
The period of development of the embryo and fetus in the womb.
multicellular diploid adults
Organisms that have two sets of chromosomes and are composed of multiple cells.
testes
oval shaped glands, suspended in the scrotum that produce sperm cells and the hormone testosterone.
scrotum
skin sac that holds the testes, protects the testes and holds the testes outside the body, at 2°C lower than body temp.
epididymis
coiled tubule on the outside of the testes but still in the scrotum that temporarily stores spermatids until they mature into sperm cells.
vas deferens
muscular tube passing from the epididymis to the urethra that transports sperm from the epididymis to the urethra.
urethra
tube which runs through the penis that transports urine and semen out of the body.
prostate gland
produces a nutrient-rich fluid that provides energy for the sperm cells and is located below the bladder, at the point where the urethra begins; the largest accessory gland.
Cowper's glands
small pair of glands found below the prostate gland that produces mucus that helps with the movement of sperm cells.
seminal vesicles
medium sized pair of glands attached to the end of the vas deferens that produces alkaline fluid to neutralise vaginal acids which would kill sperm.
seminiferous tubules
tubules lined by germinal epithelium cells which produce sperm cells.
Sertoli cells
cells that provide nutrients for the spermatids to become mature sperm cells.
Cells of Leydig
cells that produce testosterone.
testosterone
hormone that has functions including the development of the male secondary sexual characteristics and stimulating the maturation of sperm cells.
optimum temperature for sperm production
2 to 3°C lower than normal body temperature.
male infertility
condition that can result from high temperature in the scrotum, which interferes with the quality of the sperm.
temperature regulation of testes
the ability of the testes to adjust their position to maintain an optimal temperature for sperm production.
Ovaries
Produce egg cells, secrete the hormones progesterone and oestrogen.
Fallopian Tubes
Transport egg cells from the ovary to the uterus; the site of fertilisation.
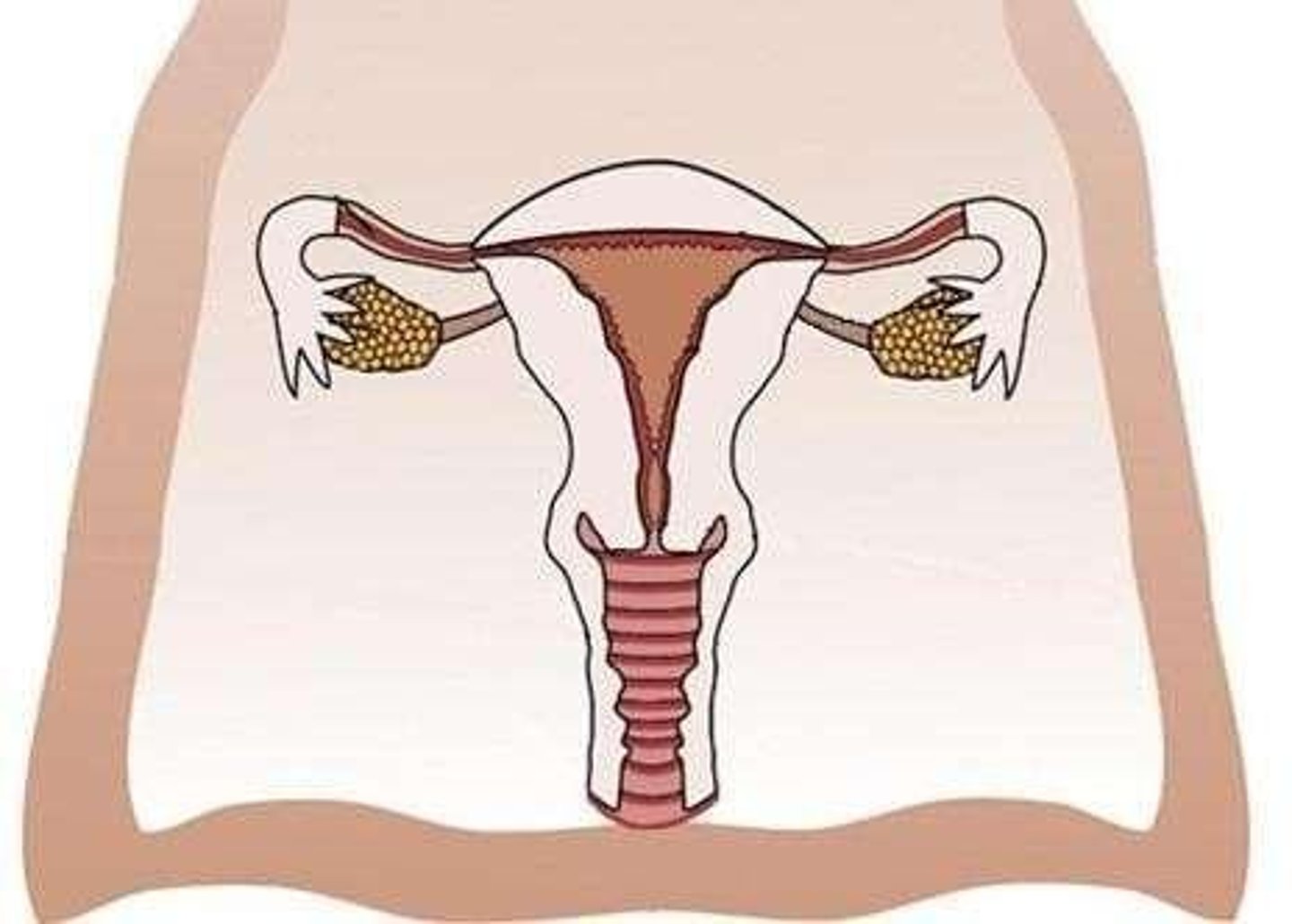
Uterus
Houses and protects the embryo and foetus during pregnancy.
Endometrium
Inner lining of the uterus; site of implantation and where the placenta forms.
Cervix
Lower, narrow opening of the uterus; stretches and opens to allow the baby through during childbirth.
Vagina
Muscular tube which runs from the cervix to the exterior; receives the penis and semen during sexual intercourse; the birth canal; passage for menstrual blood.
Vulva
Opening to the vagina; covered by two vagina covers called the labia; protects the entrance to the vagina.
Puberty
The period during which males and females reach sexual maturity, usually beginning between the ages of 11 to 15.
Testosterone
Male sex hormone produced during puberty.
Oestrogen
Female hormone produced during puberty.
Progesterone
Female hormone produced during puberty.
Gametogenesis
The process by which gametes are produced from the germinal epithelium in the sex organs.
Spermatogenesis
The production of male gametes (sperm cells) in the testes of the male.
Meiosis
The process that forms haploid sperm cells with 23 chromosomes from diploid cells with 46 chromosomes.
Diploid
A cell containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent (46 chromosomes).
Haploid
A cell containing a single set of unpaired chromosomes (23 chromosomes).
Germinal Epithelium
The layer of cells in the sex organs that produces gametes.
Secondary Sexual Characteristics
Physical features that develop during puberty, distinguishing the sexes but not directly involved in reproduction.
Labia
The two vagina covers that protect the entrance to the vagina.
Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
The type of tissue lining the fallopian tubes that helps in the movement of egg cells.
Embryo
The developing human from fertilization until the end of the eighth week.
Foetus
The developing human from the ninth week after fertilization until birth.
Spermatogenesis
The process where diploid germinal epithelial cells (2n) lining the seminiferous tubules go through meiosis to produce haploid spermatids (n).
Sperm Cell Structure
Each sperm cell is made up of a head, middle portion (neck), and a long tail.
Head of Sperm Cell
The head is mostly made up of the nucleus which contains 22 autosomes and one sex chromosome (X or Y).
Acrosome
The acrosome contains enzymes that dissolve the outer layer of the egg allowing fertilisation to occur.
Middle Portion of Sperm Cell
The middle portion contains mitochondria which provide energy for the movement of the sperm cell.
Long Tail of Sperm Cell
The long tail allows the sperm cell to propel itself forward (to swim) through fluid.
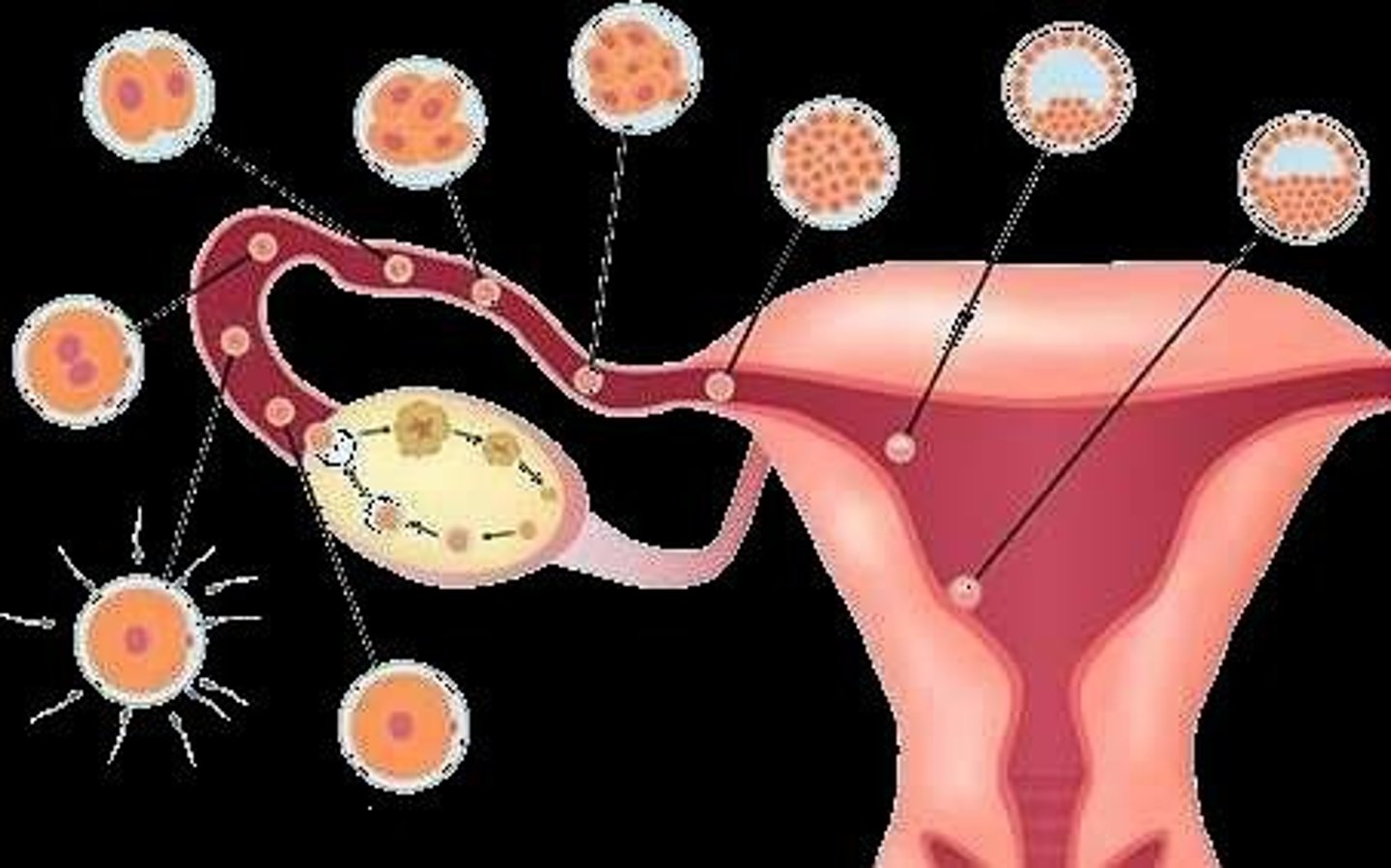
Oogenesis
The production of female gametes (ova / egg cells) in the ovaries of a female.
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
A hormone that stimulates one follicle every 28 days to enlarge and go through meiosis.
Mature Ovum
Out of the 4 haploid cells produced through meiosis, only one cell will survive to form a mature ovum.
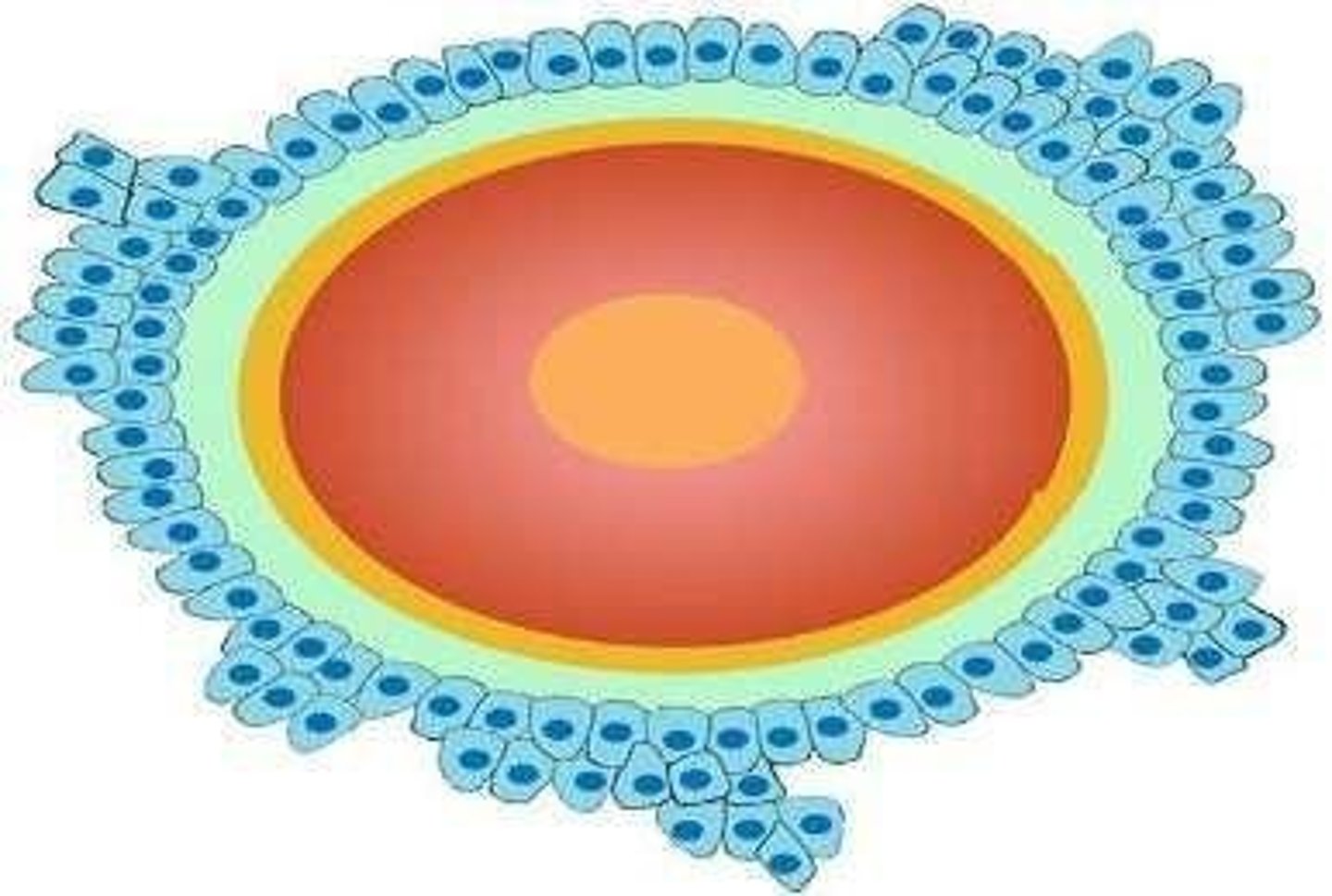
Structure of an Ovum
Each ovum is made up of follicle cells, a layer of jelly, cytoplasm, and a haploid nucleus.
Nucleus of Ovum
The nucleus contains 22 autosomes and one sex chromosome (X).
Cytoplasm of Ovum
The cytoplasm nourishes the egg.
Jelly Layer of Ovum
The jelly layer provides protection for the early developmental stages of the fertilised egg.
Graafian Follicle
A mature follicle inside the ovary filled with fluid in which the ovum grows.
Ovulation
The release of an ovum from the Graafian follicle of the ovaries.
Endometrium
The inner lining of the uterus wall.
Menstruation
The monthly loss of blood and tissue as a result of changes that occur in the lining of the uterus.
Menopause
Stage in the life of a woman when she stops ovulating and menstruating; usually occurs between the ages of 45 and 55.
Fertilisation
The fusion of the haploid sperm cell nucleus and the haploid egg cell nucleus to form a diploid nucleus of the zygote.
Implantation
The attachment of the embryo to the endometrium lining the uterus.
Menstrual Cycle
Changes that occur in the ovaries and uterus of a female over a period of 28 days.
Ovarian Cycle
Refers to the development and release of an ovum (or egg cell) inside the ovary.
Uterine Cycle
The cycle that occurs simultaneously with the ovarian cycle, involving changes in the uterus.
Graafian follicle
A mature ovarian follicle that contains a mature ovum (or egg cell).
Ovulation
The process where the Graafian follicle ruptures and releases an ovum, stimulated by Luteinising Hormone (LH).
Corpus luteum
A structure formed from the ruptured Graafian follicle that secretes progesterone.
Oestrogen
A hormone produced by the Graafian follicle that increases in the blood as the follicle develops.
Progesterone
A hormone secreted by the corpus luteum that prepares the endometrium for possible implantation of a fertilised ovum.
Menstruation
The process where the endometrium breaks down and is released if fertilisation does not take place.
Endometrium
The lining of the uterus that thickens and becomes more vascular during the uterine cycle.
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
A hormone that stimulates a primary follicle to develop into a Graafian follicle.
Luteinising Hormone (LH)
A hormone released by the pituitary gland that stimulates ovulation and the formation of the corpus luteum.
Uterine cycle
The cycle showing changes in the uterus wall as it thickens and becomes more vascular over a period of 28 days.
Days 1-7 of the menstrual cycle
New follicles develop and secrete oestrogen while the lining breaks down and is released (menstruation).
Days 8-13 of the menstrual cycle
A mature Graafian follicle develops and secretes oestrogen, stimulating the endometrium to become thicker.
Day 14 of the menstrual cycle
The Graafian follicle bursts to release an ovum (ovulation).
Days 15-22 of the menstrual cycle
The Graafian follicle becomes the corpus luteum which secretes progesterone, stimulating the endometrium.