Module 5 Advanced Mechanics
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
The only force a projectile experiences…
Gravity
Set the upwards direction as +
Therefore if an object falls down, displacment and gravity are -
What is always constant?
Horizontal Velocity.
Step One Of Projectile Motion Questions…
Decompose velocity into horizontal and vertical components.
Set up suvat with values for both the x axis and y axis.
The values you will always know…
ux = vx
ax = 0
ay = -9.8
uy = 0
Step Two Of Projectile Motion Questions…
Combine vertical and horizontal components together.
To find maximum height…
u = Hyp x Cos θ
a = -9.8 m/s
v = 0 (Think stationary point)
we are finding s
use v2 = u2 - 2as
To find time of flight…
u = Hyp x Sin θ
a = -9.8 m/s
s = 0 m (Displacement) (If it lands above of below just use that height)
t = ?
use s = ut + 1/2at2
To find horizontal range…
velocity = displacement / time
Therefore u = s / t
s = ut
Velocity right before it hits the ground…
Use pythagoras theorem…
Use vx and vy to find the hypotenuse.
Then find the angle below the horizontal.
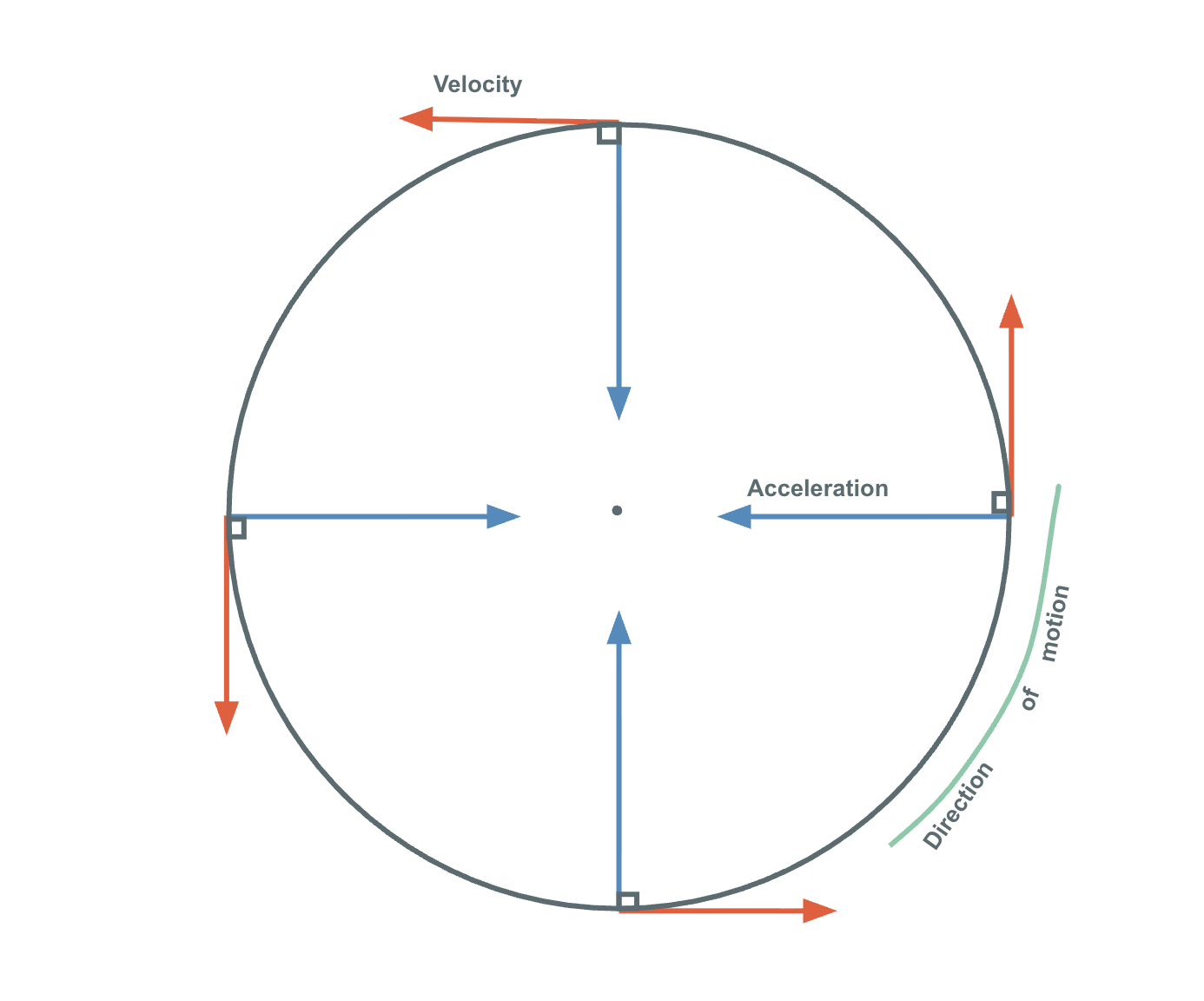
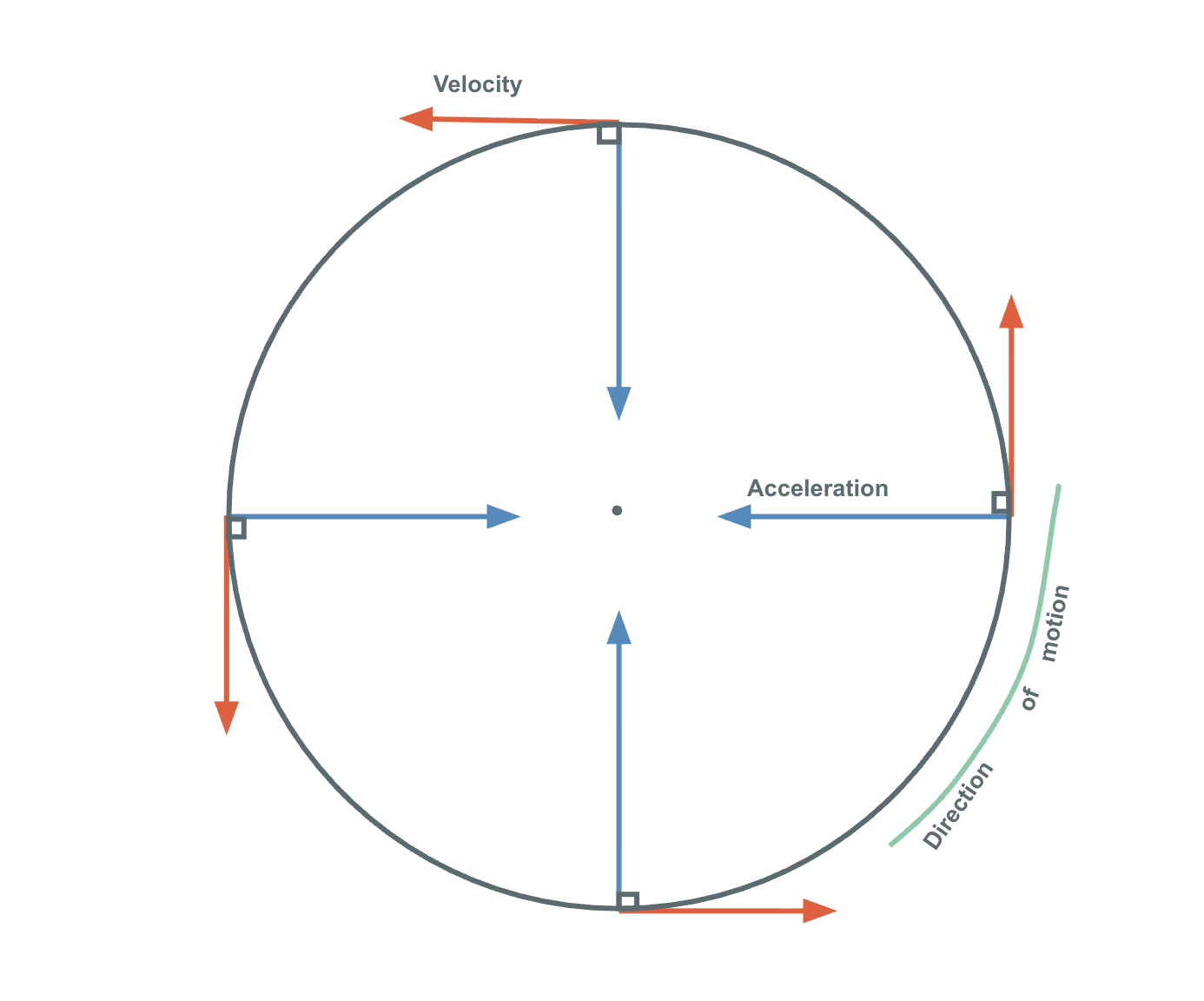
Uniform Circular Motion
Uniform circular motion can be described as the motion of an object in a circle at a constant speed. As an object moves in a circle, it is constantly changing its direction (constant speed not constant velocity). At all instances, the object is moving tangent to the circle. The net force acting on the object is always perpendicular to its velocity. The direction of the acceleration is inwards.
Period
The time taken for an object to travel once around a circle is the period (T) in seconds.
Frequency
The number of rotations in a second is the frequency (f) in Hz.
The formula that links frequency and period.
f = 1/T
To calculate the average speed of an object undergoing uniform circular motion…
Average speed = distance / time
v = 2πr / T
Where T is period
Radians and Degrees
Radians are a unit of measuring angles that are useful for calculating angular displacement and velocity
To convert between degrees and radians you use
For Radians = Degrees x π / 180
For Degrees = Radians x 180 / π
To calculate the angular velocity of an object undergoing uniform circular motion
Angular displacement, Δθ (in rad) = arc length / radius
Angular velocity, ⍵ = Δθ / t and can be measured in radians per second and degrees per second.
(Small t means it doesn’t have to be the period.)
Average speed and angular velocity are related by…
v = r⍵