6 - Capillaries, Lymphatics, Veins and MAP
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Capillary walls consist of:
A. A layer of connective tissue
B. A layer of endothelial cells
C. A layer of smooth muscle cells
D. Layers of endothelial and smooth muscle cells
B. A layer of endothelial cells
A skeletal muscle cell is using up a lot of oxygen and glucose. How does it get more oxygen and glucose from the blood? (Select two)
A. Oxygen will diffuse across the endothelial cell
B. Oxygen needs to diffuse through the intercellular cleft
A. Glucose will diffuse across the endothelial cell
B. Glucose needs to diffuse through the intercellular cleft
A. Oxygen will diffuse across the endothelial cell
B. Glucose needs to diffuse through the intercellular cleft
Movement of substances from the blood and IF via diffusion
O2
Glucose
Lactic Acid
CO2
O2 - Out
Glucose - Out
Lactic Acid - In
CO2 - In
Moving down the concentration gradient
What maintains the concentration gradients of O2, CO2, glucose, lactic acid, etc?
Metabolism by the cells
Cells are either constantly using up the oxygen or constantly produced more carbon dioxide
Mechanisms by which substances can cross from the blood to tissues (i.e. plasma to interstitial fluid) or visa versa (3)
1. Diffusion
2. Transcytosis
3. Bulk flow
Bulk flow definition
The distribution of extracellular fluid between the capillary and interstitial space through the intercellular clefts
What is the difference between plasma and interstitial fluid? (both are a part of the extracellular fluid)
A. They are both exactly the same
B. Plasma has high K+ concentration and low Na+ concentration. Interstitial fluid has the reverse.
C. Plasma has high Na+ concentration and low K+ concentration. Interstitial fluid has the reverse.
D. Plasma has very little protein. Interstitial fluid has a high amount of protein
E. Plasma has high amount of protein. Interstitial fluid has very little protein
E. Plasma has high amount of protein. Interstitial fluid has very little protein
The forces that contribute to bulk flow
Hydrostatic pressure of a fluid
Osmotic pressure of a fluid
(Starling forces)
Starling forces definition
forces that move protein free fluid across the capillary wall
Types of starling forces
Pc - Capillary hydrostatic pressure
PIF - Interstitial hydrostatic pressure
πC - Osmotic force due to plasma protein concentration (capillary oncotic pressure)
πIF - Osmotic force due to interstitial fluid protein concentration (interstitial oncotic pressure)
Another word for Oncotic pressure
Oncotic pressure = colloid osmotic pressure
Colloid = proteins
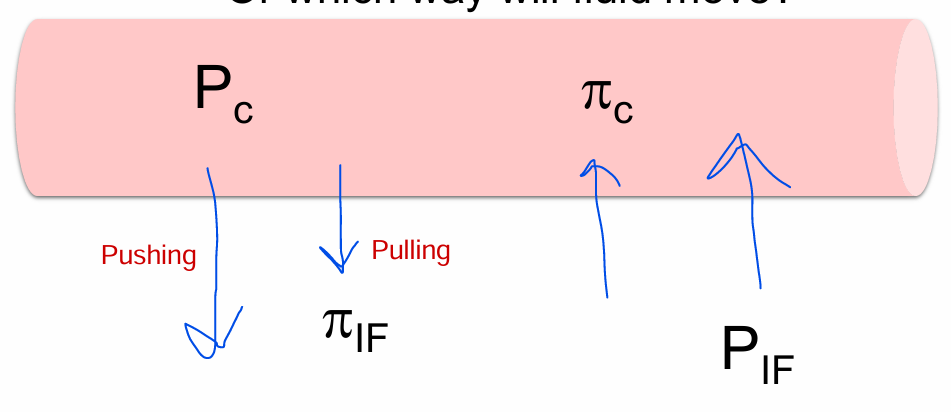
What is the direction of the Starling forces?
Or which way will fluid move?
Pc
PIF
πC
πIF
Pc - Moves out (Pushing)
PIF - Moves out (Pulling)
πC - Moves in (Pulling)
πIF - Moves in (Pushing)
net filtration pressure (NFP) equation
Pc+πIF - PIF-πC = net filtration pressure (NFP)
Filtration definition
Fluid moving out of the blood
Absorption definition
Fluid moving into the blood
Magnitude of the Starling forces on the arterial end of a capillary
Pc - Moves out (Pushing) HIGHEST
PIF - Moves out (Pulling) SMALLEST
πC - Moves in (Pulling)
πIF - 0
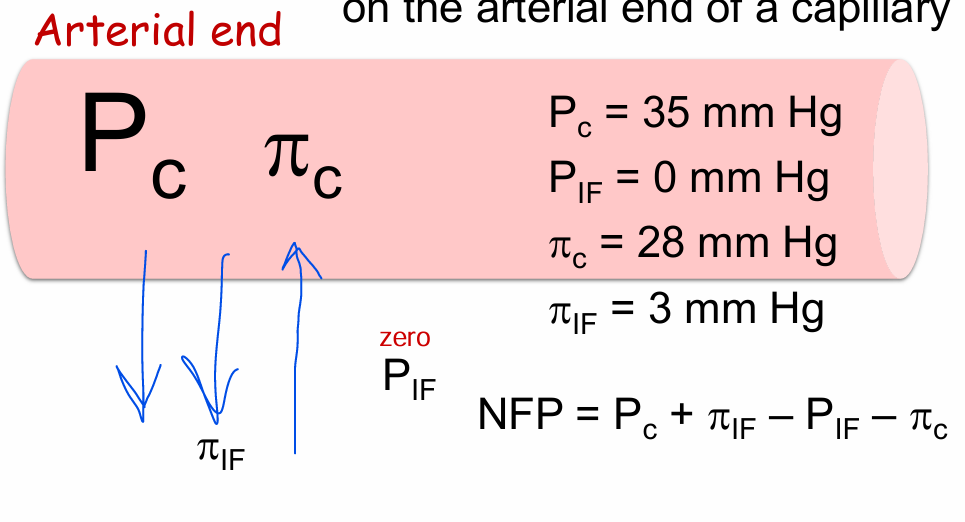
Does the atrial end favor filtration or absorption?
Filtration
What happens to the capillary hydrostatic pressure (blood pressure) at the venous end of the capillary?
A. Essentially stays the same compared to the arterial end
B. Increases compared to the arterial end
C. Decreases compared to the arterial end
C. Decreases compared to the arterial end
Magnitude of the Starling forces on the venous end of a capillary
Pc - Moves out (Pushing)
PIF - Moves out (Pulling) SMALLEST
πC - Moves in (Pulling) HIGHEST
πIF - 0
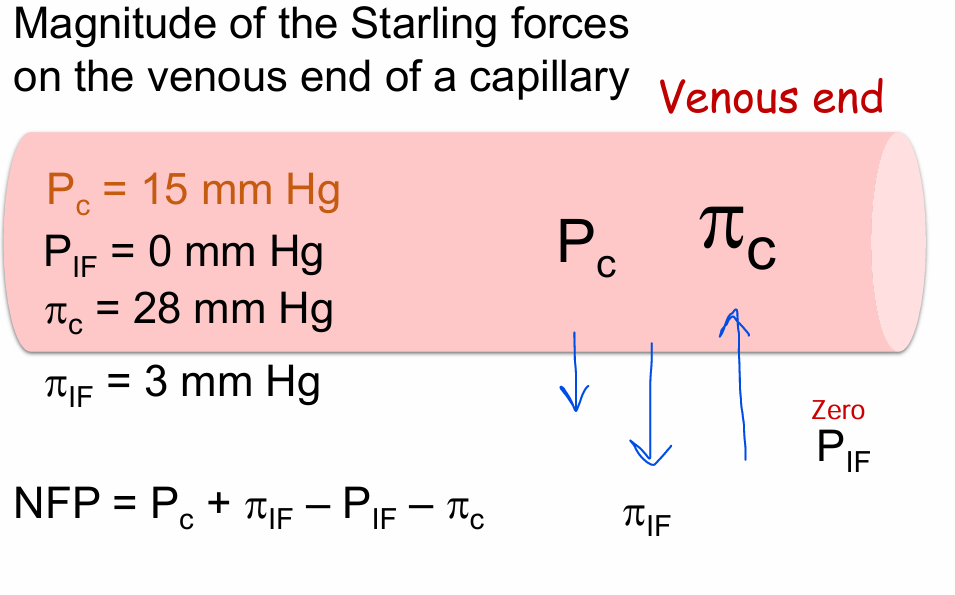
Does the venous end favor filtration or absorption?
Absorbtion
End result of forces on both ends of capillary (Atrial and venous ends)
End result is only a teeny, tiny amount of fluid that is filtered out of the blood is not absorbed back into the blood
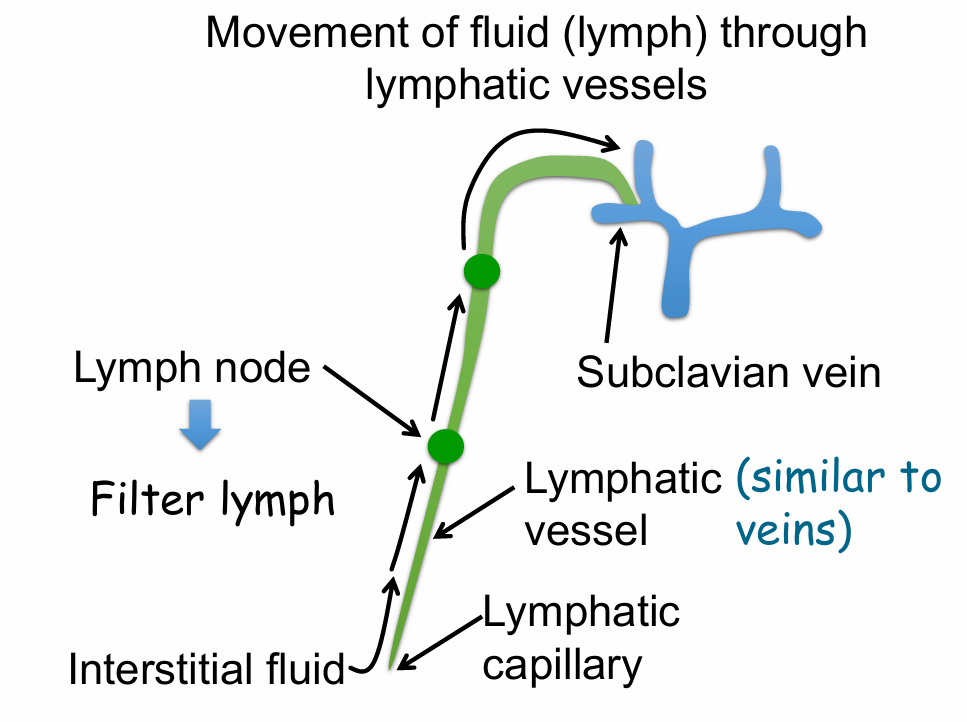
Where does that 4L/day of fluid go?
Goes into lymphatics
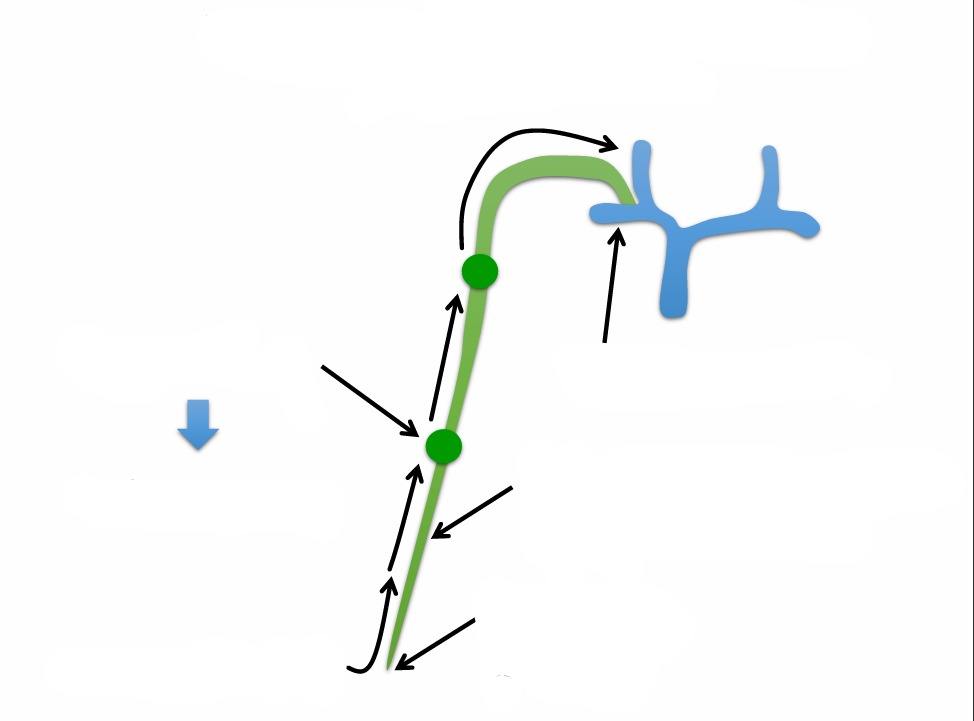
Movement of ‘excess’ interstitial fluid into lymphatics
Edema formation – some main mechanisms (4)
• Decreased lymphatic flow
• Increased capillary hydrostatic pressure
• Increased capillary permeability
• Decreased capillary oncotic pressure
Elephantitis definition
Edema caused by lymphatic obstruction
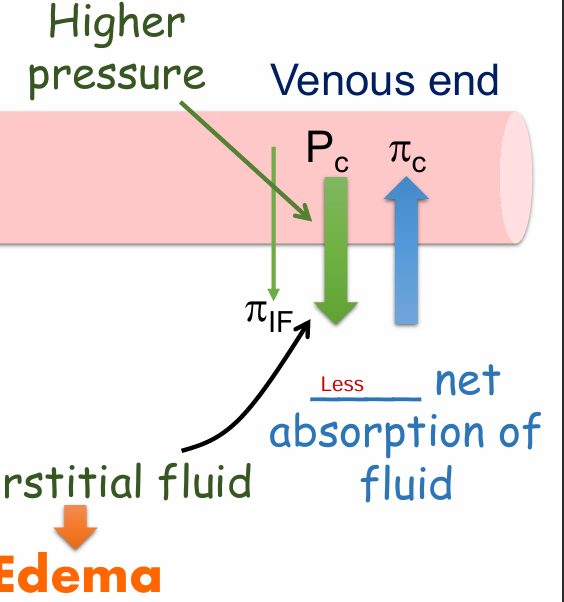
Edema is a result of
increased capillary hydrostatic pressure (Pc) – e.g. on the venous end of capillary
Less net absorption of fluid on the venous end
Examples of what can increase capillary hydrostatic pressure (Pc) on the venous end of capillaries, and thereby cause edema (4)
• Prolonged standing
• Damage to the valves in the veins
• Fluid overload
• Heart failure
How does Prolonged standing and damage to valves in the veins causes edema (3)
More difficult to return blood to the heart →
Blood ‘pools’ in the veins
Increase venous pressure
How does fluid overload cause edema? (3)
Extra Na+ and water in the blood →
Blood volume is too high →
Venous pressure is too high → EDEMA
How does heart failure cause edema (4)
Right heart failure
Too much blood in the right ventricle
Blood backs up in right atria and then the systemic veins
Increase venous pressure → peripheral edema
Example of edema from increased Pc on the arterial end of capillary
People can develop edema from an injury or infection. How does that happen? Substances, such as histamine, are released that will do which of the following?
A. Constrict arterioles and increase Pc on the arteriolar side of the capillary
B. Dilate arterioles and increase Pc on the arteriolar side of the capillary
B. Dilate arterioles and increase Pc on the arteriolar side of the capillary
Example of edema from increased capillary permeabilityHistamine can also cause an increase in capillary permeability enabling protein to leak into the interstitial space. How does this contribute to edema? Shifts fluid from the plasma to the interstitial fluid because of a(n):
A. Decrease in πIF
B. Increase in πIF
C. Decrease in PIF
D. Increase in PIF
B. Increase in πIF
Drag or pull more fluid into the interstitial space
Will bulk flow most likely affect the concentration of crystalloids in the plasma and interstitial fluid, or the volume of the plasma and interstitial fluid?
A. Concentration of crystalloids
B. Volume of fluid
B. Volume of fluid
Bulk flow does not change concentration of solutes
Crystalloids definition
low MW solutes that can easily penetrate capillary pores or intercellular clefts
Example of edema from decreased capillary oncotic pressure
Which will cause fluid to shift from blood to interstitial space. A liter of plasma or a liter of an equally concentrated crystalloid solution given to someone who has been hemorrhaging?
A. Plasma
B. Crystalloid solution
B. Crystalloid solution
Decreased πc, fluid shifts into interstitial space
Plasma has pulling pressure
Pressure and resistance of veins
They have thin walls with low pressure and low resistance
What are the other main jobs of veins? (2)
When blood volume goes up, they can remain dilated and expand and store that ‘extra’ blood
When you want to return more blood to the heart (eg exercising), veins constrict and ‘push’ more blood back to the heart
Veins and sympathetic nervous system
NE binds to α1 receptors to constrict veins which increase flow and returns more blood back to the heart.
What helps veins bring blood back to the heart? (5)
Change in pressure
Venous constriction
Skeletal muscle pump
Respiratory pump
Valves within the veins
Difference between constricting arterioles and veins
Constricting arterioles decreases flow due to increase in resistance!
Constricting veins increases flow due to decreased compliance and large change in pressure!
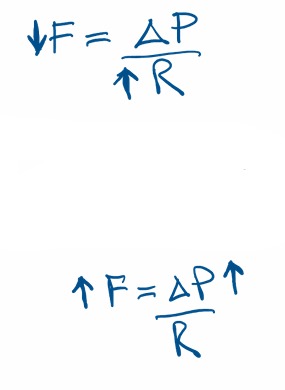
Structure of a large vein (4)
Thin wall with few layers of smooth muscle and connective tissue
Few elastic layers
Endothelium
Wide lumen
How do veins act as a blood reservoir? (2)
Veins are very compliant (i.e. can easily expand) so an increase in volume will cause a very small increase in transmural pressure
When needed, venous return can change
If more blood enters the veins…
the veins expand (remember minimal elastic recoil) and ‘stores’ that extra blood
Capacitance vessels
veins and venules that store and control the flow of blood back to the heart.
A change in venous return can be achieved by either constricting or dilating the veins. Which do you think will cause an increase in venous return?
Venous constriction
How venous constriction increases venous return (3)
Reduction in compliance
Relatively large increase in change in pressure
But relatively small increase in resistance
What causes smooth muscle contraction in your veins?
Activation of the sympathetic nervous system
A person quickly stands up and gets dizzy. How does this happen?
When laying down the veins are dilated because don’t need high pressure change to return blood to heart
Gravity pulls the blood in your veins to your feet (because of high compliance) causing less blood returning to the heart
When you stand up, what normally prevents blood from pooling in the veins of your feet and causing you to faint? (4)
Activate the SNS
Venous smooth muscle contracts
Increases pressure gradient
Sends blood back to the heart
Besides the pressure gradient and smooth muscle contraction, what else helps move venous blood back to the heart? (3)
‘Skeletal muscle pump’
‘Respiratory pump’
Valves in veins
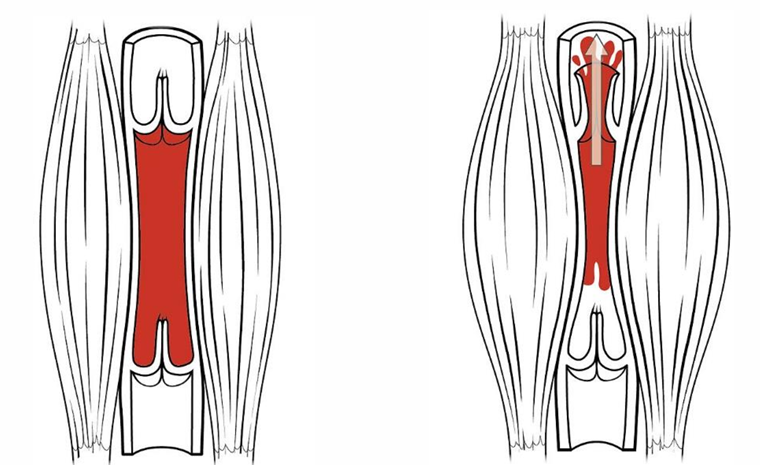
‘Skeletal muscle pump’ function
Skeletal muscle is relaxed and valves are closed
Skeletal muscle contracts and valve above open
What is total peripheral resistance (TPR)?
Adds up resistance of all systemic blood vessels
What can affect TPR? **
Anything that will cause constriction or dilation of arterioles
What can effect CO? **
Contraction and relaxation of veins changes cardiac output
Control of mean arterial pressure (4)
Short term control - Baroreceptor response
Long term control - Kidney
Fear, emotion, stress → activation of SNS
Exercise
Function of the Baroreceptors
Baroreceptors (stretch receptors) respond to a change in pressure (mean arterial pressure) MAP
Remember that sometimes you can stand up too quickly and became dizzy! Normally this doesn’t happen Why not? (4)
Rapid decrease in MAP →
Baroreceptor reflex (ANS)
Increase sympathetic outflow, decrease parasympathetic outflow
Increase MAP
Effect of baroreceptors on increase sympathetic and decrease parasympathetic outflow
Arterioles
Veins
HR
Ventricles
Constrict arterioles → Increase TP
Constrict veins → increase venous return and CO
Increase HR
Increase force of contraction of ventricles (CO and Stroke volume)
What would happen if there was a sudden RISE in blood pressure?
Decrease sympathetic activity
Increase parasympathetic activity
In people with hypertension, why doesn’t the baroreceptor response lower their blood pressure?
The baroreceptor response is ONLY for the short term regulation of BP
If BP is chronically elevated, the baroreceptors adapt to that high BP
You lost a lot of blood and became very hypotensive. Your sympathetic nerves are secreting a lot of norepinephrine. One thing the NE will do is increase TPR. How?
A. Activate B2 receptors and vasoconstrict arterioles
B. Activate B2 receptors and vasoconstrict veins
C. Activate a1 receptors and vasoconstrict arterioles
D. Activate a1 receptors and vasoconstrict veins
E. Activate muscarinic receptors and decrease phase 4 slope of the SA node
C. Activate a1 receptors and vasoconstrict arterioles
Arterioles = TPR
NE does not bind to beta 2
You lost a lot of blood and became very hypotensive. Your sympathetic nerves are secreting a lot of norepinephrine. Another thing the NE will do is increase stroke volume and cardiac output. How?
A. Activate a1 receptors and vasoconstrict veins
B. Activate B2 receptors and vasodilate veins
C. Activate B2 receptors and vasodilate arterioles
D. Activate a1 receptors and vasoconstrict arterioles
A. Activate a1 receptors and vasoconstrict veins
Veins = CO
You lost a lot of blood and became very hypotensive. Your sympathetic nerves are secreting a lot of norepinephrine. Another thing the NE will do is increase heart rate. How?
A. Activate muscarinic receptors and decrease activity of the SA node
B. Activate muscarinic receptors and increase activity of the SA node
C. Activate nicotinic receptors and increase the activity of the AV node
D. Activate B1 receptors and increase activity of the SA node
E. Activate B1 receptors and decrease activity of the SA node
D. Activate B1 receptors and increase activity of the SA node
Effects phase 4