LO6. Cross Contamination pt. 2 DONE
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What are the seven specific steps of instrument processing in order?
Holding (presoaking)
Precleaning
Corrosion control/drying/lubrication
Packaging
Sterilization (or high-level disinfection)
Sterilization monitoring
Handling processed instruments
What is the ultimate goal of sterilization regarding microbial life?
To kill all forms of microbial life on processed items
is absolute sterility possible to achieve?
no
What is “sterility assurance level” achieved with?
Proper monitoring
List the seven specific reasons why sterilization failure may result.
Not all surfaces are exposed for sufficient time
Improper cleaning (debris insulates organisms)
Incorrect packaging material/excessive
Overloading the sterilizer/ packages not separated properly”
Equipment malfunction (timer/temp errors)
Improper temperature
Improper method (e.g., putting water in a dry-heat sterilizer)
What are the three forms of sterilization monitoring employed to detect errors and which is used most often?
Biological (spore tests) - use biological spores to assess process directly (used most often)
Chemical - change in color when parameters are met
Mechanical - measures time, temp, pressure
What is biological monitoring also called?
“Spore testing”
What is the specific scientific name of the spore used for biological monitoring?
Geobacillus stearothermophilus
What does a positive biological spore test indicate?
Sterilization failure (the spores were not killed)
immediate action required
What does a negative biological spore test indicate?
Spores death ----- ensures overall thoroughness (successful)
List the steps for using spore testing (biological monitoring)
spores activated, processed through sterilizer, removed and placed in culture medium to determine vitality
Apart from the daily recommendation, list the five specific instances when you must Spore Test a sterilizer.
When using a new type of packaging or tray
After training new sterilization staff
During initial use of a new sterilizer
First run after a repair
After any change in sterilizing procedure
Once per day
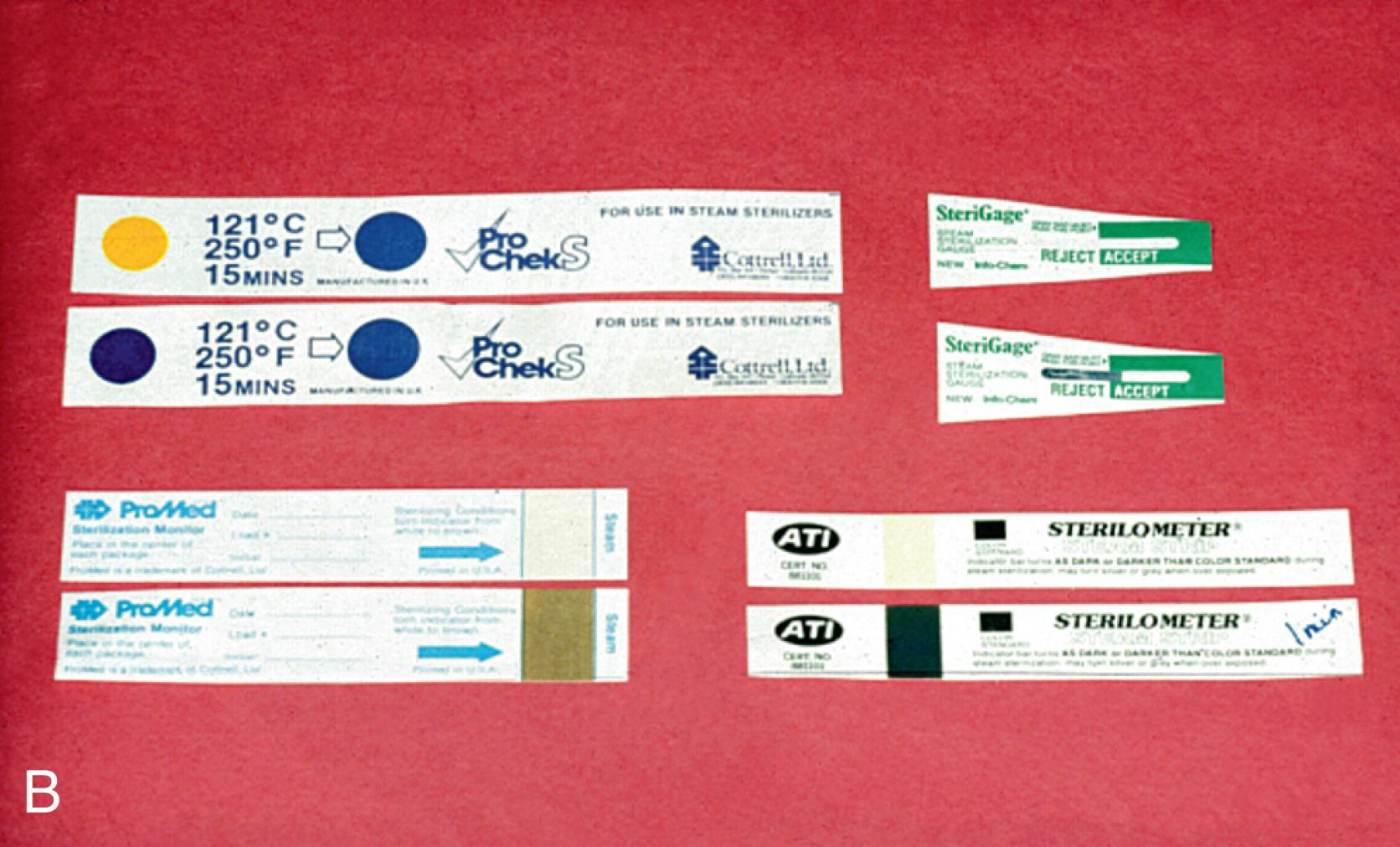
What is the difference between a "Process Indicator" (Color-changing strip) and an "Integrated Indicator"?
A process indicator (e.g., autoclave tape) changes color when one parameter is reached but does not guarantee sterility;
an Integrated indicator changes slowly in response to time, temperature, and steam to guarantee sterilization parameters were met
What are some examples of colour changing strips?
tapes, markings on bags, chemical indicator strips; tabs, packets or tubes of colored liquid

Where are “Integrated” indicators placed to confirm sterilization has occurred?
Inside packages
What does Mechanical monitoring measure and record?
Time, temperature, and pressure (via gauges and displays)
Which kind of sterilization monitoring can print out results and keeps a permanent monitoring record?
Mechanical Monitoring
Does Mechanical monitoring guarantee sterilization inside the instrument packages?
No, it only monitors conditions inside the chamber
Who addresses what to do with items that are critical, semi critical, noncritical?
Center of disease control (CDC)
What are "Critical Instruments" and how must they be treated?
Items that penetrate mucous membranes, bone, or bloodstream (e.g., scalers, burs, surgical blades, PERIO SCALERS).
They must be heat sterilized, but if they cannot tolerate heat sterilization, they must be disposed of
What are "Semi-critical Instruments" and how must they be treated?
Items that contact mucous membranes but do not penetrate soft tissue (e.g., mirrors, impression trays, amalgam condensers).
Heat sterilize or use high-level disinfection
Why must dental handpieces be heat sterilized even if they are considered semi-critical?
Because they contain internal parts that can harbor contamination
What are "Non-critical Instruments" and how are they treated?
Items contacting only intact skin (e.g., X-ray head, BP cuff - low risk for infection transmissions).
Treat with low to intermediate-level disinfectant
Low risk for infection transmission
If a non-critical item has visible blood/bodily fluids on it, what level of disinfectant must be used?
Intermediate-level (not low-level)
Why must packaged instruments be allowed to dry and cool before handling?
To prevent "wicking" of bacteria through wet packaging
What is the rule for "Unpackaged" instruments after sterilization?
They must be covered immediately to prevent contamination from the air
Where should sterilized packages be stored?
in a closed cabinet, away from sources of contamination
Where should sterile instruments NOT be stored?
Under sinks, near sewer/water pipes, near heat sources, or within a few inches of ceilings or floors
What is the shelf life for unwrapped instruments?
NO SHELF LIFE!
What does the "First in, first out" rule mean?
Use the oldest sterilized packs first
What is a key factor before opening sterilized packages?
packages must be examined carefully
What is the protocol for opening instrument packages?
Open at chairside with clean, ungloved hands after the patient is seated, then glove up before touching the patient
This prevents contamination with the glove with any micro organisms on the outside of the packaging
How does instrument sharpening present a risk for disease spread?
through accidental punctures
What is the safest workflow for instrument sharpening?
Clean, sterilize, sharpen, and then re-sterilize
What features should an operatory have to minimize infection risks?
Smooth construction (minimal knobs/crevices)
foot-controlled faucets, vinyl chairs (no cloth/seams)
recessed waste containers
All surfaces should be compatible with disinfectants and detergents
Vinyl chairs, plastic laminate cabinets opposed to wood
Vinyl flooring and smooth walls for easy cleaning
Carpet not recommended
ETC…
What are the 4 general types of antimicrobial chemicals?
Antibiotics
Antiseptic
Sterilant
High level
What is the difference between an Antibiotic and an Antiseptic?
Antibiotics kill microorganisms in/on the body; Antiseptics kill microorganisms on skin or body surfaces
Define a "Sterilant" (Immersion).
Destroys all microorganisms, including high numbers of spores
Define a "High-level Disinfectant."
Destroys all microorganisms but not high numbers of spores
Not for environmental surfaces (instruments only)
Define an "Intermediate-level Disinfectant."
Destroys vegetative bacteria, most viruses/fungi, and M. tuberculosis, but not bacterial spores
Define a "Low-level Disinfectant."
Kills most bacteria/fungi/viruses, but NOT M. tuberculosis or spores
Define “Sproricidal”
kills bacterial Spores, means it is a sterilant
What does "Tuberculocidal" mean?
Capable of killing the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacterium
What is the purpose of the "Precleaning" step in the Spray-Wipe-Spray method?
To reduce the number of microorganisms and bioburden (blood/saliva) to facilitate the action of the disinfectant
What is a precleaning and disinfection step (example)
Spray-wipe-spray (using a liquid disinfectant/cleaner) ; leave disinfectant on surface long enough to be tuberculocidal (usually 10 min.)
Wipe-discard-wipe; (using a disinfectant towelette)
What is the contact time required for Optim 33?
1 minute
What is the EPA standard for microbial quality of drinking water?
No more than 500 CFUs/mL
What is a colony-forming unit equivalent to?
one bacterial cell/mL
Is the water entering the dental unit sterile?
Water entering the dental unit is not sterile and has low levels of waterborne microbes present
What is the typical microbial count in untreated dental water exiting handpieces?
Can exceed 100,000 CFU/mL
Majority of these waterborne microorganisms are opportunistic (T/F)
True
What are the two communities of bacteria in water lines?
Planktonic (free-floating) and Biofilm (sessile/attached)
OTHER: ***All gram negative opportunistic pathogens that cause harmful infections in a compromised host
List the factors that influence biofilm formation in DUWLs.
Water stagnation
small-diameter tubing (high surface-to-volume ratio)
incoming nutrients
continuous presence of pioneer bacteria
As water flows by biofilm, it picks up bacteria from the biofilm and carries it through the handpiece or A/W syringe , scalers etc.
What two specific Gram-negative bacteria are common opportunistic pathogens in dental water?
Pseudomonas and Legionella
Describe the 2012 case study mentioned regarding DUWLs.
An 82-year-old woman died of Legionnaires' disease; L. pneumophila was found in the dental unit water line (handpiece turbine)
What types of patients are most at risk from DUWL contamination?
Immunocompromised, elderly, smokers, alcoholics, organ transplant recipients, and those with chronic disorders
What are the rates of biofilm formation for us and for dental water unit lines?
Biofilm reforms immediately after we brush
Dental unit water line forms more slowly but begins in a new unit within hours
According to the CDC, how long should water/air be discharged between patients?
20–30 seconds to reduce planktonic microbia
What water source must be used for oral surgical procedures (e.g., implants, biopsy)?
Sterile water (delivered via sterile system or hand irrigation)
What tools have help minimize sprays and spatter?
The use of the HVE
Evacuation also helps reduce Exposure for patient from the waterborne microorganisms
What is DUWQ Technologies? List some available DUWQ technology
Procedures designed to improve the quality of water
Independent reservoirs
• Decontamination and Antimicrobial Agents
• Filtration
• Sterile water delivery systems
Which DUWQ tech allows for the use of decontaminating or clearing antimicrobial agents for cleaning water lines?
Independent Water Reservoirs (Clean the bottles with soap and water every day)

Which DUWQ technology are available for using independent water reservoirs to disturb biofilm development and must be registered by the Environmental Protection Agency?
Decontaminating and Antimicrobial Agents
how are Decontaminating and Antimicrobial Agents used?
Periodically placed inside the bottles and flushed through water lines
What does Water quality monitoring entail?
Untreated dental units produce water that is below the standard for drinking water so monitoring of levels should be done periodically.
What are microfiltration cartridges used for?
Disposable microfiltration cartridges can be used to decrease dental waterline contamination
What is the limitation of Microfiltration Cartridges? What can help?
They filter microbes exiting the line but do not decrease bacterial colonization (biofilm) inside the waterline itself
filters are often used in combination with antimicrobial agents to address this issue
What should be done if a "Boil Water Notice" is issued?
Stop seeing patients; after the "all clear," flush lines and faucets for 1–5 minutes (or follow manufacturer instructions)
Why should patients NOT close their lips around the saliva ejector?
It creates a vacuum that causes "backflow" from the ejector into the patient's mouth
What specific waterline cleaner is used at CNIH?
Blue Tab
What is the CNIH protocol for flushing lines at the beginning and end of the day?
Purge all lines for 2 minutes
What is the CNIH protocol for flushing lines between clients?
Purge for 30 seconds
Handpiece asepsis steps:
Clean, package, and sterilize by heat between patients
Instrument processing can cause damage to instruments, which instruments are lease affected by corrosion?
Stainless steel instruments are the least affected by corrosion, but many dentists prefer carbon steel instruments because they retain sharp edge longer
List the steps for instrument processing
Remove items from operatory
Use holding Solutions if necessary
Clean by Automated Or manual method
Package
Sterilize
Store
What are 2 different types of environmental surfaces? list examples
Clinical contact surfaces
High potential for contamination with blood, saliva, other infectious material
Housekeeping surfaces
do not come into contact with hands or devices
Limited risk of disease transmission