CompTIA A+ 220-1101 - 3.3: Storage Devices
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
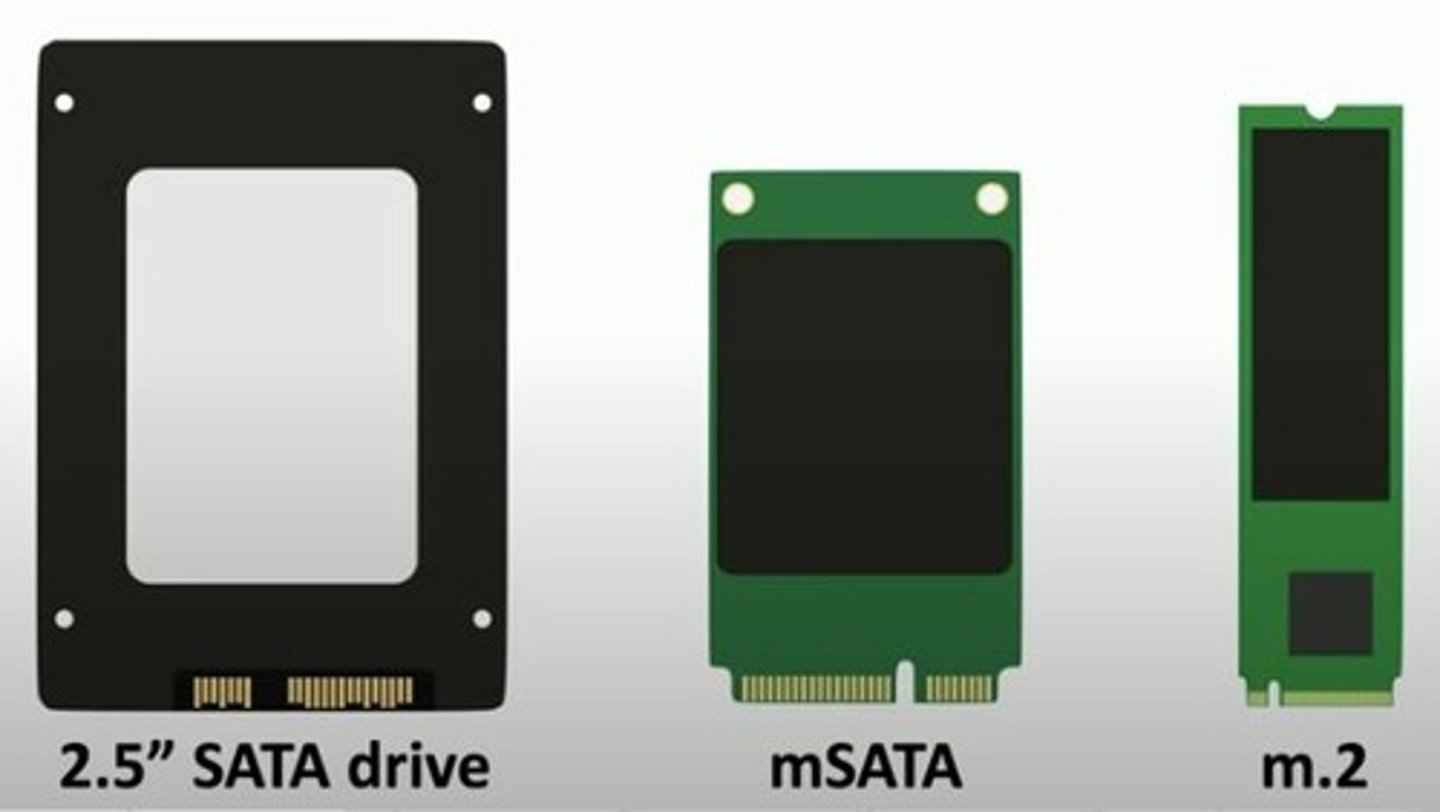
Drive Size Comparison
3.5 inch drive.
2.5 inch drive
m.2 drive
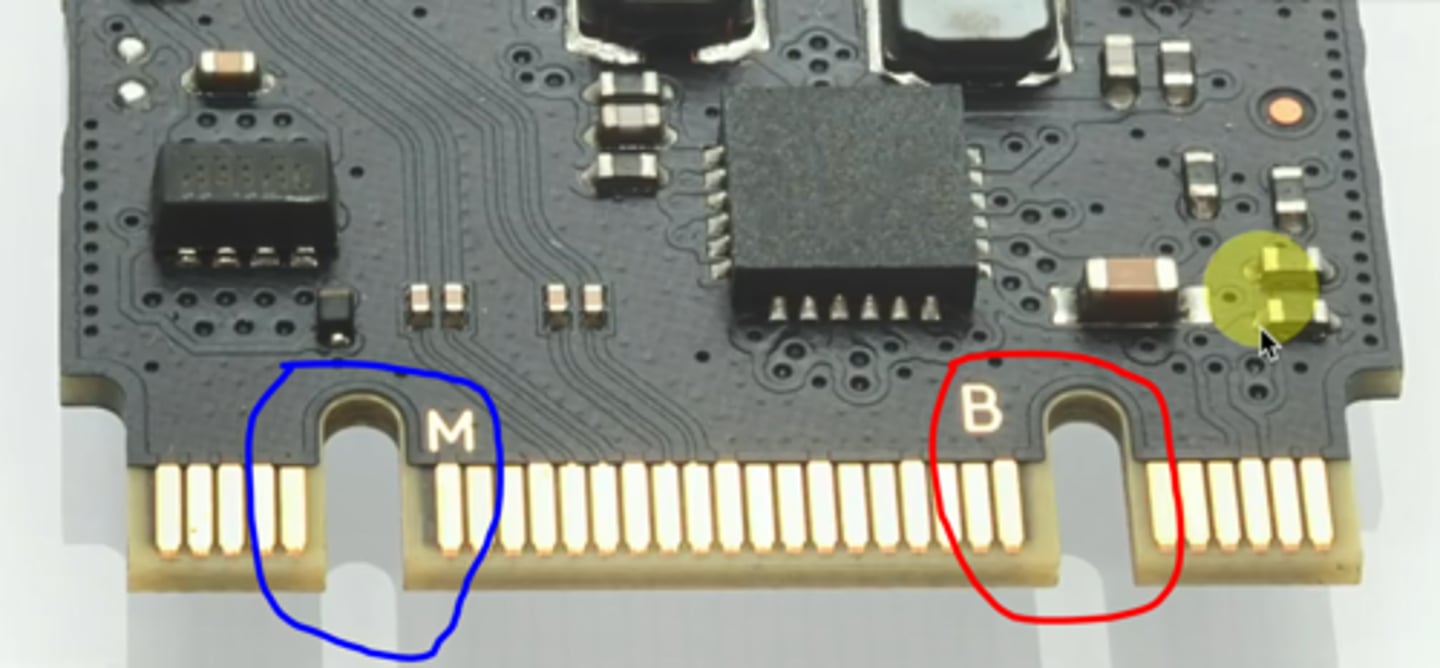
M.2 Interface
Smaller form factor
- No SATA data or power cables
Can use a PCI Express bus connection
- 4 GB/second throughput or faster when using NVMe PCIe x4
Different connector types
- Needs to be compatible with the slot key/spacer
- B key, M key, or B and M key
- Some M.2 drives will support both

B-Key and M-Key
Connector types for the M.2 interface.
M.2 doesn't guarantee NVMe.
- Your M.2 interface may be using AHCI.
- Check your documentation
Your motherboard may only support one type of M.2 key
- Check your documentation again.
CD-ROM (compact disc read-only memory)
Read-only compact storage disc for audio or video data. They are read by using CD-ROM drives and optical drives with backward compatibility, such as DVD and Blu-ray Disc drives. Cannot be written onto, only read.
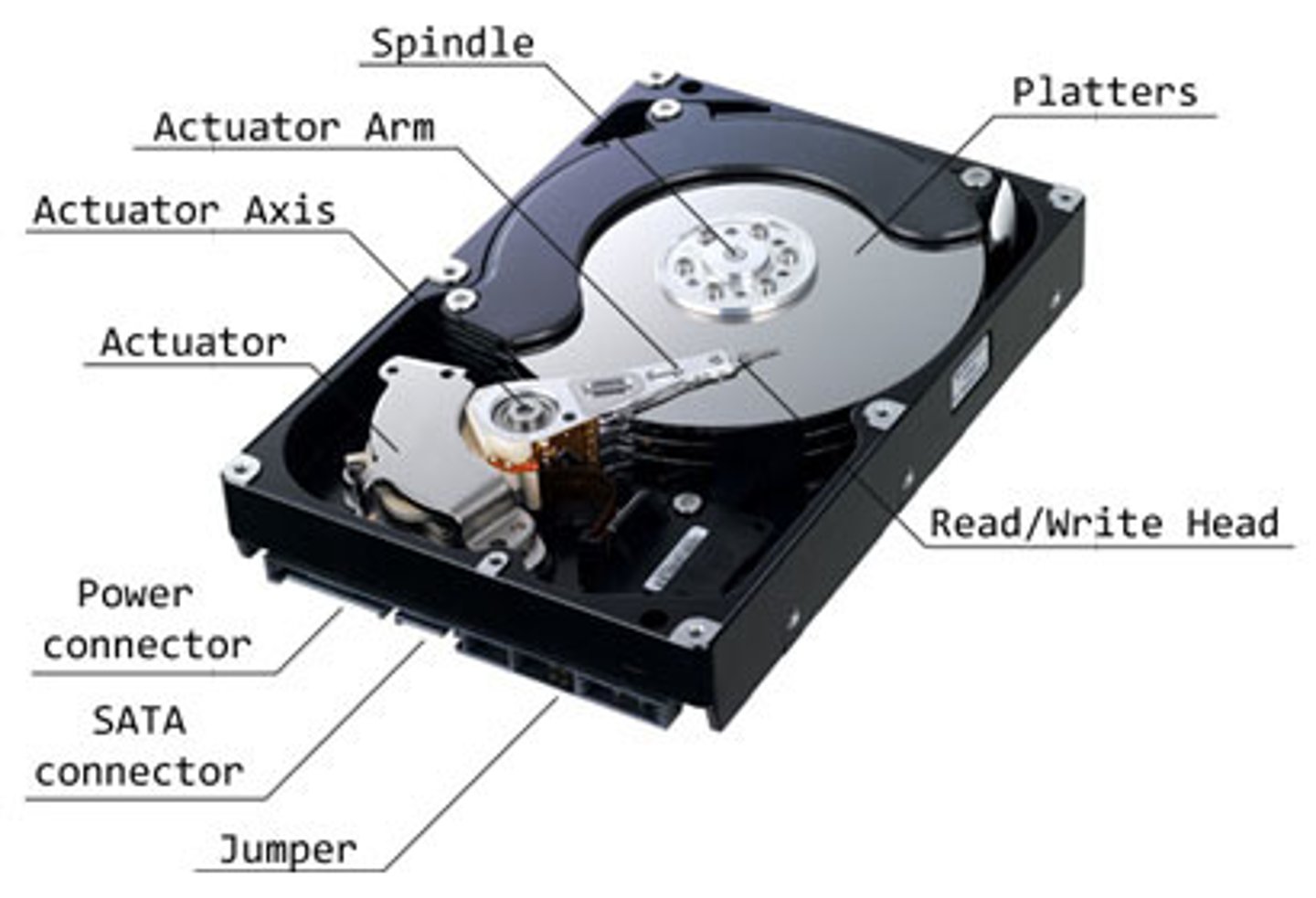
HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
A data-recording system using solid disks of magnetic material turning at high speeds to store and retrieve programs and data in a computer.
HDD details
Non-volatile (information remains when it has no power) magnetic storage.
- Rapidly rotating platters.
Random-Access
- Retrieve data from any part of the drive at any time.
Moving parts
- Spinning platters, moving actuator arm.
- Mechanical components limit the access speed.
- Mechanical components can also break.
HDD components
There are multiple heads and platters.
HDD Speeds
2.5 inch drive
- 5400 rpm
- 7200 rpm
3.5 inch drive
- 5400 rpm
- 7200 rpm
- 10,000 rpm
SSD (Solid State Drive)
A data storage device that uses flash memory to store data.
SSD details
Non-volatile memory (information remains when it has no power)
- No moving parts.
Very fast performance
- No spinning drive delays.
Can use SATA interface.
Volatile Memory vs Non-Volatile Memory
Data remains only while device receives power.
vs.
Data remains even when device receives no power.
mSATA (Mini-SATA)
Standardized smaller SATA form factor for use in portable devices.
mSATA details
Shrink the SATA drive into smaller devices.
- Same data, different form factor.
- Great for laptops and mobile devices.
Smaller than 2.5" SATA drives
- No spinning drive.
- Allows for different form factors.
Was used briefly.
- Quickly replaced by the m.2 standard.
AHCI (Advanced Host Controller Interface)
An efficient way for motherboards to work with SATA host bus adapters. Using it unlocks some of the advanced features of SATA, such as hot-swapping and native command queuing.
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express)
SSD technology that supports a communication connection between the operating system and the SSD directly through a PCIe bus lane, reducing latency and taking full advantage of the speeds of high-end SSDs.
SSDs using this come in a couple of formats, such as an add-on expansion card and a 2.5-inch drive, like the SATA drives for portables. NVMe drives are a lot more expensive currently than other SSDs, but offer much higher speeds.
AHCI vs NVMe
• Uses AHCI (Advanced Host Controller
Interface) to move drive data to RAM
• SATA revision 3 throughput up to 600 MB/s
• SSDs need a faster communication method
vs
• Designed for SSD speeds
• Lower latency, supports higher throughputs
• Take advantage of NVMe with an M.2 interface
M.2 expansion slot
Type of space efficient expansion slot common in recent portable computers. Formerly known as Next Generation Form Factor (NGFF). Also found on some desktop motherboards.
While this is a general expansion slot supporting devices such as Wi-Fi cards, it is often used to install an NVMe SSD.
Flash Drives
Flash memory.
- EEPROM (Electrically erasable programmable read-only memory).
- Non-volatile memory.
- No power required to retain data.
Limited number of writes.
- Can still read the data.
Not designed for archival storage.
- Easy to lose or damage.
- Always have a backup.
Optical Drive
Drive used to read/write to optical discs, such as CDs or DVDs.
Optical Drive details
Small bumps read with a laser beam.
- Microscopic binary storage.
Relatively slow
- Archival media.
Many different formats
- CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, Blu-Ray
Internal and external drives.
- For those uncommon application installations.
Data Redundancy
Hard drives store huge amounts of important data
Hard drives are moving components
- They will eventually break
What happens to the data when the drive fails?
- You can prepare for that;
- Use an array of drives
RAID is not backup. It is a means of retaining uptime and availability if/when a drive fails.
- A backup is backup, not RAID.
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks)
Method for creating a fault-tolerant storage system. It uses multiple hard drives in various configurations to offer differing levels of speed/data redundancy.
RAID details
Redundant array of independent disks.
- They're also inexpensive disks.
Different RAID levels
- Some redundant, some not.
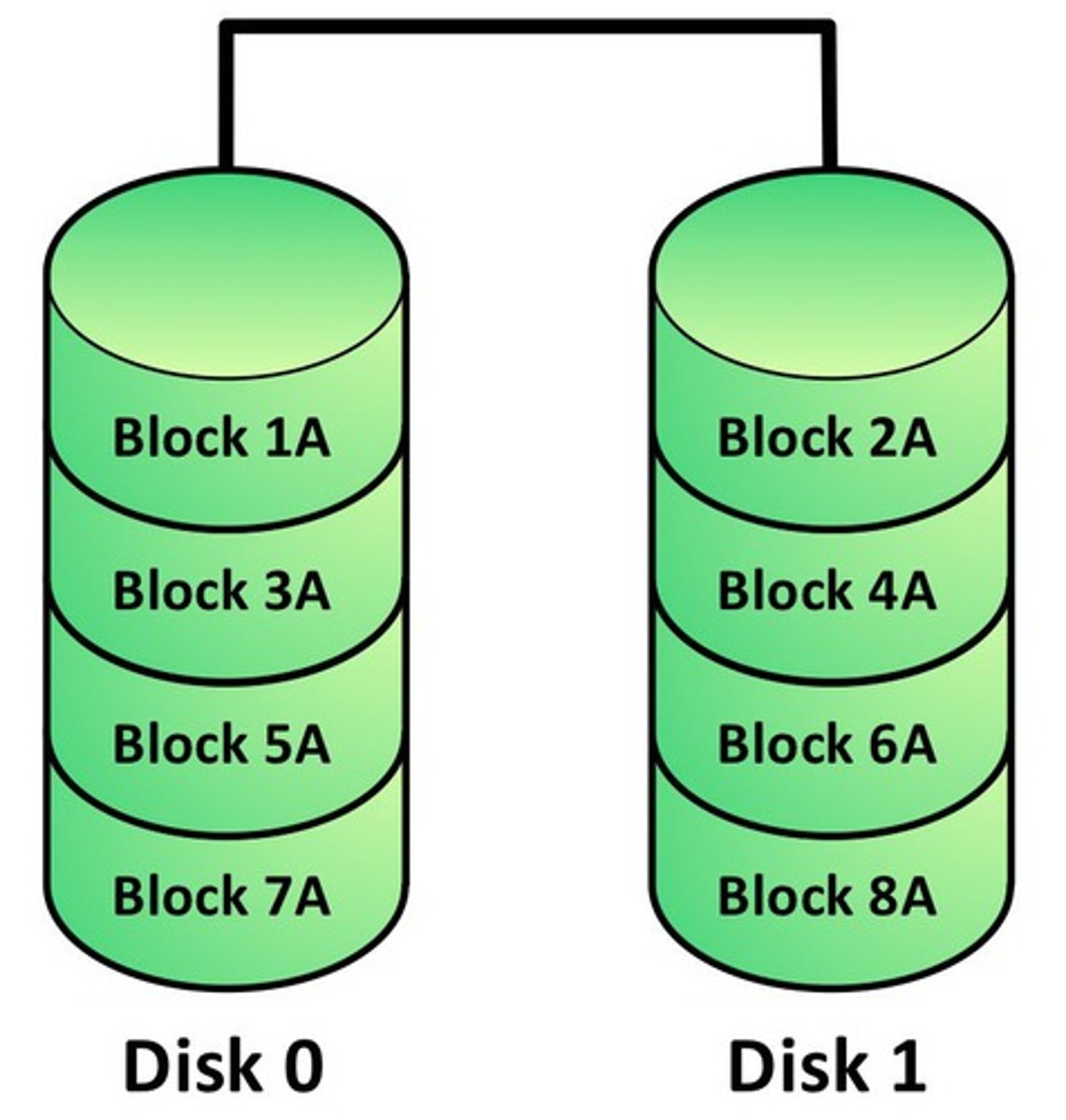
RAID 0 (Striped Volume)
Type of RAID whereby data is spread (not duplicated) across two drives for increased speed.
RAID 0 details
File blocks are split between two or more physical drives.
High performance
- Data written quickly
No redundancy
- A drive failure breaks the array.
- Raid 0 is zero redundancy.
RAID 1 (Mirroring)
Type of RAID where the data is written and read at the same time to two drives for fault tolerance purposes. Uses twice as much drive space as the previous level of RAID.
RAID 1 details
File blocks are duplicated between two or more physical drives.
High disk utilization
- Every file is duplicated.
- Required disk space is doubled.
High redundancy
- Drive failure does not affect data availability.
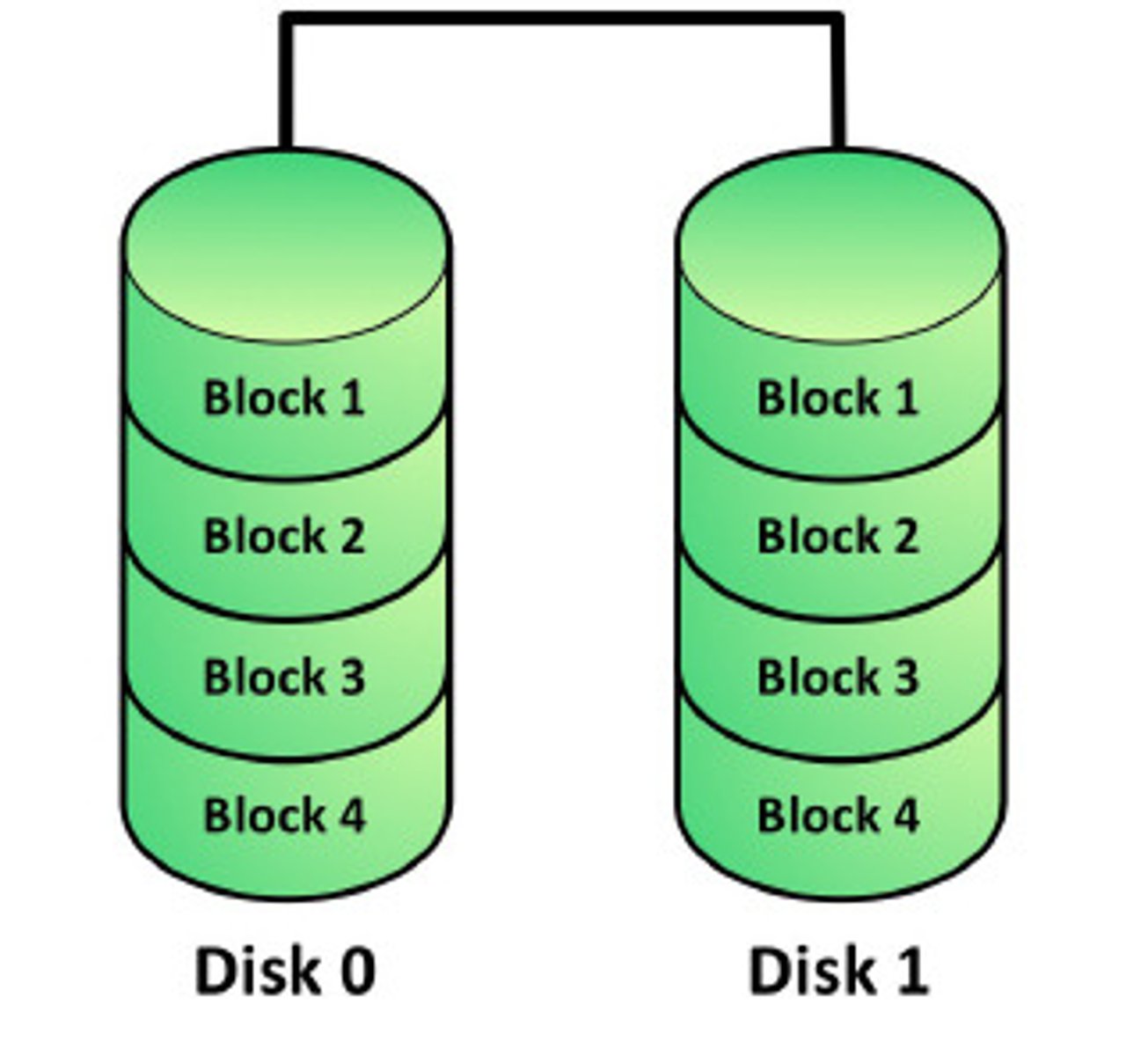
RAID 5 (Striping with Parity)
Type of RAID that uses block-level and parity data striping. Requires 3 or more drives.
RAID 5 details
File blocks are striped.
- Along with a parity block.
- Requires at least three disks.
Efficient use of disk space.
- Files aren't duplicated, but space is still used for parity.
- Parity calculation may affect performance.
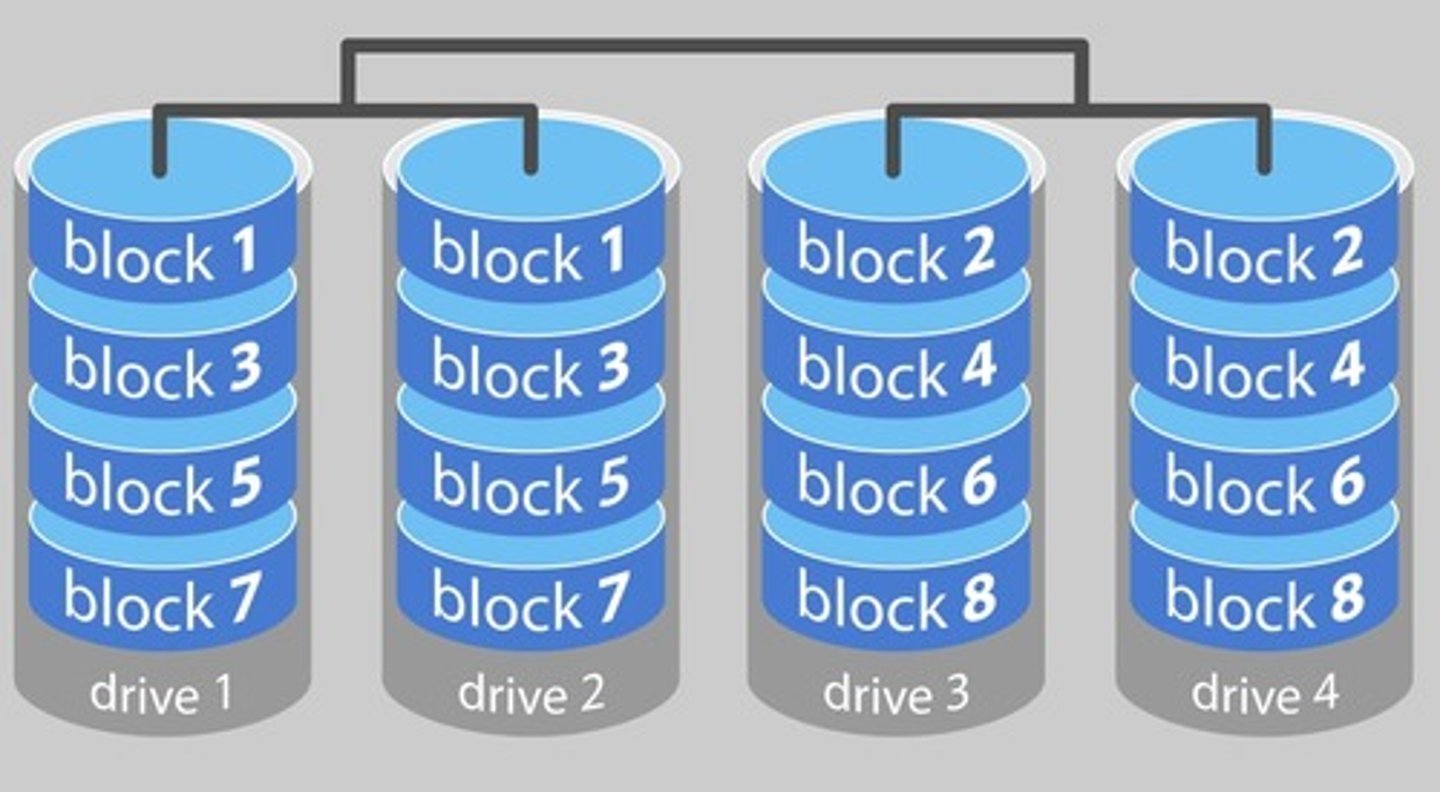
RAID 10 (or 1+0 - Striping with Mirrors)
Type of RAID that uses two mirrored RAID 0 configurations. Provides both speed and redundancy, and also requires at least four disks.
RAID 10 details
The speed of striping, the redundancy of mirroring.
Pairs of RAID 0 drives.
Needs at least four drives.
HHD (hybrid hard drive)
Storage drive that combines the flash memory used in solid-state drives with the spinning platters used in magnetic hard drives; a compromise between the speed and power efficiency of SSDs and the capacity of HDDs.
Hot Swapping
Replacing a bad drive in a RAID array without the need to reboot or power down, keeping the system running.
CD-RW (compact disc rewritable)
CD technology that accepts multiple reads/writes like a hard drive.
CD-R (CD-recordable)
CD technology that only accepts a single "burn" but cannot be erased after that one burn.
DVD-ROM (Digital video disc read only memory)
DVD equivalent of the standard CD-ROM. Cannot be written onto, only read.
CD Max Storage
700 MB or 80 minutes of audio
DVD Max Storage
8.5 GB for the double layer.
BD (Blu-Ray Disc)
Optical disc format that stores up to 100 GB of data, designed as a replacement media for DVD. Competed with HD DVD.
BD-R (Blu-ray Disc-Recordable)
Blu-Ray disc format that enables writing data to blanc discs.
BD-RE (Blu-ray Disc-REwritable)
Blue-Ray Disc equivalent of the rewritable DVD, allows writing and rewriting several times on the same BD.
BD-ROM (Blu-ray Disc-Read Only Media)
Blue ray disc equivalent of a DVD-ROM or CD-ROM. Cannot be written onto, only read.
BD Max Storage
100 GB