Clinical skills for Nursing Practice: An Introduction to Intravenous Therapy
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
• Always administered by an RGN
•IV drugs checked by 2 RGNs if advocated by local policy
oMaintain fluid balance: when patients are N.P.O or can not drink adequate fluids for other reasons, to treat dehydrated.
oDelivering certain drugs e.g. IV antibiotics
oCorrect electrolyte imbalances
oProvide a medium for administering medications and nutritional support
}Constant monitoring of the patient, flow rate and remaining fluid volume is important- this ensures early detection of under-over of infusions, allergy reactions etc.
}**Consider putting patient on fluid balance chart**
}IV fluids’ administration’s set should be changed as per local policy-usually every 96 hours
}Blood administration sets at least every 12 hours and between each unit of blood
}Sets should be labelled with date and time of change
}Replace all tubing when VAD is replaced
•Check outer wrapper is intact and not damaged in any way
\
•Check the fluid bag for leaks, presence of particles, cloudiness, or discolouration and expiry date and batch number
\
**Administration set:**
Check the contents are sterile i.e. outer wrapper not damaged
Check expiry date of sterilisation
Check administration set is appropriate for fluid to be administrated
\
}Infection control and prevention principles are critical with all aspects of IVT nursing interactions
}Fluid rate can be controlled manually by using a slide or roller clamp, which can be adjusted to deliver fluid at a number of drops per minute by a gravity administration set.
}Fluids that require exact delivery rate should be given by a syringe driver or electronic pump
•Indications for gravity infusions:
§Administration of drugs or fluids where adverse affects are not anticipated and do not require absolute precision
§Where patient’s condition does not give cause for concern
Flow rate calculated using a formula for drops per minut
\
•**Inspect Before**:
oadministration of IV medication / IV fluids
o changing the administration set
oRegulating the intravenous flow rate
•**Nurses role**:
oObserve for signs of systemic infection e.g. pyrexia
oEndure both cannula and dressing is dry and secure
oAssess the site for early signs of phlebitis or infiltration using VIP scale
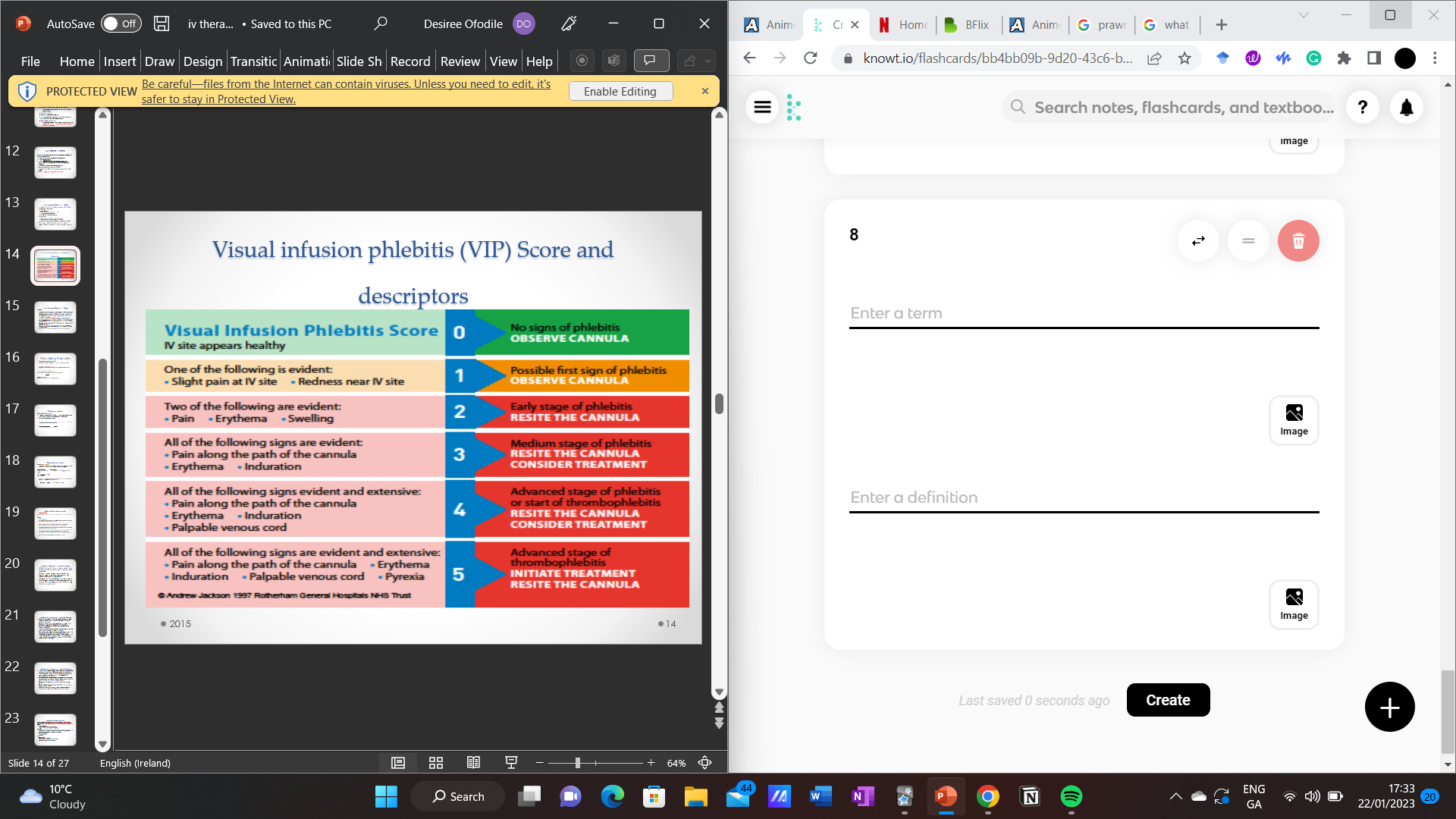
•Inspect the cannula for signs of swelling, redness, erythema (redness and flushing of the skin), (abnormal hardening of the tissue), and palpate venous cord (a hard inflamed vein is felt along the vein path with finger tips).
•Ask the patient how the site feels e.g. does the insertion site feel sore? Is the arm painful to touch?
•Look at the VIP score and compare findings with the descriptors to identify the condition of the site, and the score e.g. slight redness around the site indicates a score of 1 and indicates that the first sign of phlebitis may be present.
•To ensure accuracy, look at the next highest score to identified score and compare findings to the descriptors - If findings do not fit. Correct score had been identified.
•Refer to the VIP score to determine required action for the score e.g. if score is 1 the cannula will need observation. If VIP score 2 the cannula will need re-siting.
•Document the VIP score and any actions taken as per local policy.
\
__Volume of infusion required X drops per ml__ = flow rate in drops per minute (dpm)
Time in minutes
\
\
•Time in minutes = No. of hour X 60
•The number of drops per ml will be determined by the administration set-indication on packaging
•Standard giving set is 20 dpm
•Blood administration may state 20 drops per min but this is for water. Blood is thicker than water and forms larger drops thus dpm for blood is 15
•
E.g. 1 litre of normal saline 0.9% given over 8 hours using a standard set
__1000 x 20__ = 41.67 or 42 drops per minute
8 x 60
\
***Volumetric infusion pumps:***
Volume to be infused/ Duration of infusion=Volume per hour
E.g. 1000/8 = 125 set 125ml/hr
2\.Perform hand hygiene
3\.Explain procedure to patient
4\.Untie back of gown and remove gown from unaffected arm
5\.Support arm with IV tubing and slip gown down to IV tubing
6\.Ask patient to place arm into clean gown and cover chest
7\.Remove IV bag from hook and slip sleeve over bag, keeping IV fluid bag above the patients arm
8\.Place your hand up the distal end of the clean gown sleeve and grasp the IV bad. Pull bag and tubing through the sleeve, rehang the bag on the hook.
7\.Assist the patient to put arm through remaining sleeve.
8\.Tie gown at the back
9\.Ask staff nurse to recommence the infusion
10\.Place dirty gown in appropriate linen skip
11\.Perform hand hygiene
\
\
•Explain to patient the importance of staying still during the procedure, to prevent dislodgement of the cannula.
•Raise bed if necessary to avoid stooping as per manual handling guidelines.
•Maintaining asepsis, open the pack and new dressing on to a clean trolley and pour the cleansing solution.
•Don sterile gloves, carefully remove the old dressing using the disposal bag taking care not to dislodge the cannula. Assistance may be required to secure the cannula during this.
•If there is blood, clean the cannula site. If pus or exudate present the cannula should be removed. If phlebitis present remove cannula and report.
\
•If cannula site is healthy apply a new dressing, taking care not to touch the part that will be directly over the insertion site.
•If an intravenous infusion is running, secure the tubing of the administration set to prevent pulling and accidental dislodgement of the cannula.
•Ensure the patient is comfortable and explain any restrictions to mobility and the need to protect the cannula site. Ask the patient to report any swelling, redness or pain.
•Dispose of a soiled dressing and other waste as per local policy
•Remove PPE and discard as per local policy-clinical waste. Perform hand hygiene
•Document the visual infusion phlebitis score and dressing change as per local policy. Report any abnormalities.
•Regularly inspect the cannula site to demine if dressing needs to be changed-change if wet, blood-stained or no longer secure
•The cannula site is considered a wound so should follow aseptic technique when changing dressing and should not be exposed unnecessary or during bed making, dusting etc.
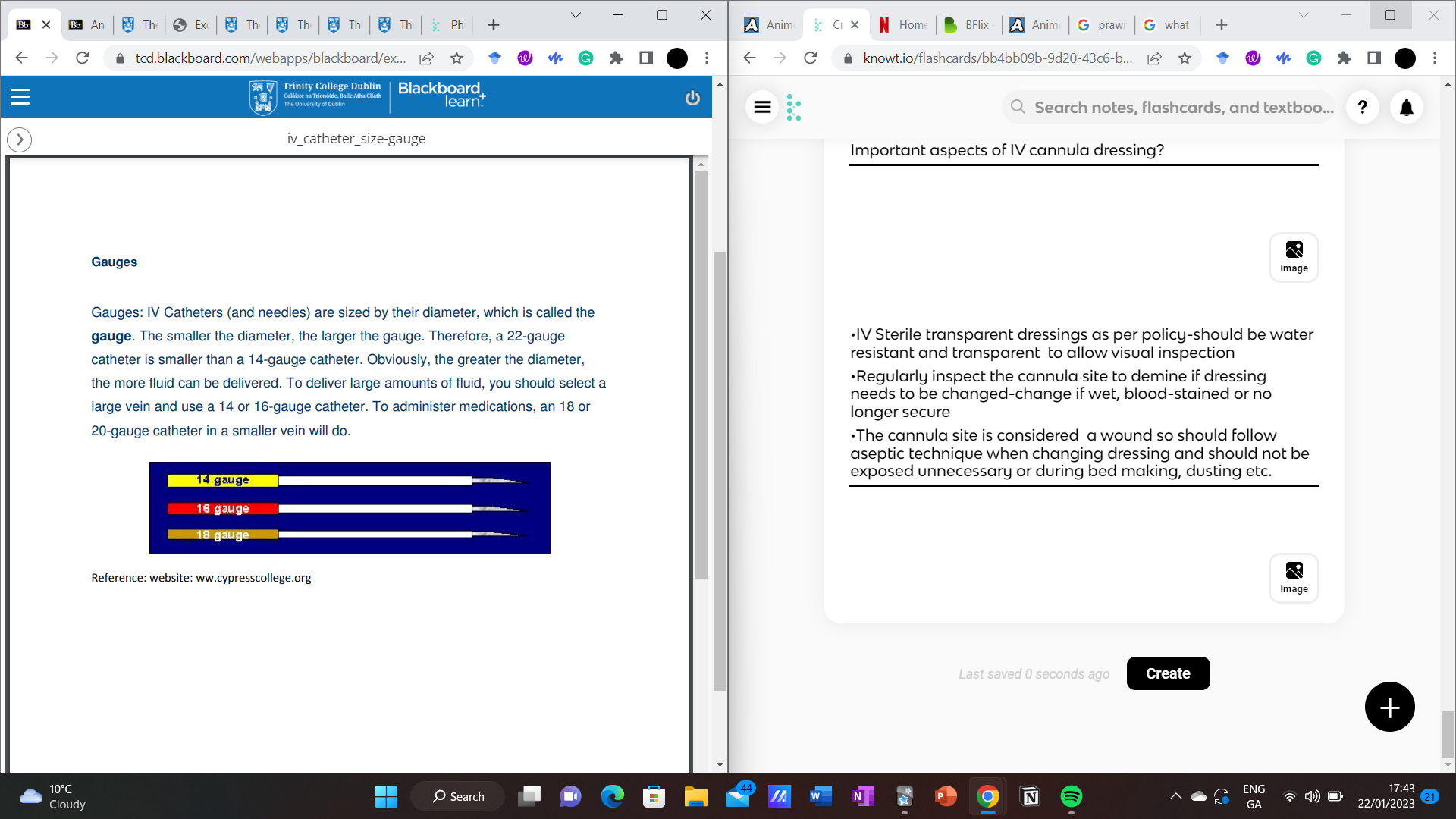
Therefore, a 22-gauge catheter is smaller than a 14-gauge catheter. Obviously, the greater the diameter, the more fluid can be delivered. To deliver large amounts of fluid, you should select a large vein and use a 14 or 16-gauge catheter. To administer medications, an 18 or 20-gauge catheter in a smaller vein will do
Isotonic fluids? And give an example
Just right juice
used for dehydration, low bp, surgery
-keeps everything balanced
-examples: Normal Saline (0.9% NaCL) - like salty water
Lactated Ringerz
Hypotonic fluids? And give examples
too watery- not enough salt
Water moves in to your cells because the outside is more watery
Used when cells are dry and need water- high blood sugar or dehydration
Examples - half normal saline (0.45% NaCL) , Dextrose 5% in water-form of glucose-helps replace lost fluids and provide carbs to the body
Too much can make brain swell
Hypertonic fluids? And give examples
-salty water -super thick and salty
-water leaves your cells and goes into your blood to even it out
-used when brain is swelling or blood has too little salt
Examples - 3% saline , Dextrose 10% sugar water